Abstract
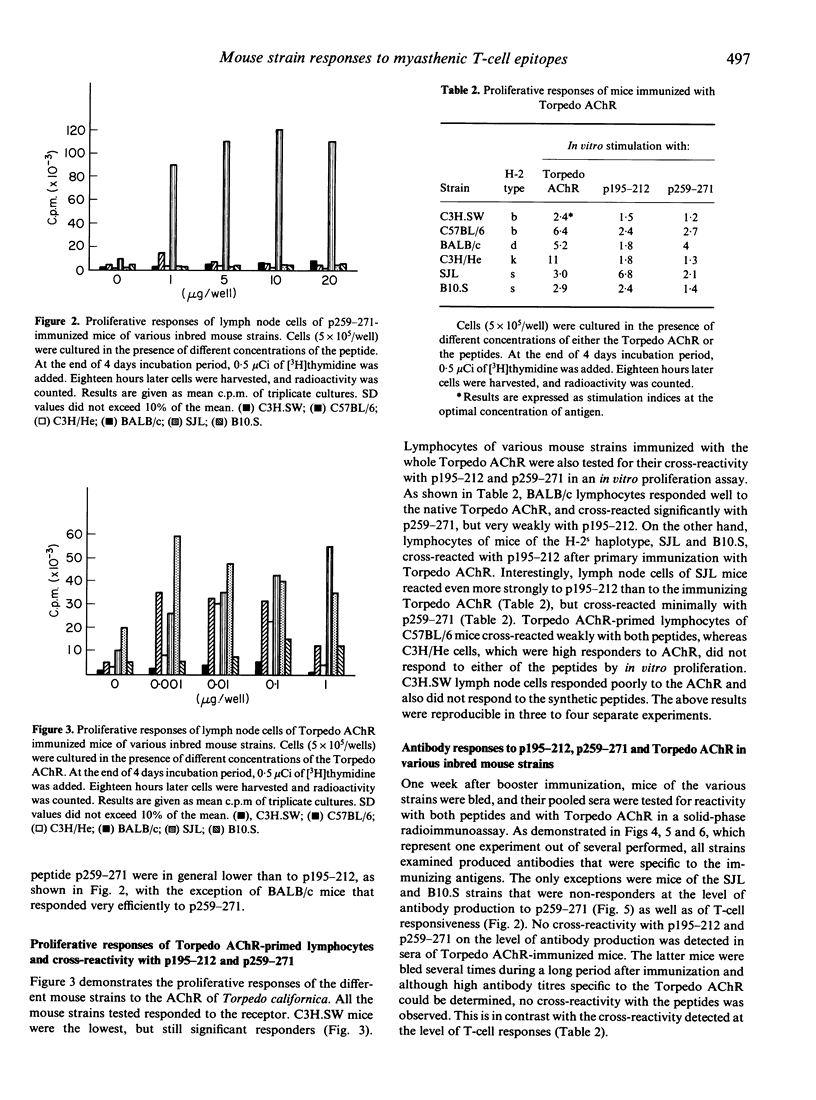
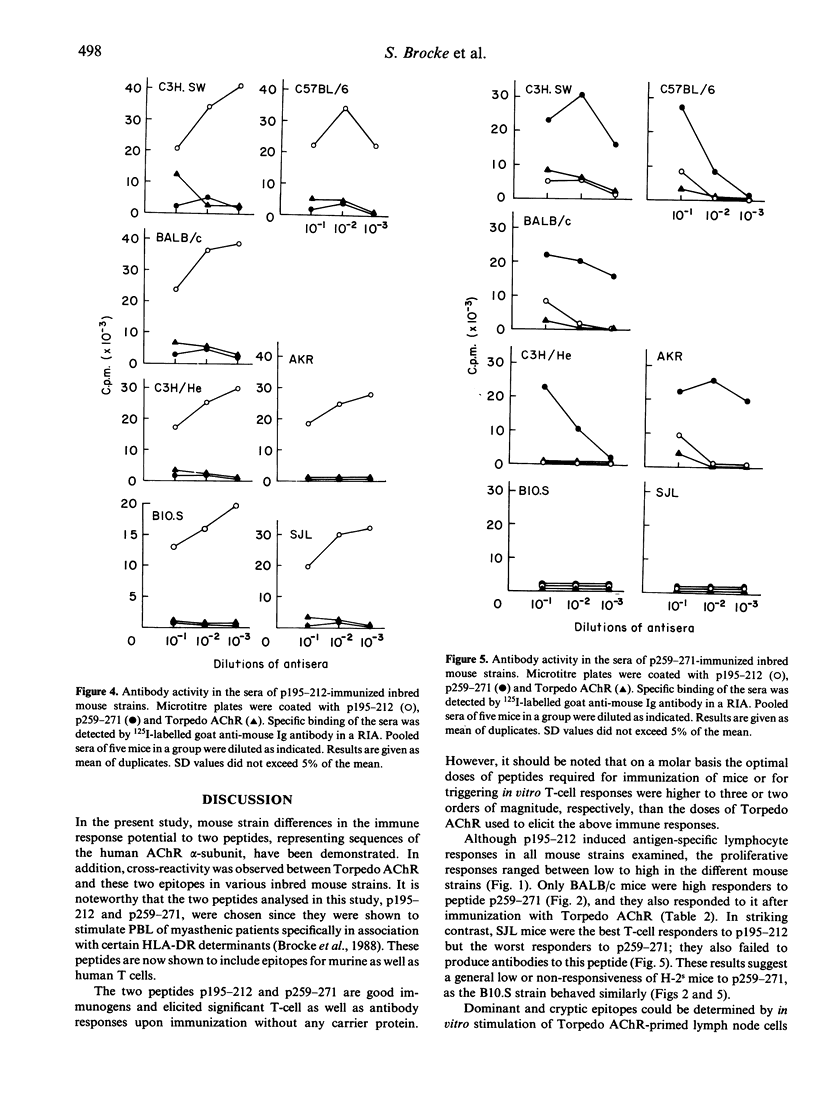
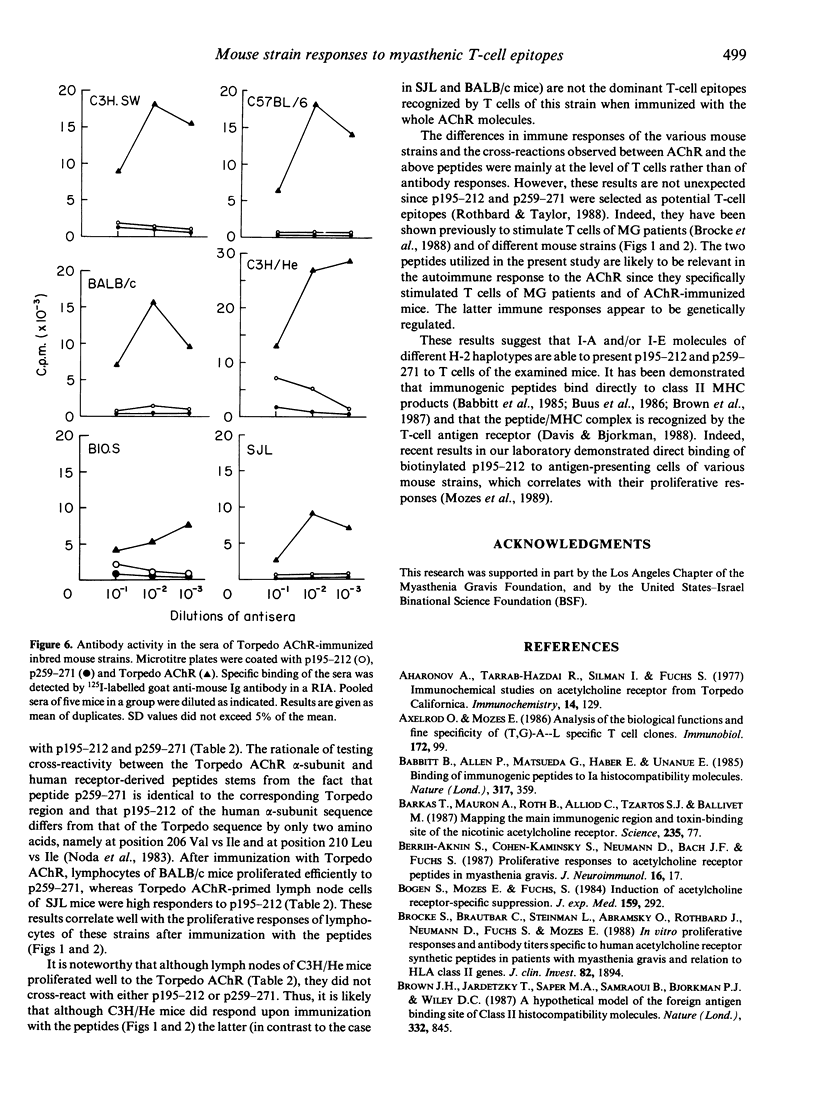
The specific recognition of the acetylcholine receptor and its alpha-subunit by T cells derived from patients with myasthenia gravis or mice with experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis raises the question of the role of autoreactive T cells in the myasthenic process. Sequences of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit previously shown to be immunogenic in myasthenic patients were tested for their immunogenicity in various inbred mouse strains. High, intermediate and low T-cell proliferative responses could be observed to peptides representing sequences 195-212 and 259-271 of the human acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. Following immunization with the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor, lymphocytes of SJL mice proliferated efficiently to p 195-212 but not to p259-271. On the other hand, lymph node cells of BALB/c mice responded well to p259-271 but not to p195-212. Thus, the influence of the genetic make-up of the examined mice on the immune response to the two peptides could be clearly demonstrated by the existence of strain-dependent immunodominant and cryptic regions on the autoantigen. The differences between the strains were less pronounced when antibody responses were measured to these two T-cell epitopes, although a partial correlation with the proliferative responses could be observed. It can be concluded that epitopes specifically recognized by T lymphocytes of patients with myasthenia gravis also represent specific T-cell epitopes in the autoreactivity to the acetylcholine receptor in mice and that immune responsiveness to these peptides is influenced by the genetic make-up of the responding mouse strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonov A., Tarrab-Hazdai R., Silman I., Fuchs S. Immunochemical studies on acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Immunochemistry. 1977 Feb;14(2):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod O., Mozes E. Analysis of the biological functions and fine specificity of (T,G)-A--L specific T cell clones. Immunobiology. 1986 Aug;172(1-2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogen S., Mozes E., Fuchs S. Induction of acetylcholine receptor-specific suppression. An in vitro model of antigen-specific immunosuppression in myasthenia gravis. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):292–304. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocke S., Brautbar C., Steinman L., Abramsky O., Rothbard J., Neumann D., Fuchs S., Mozes E. In vitro proliferative responses and antibody titers specific to human acetylcholine receptor synthetic peptides in patients with myasthenia gravis and relation to HLA class II genes. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1894–1900. doi: 10.1172/JCI113807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Colon S., Smith C., Freed J. H., Miles C., Grey H. M. Interaction between a "processed" ovalbumin peptide and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3968–3971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christadoss P., Lennon V. A., David C. Genetic control of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis in mice. I. Lymphocyte proliferative response to acetylcholine receptors is under H-2-linked Ir gene control. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2540–2543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Lindstrom J. Specificity of the T cell immune response to acetylcholine receptor in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Response to subunits and synthetic peptides. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1830–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harcourt G. C., Sommer N., Rothbard J., Willcox H. N., Newsom-Davis J. A juxta-membrane epitope on the human acetylcholine receptor recognized by T cells in myasthenia gravis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1295–1300. doi: 10.1172/JCI113729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld R., Toyka K. V., Tzartos S. J., Carson W., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Human T-helper lymphocytes in myasthenia gravis recognize the nicotinic receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5379–5383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Shelton D., Fujii Y. Myasthenia gravis. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:233–284. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60847-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozes E., Dayan M., Zisman E., Brocke S., Licht A., Pecht I. Direct binding of a myasthenia gravis related epitope to MHC class II molecules on living murine antigen-presenting cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4049–4052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Tanabe T., Shimizu S., Kikyotani S., Kayano T., Hirose T., Inayama S. Cloning and sequence analysis of calf cDNA