Abstract
The electrophilic lipid 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) is known to allow adaptation to oxidative stress in cells at low concentrations and apoptosis at high levels. The mechanisms leading to adaptation involve the covalent modification of regul-atory proteins, such as Keap1, and augmentation of antioxidant defences in the cell. The targets leading to apoptosis are less well defined, but mitochondria have been indirectly implicated in the mechanisms of cell death mediated by electrophilic lipids. To determine the potential of electrophilic cyclopentenones to induce pro-apoptotic effects in the mitochondrion, we used isolated liver mitochondria and demonstrated that 15d-PGJ2 promotes Ca2+-induced mitochondrial swelling and cytochrome c release. The mechanisms involved are consistent with direct modification of protein thiols in the mitochondrion, rather than secondary formation of reactive oxygen species or lipid peroxidation. Using proteomic analysis in combination with biotinylated 15d-PGJ2, we were able to identify 17 potential targets of the electrophile-responsive proteome in isolated liver mitochondria. Taken together, these results suggest that electrophilic lipid oxidation products can target a sub-proteome in mitochondria, and this in turn results in the transduction of the electrophilic stimulus to the cell through cytochrome c release.
Keywords: cyclopentenone; 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2; electrophile-responsive proteome; electrophilic lipid; proteomics
Abbreviations: ANT, adenine nucleotide translocase; 1D and 2D, one and two dimensional; 15d-PGJ2, 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2; bt-15d-PGJ2, biotinylated 15d-PGJ2; DNPH, 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine; IEF, isoelectric focusing; MALDI–TOF, matrix-assisted laser-desorption ionization–time-of-flight; MnTBAP, Mn(III)tetrakis(4-benzoic acid)porphyrin chloride; Mito E, 2-[2-(triphenylphosphonio)ethyl]-3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol bromide; NEM, N-ethylmaleimide; PIC, protease inhibitor cocktail; PT, permeability transition; PTP, permeability transition pore; ROS, reactive oxygen species
INTRODUCTION
Exposure of cells to lipid oxidation products has a diverse range of effects which depend on concentration and length of exposure. Of particular interest are those compounds, such as 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2), which contain electrophilic carbon centres and can induce apoptosis in a wide range of cells [1–6]. This reactive lipid product and related compounds have attracted particular interest due to their potential as anti-tumour agents through their ability to promote apoptosis [7]. The detailed mechanisms have not been defined, but are likely to involve the direct modification of nucleophilic centres in target proteins by electrophilic lipids and/or the secondary formation of ROS (reactive oxygen species) in the cell [2,6,8–11]. It is well recognized that the mitochondrion can play an important role in the apoptotic process, and evidence suggests that 15d-PGJ2 may interact either directly or indirectly with mitochondria. For example, exposure of cells to oxidized low-density lipoprotein, which contains electrophiles, leads to the formation of ROS from the mitochondrion [12]. In addition, low non-toxic concentrations of 15d-PGJ2 induce the activity of complex I in endothelial cells through a GSH-independent mechanism [13]. In contrast, a recent study [14] with purified rat cerebral mitochondria demonstrated that high concentrations of 15d-PGJ2 are capable of inhibiting complex I of the respiratory chain. Studies with purified 15d-PGJ2 also suggest that exposure of the electrophile to human neuroblastoma and breast cancer cells decreases the mitochondrial membrane potential and induces ROS formation [11,15]. Furthermore, this ROS formation is inhibited by exposure of the cells to a proton ionophore which depolarizes the mitochondrial membrane [15]. Other potential targets within the mitochondrion have not been examined to date. Of particular interest is the mitochondrial PTP (permeability transition pore) which is formed from a number of proteins within the matrix, and mitochondrial inner and outer membranes [16,17]. The opening of this Ca2+-dependent channel is thought to play an important role in controlling the commitment of the cell to death through apoptotic or necrotic mechanisms [18,19]. It has also been shown that pre-treatment of isolated mitochondria with pro-oxidants, such as peroxynitrite, can lower the threshold at which opening of the PTP occurs [20]. The impact of 15d-PGJ2 on the functioning of the PTP has not been examined.
