Abstract
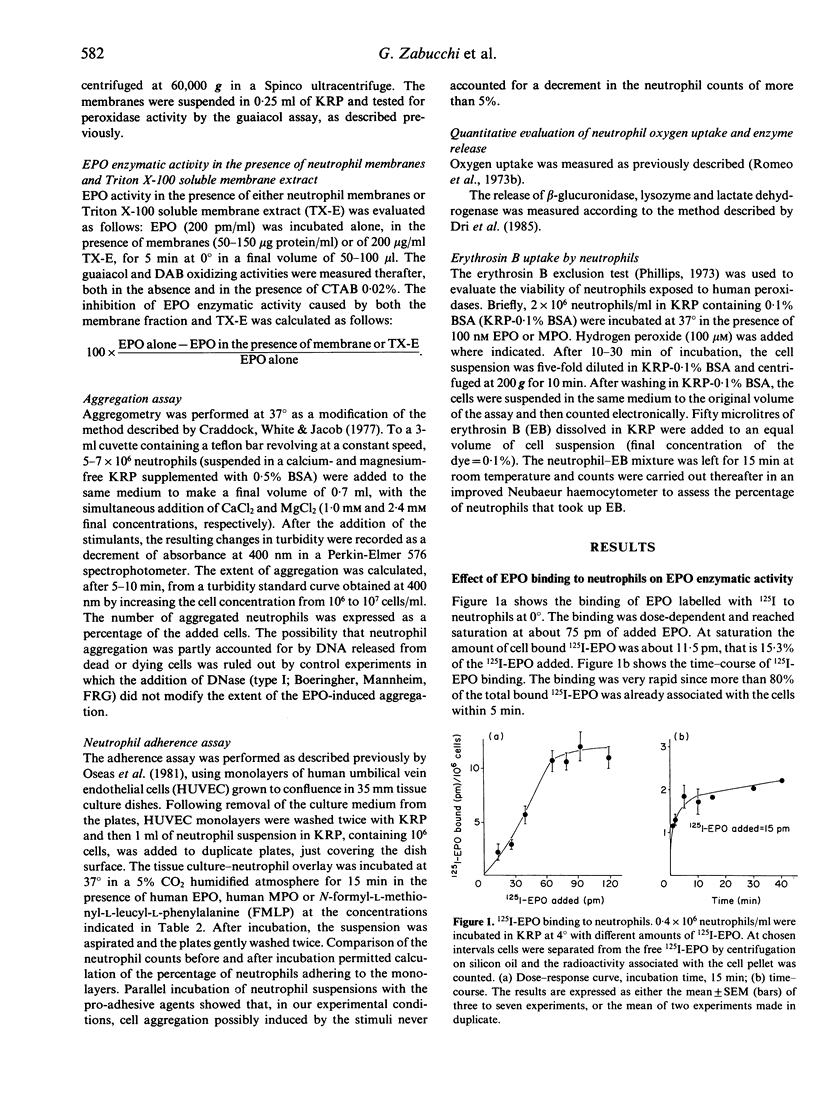
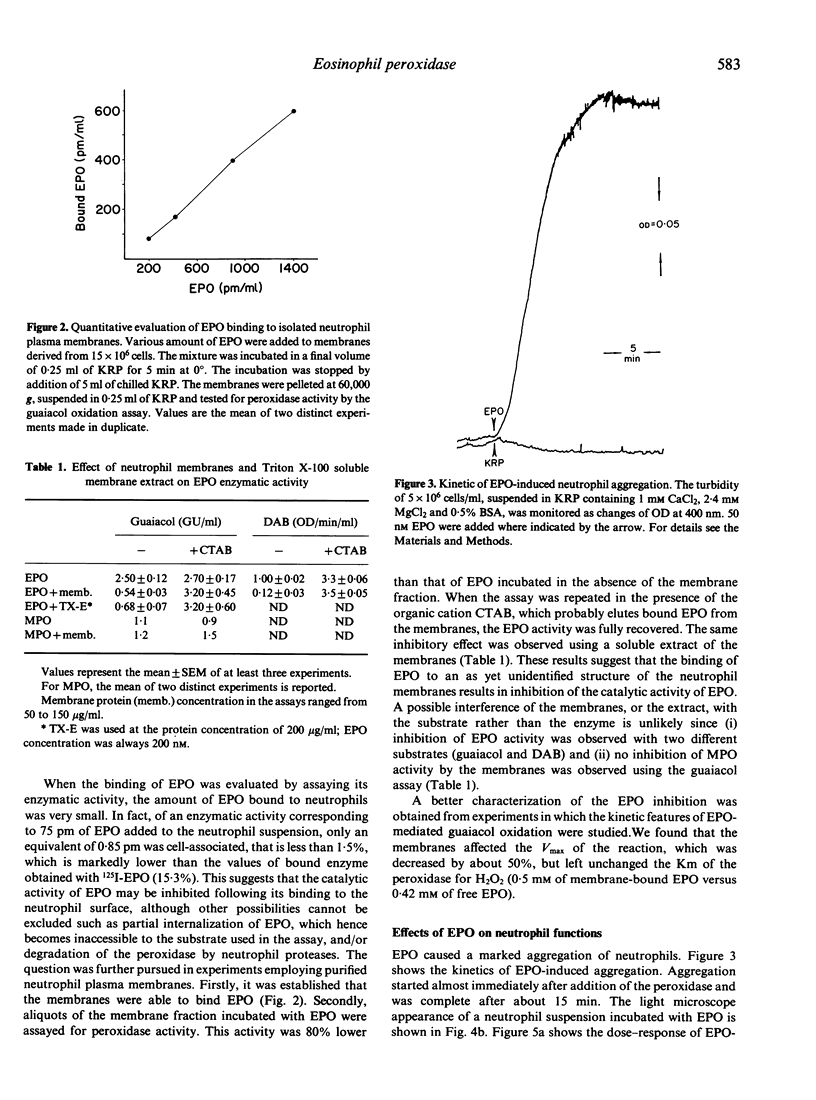
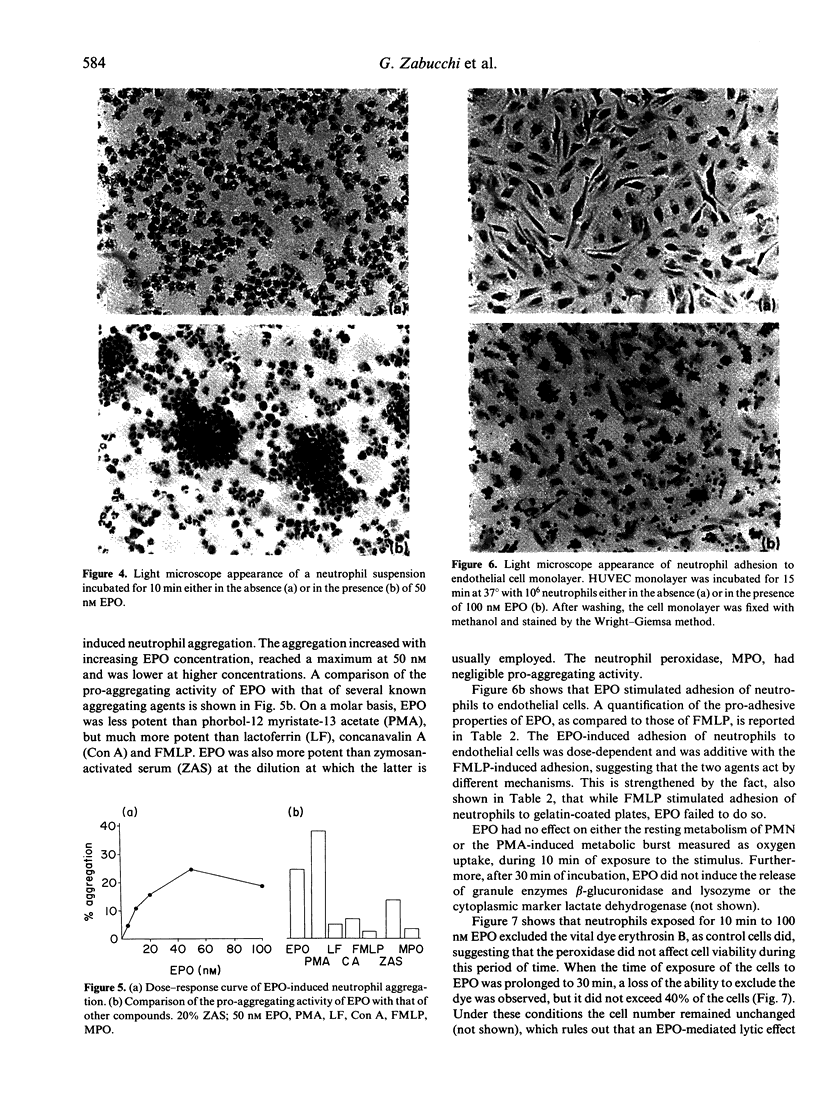
The effects of the interactions between eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) and neutrophils were studied. It is shown that binding of EPO to neutrophils results on the one hand in reversible inhibition of EPO peroxidase activity and, on the other, in an increased neutrophil aggregation and neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cell monolayers. After prolonged periods of exposure to EPO, neutrophils also show a decreased ability to exclude the vital dye erythrosin B. The reversible inhibition of EPO activity may represent a means of keeping under control the oxidative potential of EPO, while the increased neutrophil aggregation and adherence to endothelial cells suggest that EPO may influence at least two key events of inflammation, that is, the margination of neutrophils and/or their accumulation in the inflammatory site.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agosti J. M., Altman L. C., Ayars G. H., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J., Klebanoff S. J. The injurious effect of eosinophil peroxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and halides on pneumocytes in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987 Mar;79(3):496–504. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(87)90368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolscher B. G., Plat H., Wever R. Some properties of human eosinophil peroxidase, a comparison with other peroxidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 31;784(2-3):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Haak R. A., Yang H. H., Wolach J. B., Whitcomb J. A., Butterick C. J., Baehner R. L. Membrane-bound lactoferrin alters the surface properties of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1049–1057. doi: 10.1172/JCI110692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M. G., Peterson C. G., Venge P. Human eosinophil peroxidase: purification and characterization. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1875–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Litt M. The entry of granule-associated peroxidase into the phagocytic vacuoles of eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1291–1306. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., White J. G., Jacob H. S. Potentiation of complement (C5a)-induced granulocyte aggregation by cytochalasin B. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Mar;91(3):490–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer R., Soranzo M. R., Dri P., Menegazzi R., Pitotti A., Zabucchi G., Patriarca P. A simple reliable assay for myeloperoxidase activity in mixed neutrophil-eosinophil cell suspensions: application to detection of myeloperoxidase deficiency. J Immunol Methods. 1984 May 11;70(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dri P., Cramer R., Menegazzi R., Patriarca P. Increased degranulation of human myeloperoxidase-deficient polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Haematol. 1985 Jan;59(1):115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Klebanoff S. J., Henderson W. R., Monahan R. A., Pyne K., Galli S. J. Vesicular uptake of eosinophil peroxidase by guinea pig basophils and by cloned mouse mast cells and granule-containing lymphoid cells. Am J Pathol. 1985 Mar;118(3):425–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Adolphson C. R. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:177–253. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Chi E. Y., Klebanoff S. J. Eosinophil peroxidase-induced mast cell secretion. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):265–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong E. C., Klebanoff S. J. Eosinophil-mediated mammalian tumor cell cytotoxicity: role of the peroxidase system. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1949–1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalife J., Capron M., Grzych J. M., Bazin H., Capron A. Extracellular release of rat eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) I. Role of anaphylactic immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1968–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., Mackenzie C. D., Ramalho-Pinto F. J. Ultrastructural observations on the in vitro interaction between rat eosinophils and some parasitic helminths (Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis and Nippostrongylus brasiliensis). Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):105–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menegazzi R., Zabucchi G., Patriarca P. A simple procedure for the purification of eosinophil peroxidase from normal human blood. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jul 24;91(2):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseas R., Yang H. H., Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A. Lactoferrin: a promoter of polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesiveness. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):939–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Cramer R., Marzi T., Soranzo M. R., Zabucchi G., Rossi F. Peroxidase activity of alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 May;13(5):399–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Zabucchi G., Marzi T., Rossi F. Kinetic and enzymatic features of metabolic stimulation of alveolar and peritoneal macrophages challenged with bacteria. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Apr;78(2):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M. K., Petersen A., Gidanian F., Rietveld C. Cytophilic and cytotoxic properties of human eosinophil peroxidase plus major basic protein. Am J Pathol. 1988 Sep;132(3):455–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabucchi G., Menegazzi R., Soranzo M. R., Patriarca P. Uptake of human eosinophil peroxidase by human neutrophils. Am J Pathol. 1986 Sep;124(3):510–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabucchi G., Soranzo M. R., Menegazzi R., Bertoncin P., Nardon E., Patriarca P. Uptake of human eosinophil peroxidase and myeloperoxidase by cells involved in the inflammatory process. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Apr;37(4):499–508. doi: 10.1177/37.4.2538504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




