Abstract
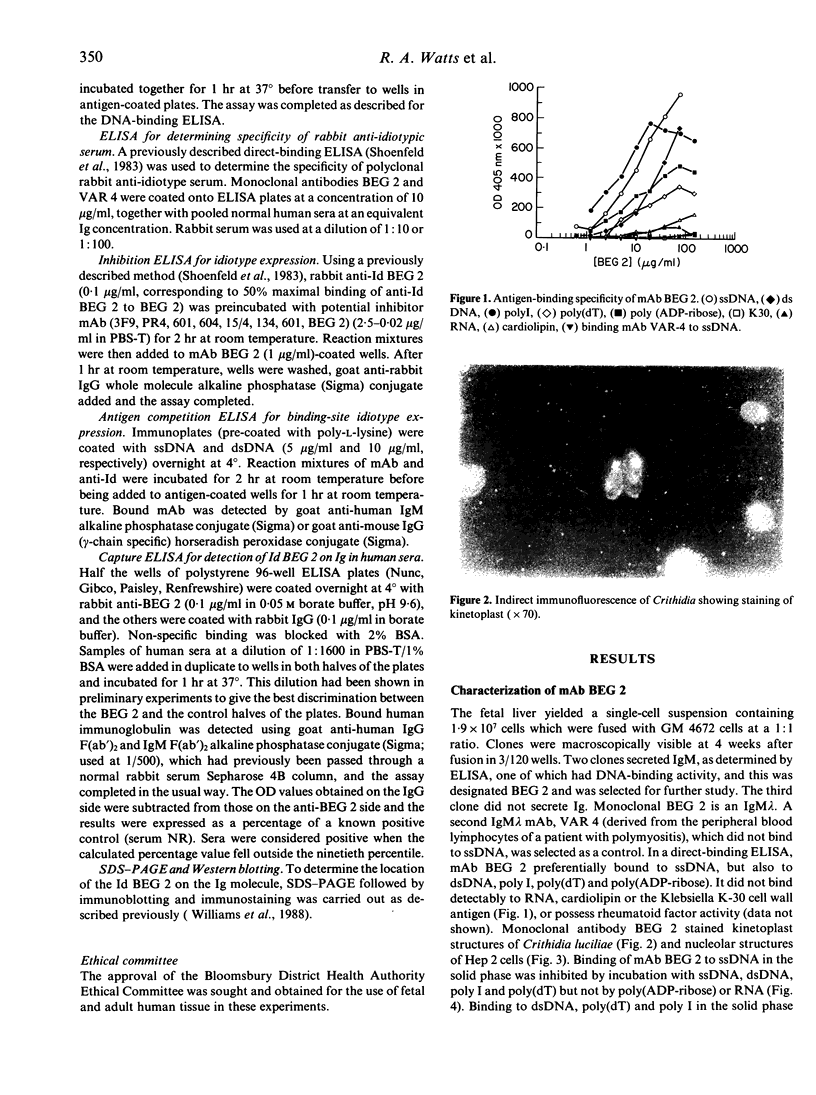
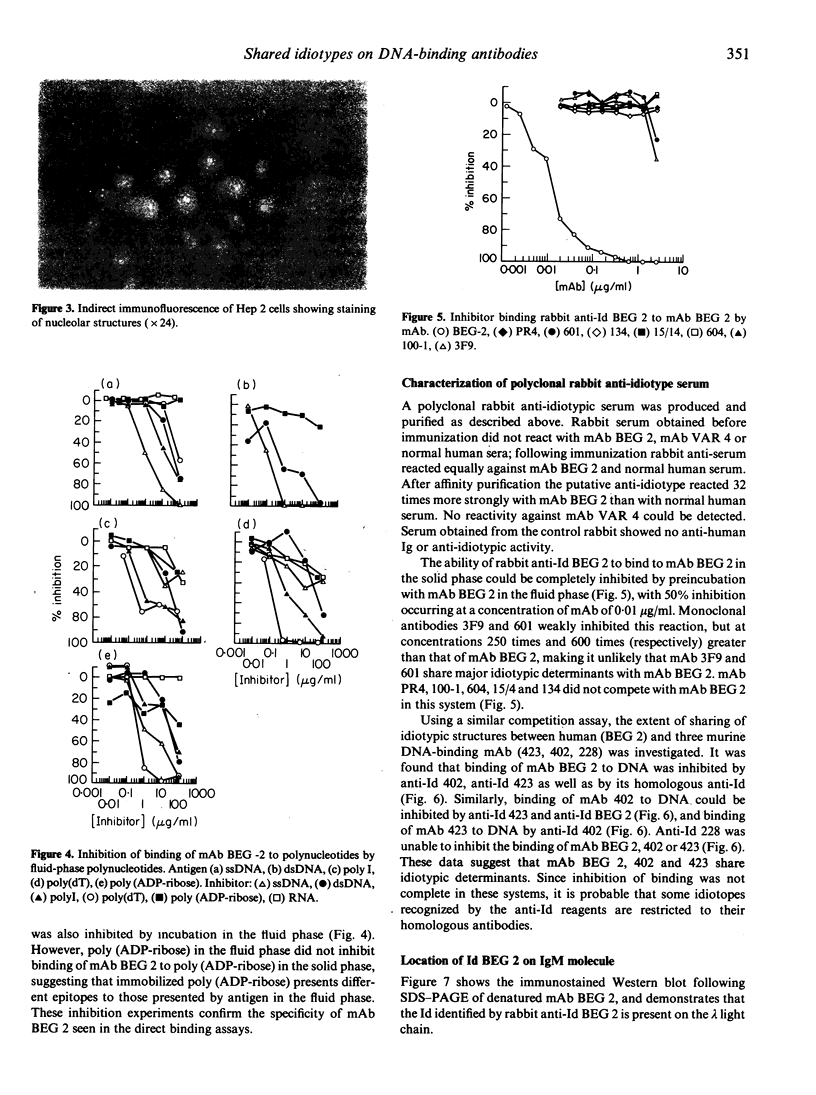
A human DNA-binding monoclonal antibody was produced by fusing the hepatocytes from a 12-week-old human fetus with the lymphoblastoid cell line GM 4672 using polyethylene glycol. This antibody, designated BEG 2, binds to single-stranded (ss) DNA but also binds to double-stranded (ds) DNA, poly(dT), polyI and poly(ADP-ribose), but not to RNA, cardiolipin or K-30. The binding of BEG 2 to these polynucleotides can be inhibited by incubation with polynucleotides in the fluid phase. A rabbit polyclonal anti-idiotype was raised, and using this reagent it was shown that the BEG 2 idiotype is present in normal human serum (7%), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) sera (8%) and rheumatoid arthritis sera (23%). The extent of idiotypic sharing between BEG 2 and murine monoclonal DNA-binding antibodies, in particular monoclonal antibody (mAb) 423 (derived from a 15-day-old fetal MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mouse) and mAb 402 (derived from an adult MRL/lpr mouse), was also investigated. Using a competition ELISA, it was shown that preincubation of BEG 2 with rabbit anti-423 and rabbit anti-402 inhibits the binding of BEG 2 to DNA, and the binding of 402 to DNA by anti-BEG 2 and anti-423. These data suggest that mAb BEG 2, 423 and 402 share common idiotypes, that autoreactivity is present in early fetal life, and that autoantibodies may be encoded for by germline genes, which have been conserved through evolution.
