Abstract
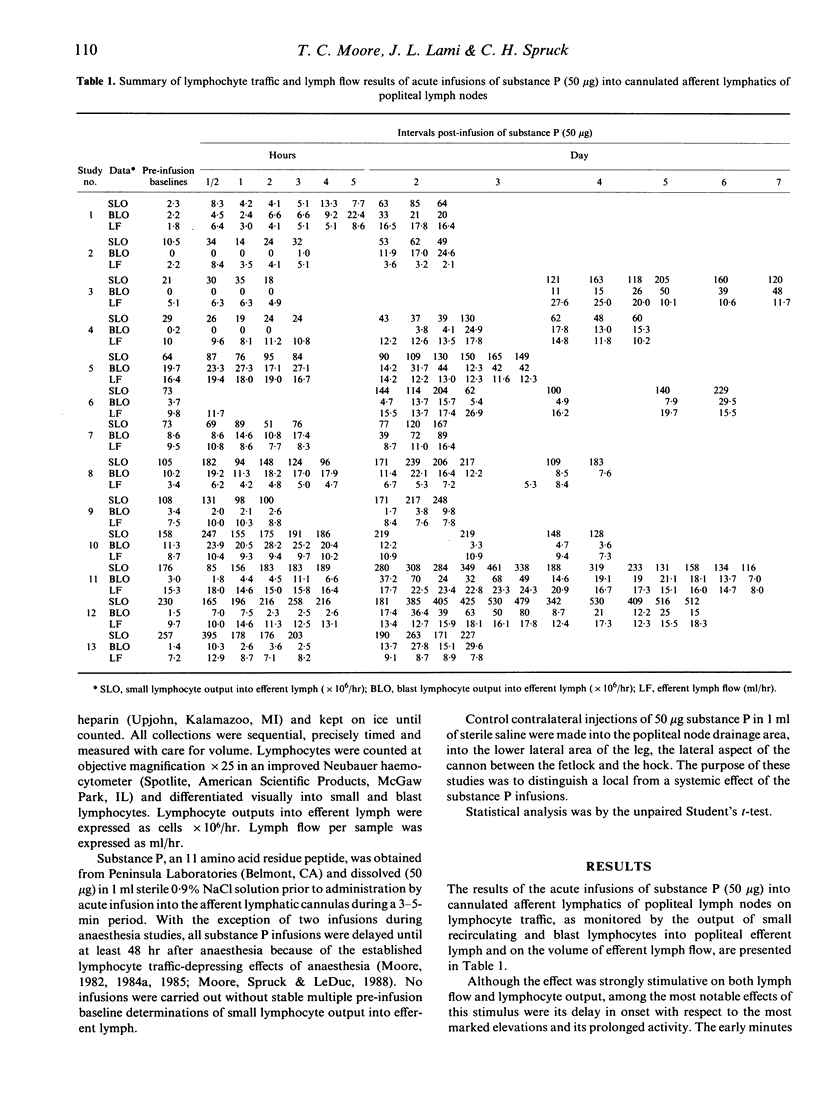
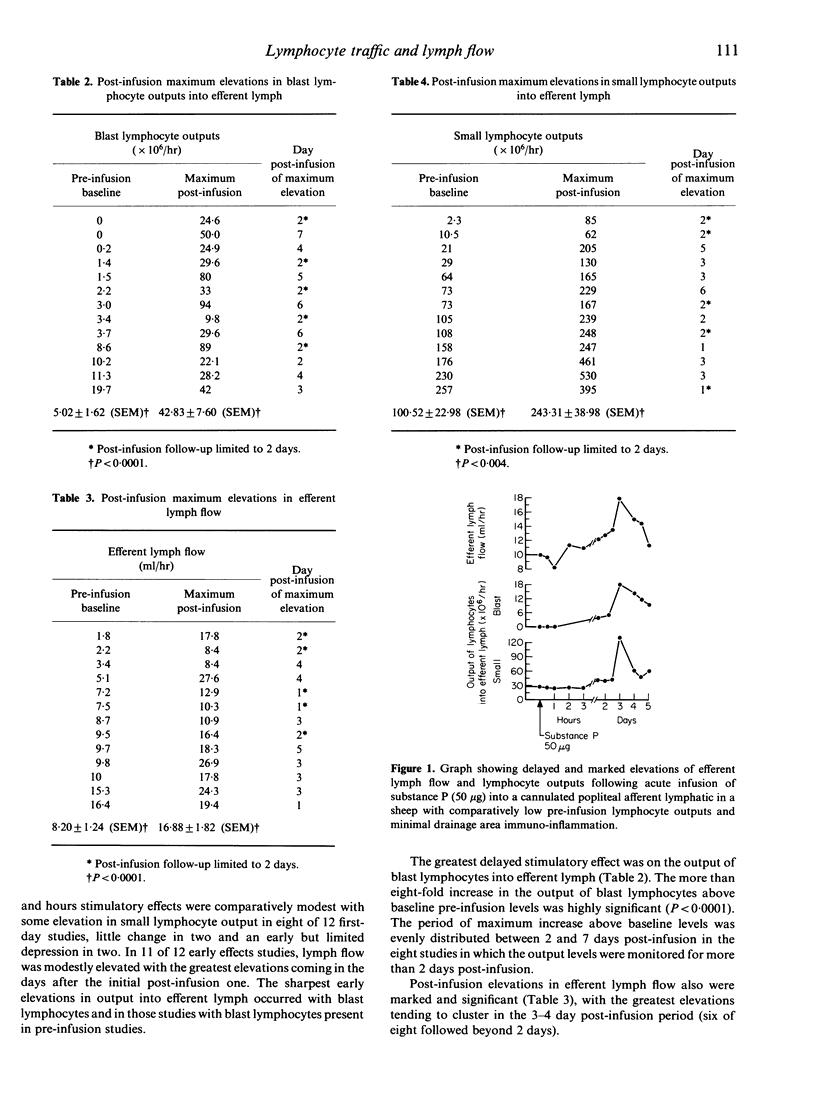
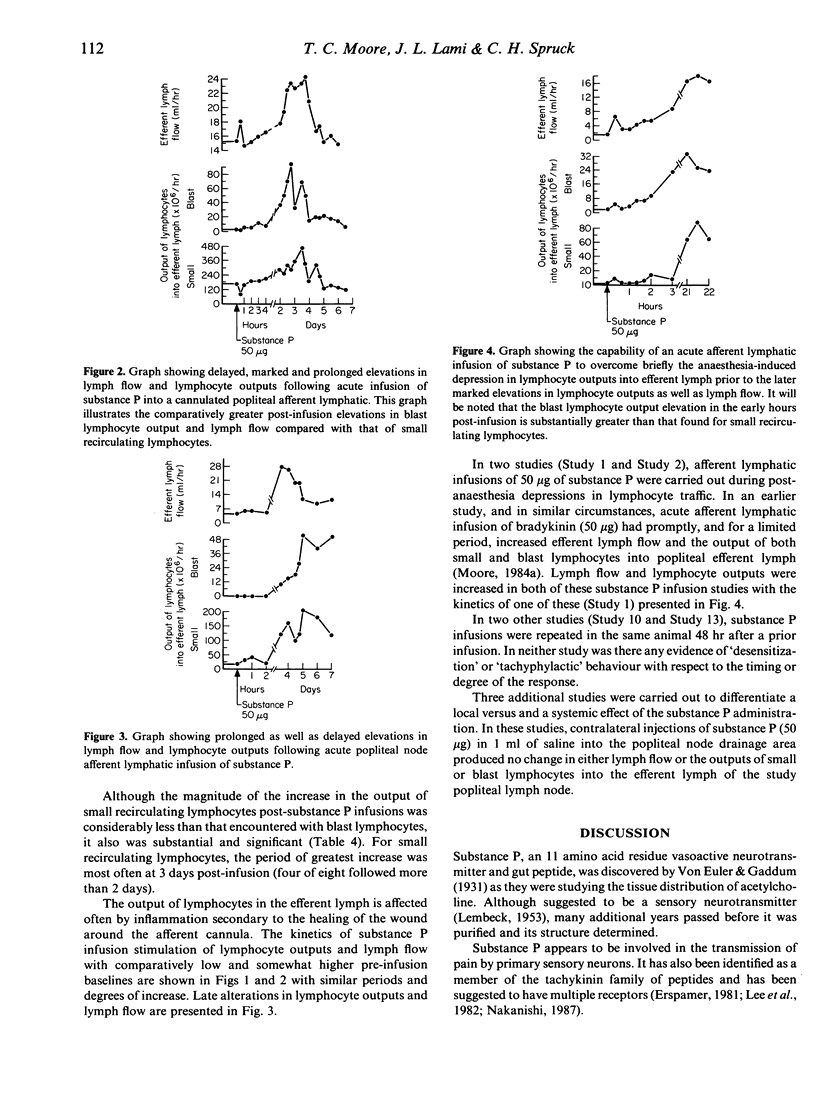
Substance P, an 11 amino acid residue vasoactive neurotransmitter peptide, has been found on acute infusion (50 micrograms) into cannulated afferent lymphatics of popliteal lymph nodes of sheep to produce marked elevations in both efferent lymph flow and in the outputs of both blast and small recirculating lymphocytes into popliteal node efferent lymph (chronically cannulated). These elevations were characterized by a delay in the onset of major elevations, a marked prolongation of the elevations and a substantially greater stimulative effect on the output of blast lymphocytes. It is suggested that the number and types of substance P receptors on lymphocytes and in sheep peripheral lymph nodes may be responsible for these observations. Infusion of substance P, known for involvement in pain impulse transmission, was able to briefly overcome anaesthesia-induced depression in lymphocyte traffic. The substance P-induced alterations in lymph flow and lymphocyte traffic in vivo were demonstrated to be due to local rather than systemic effects of substance P.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Shavit Z., Goldman R., Stabinsky Y., Gottlieb P., Fridkin M., Teichberg V. I., Blumberg S. Enhancement of phagocytosis - a newly found activity of substance P residing in its N-terminal tetrapeptide sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1445–1451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Moore T. C. Accumulation of lymphotoxin-secreting lymphoid cells in rat heart allografts. Surgery. 1974 Oct;76(4):542–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. The lymph-borne cells of the immune response. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1963 Jul;48:235–247. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1963.sp001660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. The output of cells in lymph from the popliteal node of sheep. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Oct;47:360–369. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helme R. D., Eglezos A., Dandie G. W., Andrews P. V., Boyd R. L. The effect of substance P on the regional lymph node antibody response to antigenic stimulation in capsaicin-pretreated rats. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3470–3473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppelmann L. E., Moore T. C., Lemmi C. A., Porter D. D. Accumulation of mononuclear cells in tumors with growth slowing and elevation in host splenic histidine decarboxylase activity following repeated tumor injections with bradykinin. Surgery. 