Abstract
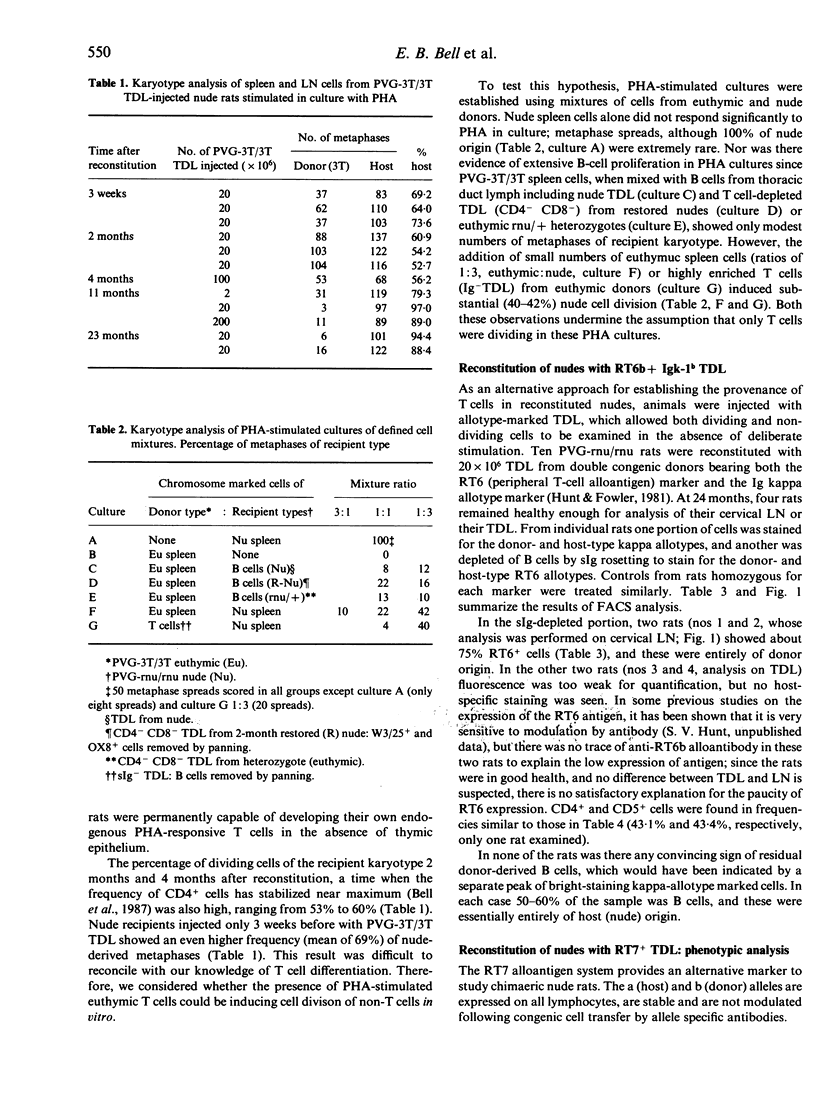
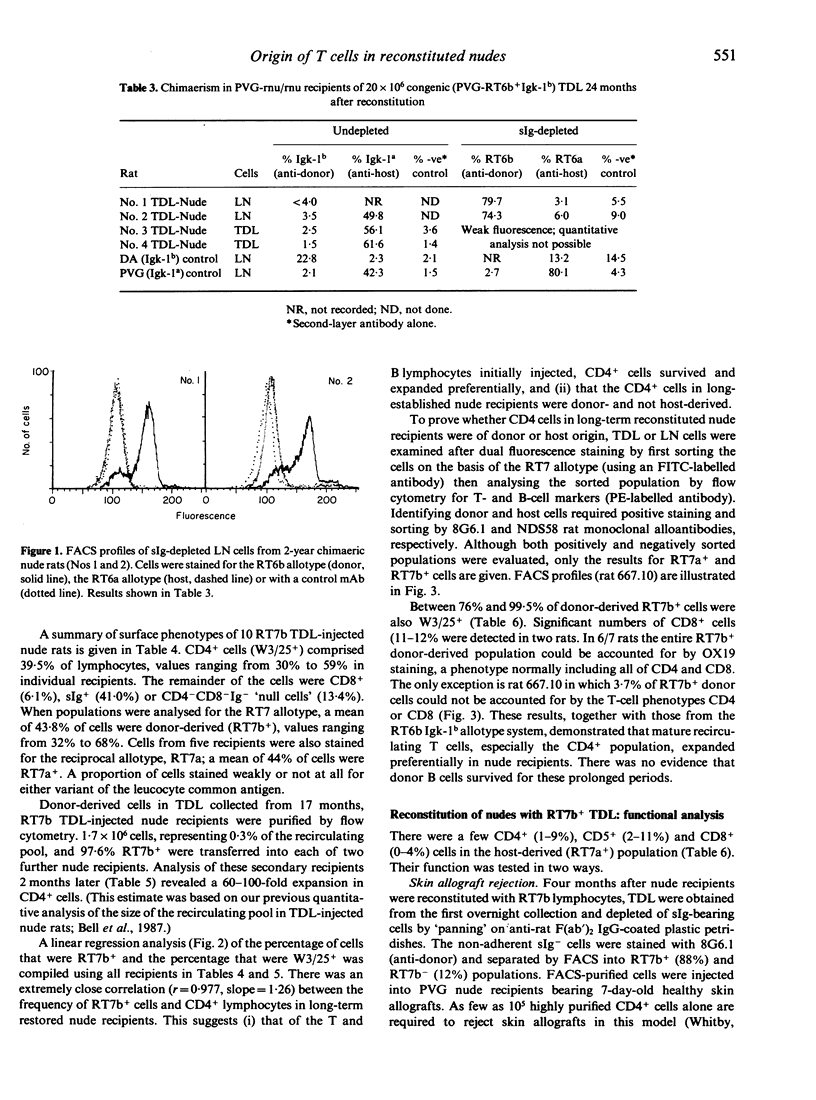
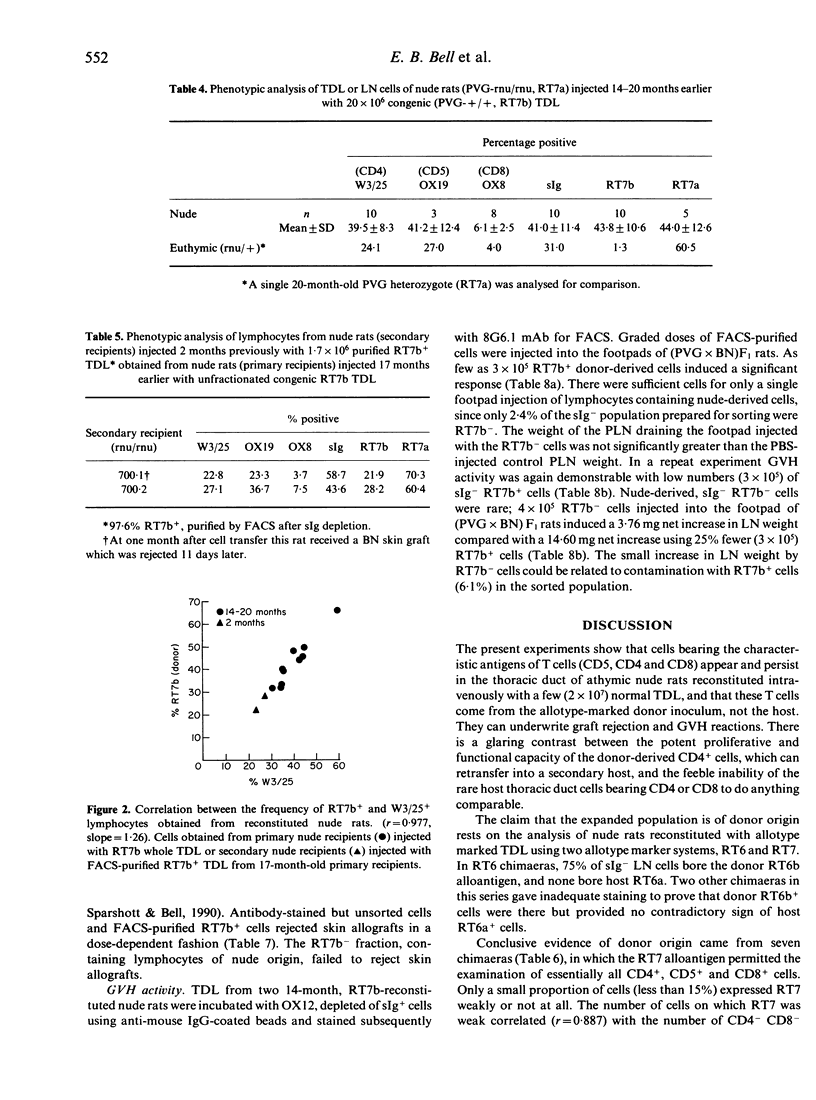
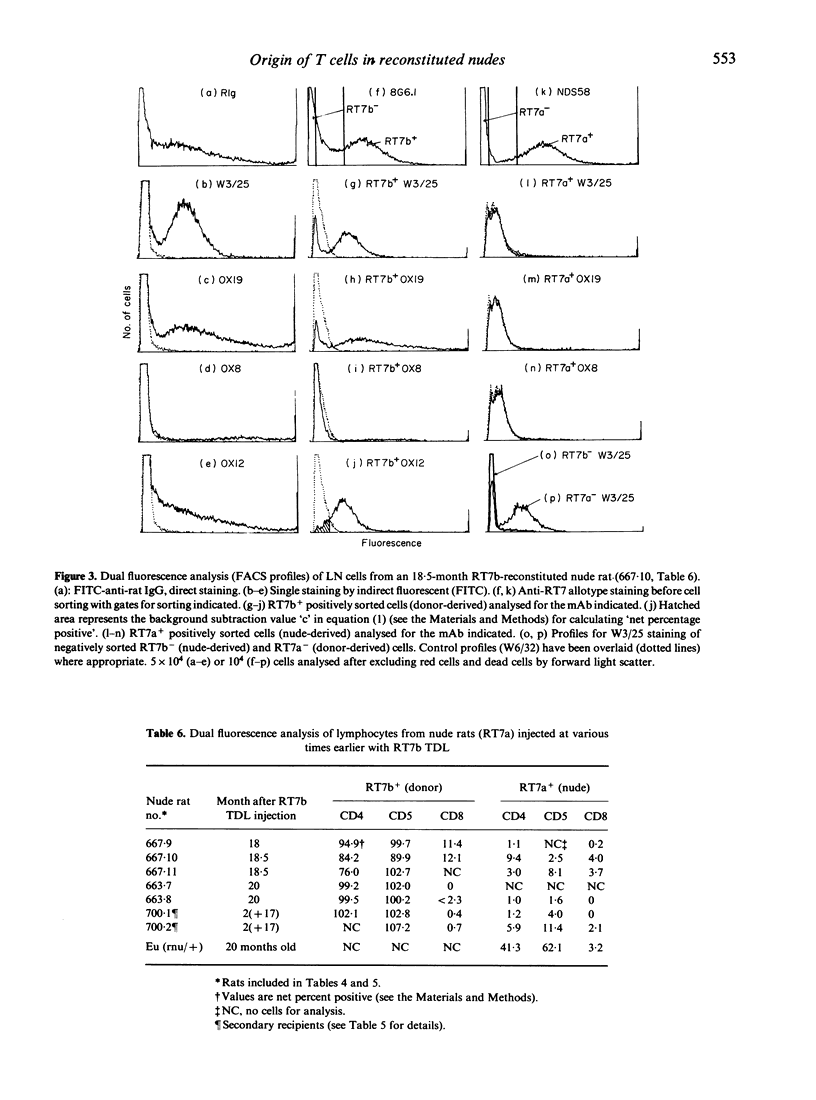
Athymic PVG-rnu/rnu rats receiving a single intravenous injection of syngeneic euthymic thoracic duct lymphocytes (TDL) develop normal levels of CD4+ T lymphocytes and survive for more than 2 years in a conventional animal house. We investigated the origin of the T cells (and B cells) in reconstituted nude recipients by transferring TDL carrying either the 3T chromosome marker or the RT6b + Igk-1b allotype or the RT7b (leucocyte-common) allotype markers. Karyotype analysis of spleen and lymph node (LN) cells from 1- to 2-year-old PVG-3T/3T-reconstituted nude recipients, stimulated in vitro with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), unexpectedly revealed that a majority (79-97%) of dividing cells were of nude origin. However, extensive nude cell division was also recorded in PHA-stimulated cultures using mixtures of euthymic (PVG-3T/3T) and unreconstituted nude spleen cells; the assumption that only T cells divide in PHA-stimulated cultures thus appears to be erroneous. In contrast to the karyotype analysis, sIg- RT6b+ LN cells obtained from nude recipients reconstituted 2 years earlier with PVG-RT6b allotype-marked TDL, were all of donor origin with no indication of a nude-derived sIg- RT6a+ population. Igk-1b+ donor B cells were not found in these same recipients. Dual fluorescence analysis of TDL from 18- to 20-month RT7b-reconstituted nudes showed that 91-100% of CD4+ cells were donor-derived. When tested functionally, sIg- RT7b+ (donor) cells, but not sIg- RT7b- (nude-derived) cells, were able to reject skin allografts and induce local graft-versus-host (GVH) responses. Donor T cells, in contrast to CD4+ cells of nude origin, divided extensively in nude recipients; FACS-purified RT7b+ (donor) TDL retransferred from 17-month primary reconstituted nude rats, expanded further (60-100-fold) in secondary nude recipients. In conclusion, only the donor-derived CD4+ cells in reconstituted nude rats displayed T-cell function; evidence to the contrary from karyotype analysis was flawed. At no stage in their life did uninjected or T-cell reconstituted nude rats develop endogenous cells that in any way resembled CD4+ products of the thymus.