In the present study we examined the effects of 15d-PGJ2 in isolated rat liver mitochondria. 15d-PGJ2 was found to enhance the Ca2+-dependent PT (permeability transition) and cytochrome c release. This property was not shared by products of the cyclo-oxygenase pathway, which do not contain an electrophilic centre. Using a combination of proteomic approaches with biotin-tagged 15d-PGJ2, a number of protein targets within the organelle have been defined, and are discussed in the context of the mechanisms of toxicity mediated by lipid-derived electrophiles.
EXPERIMENTAL
Materials
All biochemicals were from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, U.S.A.), except cyclosporin A and NONOate compounds (Alexis, San Diego, CA, U.S.A.), Neutravidin-Ultralink resin and 5-(biotinamido)-pentylamine (Pierce, Rockford, IL, U.S.A.), and PIC (protease inhibitor cocktail) (Roche, Indianapolis, IN, U.S.A.). Mito E {2-[2-(triphenylphosphonio)ethyl]-3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol bromide} was a gift from Dr Balaraman Kalyanaraman (Biophysics Research Institute, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, U.S.A.). All other reagents used were of analytical grade.
Biotinylation of 15d-PGJ2
The biotin group was adducted to 15d-PGJ2 via a carbodi-imide-mediated condensation reaction with 5-(biotinamido)pentylamine (Pierce) as described previously [2]. Biotinylation was confirmed by electrospray MS, and concentrations were measured by spectroscopy at A306 using a molar absorption coefficient 12000 M−1·cm−1.
Mitochondrial preparation
Male Sprague–Dawley rats (250–300 g) were from Harlan (Indianapolis, IN, U.S.A.) and handled in accordance with recommendations in ‘The Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals’ (DHEW Publication # NIH85-23). Food and water were available ad libitum. Liver mitochondria were isolated as described in [20], with the final centrifugation step and resuspension performed in EGTA-free medium.
Mitochondrial PTP assay
Mitochondrial PTP opening was assayed as described in [21]. Mitochondrial swelling was assayed as a decrease in the absorbance of a mitochondrial suspension (measured at 540 nm) at 37 °C. Mitochondria (1 mg of protein) were suspended in 1 ml of buffer containing 40 mM Hepes, 195 mM mannitol, 25 mM sucrose, 5 mM succinate and 1 μM rotenone, pH 7.2. After a 2 min equilibration period, CaCl2 (20–120 μM) was added and the absorbance monitored for 20 min. A concentration of Ca2+ was used that gave approx. 50% swelling, in order that the potentiation effects by 15d-PGJ2 could be detected. As is frequently found in this type of experiment the precise amount of Ca2+ required was specific for each mitochondrial preparation. To determine the effects of 15d-PGJ2 on oxygen consumption, mitochondria (1 mg) were suspended in respiration buffer (120 mM KCl, 25 mM sucrose, 10 mM Hepes, 1 mM KH2PO4 and 5 mM MgCl2) in a 1 ml sealed chamber fitted with a Clark-type O2 electrode (Instech, Plymouth Meeting, PA, U.S.A.). In respiration experiments to mimic swelling conditions, succinate (5 mM) and rotenone (1 μM) were used, and Ca2+ was added 2 min after resuspending the mitochondria. Data were collected using a digital recording device (Dataq, Akron, OH, U.S.A.) connected to a PC.
For measurement of cytochrome c release during the swelling experiments, cyclosporin A (5 μM) and EGTA (1 mM) were added to mitochondrial suspensions to prevent further swelling 1 min after the addition of Ca2+. Aliquots were then centrifuged at 14000 g for 10 min. Supernatants were immediately diluted 1:2 in 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid and cytochrome c concentrations were measured by HPLC, as described by Picklo et al. [22]. Glutathione levels and protein thiols were determined in mitochondria suspended in a buffer containing sucrose (25 mM), and incubated in either the presence or absence of 15d-PGJ2 for 15 min. The mitochondrial suspensions were then centrifuged at 14000 g for 10 min and total glutathione was measured spectrophotometrically [23]. Total thiol concentrations were measured by adding DTNB [5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)] to the sample and measuring the absorbance at 412 nm.
