Abstract
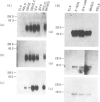
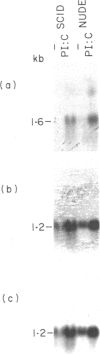
Serine protease genes (C11, B10 and HF) derived from activated cytolytic T lymphocytes have been shown to be important in CTL-mediated cytotoxicity. In this study, we examined the expression of these genes in fresh natural killer (NK) cells from severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and athymic nude mice, as well as in T-cell lines with NK activity. All of these serine protease genes were expressed in NK cells freshly isolated from SCID and athymic nude mice. In addition, all lines showed similar strong levels of expression of C11 and B10 genes, but not the HF gene. However, levels of expression in the T-cell lines did not correlate with levels of NK-like cytotoxicity. These results suggest that C11, B10 and HF serine protease genes are necessary but not sufficient for NK-like cytotoxicity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Holscher M. Cell surface molecules involved in NK recognition by cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpén O., Saksela E. Directed exocytosis in the NK-cell-mediated cytotoxicity. A review. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1988;7(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpén O., Saksela O., Saksela E. Identification and localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human NK-cells. Int J Cancer. 1986 Sep 15;38(3):355–360. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Eisen H. N. Effects of N alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethylketone on the activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1028–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K., Pollack S. B., Bosma M. J., Phillips R. A. Natural killer (NK) cells are present in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (scid). J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3798–3801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. L., Pollack S. B. Murine NK cell heterogeneity: subpopulations of C57BL/6 splenic NK cells detected by NK-1.1 and NK-2.1 antisera. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1985;4(4):169–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farram E., Targan S. R. Identification of human natural killer soluble cytotoxic factors (NKCF) derived from NK-enriched lymphocyte populations: specificity of generation and killing. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1252–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershenfeld H. K., Weissman I. L. Cloning of a cDNA for a T cell-specific serine protease from a cytotoxic T lymphocyte. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):854–858. doi: 10.1126/science.2422755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb R. H. Cell-mediated cytotoxic reactions. Hum Pathol. 1986 Feb;17(2):138–145. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Fukui H., Shimamura K., Kasai M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tamaoki N. In vivo effects of anti-asialo GM1. I. Reduction of NK activity and enhancement of transplanted tumor growth in nude mice. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Jr, Bosma G. C., Bosma M. J., Bennett M., Kumar V. Transplantable progenitors of natural killer cells are distinct from those of T and B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3427–3431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Andresen P. B., Larsson L. I., Danø K. Immunocytochemical demonstration of tissue-type plasminogen activator in endocrine cells of the rat pituitary gland. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):305–311. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauzon R. J., Siminovitch K. A., Fulop G. M., Phillips R. A., Roder J. C. An expanded population of natural killer cells in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) lack rearrangement and expression of T cell receptor genes. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1797–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauzon R. J., Siminovitch K. A., Roder J. C. T cell receptor gene rearrangements in cells with natural killer activity in the mouse. Immunol Res. 1986;5(3):191–200. doi: 10.1007/BF02919200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe C. G., Havele C., Bleackley R. C. Cloning of two genes that are specifically expressed in activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Henkart M. P., Reynolds C. W., Henkart P. A. Purification and properties of cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat LGL tumors. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Baines M. G., Rubin P., Shragge P., Patterson M. S. Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IX. The quantitation of natural killer cell activity. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00915477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan P. C., Ishizaka T., Bloom B. R. Studies on the mechanism of NK cell lysis. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1786–1791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R., Biberfeld P., Andersson B. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK) cell system. II. The isolation of NK cells and studies on the mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2509–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R., Newman W. Definition of a "trigger" stage in the NK cytolytic reaction sequence by a monoclonal antibody to the glycoprotein T-200. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1149–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutt M. M., Schuler W., Kuziel W. A., Tucker P. W., Bennett M., Bosma M. J., Kumar V. T cell receptor genes do not rearrange or express functional transcripts in natural killer cells of scid mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2338–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Cell-mediated killing: a common mechanism? Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):641–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Role of granule proteins in lymphocyte-mediated killing. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(2):151–167. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]