Abstract
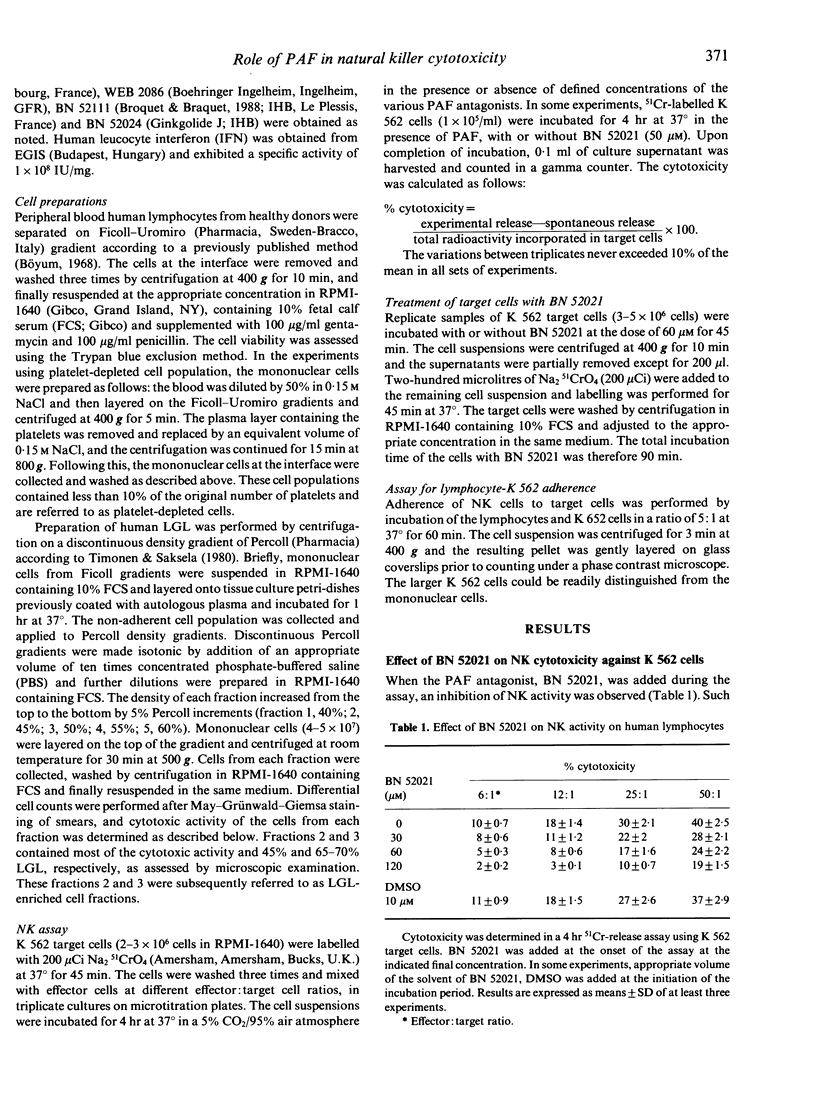
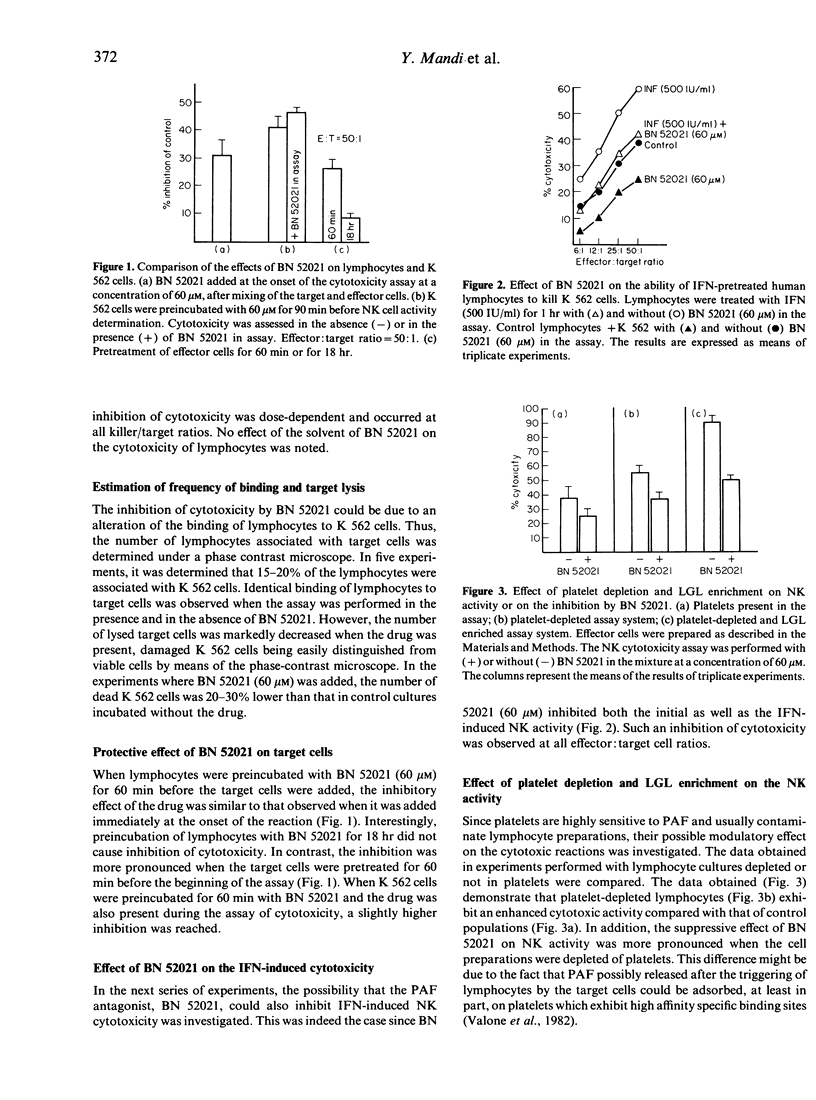
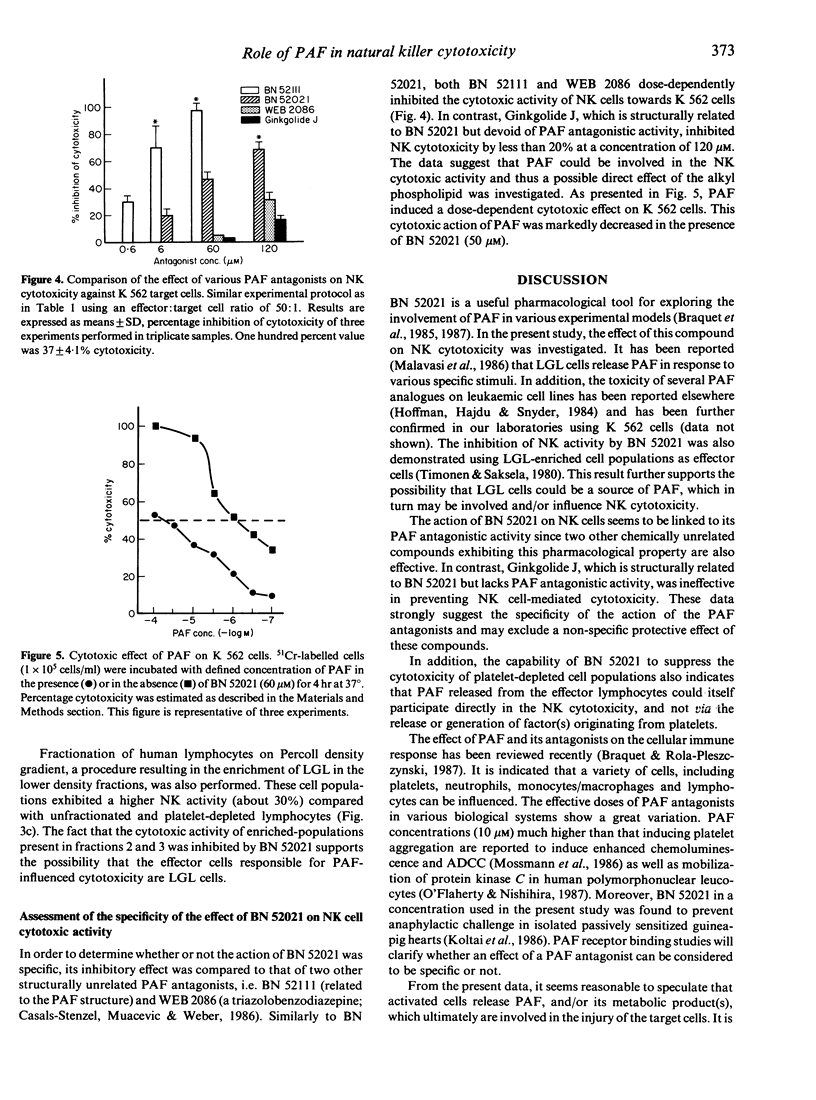
The influence of the platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonist, BN 52021, on human natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity against K 562 target cells was determined. Cytotoxicity was measured by a short-term (4 hr) 51Cr-release assay. The cytotoxicity was significantly reduced in the presence of PAF antagonist at concentrations from 30 to 120 microM. This reduction of killing was not due to the impairment of binding of effector cells to target cells. Pretreatment of K 562 target cells with the PAF antagonist led to a greater inhibition of NK cell cytotoxicity compared with that observed when the effector cells were preincubated with BN 52021. Thus, the inhibition of cytotoxicity appears to be due to an effect of BN 52021 on target cells rather than on lymphocytes. Furthermore, the increase in NK activity induced by interferon was less pronounced when BN 52021 was added in the incubation medium. The natural cytotoxicity of platelet-depleted or large granular lymphocyte-enriched effector cell populations was inhibited by the PAF antagonist in a similar manner. The effect of BN 52021 appears to be related to its specific PAF antagonistic activity since a similar action on NK cells was noted with two other structurally unrelated PAF antagonists, BN 52111 and WEB 2086. In