Measurement of mitochondrial protein carbonyls
Protein carbonyl formation was detected using the oxyblot kit supplied by CHEMICON International and as described in [24]. Briefly, 20 μl of the mitochondria suspension treated in identical conditions in which the PT was measured was solubilized with 2.5% SDS. The carbonyl groups formed on mitochondrial proteins were derivatized by reaction with DNPH (2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine) for 15 min at room temperature. For the positive control, the same amount of rat liver mitochondrial pellets was incubated at 37 °C, for 5 h with 25 mM ascorbic acid and 100 μM FeCl3 in 25 mM Hepes buffer (pH 7.4). After incubation the sample was dialysed against 1 mM EDTA in 50 mM Hepes buffer overnight. The negative controls were prepared with derivatization-control solution which did not contain DNPH. The 2,4-dinitrophenyl-derivatized mitochondrial proteins were then separated by SDS/PAGE, followed by Western blotting. The membrane was blocked with 1% BSA in TBS-T (0.25 M Tris/HCl, 35 mM NaCl, 27 mM KCl and 0.5% Tween 20) for 1 h. The membranes were then incubated with a primary antibody against 2,4-dinitrophenyl overnight, followed by secondary antibody incubation against HRP (horseradish peroxidase) conjugated to a goat anti-rabbit IgG (Amersham). The signal was detected using chemiluminescence (Pierce).
bt-15d-PGJ2 (biotinylated 15d-PGJ2) labelling and affinity purification of mitochondrial proteins
Rat liver mitochondria were isolated as described above, centrifuged at 14000 g for 10 min, and the pellet was resuspended in respiration buffer containing PIC at a final concentration of 1 mg of mitochondrial protein per ml. Mitochondria (0.5 mg of protein) were incubated without or with 20 μM or 50 μM bt-15d-PGJ2 for 15 min at 37 °C. The reaction was stopped by centrifugation of the mitochondria at 14000 g for 10 min and removing the supernatant. For affinity purification, pellets were resuspended in 0.5 ml of IP wash buffer containing 50 mM Tris/HCl, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100 and PIC. To each sample, 50 μl of Neutravidin-Ultralink resin was added, and the samples were incubated overnight at 4 °C with continuous mixing. Unbound and non-specifically bound proteins were removed by washing the resin extensively with IP wash buffer. For 1D (one-dimensional) gel separation, proteins were eluted with 1 column volume of 1×gel loading buffer, and heated to 95 °C for 5 min, followed by SDS/PAGE using a 10% polyacrylamide gel. After electrophoresis, proteins were stained with Coomassie Blue.
Samples for 2D (two-dimensional) SDS/PAGE were eluted twice with 5 column volumes of 8 M guanidine, pH 1.5. Both elution fractions were pooled and the buffer was exchanged with rehydration buffer [7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 2% CHAPS, 0.5% dodecyl maltoside, 2% ampholytes (pH 3–10) and PIC] using a microconcentration device (Millipore, Billerica, MA, U.S.A.). A small amount of Bromophenol Blue was added to samples immediately before rehydrating IEF (isoelectric focusing) strips.
Proteomic analysis and MS
Separation of mitochondrial proteins using a proteomic approach was undertaken as described in [25]. Affinity-purified proteins were prepared as described above and applied to IEF strips (pH 3–10) (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, U.S.A.), and allowed to rehydrate overnight. IEF was performed for 5 min at 175 V, 30 min at a 175–2000 V gradient, and then held at 2000 V for 30 min using a ZOOM® IPGRunner IEF system (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, U.S.A.). After IEF, the IPG (immobilized pH gradient) strips were equilibrated for 10 min in equilibration buffer (375 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.8, 6 M urea, 20% glycerol, 2% SDS and 130 mM dithiothreitol) before SDS/PAGE. 2D SDS/PAGE was performed using 12.5% homogeneous Tris/glycine acrylamide gels. After electrophoresis, proteins were stained with Coomassie Blue.
Protein spots were excised from gels and subjected to MALDI–TOF (matrix-assisted laser-desorption ionization–time-of-flight) MS, as described in [25]. After the in-gel tryptic digest was extracted, an aliquot was mixed with an equal volume of the matrix α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid in 50% acetonitrile and subjected to MALDI–TOF MS analysis using a PE-Biosystems Voyager Elite instrument (Framingham, MA, U.S.A.) equipped with a nitrogen laser (337 nm) and operated using a delayed extraction mode. The peptide masses were entered into the MASCOT search engine accessed at http://www.matrixscience.com, and the NCBI database was searched to match the tryptic peptide fingerprint with a parent polypeptide.
