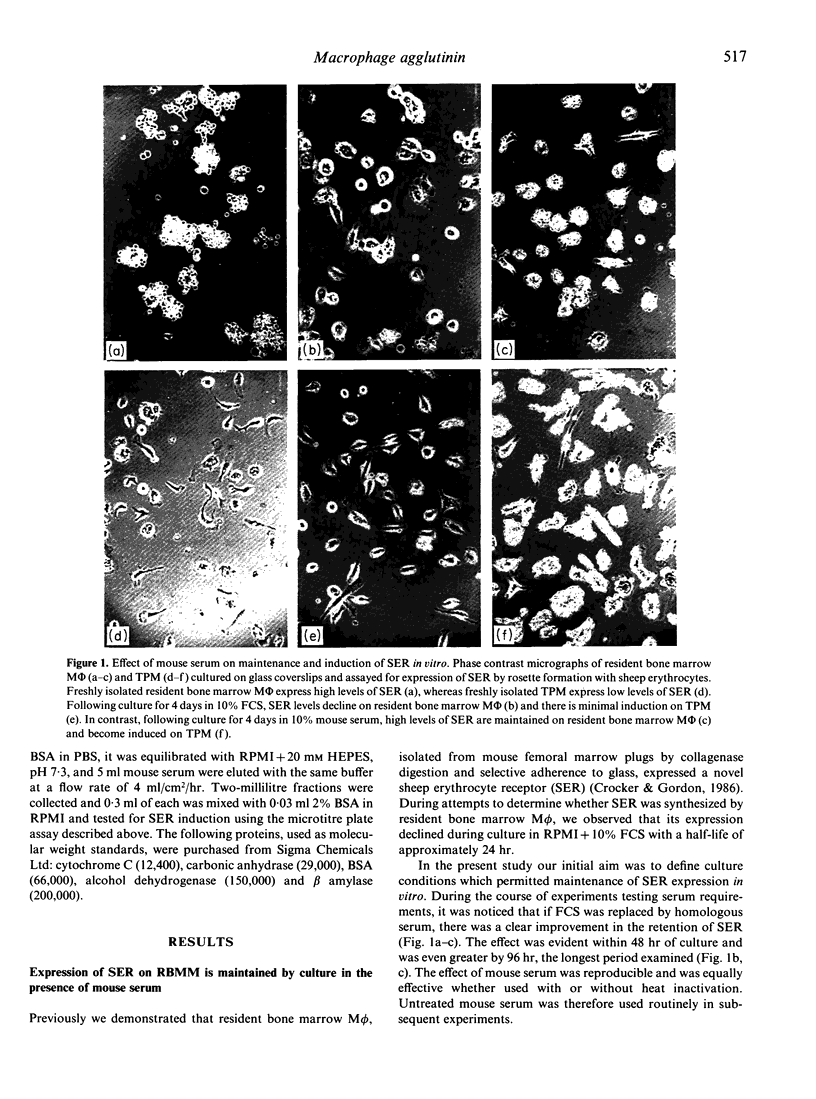
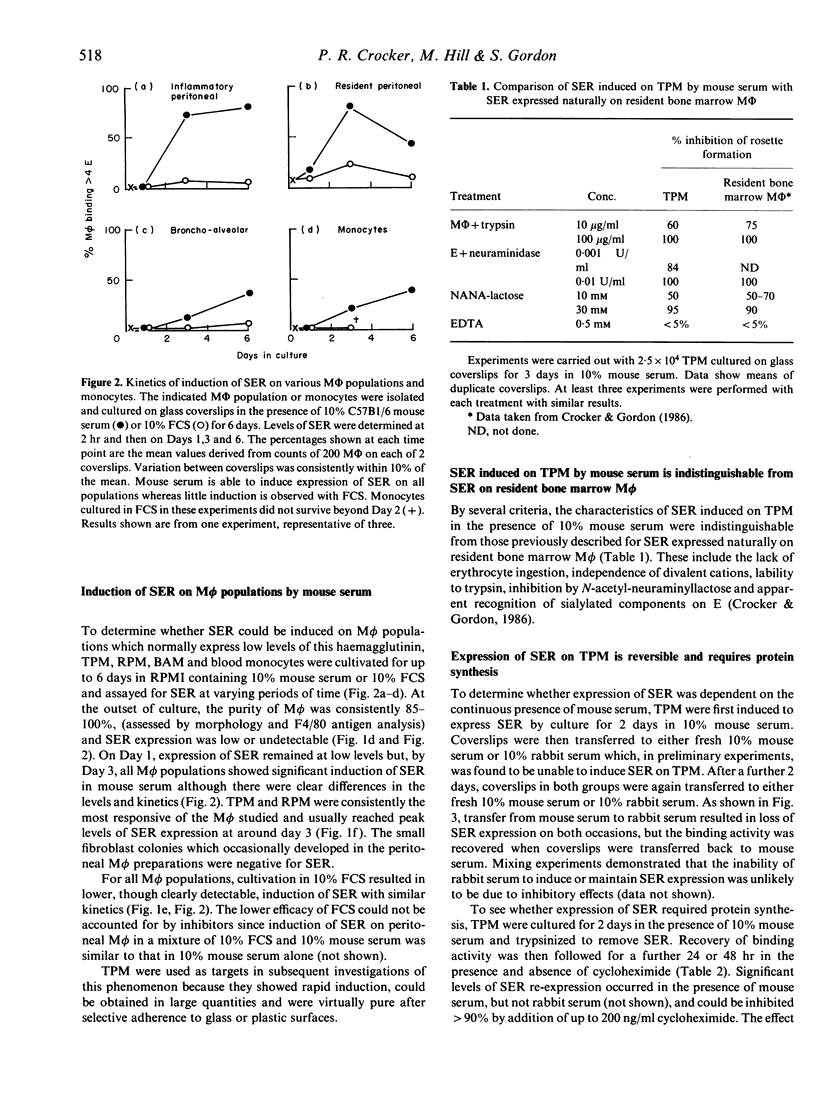
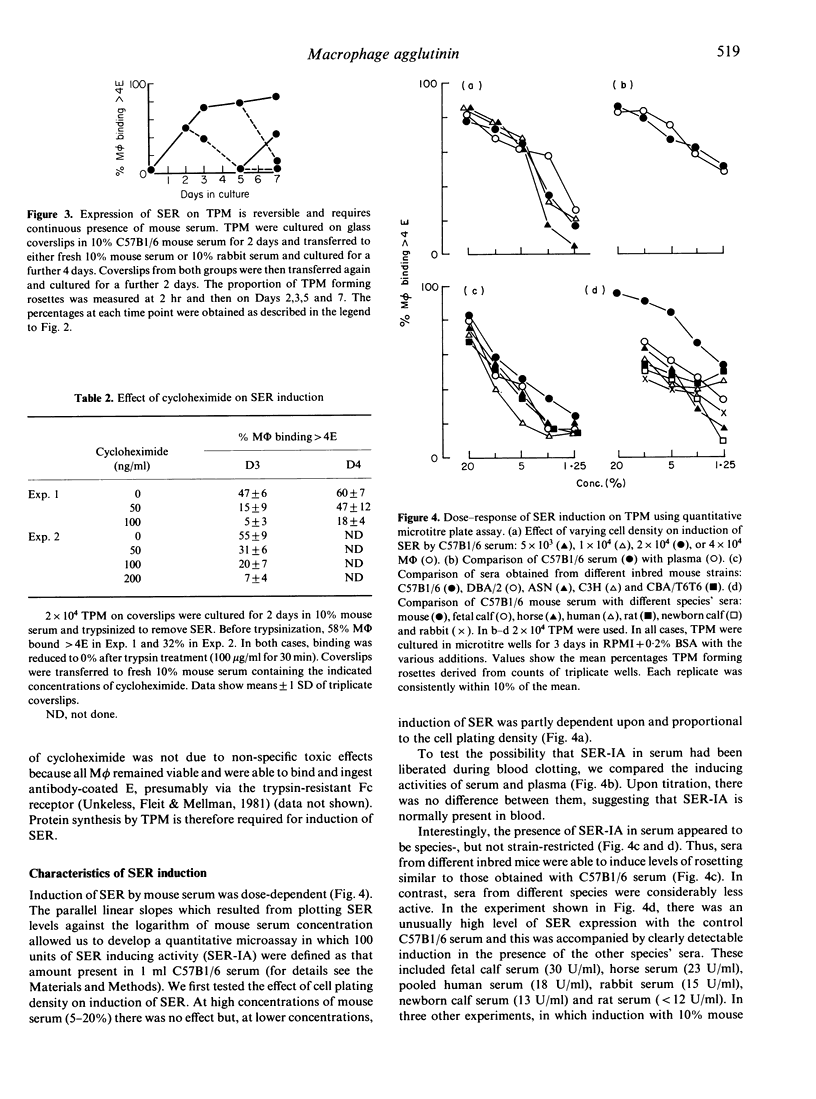
Abstract
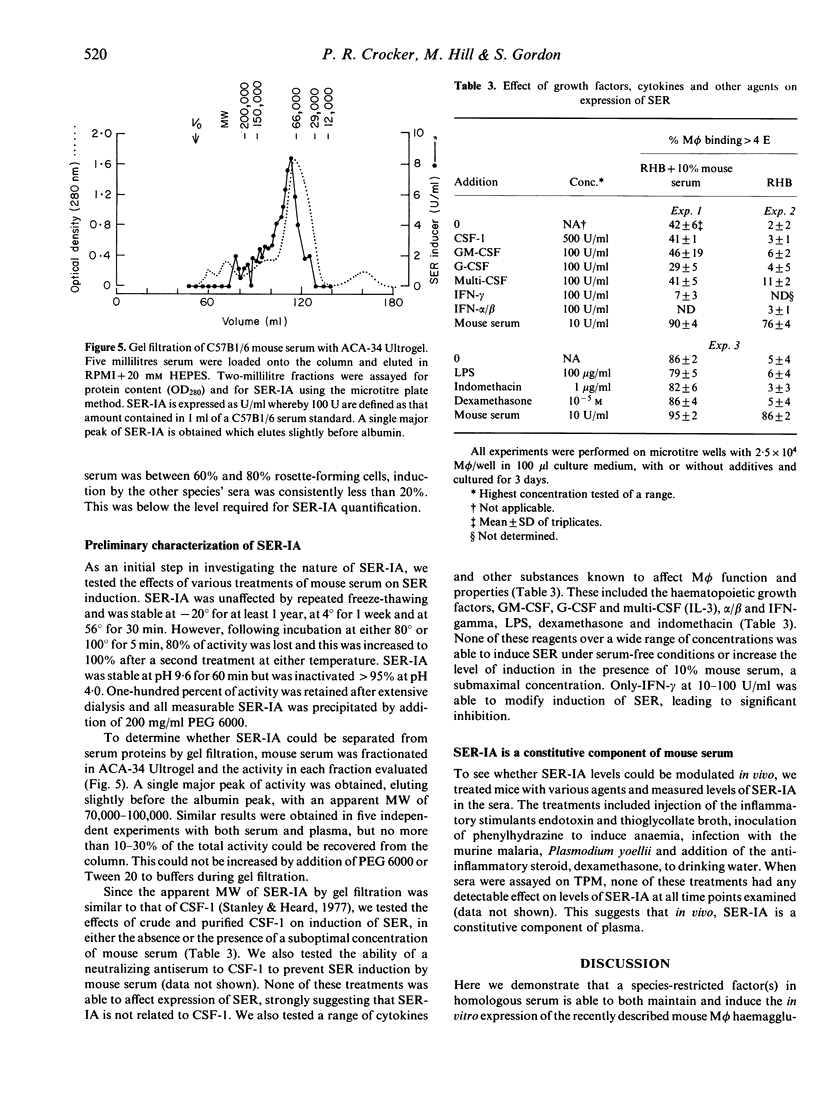
The mechanisms which generate heterogeneity amongst resident tissue macrophages (M phi) are poorly understood. In a previous study we described a novel mouse M phi haemagglutinin, which binds unopsonized sheep erythrocytes. This sheep erythrocyte receptor (SER) is expressed at high levels on stromal M phi from bone marrow and lymph nodes, but at low levels on M phi from serous cavities and broncho-alveolar spaces. In this paper we demonstrate that a species-restricted factor in mouse serum is required in vitro for optimal maintenance of SER on resident bone marrow M phi and for its induction on M phi populations which normally lack this receptor. Using thioglycollate-elicited peritoneal M phi, induction of SER by mouse serum was dose-dependent, reached maximal levels by 3-4 days, required the continuous presence of mouse serum, and was fully reversible. Re-expression following trypsinization was inhibited by cycloheximide, showing that protein synthesis by M