Abstract
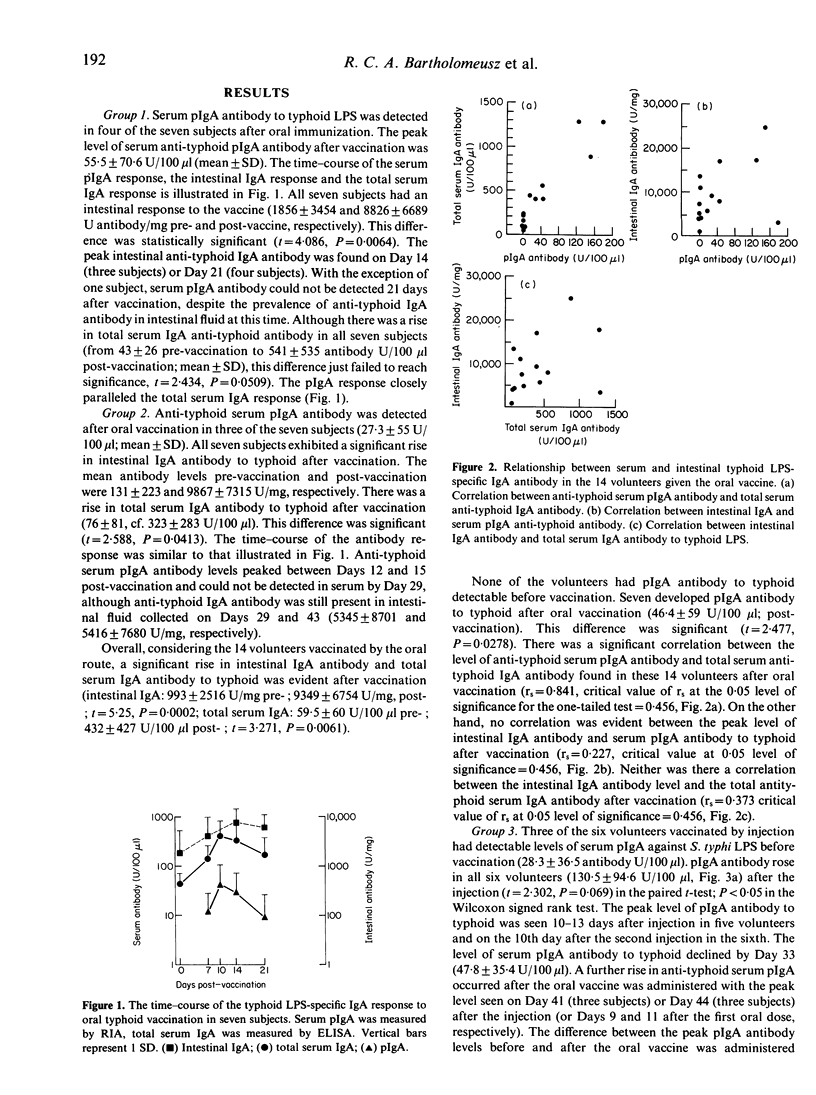
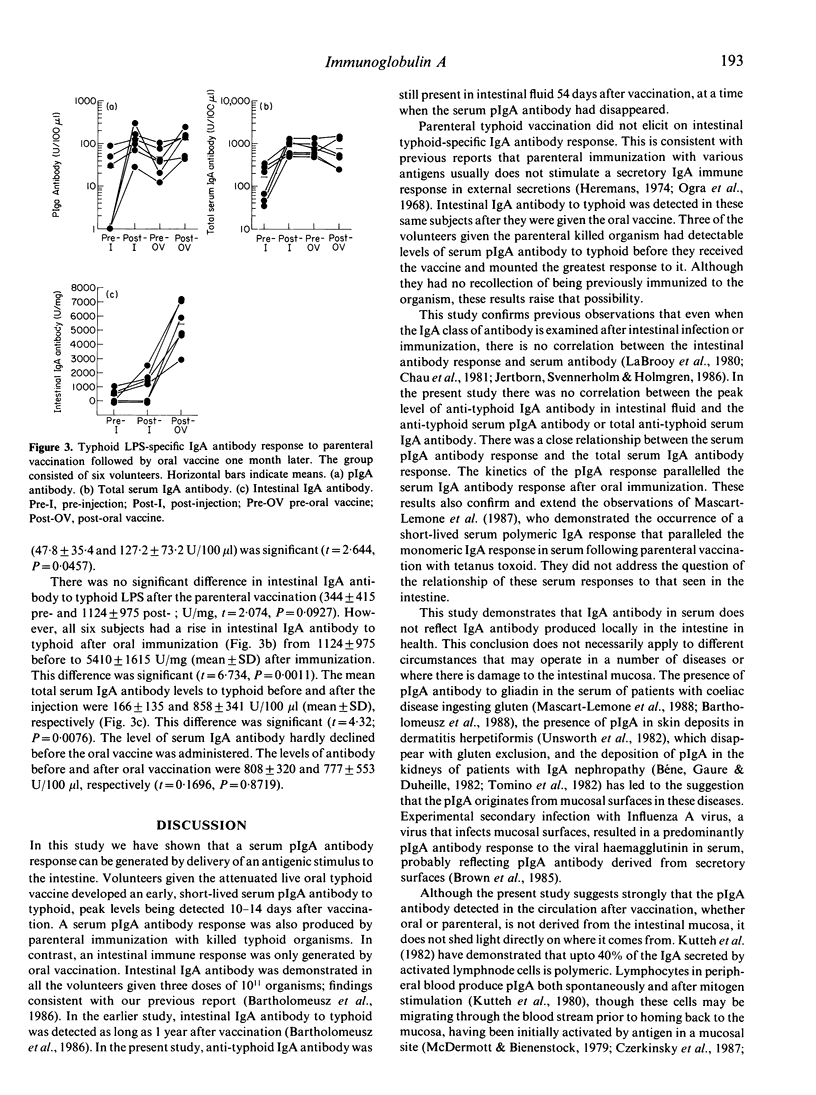
The relationship between the IgA antibody response in serum (total and polymeric IgA) and intestinal secretions was examined in volunteers subjected to oral and parenteral typhoid vaccination. After oral vaccination (three doses of 10(11) live Ty21a vaccine given at 48-hr intervals), serum pIgA antibody to typhoid lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was detected in seven of the 14 subjects (46.4 +/- 59 U/100 microliters, mean +/- SD). However, all 14 showed a significant intestinal IgA response (993 +/- 2516 and 9349 +/- 6754 U/mg pre- and post-vaccine; t = 5.25, P = 0.0002). The level of pIgA antibody declined rapidly, whereas intestinal IgA antibody levels remained elevated. Serum pIgA antibody was also found after parenteral immunization (two doses of 5 X 10(8) heat-killed bacteria given 14 days apart to six subjects), but an intestinal IgA antibody response was detected in these individuals only after a subsequent course of the oral vaccine given 1 month after initial parenteral immunization. Changes in serum pIgA antibody followed those of total serum IgA antibody rather than those of intestinal antibody. The results indicate that a serum pIgA response can be induced by an antigenic stimulus delivered either orally or parenterally, whereas an intestinal IgA response is induced only by a local antigen stimulus. The regulation of serum pIgA and intestinal IgA appear to be independent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André C., Berthoux F. C., André F., Gillon J., Genin C., Sabatier J. C. Prevalence of IgA2 deposits in IgA nephropathies: a clue to their pathogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 4;303(23):1343–1346. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012043032306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomeusz R. C., LaBrooy J. T., Ey P. L., Di Matteo A. C., Daniels D. A., Anderson C. S., Rowley D. Assays for total and antigen-specific polymeric IgA in serum based on binding to secretory component. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Feb 24;117(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bene M. C., Faure G., Duheille J. IgA nephropathy: characterization of the polymeric nature of mesangial deposits by in vitro binding of free secretory component. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):527–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Polymeric IgA is complexed with secretory component (SC) on the surface of human intestinal epithelial cells. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(1):39–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Murphy B. R., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Mestecky J. Subclass distribution and molecular form of immunoglobulin A hemagglutinin antibodies in sera and nasal secretions after experimental secondary infection with influenza A virus in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):259–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.259-264.