RESULTS
15d-PGJ2 promotes the PT in isolated rat liver mitochondria
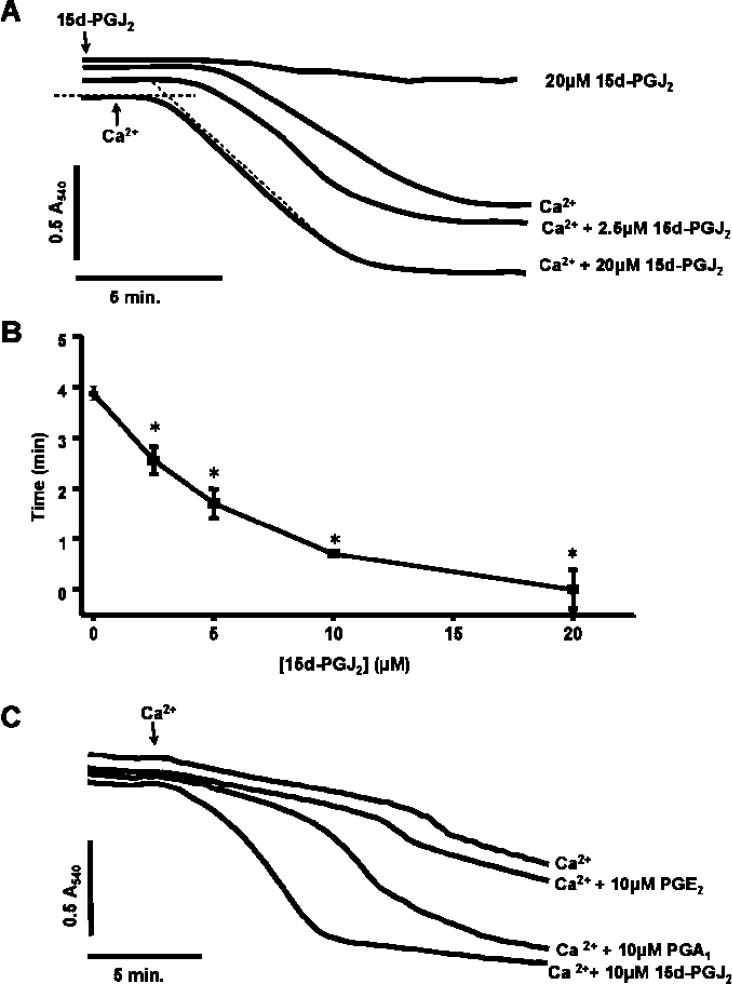
In the first series of experiments, the response of isolated rat liver mitochondria to Ca2+ with and without pre-treatment with 15d-PGJ2 was determined. Under these conditions Ca2+ alone promoted swelling as shown by a decrease in absorbance measured by the spectrophotometer (Figure 1A). Incubation of mitochondria with 15d-PGJ2 alone did not cause swelling. On the addition of Ca2+, a concentration-dependent enhancement of both the time before onset of swelling and the absolute magnitude of the response was observed in the presence of 15d-PGJ2 (Figures 1A and 1B). The effects of structurally similar lipids, with (PGA1) and without (PGE2) electrophilic functional groups, were also analysed (Figure 1C). Only the compound containing a reactive electrophilic centre (PGA1) was found to promote the PT in a similar manner to that of 15d-PGJ2. These data suggest that induction of the PTP by cyclopentenones requires an electrophilic carbon. It is possible that changes in the swelling of the mitochondria induced by 15d-PGJ2 could be due to effects on the mitochondria that are independent of the PTP. However, both cyclosporine A and NO were found to prevent the potentiation of Ca2+-induced swelling in response to 15d-PGJ2 (results not shown), supporting the hypothesis that the process being monitored is indeed the PT.
Figure 1. Ca2+-induced pore opening is accelerated by 15d-PGJ2 in a concentration-dependent manner.