1975 Aug;78(2):181–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMBECK F. Zur Frage der zentralen Ubertragung afferenter Impulse. III. Das Vorkommen und die Bedeutung der Substanz P in den dorsalen Wurzeln des Rückenmarks. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;219(3):197–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Iversen L. L., Hanley M. R., Sandberg B. E. The possible existence of multiple receptors for substance P. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;318(4):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00501166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E., SCHOEFL G. I. Studies on inflammation. II. The site of action of histamine and serotonin along the vascular tree: a topographic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:607–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majno G., Gilmore V., Leventhal M. On the mechanism of vascular leakage caused by histaminetype mediators. A microscopic study in vivo. Circ Res. 1967 Dec;21(6):833–847. doi: 10.1161/01.res.21.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C. Anesthesia-associated depression in lymphocyte traffic and its modulation. Am J Surg. 1984 Jun;147(6):807–812. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C., Chang J. K. Urinary histamine excretion in the rat following skin homografting and autografting. Ann Surg. 1968 Feb;167(2):232–238. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196802000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C. Histidine decarboxylase inhibitors and the survival of skin homofrafts. Nature. 1967 Aug 19;215(5103):871–872. doi: 10.1038/215871a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C., Jaffe B. M. Prostaglandin E levels of heterotopic rat heart allografts and host lymphoid tissues at intervals postgrafting. Transplantation. 1974 Oct;18(4):383–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C., Koppelman L. E., Lemmi C. A. Decreases in histamine forming enzyme activity of non-metastasizing fibrosarcomas in hamsters with progressive tumor growth. Ann Surg. 1978 Aug;188(2):175–180. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197808000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C. Modification of lymphocyte traffic by vasoactive neurotransmitter substances. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):511–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C., Sinclair M. C., Lemmi C. A. Elevation in plasma kallikrein activity after rat kidney allografting. Am J Surg. 1974 Mar;127(3):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C., Spruck C. H., Leduc L. E. Depression of lymphocyte traffic in sheep by anaesthesia and associated changes in efferent-lymph PGE2 and antibody levels. Immunology. 