Abstract
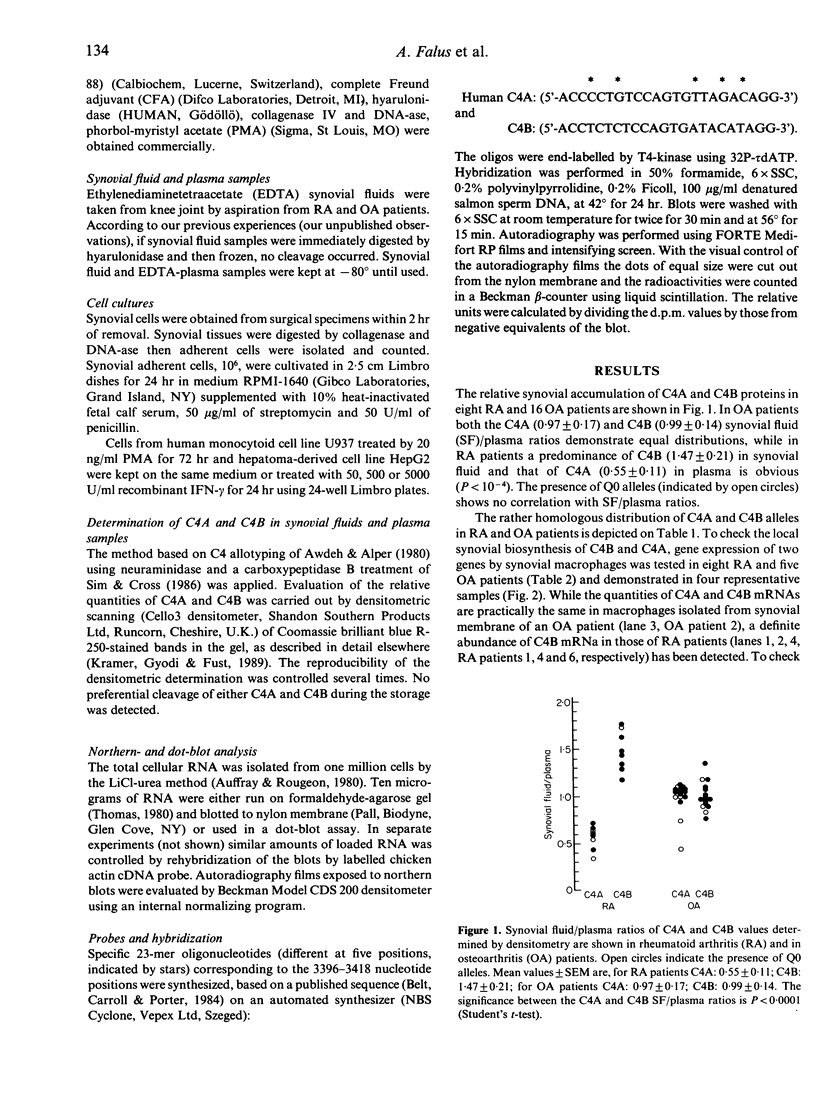
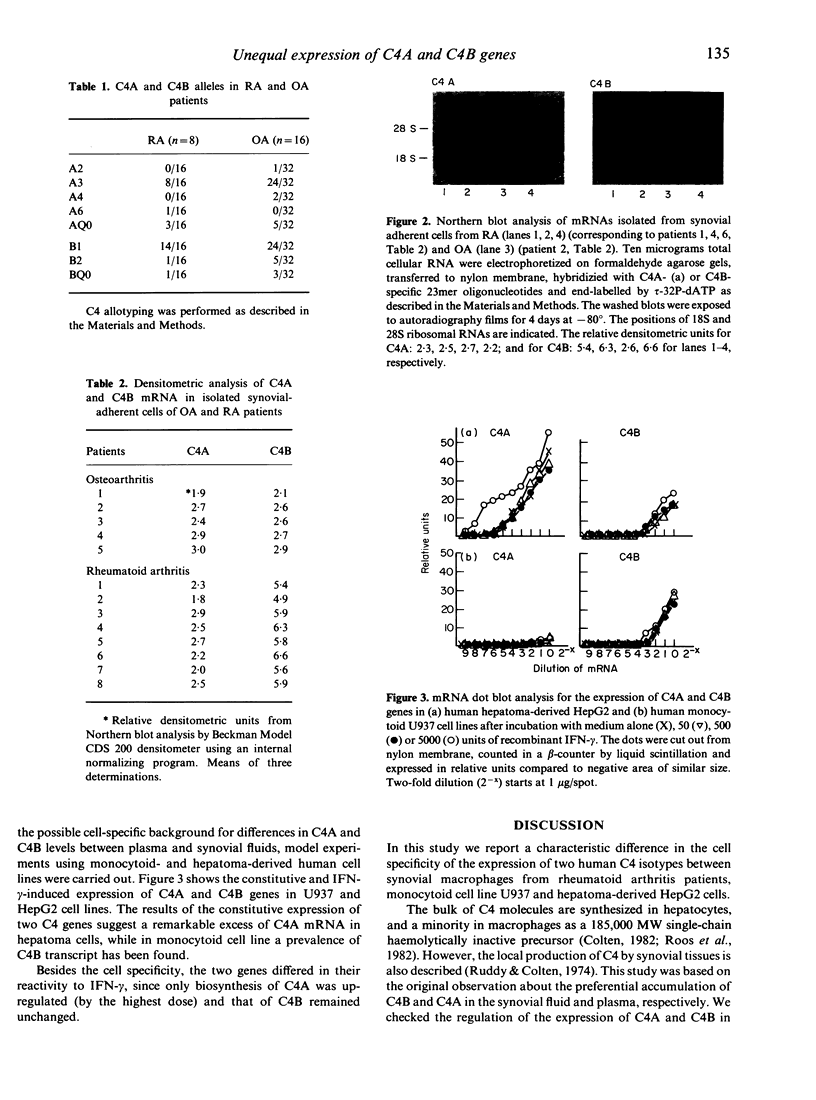
C4A and C4B are closely related homologous complement proteins encoded in the class III region of major histocompatibility complex (MHC). The regulation of their expression is under genetic and hormonal control. In this study we investigated the synovial fluid plasma ratio of C4A and C4B of rheumatoid (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) patients, and a predominance of the C4B gene expression by the synovial macrophages of RA patients was demonstrated. To clarify the tissue specificity of the expression of C4A and C4B genes, human monocytoid cell line U937 and hepatoma-derived HepG2 cells were studied. The gene expression of C4A and C4B were markedly different in these cells since a relative predominance of C4B mRNA in U937 cells and excess of that of C4A in HepG2 cells were detected. Recombinant interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) up-regulated the expression of C4A gene in both cells, but had apparently no effect on the C4B gene. Our results demonstrate dissimilar expression patterns for the two human C4 genes, suggesting different tissue specific regulation of human C4A and C4B.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. D., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The molecular genetics of components of complement. Adv Immunol. 1986;38:203–244. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. Cloning of a human complement component C4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):264–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Biosynthesis of the MHC-linked complement proteins (C2, C4 and factor B) by mononuclear phagocytes. Mol Immunol. 1982 Oct;19(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J., Gyódi E., Füst G. Usefulness of densitometry in typing of human complement component C4. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(2):121–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00395861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Dodds A. W., Porter R. R. A comparison of the properties of two classes, C4A and C4B, of the human complement component C4. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1819–1823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura N., Prentice H. L., Schneider P. M., Perlmutter D. H. Synthesis and regulation of the two human complement C4 genes in stable transfected mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7298–7305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Mollenhauer E., Démant P., Rittner C. A molecular basis for the two locus model of human complement component C4. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):854–856. doi: 10.1038/298854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Colten H. R. Rheumatoid arthritis. Biosynthesis of complement proteins by synovial tissues. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 6;290(23):1284–1288. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406062902304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Paccaud J. P. Two isotypes of human C4, C4A and C4B have different structure and function. Complement Inflamm. 1989;6(1):19–26. doi: 10.1159/000463068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim E., Cross S. J. Phenotyping of human complement component C4, a class-III HLA antigen. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):763–767. doi: 10.1042/bj2390763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teisberg P., Olaisen B., Nordhagen R., Thorsby E., Geddedahl T., Jr A haemolytically non-active C4 gene product. Immunobiology. 1980;158(1-2):91–95. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(80)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. Y., Belt K. T., Giles C. M., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Structural basis of the polymorphism of human complement components C4A and C4B: gene size, reactivity and antigenicity. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2873–2881. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