phi was necessary. Using a quantitative microtitre plate assay to measure levels of the inducing activity (SER-IA) in different samples, it was found to be heat-labile, non-dialysable, precipitable by polyethylene glycol and inactivated at pH 4 but not at pH 9.6. On gel filtration of mouse serum, a single major peak of activity was obtained with an apparent MW of around 70,000. SER-IA appears to be unrelated to a variety of factors and cytokines which affect M phi function, including colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1). The possible role of SER-IA in regulating the differential expression of SER in vivo is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crocker P. R., Gordon S. Properties and distribution of a lectin-like hemagglutinin differentially expressed by murine stromal tissue macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1862–1875. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A., Joling P., Kraal G. The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophage subpopulations in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen A. G., Muggenburg B. A., Snipes M. B., Bice D. E. The role of macrophages in particle translocation from lungs to lymph nodes. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1277–1280. doi: 10.1126/science.4071052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Sundaram V. Origin and turnover of follicular dendritic cells and marginal zone macrophages in the mouse spleen. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;186:167–170. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2463-8_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nogueira N., Witmer M. D., Tydings J. D., Mellman I. S. Lymphokine enhances the expression and synthesis of Ia antigens on cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1248–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Fleit H., Mellman I. S. Structural Aspects and Heterogeneity of Immunoglobulin Fc Receptors. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:247–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60922-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A. The origin and kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):415–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]