Abstract
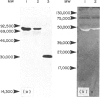
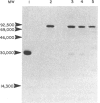
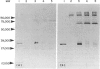
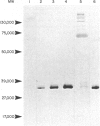
The interaction of mouse intestinal mast cell proteinase (IMCP) with serine proteinase inhibitors (serpins) in blood was analysed: (i) by examining the capacity of the inhibitors in blood to block the binding of the irreversible serine esterase inhibitor [3H]diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP); (ii) by Western blotting. The binding of [3H]DFP to IMCP was blocked very rapidly by inhibitors in mouse serum and, by Western blotting, this inhibition was associated with the appearance of a 73,000 MW proteinase/inhibitor complex together with a series of higher (greater than 100,000) MW complexes. IMCP was not dissociated from these complexes when electrophoresed under reducing conditions, although prior heat treatment of mouse serum (60 for 30-160 min) abolished the formation of all proteinase/inhibitor complexes. Similarly, the activity of a 48,000 MW inhibitor of chymotrypsin was abolished by heat treatment. A titration experiment established that between 0.5 and 5 mg IMCP were inhibited per ml of serum. The properties and MW of the IMCP inhibitor complexes are typical of serpins and suggest that IMCP secreted during intestinal immunological reactions would be rapidly and irreversibly inactivated by plasma-derived inhibitors.
Full text
PDF

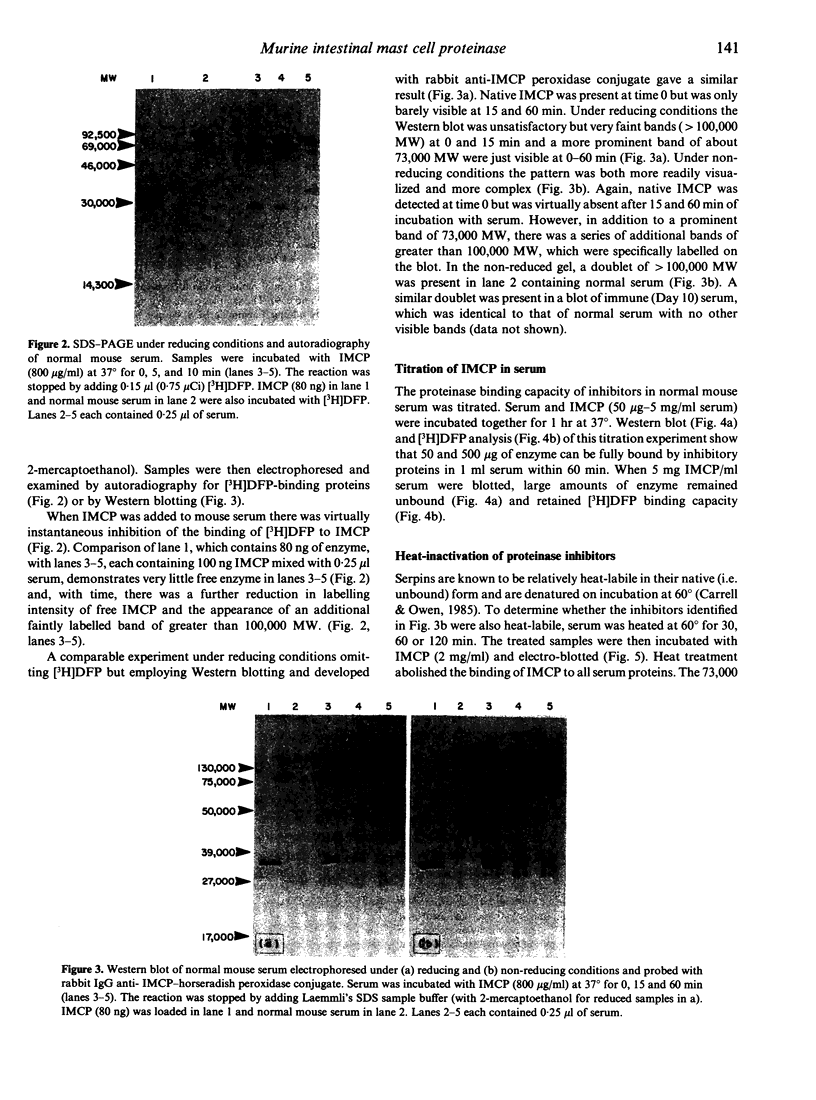
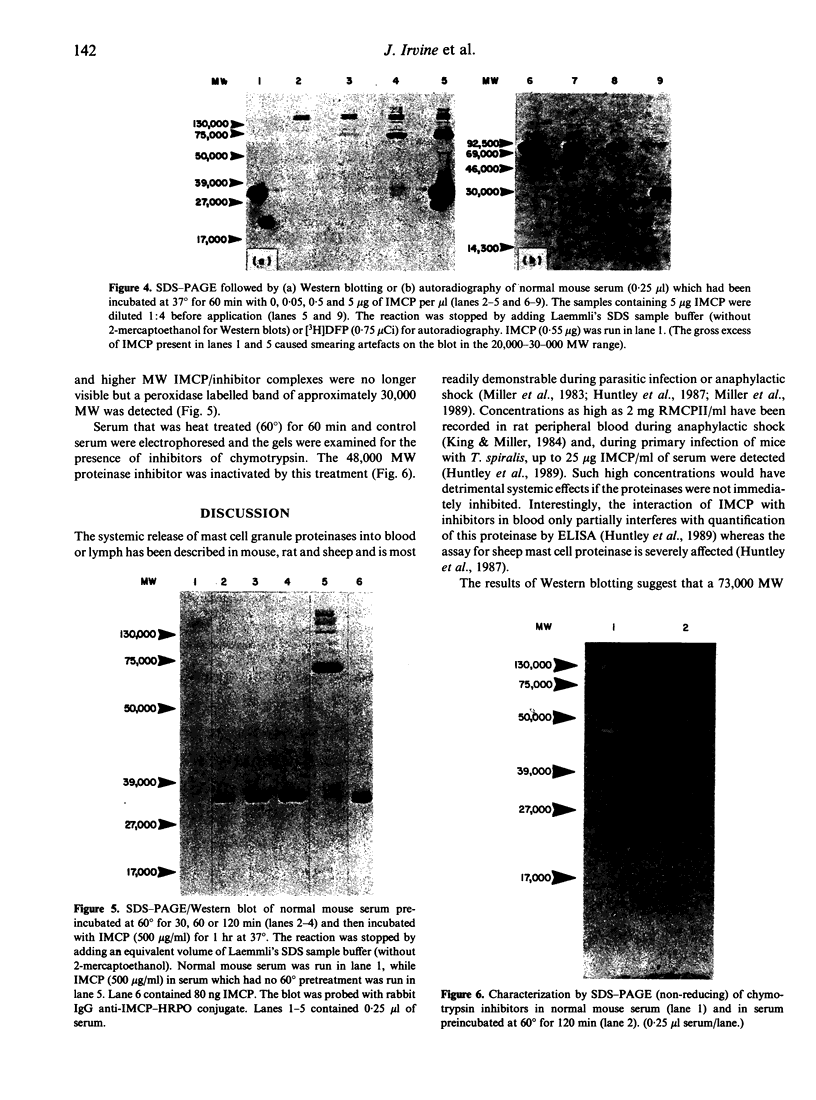


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alizadeh H., Wakelin D. Comparison of rapid expulsion of Trichinella spiralis in mice and rats. Int J Parasitol. 1982 Feb;12(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(82)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Alpha 2-macroglobulin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):737–754. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Owen M. C. Plakalbumin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, antithrombin and the mechanism of inflammatory thrombosis. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):730–732. doi: 10.1038/317730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins A. G., Munro G. H., Miller H. R., Ferguson A. Association of maturation of the small intestine at weaning with mucosal mast cell activation in the rat. Immunol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct-Dec;66(Pt 5-6):417–422. doi: 10.1038/icb.1988.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercz A. Recovery of protease activities from complexes with alpha 1-antitrypsin. Can J Biochem. 