contrast, Ginkgolide J (BN 52024), which is structurally related to BN 52021 but lacks PAF antagonistic activity, was ineffective in inhibiting NK cell cytotoxicity. Finally, synthetic PAF induces a dose-dependent cytotoxic action on K 562 cells and this effect of the autacoid is inhibited by BN 52021. These observations provide indirect evidence that PAF could play a role in the mechanism(s) of NK cytotoxity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Droller M. J., Schneider M. U., Perlmann P. A possible role of prostaglandins in the inhibition of natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Aug;39(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. R., Hajdu J., Snyder F. Cytotoxicity of platelet activating factor and related alkyl-phospholipid analogs in human leukemia cells, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, and skin fibroblasts. Blood. 1984 Mar;63(3):545–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman T., Hirata F., Bougnoux P., Fraser B. A., Goldfarb R. H., Herberman R. B., Axelrod J. Phospholipid methylation and phospholipase A2 activation in cytotoxicity by human natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3839–3843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltai M., Lepran I., Szekeres L., Viossat I., Chabrier E., Braquet P. Effect of BN 52021, a specific PAF-acether antagonist, on cardiac anaphylaxis in Langendorff hearts isolated from passively sensitized guinea-pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malavasi F., Tetta C., Funaro A., Bellone G., Ferrero E., Franzone A. C., Dellabona P., Rusci R., Matera L., Camussi G. Fc receptor triggering induces expression of surface activation antigens and release of platelet-activating factor in large granular lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossmann H., Bamberger U., Velev B. A., Gehrung M., Hammer D. K. Effect of platelet-activating factor on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte enhancement of chemiluminescence and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Feb;39(2):153–165. doi: 10.1002/jlb.39.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Nishihira J. Arachidonate metabolites, platelet-activating factor, and the mobilization of protein kinase C in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1889–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Isolation of human NK cells by density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Coles E., Reinhold V. R., Goetzl E. J. Specific binding of phospholipid platelet-activating factor by human platelets. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1637–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Hengartner H., Podack E. R., Cohn Z. A. Purification and characterization of a cytolytic pore-forming protein from granules of cloned lymphocytes with natural killer activity. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