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell E. B., Sparshott S. M., Drayson M. T., Ford W. L. The stable and permanent expansion of functional T lymphocytes in athymic nude rats after a single injection of mature T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1379–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Webb P. J., Robins R. A., Robinson G., Baldwin R. W., Festing M. F. Studies on the immunobiology of rnu/rnu "nude" rats with congenital aplasia of the thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jan;10(1):58–65. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. W. A list of monoclonal antibodies specific for alloantigens of the rat. J Immunogenet. 1987 Apr-Jun;14(2-3):163–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1987.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. F., Scollay R., Shortman K., Skinner M., Marbrook J. T-cell development in the absence of a thymus: the number, the phenotype, and the functional capacity of T lymphocytes in nude mice. Am J Anat. 1984 Jul;170(3):339–347. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001700309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenhoff M. J., Davies A. J. Reconstitution of the T-cell pool after irradiation of mice. Cell Immunol. 1971 Feb;2(1):82–90. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayson M. T., Sparshott S. M., Bell E. B. Fidelity of the repertoire in T cell reconstituted athymic nude rats. Preservation of a deficit in alloresponsiveness over one year. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):691–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer M. J., Hunt S. V. Committed T lymphocyte stem cells of rats. Characterization by surface W3/13 antigen and radiosensitivity. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1164–1177. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford W. L., Burr W., Simonsen M. A lymph node weight assay for the graft-versus-host activity of rat lymphoid cells. Transplantation. 1970 Sep;10(3):258–266. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197009000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum S., Smith M. E., Bell E. B., Ford W. L. The architecture of rat lymph nodes. III. The lymph nodes and lymph-borne cells of the congenitally athymic nude rat (rnu). Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(5):421–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Union N. A., Baker P. E., Smith K. A. The in vitro generation and sustained culture of nude mouse cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1460–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. A community effect in animal development. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):772–774. doi: 10.1038/336772a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Quillet A., Marchiol C., Gerard J. P., Fradelizi D. Lack of reconstitution of nude mice alloreactivity by purified interleukin 2 and induction of non-H-2-specific effector cells by crude supernatants. Cell Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;105(2):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. C., Scott D. W. The identification of sera distinguishing marrow-derived and thymus-derived lymphocytes in the rat thoracic duct. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):903–922. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. V., Fowler M. H. A repopulation assay for B and T lymphocyte stem cells employing radiation chimaeras. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1981 Jul;14(4):445–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1981.tb00551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Bevan M. J. Specificity of cytotoxic T cells from athymic mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):688–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindred B. Nude mice in immunology. Prog Allergy. 1979;26:137–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishihara K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Mak T. W., Nomoto K. Functional alpha and beta T cell chain receptor messages can be detected in old but not in young athymic mice. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):477–482. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung J. T. Impaired clonal expansion in athymic nude CD8+CD4- T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3727–3735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung J. T., Thomas C. A., 3rd Athymic nude CD4+8- T cells produce IL-2 but fail to proliferate in response to mitogenic stimuli. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3691–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawetzky A., Hünig T. Analysis of CD3 and antigen receptor expression on T cell subpopulations of aged athymic mice. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Mar;18(3):409–416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Blanc C., Lees R. K., Sordat B. Abnormal distribution of T cell subsets in athymic mice. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4337–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Lees R. K., Bron C., Sordat B., Miescher G. T cell antigen receptor expression in athymic (nu/nu) mice. Evidence for an oligoclonal beta chain repertoire. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):195–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Lees R. K., Sordat B., Zaech P., Maryanski J. L., Bron C. Age-associated increase in expression of the T cell surface markers Thy-1, Lyt-1, and Lyt-2 in congenitally athymic (nu/nu) mice: analysis by flow microfluorometry. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):865–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G., McHugh L. L., Rothstein T. L. Mouse lymphocytes with and without surface immunoglobulin: preparative scale separation in polystyrene tissue culture dishes coated with specifically purified anti-immunoglobulin. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleckar J. R., Sherman L. A. The composition of the T cell receptor repertoire in nude mice. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3873–3876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., MacDonald H. R., Sordat B., Cerottini J. C. Cytolytic T lymphocyte precursor cells in congenitally athymic C57BL/6 nu/nu mice: quantitation, enrichment, and specificity. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):871–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Cron R., Bluestone J. A. Major histocompatibility complex-linked specificity of gamma delta receptor-bearing T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):262–264. doi: 10.1038/330262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojcik C. F., Greiner D. L., Goldschneider I., Lubaroff D. M. Monoclonal antibodies to RT7 and LCA antigens in the rat: cell distribution and segregation analysis. Hybridoma. 