1988 Jan;63(1):139–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. C. The modulation by prostaglandins of increases in lymphocyte traffic induced by bradykinin. Immunology. 1984 Mar;51(3):455–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Substance P precursor and kininogen: their structures, gene organizations, and regulation. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1117–1142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Doteuchi M., Igano K., Inouye K., Nakanishi S. Substance K: a novel mammalian tachykinin that differs from substance P in its pharmacological profile. Life Sci. 1984 Mar 19;34(12):1153–1160. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Organist M. L., Harvey J., McGillis J. P., Mitsuhashi M., Melera P., Payan D. G. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody against the lymphoblast substance P receptor. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3050–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaway C. A., Greenberg G. R. Interaction of vasoactive intestinal peptide with mouse lymphocytes: specific binding and the modulation of mitogen responses. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):417–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., Brewster D. R., Goetzl E. J. Specific stimulation of human T lymphocytes by substance P. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1613–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., Brewster D. R., Missirian-Bastian A., Goetzl E. J. Substance P recognition by a subset of human T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1532–1539. doi: 10.1172/JCI111567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Lichtenstein L. M., Henney C. S. Properties of a subpopulation of T cells bearing histamine receptors. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):856–874. doi: 10.1172/JCI107997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M. R., Wahl S. M., Pert C. B. Substance P receptor-mediated chemotaxis of human monocytes. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicchitano R., Biennenstock J., Stanisz A. M. In vivo immunomodulation by the neuropeptide substance P. Immunology. 1988 Apr;63(4):733–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz A. M., Befus D., Bienenstock J. Differential effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P, and somatostatin on immunoglobulin synthesis and proliferations by lymphocytes from Peyer's patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, and spleen. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


