Abstract
The pathogenic mechanism leading to liver tissue injury in hepatitis caused by hepatitis A virus is unclear. We have randomly established T-cell clones from liver biopsies from four patients with hepatitis A. A total of 578 clones was phenotypically analysed. During the acute phase of the disease CD8+ clones dominated over CD4+ clones, whereas in a biopsy taken late after onset of clinical syndromes more CD4+ than CD8+ clones were obtained. Interestingly, in a patient with a second exacerbation of the disease, more than 20% of all clones had the CD3+ WT31- CD4- CD8- 'NK-like' phenotype. All CD8+ clones had cytotoxic activity and approximately 50% of all CD8+ clones showed specific cytotoxicity against autologous fibroblasts infected with hepatitis A virus. The CD8+ cells also produced IFN-gamma in response to these target cells. Variable IFN-gamma production was observed with all types of T-cell clones. These results suggest that the liver injury in hepatitis A is not caused by a viral cytopathogenic effect but is due to an immunopathological reaction of sensitized cytotoxic T lymphocytes against infected hepatocytes. In addition, these studies show an enrichment of CD4-8-T-cell receptor alpha beta-chain-negative T lymphocytes at the site of an inflammation and suggest a role of these cells in an anti-viral reaction.
Full text
PDF

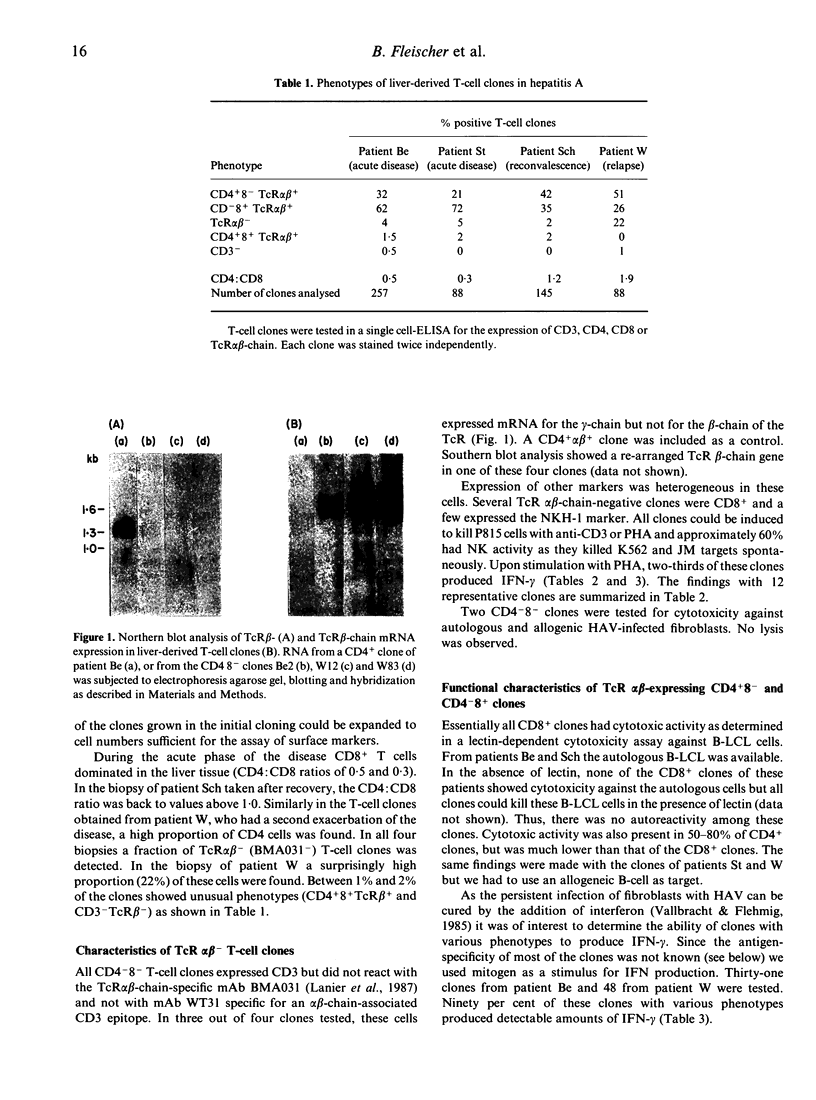
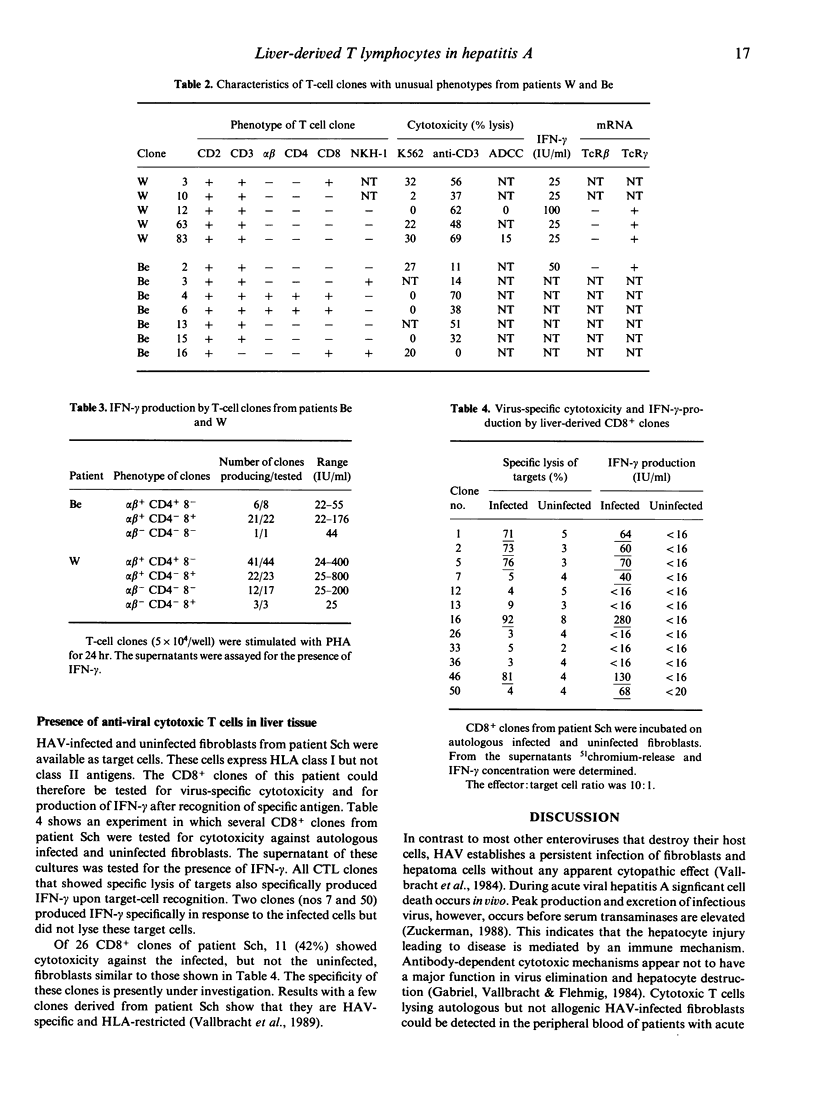


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ang S. L., Seidman J. G., Peterman G. M., Duby A. D., Benjamin D., Lee S. J., Hafler D. A. Functional gamma chain-associated T cell receptors on cerebrospinal fluid-derived natural killer-like T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1453–1458. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H., Buckler-White A., Baroudy B. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus: comparison with different strains of hepatitis A virus and other picornaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.50-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maria A., Malnati M., Moretta A., Pende D., Bottino C., Casorati G., Cottafava F., Melioli G., Mingari M. C., Migone N. CD3+4-8-WT31-(T cell receptor gamma+) cells and other unusual phenotypes are frequently detected among spontaneously interleukin 2-responsive T lymphocytes present in the joint fluid in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. A clonal analysis. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1815–1819. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. Acquisition of specific cytotoxic activity by human T4+ T lymphocytes in culture. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):365–367. doi: 10.1038/308365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Kreth H. W. Clonal analysis of HLA-restricted virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes from cerebrospinal fluid in mumps meningitis. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2187–2190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. Non-specific propagation of human antigen-dependent T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schrezenmeier H., Wagner H. Function of the CD4 and CD8 molecules on human cytotoxic T lymphocytes: regulation of T cell triggering. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1625–1628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming K. A., McMichael A., Morton J. A., Woods J., McGee J. O. Distribution of HLA class 1 antigens in normal human tissue and in mammary cancer. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jul;34(7):779–784. