Abstract
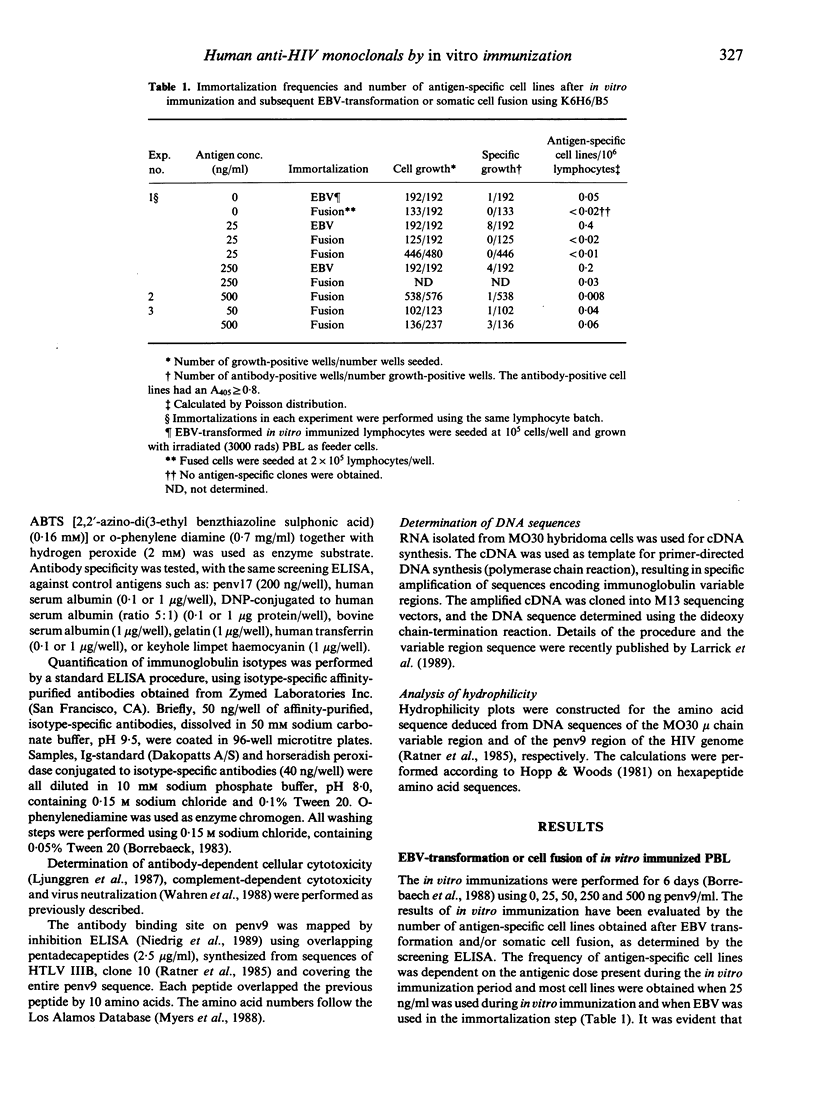
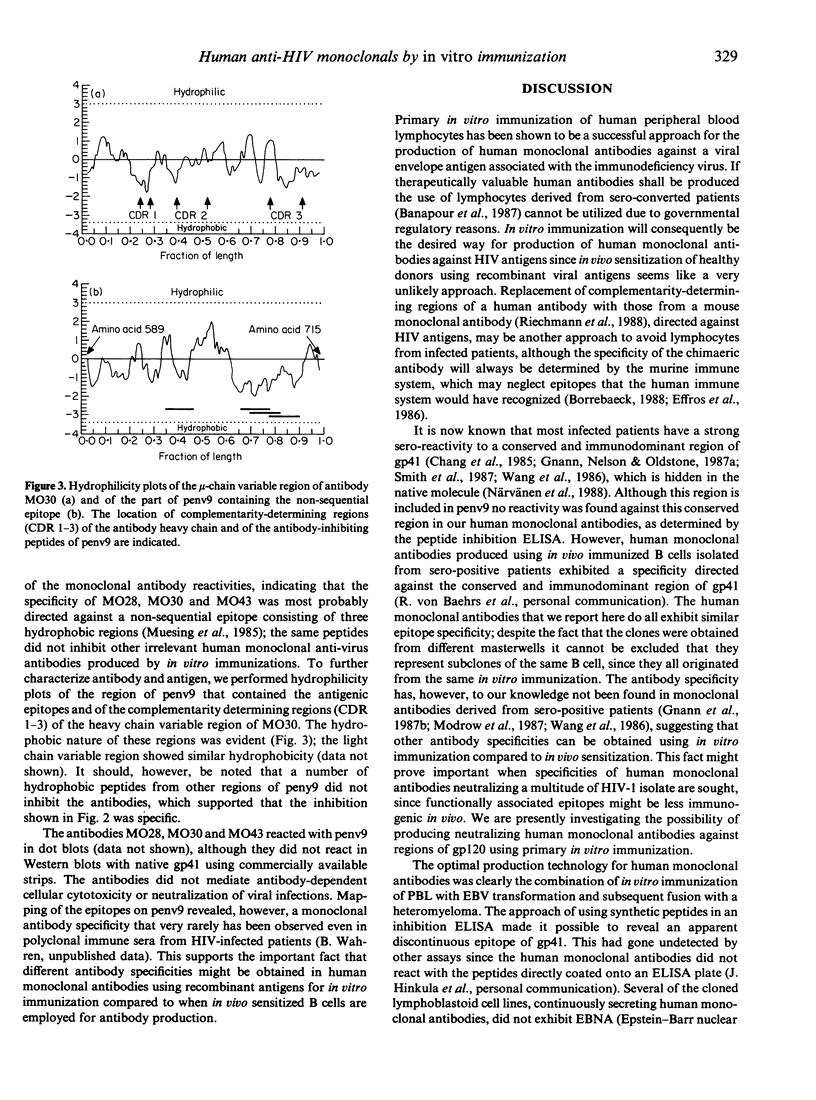
Peripheral blood lymphocytes from healthy, HIV sero-negative blood donors have been in vitro immunized using penv9, a recombinant fragment of the envelope of HIV-1. This primary in vitro immunization followed by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transformation and somatic cell fusion subsequently gave rise to several specific anti-penv9 monoclonal antibodies (MO28, MO30 and MO43) of mu isotype. The hybridomas have been kept in culture for over 6 months and the antibody productivity for MO30 was measured to 18 micrograms x (24 hr x 10(6) cells)-1. The fine specificity of the antibodies was mapped by a peptide inhibition enzyme immunoassay, using overlapping synthetic pentadeca peptides covering the whole penv9. These human monoclonal antibodies exhibited a similar epitope specificity directed against a non-sequential determinant, including the amino acids 632-646, 677-681 and 687-691. This specificity is very rarely found in immune sera from seropositive patients and presently not reported in human monoclonal antibodies derived from in vivo immunized individuals, indicating that different antibody specificities can be obtained by the in vitro immunization technology. These human monoclonal antibodies did not neutralize HIV. The results presented here demonstrate the feasability of generating human monoclonal antibodies against HIV by primary in vitro immunizations, thereby avoiding the use of lymphocytes derived from infected patients when human monoclonal antibodies for therapeutic purposes are to be produced.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aman P., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G. Epstein-Barr virus susceptibility of normal human B lymphocyte populations. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):208–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banapour B., Rosenthal K., Rabin L., Sharma V., Young L., Fernandez J., Engleman E., McGrath M., Reyes G., Lifson J. Characterization and epitope mapping of a human monoclonal antibody reactive with the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4027–4033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklock H. A., Griffiths P., Stirk P., Prentice H. G. Specific hyperimmune globulin for cytomegalovirus pneumonitis. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):152–153. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrebaeck C. A., Danielsson L., Möller S. A. Human monoclonal antibodies produced by primary in vitro immunization of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3995–3999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrebaeck C. A., Danielsson L., Möller S. A. Human monoclonal antibodies produced from L-leucine methyl ester-treated and in vitro immunized peripheral blood lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):941–946. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80223-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrebaeck C. A. Human mAbs produced by primary in-vitro immunization. Immunol Today. 1988 Nov;9(11):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrebaeck C. A. In vitro immunization for the production of antigen-specific lymphocyte hybridomas. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jul;18(1):9–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll W. L., Thielemans K., Dilley J., Levy R. Mouse x human heterohybridomas as fusion partners with human B cell tumors. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 1;89(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. A., Stein L. D., Dosch H. M., Sigal N. H. Heterogeneity of EBV-transformable human B lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):106–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J., Haase A., Levy J. A., Montagnier L., Oroszlan S., Teich N., Temin H., Toyoshima K., Varmus H., Vogt P. Human immunodeficiency viruses. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):697–697. doi: 10.1126/science.3008335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie R. M., O'Reilly R. J. Prevention of cytomegalovirus infection by prophylaxis with an intravenous, hyperimmune, native, unmodified cytomegalovirus globulin. Randomized trial in bone marrow transplant recipients. Am J Med. 1984 Mar 30;76(3A):134–141. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Chanh T. C., Kennedy R. C., Kanda P., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A. Neutralization of diverse HIV-1 strains by monoclonal antibodies raised against a gp41 synthetic peptide. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90674-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Effros R. B., Hulette C. M., Ettenger R., Dillard L. C., Zeller E., Duong R., Walford R. L. A human-human hybridoma secreting anti-HLA class II antibody. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1599–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Fine mapping of an immunodominant domain in the transmembrane glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2639–2641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2639-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Schwimmbeck P. L., Nelson J. A., Truax A. B., Oldstone M. B. Diagnosis of AIDS by using a 12-amino acid peptide representing an immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):261–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Sarngadharan M. G., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Rota T. R., Kennedy R. C., Chanh T. C., Sato V. L. Human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibodies recognize several conserved domains on the envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2024–2028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2024-2028.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Danielsson L., Brenner C. A., Abrahamson M., Fry K. E., Borrebaeck C. A. Rapid cloning of rearranged immunoglobulin genes from human hybridoma cells using mixed primers and the polymerase chain reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1250–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren K., Böttiger B., Biberfeld G., Karlson A., Fenyö E. M., Jondal M. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-inducing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus. Presence at different clinical stages. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2263–2267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F., Wolf H. Computer-assisted analysis of envelope protein sequences of seven human immunodeficiency virus isolates: prediction of antigenic epitopes in conserved and variable regions. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.570-578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Gordon C., Potter A., Zola H. The purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jul 24;91(2):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedrig M., Hinkula J., Weigelt W., L'age-Stehr J., Pauli G., Rosen J., Wahren B. Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 structural proteins by using peptides. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3525–3528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3525-3528.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Närvänen A., Korkolainen M., Kontio S., Suni J., Turtianen S., Partanen P., Soos J., Vaheri A., Huhtala M. L. Highly immunoreactive antigenic site in a hydrophobic domain of HIV-1 gp41 which remains undetectable with conventional immunochemical methods. AIDS. 1988 Apr;2(2):119–123. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198804000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Langlois A. J., Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Randall R. R., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Type-specific neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus with antibodies to env-encoded synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Horowitz B., Baker L., Shulman R. W., Ralph H., Valinsky J., Cundell A., Brotman B., Boehle W., Rey F. Failure of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) immune globulin to protect chimpanzees against experimental challenge with HIV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Matthews T. J., Robey W. G., Lynn D. L., Robert-Guroff M., Mueller W. T., Langlois A. J., Ghrayeb J., Petteway S. R., Jr, Weinhold K. J. HTLV-III/LAV-neutralizing antibodies to an E. coli-produced fragment of the virus envelope. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1392–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.2431482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riechmann L., Clark M., Waldmann H., Winter G. Reshaping human antibodies for therapy. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):323–327. doi: 10.1038/332323a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarngadharan M. G., Popovic M., Bruch L., Schüpbach J., Gallo R. C. Antibodies reactive with human T-lymphotropic retroviruses (HTLV-III) in the serum of patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):506–508. doi: 10.1126/science.6324345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Gnann J. W., Jr, Langlois A. J., Shriver K., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. B- and T-lymphocyte responses to an immunodominant epitope of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2531–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2531-2536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Naso R. B., Rosen J., Whalley A., Hom Y. L., Hoey K., Kennedy C. J., McCutchan J. A., Spector S. A., Richman D. D. Antibody to a synthetic oligopeptide in subjects at risk for human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1498–1504. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1498-1504.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Chiodi F., Ljunggren K., Putney S., Kurth R., Gallo R. C., Fenyö E. M. B and T cell reactivities after immunization of macaques with HIV subcomponents. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Jun;4(3):199–210. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. J., Steel S., Wisniewolski R., Wang C. Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type III by using a synthetic peptide of 21 amino acid residues corresponding to a highly antigenic segment of gp41 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6159–6163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. N., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Parker D., Roberts C., Duncan J., Weller I., Carne C., Tedder R. S., Pinching A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in two cohorts of homosexual men: neutralising sera and association of anti-gag antibody with prognosis. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Dalgleish A. G., Lasky L. A., Berman P. W. Variable and conserved neutralization antigens of human immunodeficiency virus. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):572–575. doi: 10.1038/324572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Human T-lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):395–403. doi: 10.1038/317395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