and human genomic DNA encoding alpha-subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):818–823. doi: 10.1038/305818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston S., Sarin V., Thanh H. L., Rivier J., Fox J. L., Lindstrom J. Synthetic peptides used to locate the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site and immunogenic regions on alpha subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3261–3266. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Taylor W. R. A sequence pattern common to T cell epitopes. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souroujon M. C., Neumann D., Pizzighella S., Safran A., Fuchs S. Localization of a highly immunogenic region on the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90945-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tami J. A., Urso O. E., Krolick K. A. T cell hybridomas reactive with the acetylcholine receptor and its subunits. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):732–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Seybold M. E., Lindstrom J. M. Specificities of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors in sera from myasthenia gravis patients measured by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Lindstrom J. Demonstration of a main immunogenic region on acetylcholine receptors from human muscle using monoclonal antibodies to human receptor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 11;158(1):116–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi T., Mulac-Jericević B., Kurisaki J., Atassi M. Z. T lymphocyte recognition of acetylcholine receptor: localization of the full T cell recognition profile on the extracellular part of the alpha chain of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1697–1702. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Moore A. C., Kitamura K., Steinman L., Rothbard J. B. T-cell epitope of the autoantigen myelin basic protein that induces encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):258–260. doi: 10.1038/324258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Barkas T., Juillerat M., Schwendimann B., Wekerle H. T cell epitopes in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis of the rat: strain-specific epitopes and cross-reaction between two distinct segments of the alpha chain of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (Torpedo californica). Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):551–557. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