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.7.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel P., Vallbracht A., Flehmig B. Lack of complement-dependent cytolytic antibodies in hepatitis A virus infection. J Med Virol. 1986 Sep;20(1):23–31. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann B., Johnson J. P. A beta-galactosidase linked immunoassay for the analysis of antigens on individual cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jun 10;60(3):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr Frontiers of the immune system. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):804–806. doi: 10.1038/333804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier K., Gabriel P., Koscielniak E., Stierhof Y. D., Wiedmann K. H., Flehmig B., Vallbracht A. Human gamma interferon production by cytotoxic T lymphocytes sensitized during hepatitis A virus infection. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3756–3763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3756-3763.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild G. C., Oxford J. S., de Jong J. C., Webster R. G. Evidence for host-cell selection of influenza virus antigenic variants. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):706–709. doi: 10.1038/303706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass H. R., Kisielow P., Kiefer M., Steinmetz M., von Boehmer H. Ontogeny of the T-cell antigen receptor within the thymus. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):592–595. doi: 10.1038/313592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Gabriel P., Maier K., Hartmann F., Steinhardt H. J., Müller C., Wolf A., Manncke K. H., Flehmig B. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity in hepatitis A virus infection. Hepatology. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):1308–1314. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Gabriel P., Zahn J., Flehmig B. Hepatitis A virus infection and the interferon system. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):211–213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Hofmann L., Wurster K. G., Flehmig B. Persistent infection of human fibroblasts by hepatitis A virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Maier K., Stierhof Y. D., Wiedmann K. H., Flehmig B., Fleischer B. Liver-derived cytotoxic T cells in hepatitis A virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):209–217. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Treuner J., Flehmig B., Joester K. E., Niethammer D. Interferon-neutralizing antibodies in a patient treated with human fibroblast interferon. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):496–497. doi: 10.1038/289496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbracht A., Treuner J., Manncke K. H., Niethammer D. Autoantibodies against human beta interferon following treatment with interferon. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(1):107–110. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Leggett K., Clark S. P., Aleksander I., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone encodes a protein having extensive homology to immunoglobulin chains. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):145–149. doi: 10.1038/308145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikai Y., Toyonaga B., Koga Y., Kimura N., Griesser H., Mak T. W. Repertoire of the human T cell gamma genes: high frequency of nonfunctional transcripts in thymus and mature T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jan;17(1):119–126. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