Mitochondria (1 mg/ml) were incubated in the spectrophotometer in swelling buffer with succinate (5 mM) and rotenone (1 μM). (A) Where indicated, increasing concentrations of 15d-PGJ2 were present from the beginning of the experiment and Ca2+ (10 μM) was added after 2 min. (B) Lag time (after the addition of Ca2+) was measured by determining the intercepts of minimum and maximum rates of change in absorbance as shown in (A) for the Ca2++15d-PGJ2 sample (20 μM). Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. for at least three experiments. *P<0.001 versus 0 μM 15d-PGJ2. (C) Prostaglandins A (10 μM), E (10 μM) and J2 (10 μM) were present from the beginning of the experiment and Ca2+ (5 μM) was added at 2 min. Data are single traces representative of 5–7 individual experiments.
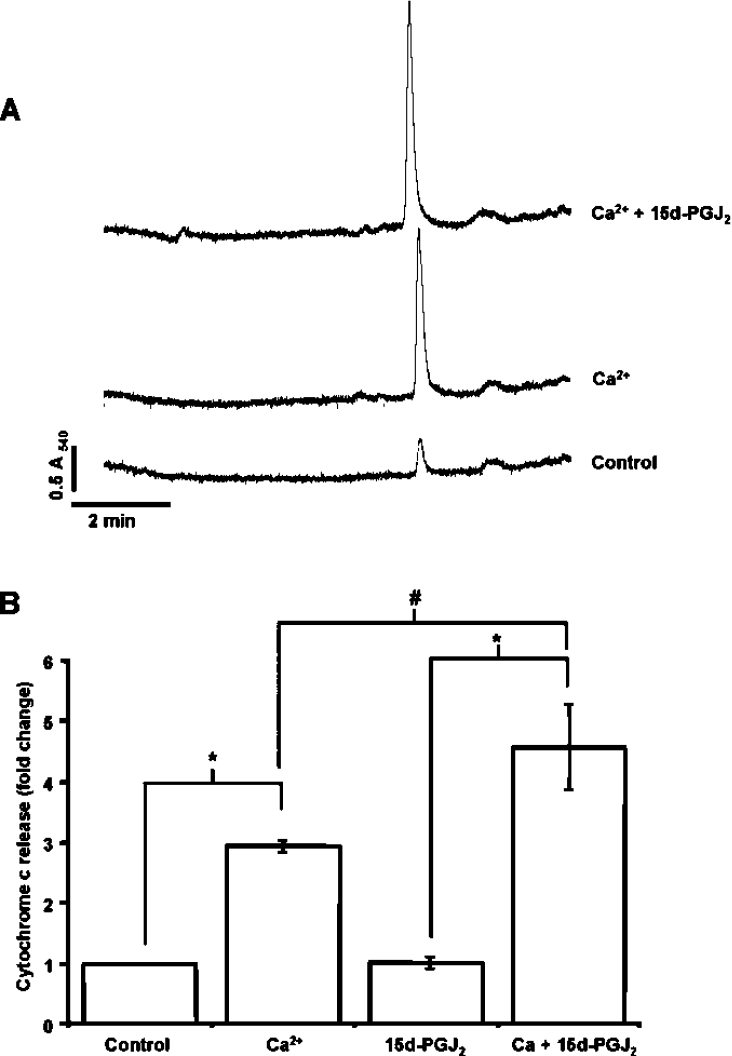
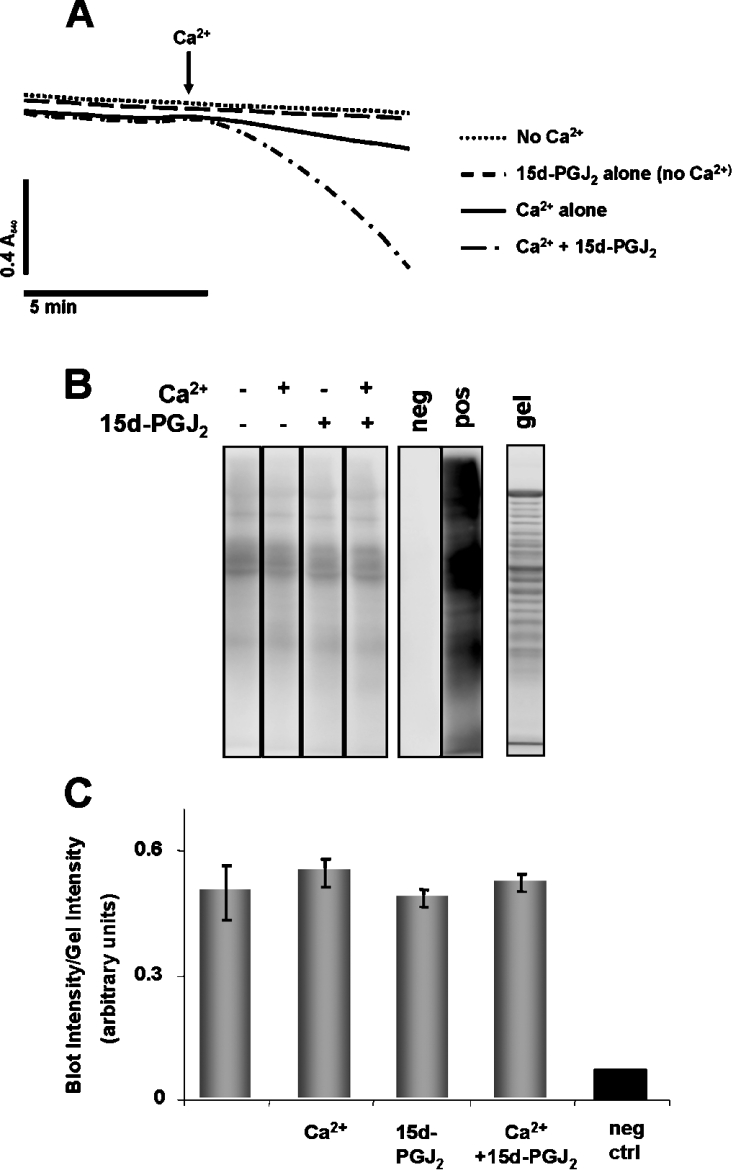
As an additional index of PTP opening, cytochrome c release from the organelle was measured in mitochondria incubated with Ca2+ for 1 min with or without pre-treatment with 15d-PGJ2. To prevent further swelling during separation of the mitochondria from released cytochrome c, the Ca2+ chelator EGTA and cyclosporine A were added and the mitochondria were immediately pelleted by centrifugation. Figure 2(A) shows the HPLC analysis of the cytochrome c not retained in the mitochondrion before and after treatment with Ca2+ and 15d-PGJ2. Treatment of mitochondria with 15d-PGJ2 