Full text
PDF

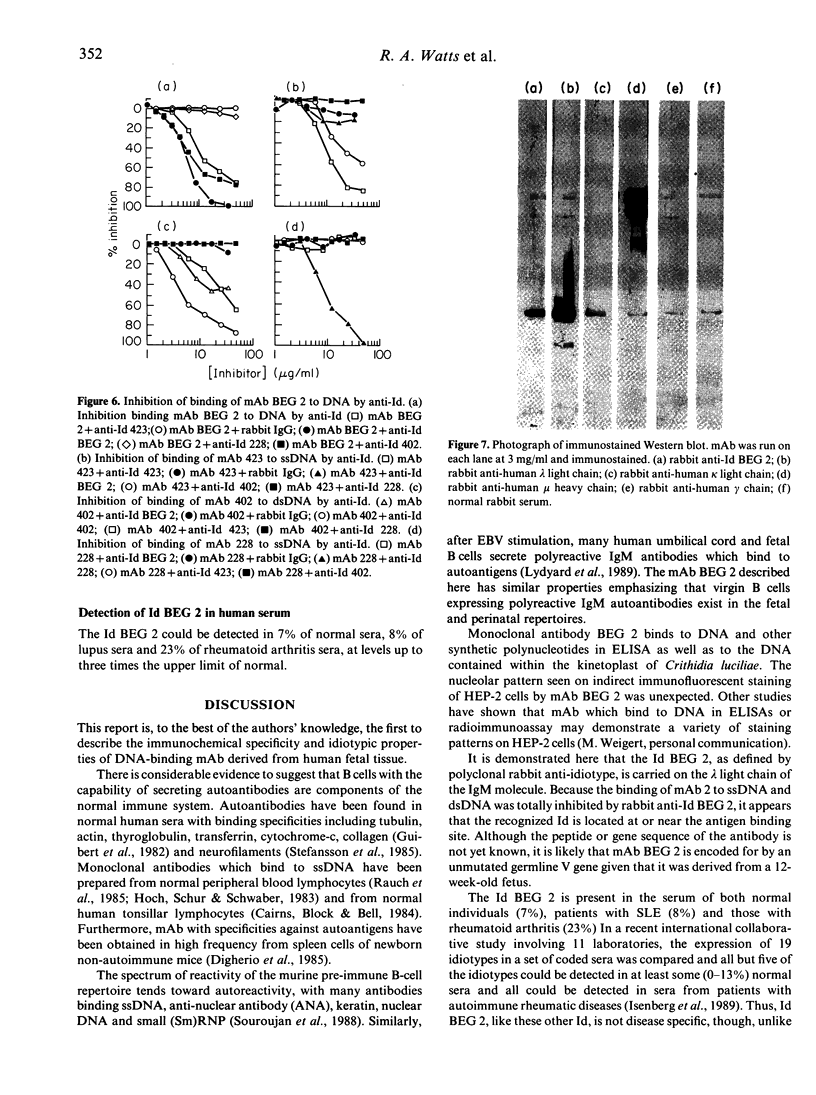


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson P. M., Lampman G. W., Furie B. C., Naparstek Y., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D., Furie B. Homology of the NH2-terminal amino acid sequences of the heavy and light chains of human monoclonal lupus autoantibodies containing the dominant 16/6 idiotype. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1138–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI111808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns E., Block J., Bell D. A. Anti-DNA autoantibody-producing hybridomas of normal human lymphoid cell origin. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):880–887. doi: 10.1172/JCI111505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Liu M. F., Sinha S., Carson D. A. A 16/6 idiotype-positive anti-DNA antibody is encoded by a conserved VH gene with no somatic mutation. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1429–1431. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang H., Takei M., Isenberg D., Shoenfeld Y., Backimer R., Rauch J., Talal N. Expression of an interspecies idiotype in sera of SLE patients and their first-degree relatives. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Mar;71(3):445–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Normal mice express idiotypes related to autoantibody idiotypes of lupus mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2723–2727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighiero G., Lymberi P., Holmberg D., Lundquist I., Coutinho A., Avrameas S. High frequency of natural autoantibodies in normal newborn mice. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):765–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudeney C., Shoenfeld Y., Rauch J., Jones M., Mackworth Young C., Tavassoli M., Shall S., Isenberg D. A. A study of anti-poly (ADP-ribose) antibodies and an anti-DNA antibody idiotype and other immunological abnormalities in lupus family members. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jun;45(6):502–507. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.6.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Fischel R., Zlotnick A. A central anti-DNA idiotype in human and murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Apr;15(4):368–375. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert B., Dighiero G., Avrameas S. Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in human sera. I. Detection, isolation and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S., Schur P. H., Schwaber J. Frequency of anti-DNA antibody producing cells from normals and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Apr;27(1):28–37. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Feldman R., Dudeney C., Konikoff F., Jones D., Ebringer A., Shoenfeld Y. A study of antipolynucleotide antibodies, anti-Klebsiella (K30) antibodies and anti-DNA antibody idiotypes in ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1987 Jun;26(3):168–171. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/26.3.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Williams W., Le Page S., Swana G., Feldman R., Addison I., Bakimer R., Shoenfeld Y. A comparison of autoantibodies and common DNA antibody idiotypes in SLE patients and their spouses. Br J Rheumatol. 1988 Dec;27(6):431–435. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/27.6.