1987 Oct;6(5):531–543. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1987.6.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard H., Micklem H. S. Haemopoietic stem cells and progenitors of functional T-lymphocytes in the bone marrow of 'nude' mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Aug;14(4):597–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen L. M., Broekhuizen R., Rozing J., Vos J. G., Schuurman H. J. T-cell development during ageing in congenitally athymic (nude) rats. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Aug;24(2):223–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vliet E., Jenkinson E. J., Kingston R., Owen J. J., Van Ewijk W. Stromal cell types in the developing thymus of the normal and nude mouse embryo. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):675–681. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Heeg K., Röllinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K. T-cell-derived helper factor allows in vivo induction of cytotoxic T cells in nu/nu mice. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):278–278. doi: 10.1038/284278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Takeda Y., Ohga S., Kishihara K., Yuuki H., Nomoto K. Functional T cell receptor delta chain gene messages in athymic nude mice. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1039–1043. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Reis M. D., Mak T. W. Athymic mice express a high level of functional gamma-chain but greatly reduced levels of alpha- and beta-chain T-cell receptor messages. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):482–485. doi: 10.1038/324482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Takeda Y., Ohga S., Kishihara K., Matsuzaki G., Nomoto K. Rearrangements of T-cell antigen receptor gamma and delta chain genes are detected in the long-term cultured bone marrow cells of athymic nude mice but not in those of euthymic mice. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):512–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



