Abstract
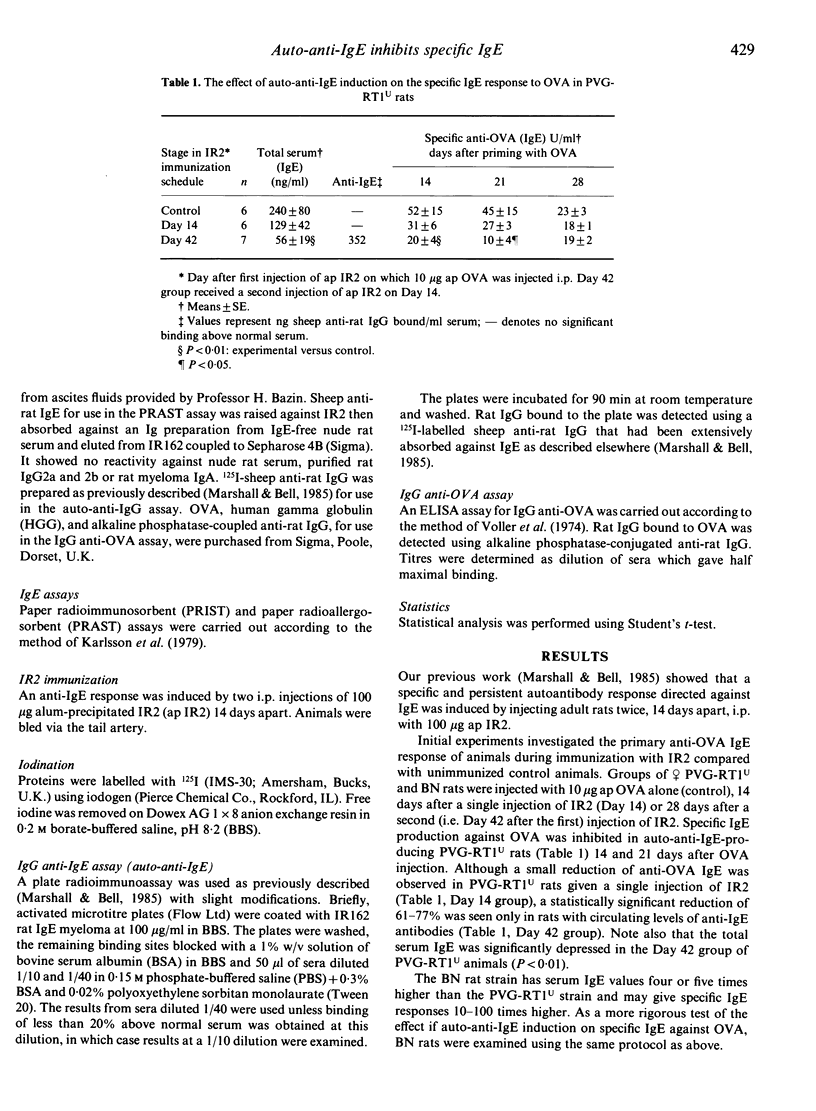
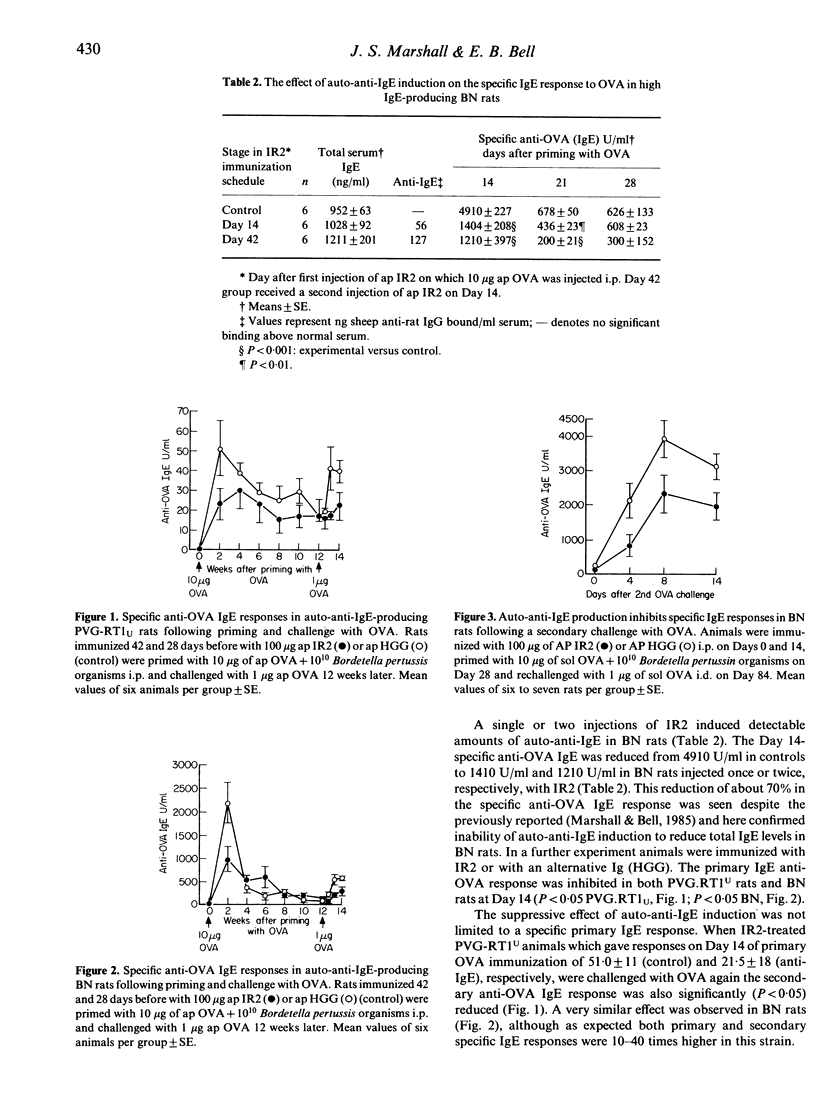
An auto-anti-IgE response was induced in conventional (PVG-RT1U and high IgE-producing (BN) rat strains by immunization with a highly purified rat IgE myeloma IR2. Earlier work established that total serum IgE levels were decreased by this procedure (Marshall & Bell, 1985) but only in the PVG-RT1U strain. IR2-immunized rats were tested for their ability to produce a specific IgE response to ovalbumin (OVA). The primary anti-OVA IgE response was inhibited by 60-75% in both rat strains, regardless of whether the total serum levels of IgE were reduced. The secondary IgE response to OVA was also inhibited in anti-IgE-producing animals but not in rats primed with OVA before anti-IgE induction. The inhibition of the anti-OVA response was isotype specific; the IgG response to OVA was unaffected. These studies may help elucidate the regulatory role played by naturally occurring anti-IgE antibodies found particularly in atopic individuals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basten A., Miller J. F., Warner N. L., Pye J. Specific inactivation of thymus-derived (T) and non-thymus-derived (B) lymphocytes by 125I-labelled antigen. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 26;231(21):104–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio231104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser K., Nakagawa T., de Weck A. L. Suppression of the benzylpenicilloyl- (BPO) specific IgE formation with isologous anti-idiotypic antibodies in BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozelka B. E., McCants M. L., Salvaggio J. E., Lehrer S. B. IgE isotype suppression in anti-epsilon-treated mice. Immunology. 1982 Jul;46(3):527–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessein A. J., Parker W. L., James S. L., David J. R. IgE antibody and resistance to infection. I. Selective suppression of the IgE antibody response in rats diminishes the resistance and the eosinophil response to Trichinella spiralis infection. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):423–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsche R., Spiegelberg H. L. Fc receptors for IgE on normal rat lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):471–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froese A. Structure and function of the receptor for IgE. Crit Rev Immunol. 1980 May;1(2):79–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Induction of high titers of anti-IgE by immunization of inbred mice with syngeneic IgE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5009–5013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inganäs M., Johansson S. G., Bennich H. Anti-IgE antibodies in human serum: occurrence and specificity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;65(1):51–61. doi: 10.1159/000232737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E., Hall E., Karlsson