Abstract
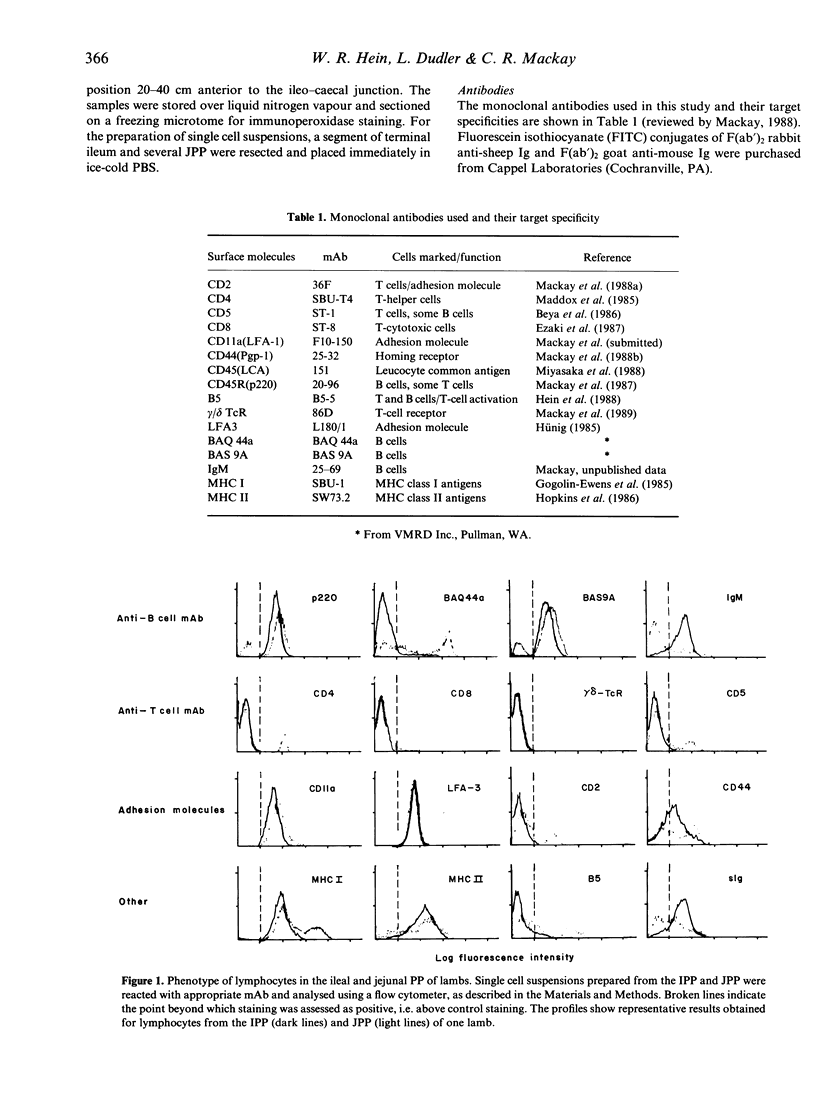
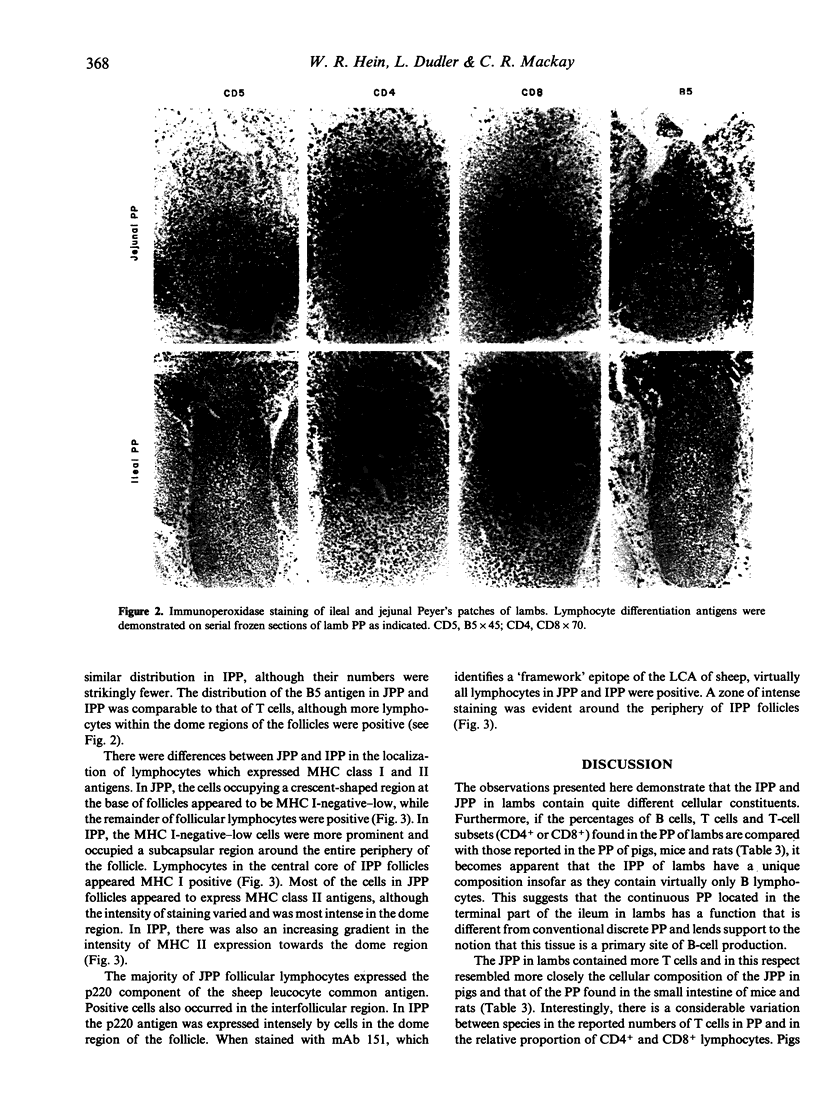
The surface phenotype of lymphocytes in the ileal (IPP) and jejunal (JPP) Peyer's patches (PP) of lambs was compared using flow cytometry and immunohistology with a panel of monoclonal antibodies (mAb). The B-cell markers p220, BAS9A and surface Ig molecules were detected on 70-95% of cells from the IPP. T-cell markers were detected on less than 1% of IPP lymphocytes, confirming that the IPP in lambs contains virtually only B lymphocytes. The JPP contained a lower proportion of B cells and 16% T cells, nearly all of which expressed the CD4 molecule. Interestingly, the reactivity of a fourth B-cell markers, BAQ44a, differed from this pattern; only 12% of IPP lymphocytes were positive whereas 70% of JPP lymphocytes expressed this marker. A majority of both IPP and JPP lymphocytes (80-95%) expressed the cell adhesion molecules CD11a (LFA-1) and LFA-3. Other adhesion molecules, such as CD2 and CD44, were expressed by fewer cells from the IPP than from the JPP. MHC class I antigens were detected on more than 95% of lymphocytes from both the IPP and JPP. In the case of MHC class II antigens, more positive cells occurred in the IPP (greater than 95%) than in the JPP (80%). The in situ localization of cell-surface antigens was assessed by immunohistology. CD4+ T cells occurred in the interfollicular T-cell regions and in JPP follicles, whereas CD8+ T cells localized only in the interfollicular regions and were absent from follicles. The pattern of expression of B-cell markers, adhesion molecules and MHC antigens indicated that a gradient of increasing maturity of B cells existed within follicles from the base towards the dome region. The data presented here lend support to the notion that the IPP in lambs represents a novel B-cell lymphoid tissue with a function different from that of the conventional Peyer's patches found in the jejunum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beya M. F., Miyasaka M., Dudler L., Ezaki T., Trnka Z. Studies on the differentiation of T lymphocytes in sheep. II. Two monoclonal antibodies that recognize all ovine T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):115–121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki T., Miyasaka M., Beya M. F., Dudler L., Trnka Z. A murine anti-sheep T8 monoclonal antibody, ST-8, that defines the cytotoxic T lymphocyte population. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;82(2):168–177. doi: 10.1159/000234183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber H. A., Morris B., Trevella W. The role of gut-associated lymphoid tissues in the generation of immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes in sheep. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1986 Jun;64(Pt 3):201–213. doi: 10.1038/icb.1986.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolin-Ewens K. J., Mackay C. R., Mercer W. R., Brandon M. R. Sheep lymphocyte antigens (OLA). I. Major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Immunology. 1985 Dec;56(4):717–723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein W. R., McClure S., Beya M. F., Dudler L., Trnka Z. A novel glycoprotein expressed on sheep T and B lymphocytes is involved in a T cell activation pathway. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2869–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J., Dutia B. M., McConnell I. Monoclonal antibodies to sheep lymphocytes. I. Identification of MHC class II molecules on lymphoid tissue and changes in the level of class II expression on lymph-borne cells following antigen stimulation in vivo. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):433–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T. The cell surface molecule recognized by the erythrocyte receptor of T lymphocytes. Identification and partial characterization using a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):890–901. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi H., Saltzman L. E., Strober W. Mechanisms regulating IgA class-specific immunoglobulin production in murine gut-associated lymphoid tissues. I. T cells derived from Peyer's patches that switch sIgM B cells to sIgA B cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):433–450. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen H. J., Landsverk T. Distribution of T and B lymphocytes in jejunal and ileocaecal Peyer's patches of lambs. Res Vet Sci. 1986 Jan;40(1):105–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyscom N., Brueton M. J. Intraepithelial, lamina propria and Peyer's patch lymphocytes of the rat small intestine: isolation and characterization in terms of immunoglobulin markers and receptors for monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):775–783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Hein W. R., Brown M. H., Matzinger P. Unusual expression of CD2 in sheep: implications for T cell interactions. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1681–1688. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Maddox J. F., Brandon M. R. A monoclonal antibody to the p220 component of sheep LCA identifies B cells and a unique lymphocyte subset. Cell Immunol. 1987 Nov;110(1):46–55. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. Sheep leukocyte molecules: a review of their distribution, structure and possible function. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jul;19(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox J. F., Mackay C. R., Brandon M. R. Surface antigens, SBU-T4 and SBU-T8, of sheep T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):739–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka M., Dudler L., Bordmann G., Leiserson W. M., Gerber H. A., Reynolds J., Trnka Z. Differentiation of B lymphocytes in sheep. I. Phenotypic analysis of ileal Peyer's patch cells and the demonstration of a precursor population for sIg+ cells in the ileal Peyer's patches. Immunology. 1984 Nov;53(3):515–523. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst R., Reynolds J. D. Evidence of extensive lymphocyte death in sheep Peyer's patches. II. The number and fate of newly-formed lymphocytes that emigrate from Peyer's patches. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2011–2017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., McCluskey R. T., Schlossman S. F. Distribution of T cell subsets in human lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):30–41. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. D. Evidence of extensive lymphocyte death in sheep Peyer's patches. I. A comparison of lymphocyte production and export. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2005–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. D. Mitotic rate maturation in the Peyer's patches of fetal sheep and in the bursa of Fabricius of the chick embryo. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):503–507. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. D., Morris B. The effect of antigen on the development of Peyer's patches in sheep. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jan;14(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. D., Morris B. The evolution and involution of Peyer's patches in fetal and postnatal sheep. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):627–635. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothkötter H. J., Pabst R. Lymphocyte subsets in jejunal and ileal Peyer's patches of normal and gnotobiotic minipigs. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):103–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse R. V., Ledbetter J. A., Weissman I. L. Mouse lymph node germinal centers contain a selected subset of T cells--the helper phenotype. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2243–2246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]