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Isobe Y., Nakane P. K. Studies on translocation of immunoglobulins across intestinal epithelium. II. Immunoelectron-microscopic localization of immunoglobulins and secretory component in human intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1976 Dec;71(6):985–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Tsang R. S., Lam S. K., La Brooy J. T., Rowley D. Antibody response to the lipopolysaccharide and protein antigens of Salmonella typhi during typhoid infection. II. Measurement of intestinal antibodies by radioimmunoassay. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):515–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Delacroix D. L. Intravascular and mucosal immunoglobulin A: two separate but related systems of immune defense? Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jun;106(6):892–899. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-6-892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Prince S. J., Michalek S. M., Jackson S., Russell M. W., Moldoveanu Z., McGhee J. R., Mestecky J. IgA antibody-producing cells in peripheral blood after antigen ingestion: evidence for a common mucosal immune system in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2449–2453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Elkom K. B., Geubel A. P., Hodgson H. F., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. Changes in size, subclass, and metabolic properties of serum immunoglobulin A in liver diseases and in other diseases with high serum immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):358–367. doi: 10.1172/JCI110777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Ogra P. L. Local immune responses. Br Med Bull. 1985 Jan;41(1):28–33. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Füer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):553–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Schuit H. R., Hulsing-Hesselink E. An immunofluorescence study on intracellular immunoglobulins in human bone marrow cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:290–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jertborn M., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Saliva, breast milk, and serum antibody responses as indirect measures of intestinal immunity after oral cholera vaccination or natural disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):203–209. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.203-209.