T., Bennich H. Adjuvants in the induction and enhancement of rat IgE responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jan;39(1):183–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson T., Ellerson J. R., Dahlbom I., Bennich H. Analysis of the serum IgE levels in nonimmunized rats of various strains by a radioimmunoassay. Scand J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):217–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D. In vivo immune stimulation of mice by anti-mu antibodies: generation of high serum levels of a low molecular weight IgM product. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 15;50(2):348–360. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Jutila J. W. Immunosuppression in mice injected with heterologous anti-immunoglobulin antisera. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):282–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Jutila J. W. Immunosuppression in mice injected with heterologous anti-immunoglobulin antisera. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):282–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Jutila J. W. Immunosuppression of mice injected with heterologous anti-immunoglobulin heavy chain antisera. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1316–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Manning J. K., Reed N. D. Suppression of reaginic antibody (IgE) formation in mice by treatment with anti-mu antiserum. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):288–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Bell E. B. Induction of an auto-anti-IgE response in rats I. Effects on serum IgE concentrations. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):272–277. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Prout S. J., Jaffery G., Bell E. B. Induction of an auto-anti-IgE response in rats. II. Effects on mast cell populations. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):445–451. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. S., Wells P. D., Bell E. B. Accelerated elimination of N. brasiliensis from the small intestine after auto-anti-IgE induction. Immunology. 1987 Feb;60(2):303–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawata Y., Koike T., Hosokawa H., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Anti-IgE autoantibody in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):478–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawata Y., Koike T., Yanagisawa T., Iwamoto I., Itaya T., Yoshida S., Tomioka H. Anti-IgE autoantibody in patients with bronchial asthma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Nov;58(2):348–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D., Huldt G., Engvall E. A microplate method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and its application to malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(2):209–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