in the absence of Ca2+ did not induce significant cytochrome c release compared with Ca2+-free controls (Figure 2B). In support of the concept that 15d-PGJ2 can induce an apoptotic response at the level of the mitochondrion, the levels of cytochrome c released from the mitochondria treated with 15d-PGJ2 were significantly higher than in the control samples after the addition of Ca2+ (Figure 2B). We have previously shown that cytochrome c release is a very early event in the Ca2+-induced PTP opening, which occurs prior to a significant increase in mitochondrial swelling [21]. These results support the hypothesis that 15d-PGJ2 is involved in the initiating mechanisms leading to the opening of the PTP.
Figure 2. Promotion of cytochrome c release from isolated mitochondria by 15d-PGJ2.
Mitochondria were incubated with and without 15d-PGJ2 (10 μM), 2 min after which Ca2+ was added. Cyclosporin A (1 μM) and EGTA (20 μM) were added at 1 min to stop further pore opening and cytochrome c release, and mitochondria were separated by centrifugation for measurement of cytochrome c in the supernatant. (A) Representative HPLC trace for mitochondria that were untreated or treated with Ca2+ alone, or Ca2+ and 15d-PGJ2. (B) Quantitation of cytochrome c released at 1 min expressed as fold change of the concentration of cytochrome c at time 0. Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. for at least three experiments. *, P<0.001; #, P<0.05.
