Abstract
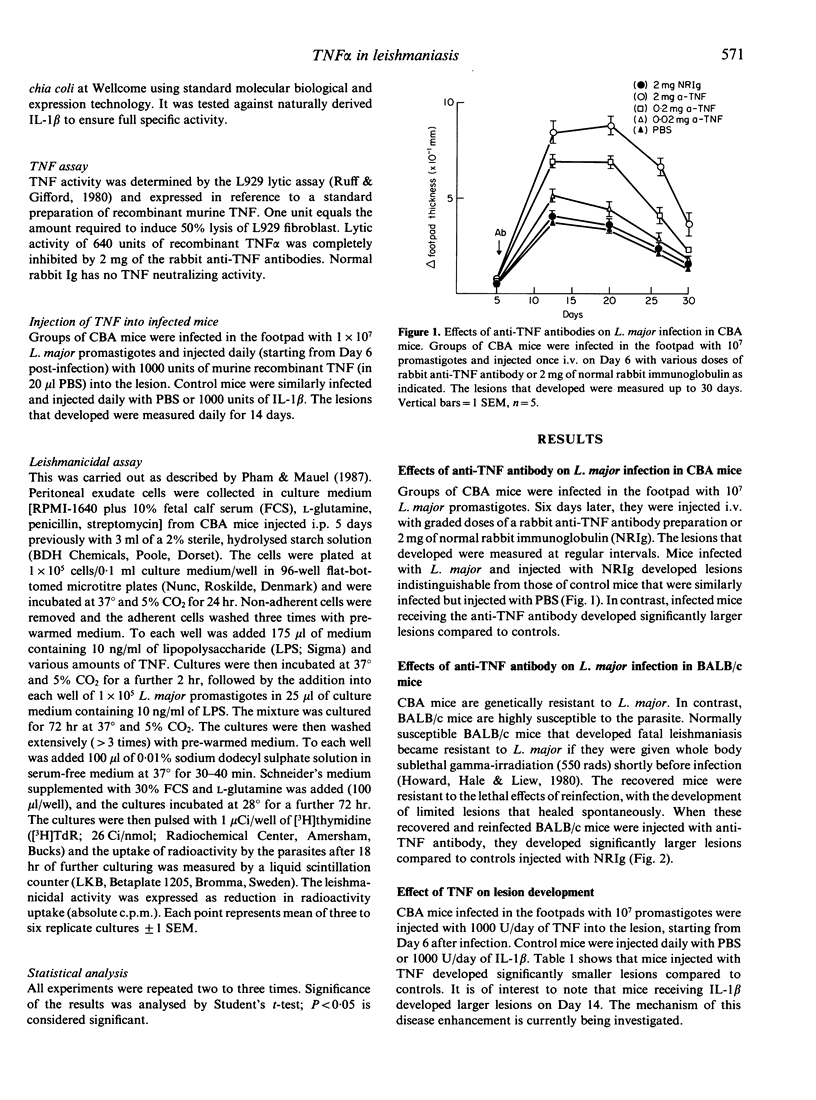
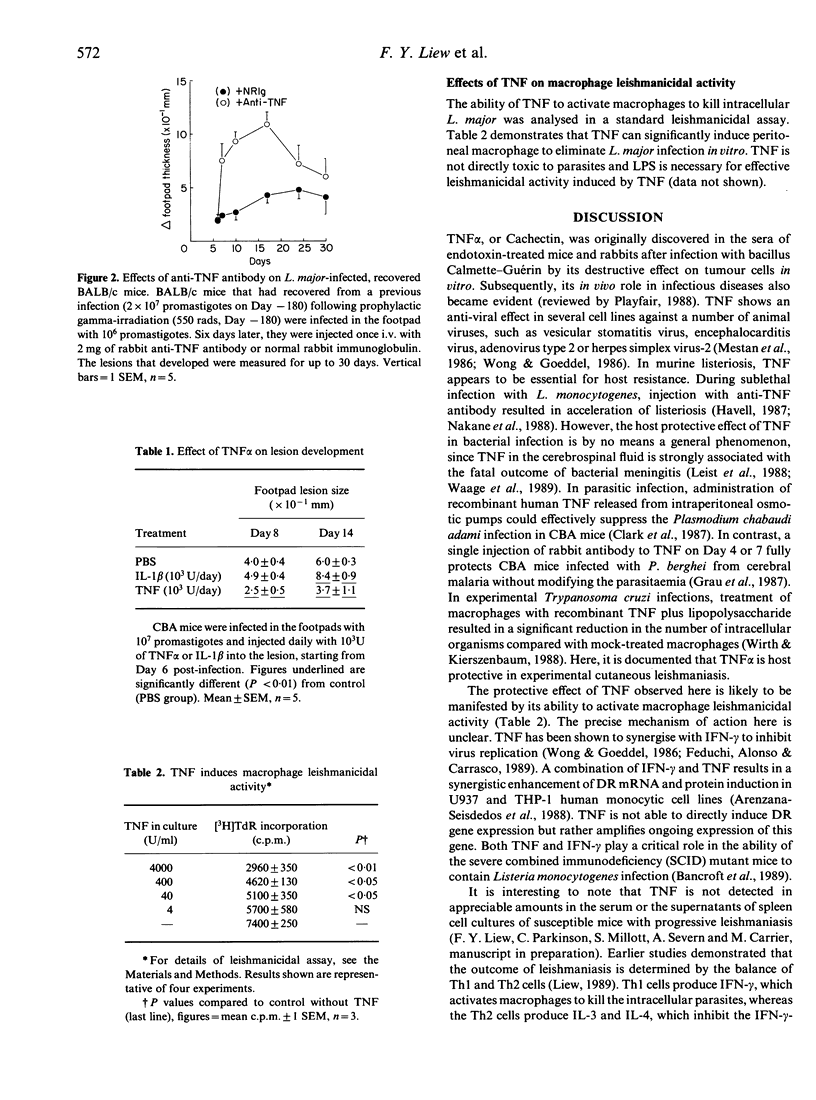
Genetically resistant CBA mice developed significantly larger lesions to Leishmania major infection when they were injected with rabbit anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-specific antibodies compared to control mice injected with normal rabbit immunoglobulin. BALB/c mice recovered from a previous infection following prophylactic sublethal irradiation also developed exacerbated lesions when treated with the anti-TNF antibody. Injection of TNF into the lesion of infected CBA mice significantly reduced the lesion development. Furthermore, TNF activates macrophages to kill Leishmania in vitro. These data demonstrate that TNF plays an important role in mediating host-protection against cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Mogensen S. C., Vuillier F., Fiers W., Virelizier J. L. Autocrine secretion of tumor necrosis factor under the influence of interferon-gamma amplifies HLA-DR gene induction in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6087–6091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G. J., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Unanue E. R. Tumor necrosis factor is involved in the T cell-independent pathway of macrophage activation in scid mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Hunt N. H., Butcher G. A., Cowden W. B. Inhibition of murine malaria (Plasmodium chabaudi) in vivo by recombinant interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor, and its enhancement by butylated hydroxyanisole. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3493–3496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feduchi E., Alonso M. A., Carrasco L. Human gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor exert a synergistic blockade on the replication of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1354–1359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1354-1359.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Fajardo L. F., Piguet P. F., Allet B., Lambert P. H., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1210–1212. doi: 10.1126/science.3306918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. H., Vitti G. F., Burgess D. R., Whitty G. A., Piccoli D. S., Hamilton J. A. Potential antiinflammatory effects of interleukin 4: suppression of human monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3803–3807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. III. Nature and significance of specific suppression of cell-mediated immunity in mice highly susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):594–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Frei K., Kam-Hansen S., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in cerebrospinal fluid during bacterial, but not viral, meningitis. Evaluation in murine model infections and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1743–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Howard J. G., Hale C. Prophylactic immunization against experimental leishmaniasis. III. Protection against fatal Leishmania tropica infection induced by irradiated promastigotes involves Lyt-1+2- T cells that do not mediate cutaneous DTH. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):456–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Millott S., Li Y., Lelchuk R., Chan W. L., Ziltener H. Macrophage activation by interferon-gamma from host-protective T cells is inhibited by interleukin (IL)3 and IL4 produced by disease-promoting T cells in leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1227–1232. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestan J., Digel W., Mittnacht S., Hillen H., Blohm D., Möller A., Jacobsen H., Kirchner H. Antiviral effects of recombinant tumour necrosis factor in vitro. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):816–819. doi: 10.1038/323816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham T. V., Mauël J. Studies on intracellular killing of Leishmania major and lysis of host macrophages by immune lymphoid cells in vitro. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Nov;9(6):721–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M. R., Gifford G. E. Purification and physico-chemical characterization of rabbit tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1671–1677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Natovitz P., Coffman R. L., Pearce E., Sher A. Immunoregulation of cutaneous leishmaniasis. T cell lines that transfer protective immunity or exacerbation belong to different T helper subsets and respond to distinct parasite antigens. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1675–1684. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Sherry B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor plays a protective role in experimental murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2097–2104. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth J. J., Kierszenbaum F. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor enhances macrophage destruction of Trypanosoma cruzi in the presence of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):286–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