1973 Oct;51(10):1447–1450. doi: 10.1139/o73-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. A surprising new protein superfamily containing ovalbumin, antithrombin-III, and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 31;95(2):864–871. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90867-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley J. F., Gibson S., Brown D., Smith W. D., Jackson F., Miller H. R. Systemic release of a mast cell proteinase following nematode infections in sheep. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Sep;9(5):603–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. J., Miller H. R. Anaphylactic release of mucosal mast cell protease and its relationship to gut permeability in Nippostrongylus-primed rats. Immunology. 1984 Apr;51(4):653–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Huntley J. F., Newlands G. F., Mackellar A., Lammas D. A., Wakelin D. Granule proteinases define mast cell heterogeneity in the serosa and the gastrointestinal mucosa of the mouse. Immunology. 1988 Dec;65(4):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Jackson F., Newlands G., Appleyard W. T. Immune exclusion, a mechanism of protection against the ovine nematode Haemonchus contortus. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Nov;35(3):357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlands G. F., Gibson S., Knox D. P., Grencis R., Wakelin D., Miller H. R. Characterization and mast cell origin of a chymotrypsin-like proteinase isolated from intestines of mice infected with Trichinella spiralis. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):629–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trong H. L., Newlands G. F., Miller H. R., Charbonneau H., Neurath H., Woodbury R. G. Amino acid sequence of a mouse mucosal mast cell protease. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):391–395. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uriel J., Berges J. Characterization of natural inhibitors of trypsin and chymotrypsin by electrophoresis in acrylamide-agarose gels. Nature. 1968 May 11;218(5141):578–580. doi: 10.1038/218578b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Miller H. R., Huntley J. F., Newlands G. F., Palliser A. C., Wakelin D. Mucosal mast cells are functionally active during spontaneous expulsion of intestinal nematode infections in rat. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):450–452. doi: 10.1038/312450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]