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonard P. P., Rambaud J. C., Dive C., Vaerman J. P., Galian A., Delacroix D. L. Secretion of immunoglobulins and plasma proteins from the jejunal mucosa. Transport rate and origin of polymeric immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):525–535. doi: 10.1172/JCI111450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Koopman W. J., Conley M. E., Egan M. L., Mestecky J. Production of predominantly polymeric IgA by human peripheral blood lymphocytes stimulated in vitro with mitogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1424–1429. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Prince S. J., Mestecky J. Tissue origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):990–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Brooy J. T., Davidson G. P., Sherman D. J., Rowley D. The antibody response to bacterial gastroenteritis in serum and secretions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):290–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascart-Lemone F., Cadranel S., Delacroix D. L., Duchateau J., Vaerman J. P. Change in molecular size of antigliadin IgA in serum related to presence of antigen in the gut. Monogr Allergy. 1988;24:310–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascart-Lemone F., Duchateau J., Conley M. E., Delacroix D. L. A polymeric IgA response in serum can be produced by parenteral immunization. Immunology. 1987 Aug;61(4):409–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. Translocation of dimeric IgA through neoplastic colon cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2359–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk M. M., Klein M. H., Katz A., Fisher M. M., Underdown B. J. Estimation of polymeric IgA in human serum: an assay based on binding of radiolabeled human secretory component with applications in the study of IgA nephropathy, IgA monoclonal gammopathy, and liver disease. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1176–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radl J., Schuit H. R., Mestecky J., Hijmans W. The origin of monomeric and polymeric forms of IgA in man. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):57–65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TAN E. M., SOLOMON A., PRENDERGAST R. A. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IMMUNE SYSTEM COMMON TO CERTAIN EXTERNAL SECRETIONS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:101–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Bienenstock J. Secretory immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomino Y., Sakai H., Miura M., Endoh M., Nomoto Y. Detection of polymeric IgA in glomeruli from patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Aug;49(2):419–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Payne A. W., Leonard J. N., Fry L., Holborow E. J. IgA in dermatitis-herpetiformis skin is dimeric. Lancet. 1982 Feb 27;1(8270):478–479. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