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Page S. H., Williams W., Parkhouse D., Cambridge G., MacKenzie L., Lydyard P. M., Isenberg D. A. Relation between lymphocytotoxic antibodies, anti-DNA antibodies and a common anti-DNA antibody idiotype PR4 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, their relatives and spouses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Sep;77(3):314–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locniskar M., Zumla A., Mudd D. W., Isenberg D. A., Williams W., McAdam K. P. Human monoclonal antibodies to phenolic glycolipid-I derived from patients with leprosy, and production of specific anti-idiotypes. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):245–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayus J. L., Pisetsky D. S. Expression of a highly conserved anti-DNA idiotype in normal and autoimmune mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Mar;34(3):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Isenberg D. A., Naparstek Y., Rauch J., Duggan D., Khiroya R., Staines N. A., Schattner A. Shared idiotypes are expressed on mouse and human anti-DNA autoantibodies. Immunology. 1985 Nov;56(3):393–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Massicotte H., Tannenbaum H. Hybridoma anti-DNA autoantibodies from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus demonstrate similar nucleic acid binding characteristics. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Hsu-Lin S. C., Gabriels J. E., Silberstein L. E., Furie B. C., Furie B., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Production of autoantibodies by human-human hybridomas. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):205–208. doi: 10.1172/JCI110595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A., Rauch J., Madaio M. P., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Idiotypic cross-reactions of monoclonal human lupus autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):718–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souroujon M., White-Scharf M. E., Andreschwartz J., Gefter M. L., Schwartz R. S. Preferential autoantibody reactivity of the preimmune B cell repertoire in normal mice. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4173–4179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson K., Marton L. S., Dieperink M. E., Molnar G. K., Schlaepfer W. W., Helgason C. M. Circulating autoantibodies to the 200,000-dalton protein of neurofilaments in the serum of healthy individuals. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1117–1119. doi: 10.1126/science.4039466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepicchio W., Jr, Maruya A., Barrett K. J. The heavy chain genes of a lupus anti-DNA autoantibody are encoded in the germ line of a nonautoimmune strain of mouse and conserved in strains of mice polymorphic for this gene locus. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3139–3145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. A., Williams W., Le Page S., Norden A., Soltys A., Swana G., Addison I., Hay F. C., Isenberg D. A. Analysis of autoantibody reactivity and common idiotype PR4 expression of myeloma proteins. J Autoimmun. 1989 Oct;2(5):689–700. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(89)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W., Zumla A., Behrens R., Locniskar M., Voller A., McAdam K. P., Isenberg D. A. Studies of a common idiotype PR4 in autoimmune rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Sep;31(9):1097–1104. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]