Effect of cyclopentenone prostaglandins on mitochondrial oxygen consumption
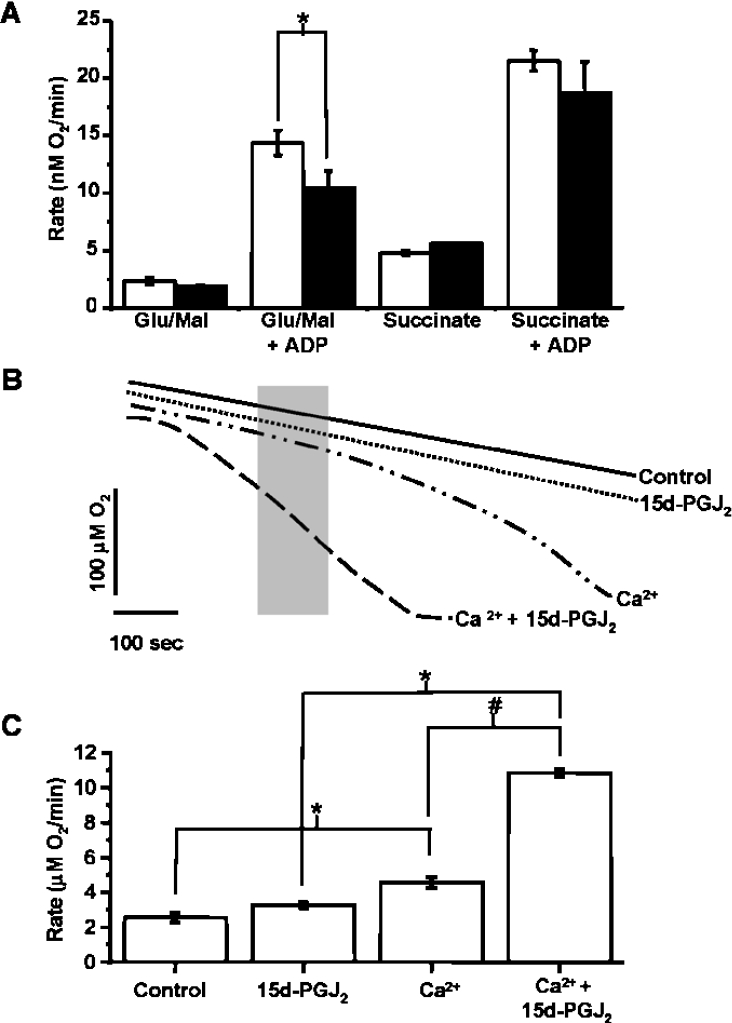
We next assessed the effects of 15d-PGJ2 on mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Figure 3(A) shows the rate of respiration of mitochondria incubated with an oxygen electrode with 10 μM 15d-PGJ2 in the presence of succinate or glutamate/malate to initiate state 4 respiration through either complex II or I respectively, and with ADP to stimulate state 3 respiration. In agreement with a recent report [14] describing the effects of 15d-PGJ2 on brain mitochondria, there is no significant change in state 4 respiration. However, there is a slight, but significant, decrease in respiration in the presence of ADP with complex I substrates.
Figure 3. Ca2+-induced increase in respiration is accelerated by 15d-PGJ2.
(A) Respiration rate of mitochondria (1 mg/ml) in the absence (open bars) or presence (closed bars) of 15d-PGJ2 (10 μM). The respiration rate is shown in the presence of 5 mM succinate or glutamate (10 mM) and malate (2.5 mM), with or without ADP (10 mM). (B) Representative respiration traces of mitochondria in the presence of succinate (5 mM) and rotenone (1 μM) in which 15d-PGJ2 (10 μM) was present from the beginning of the incubation and Ca2+ (10 μM) was added 2 min after incubation. Traces shown are untreated control, 15d-PGJ2 alone, Ca2+ alone and Ca2+ added after the addition of 15d-PGJ2. (C) Respiration rates measured from traces such as those shown in (B) over the 100 s indicated by the grey box in (B). Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. for at least three experiments. *, P<0.01; #, P<0.001.
To determine whether there is an effect of 15d-PGJ2 on O2 consumption during PT, mitochondria were incubated in the chamber with succinate and rotenone, with or without 15d-PGJ2, for a period of 2 min before the addition of Ca2+ (Figure 3B). Upon the addition of Ca2+, respiration gradually increased until all O2 in the chamber was consumed. As in the swelling experiments, there was no effect of 15d-PGJ2 on the basal respiration rate in the absence of Ca2+. However, in the presence of Ca2+, 15d-PGJ2 accelerated the Ca2+-induced increase in O2 consumption. This is shown in Figure 3(C) by the measurement of O2 consumption over the time period indicated by the grey box of the oxygen trace in Figure 3(B). The change in O2 consumption is consistent with the opening of the PTP and the consequent increase in permeability across the mitochondrial inner membrane for ions and low-molecular-mass compounds [16]. Interestingly, the rate of respiration of the two groups is identical over the last minute of the trace, suggesting that 15d-PGJ2 accelerates an early event in PT.
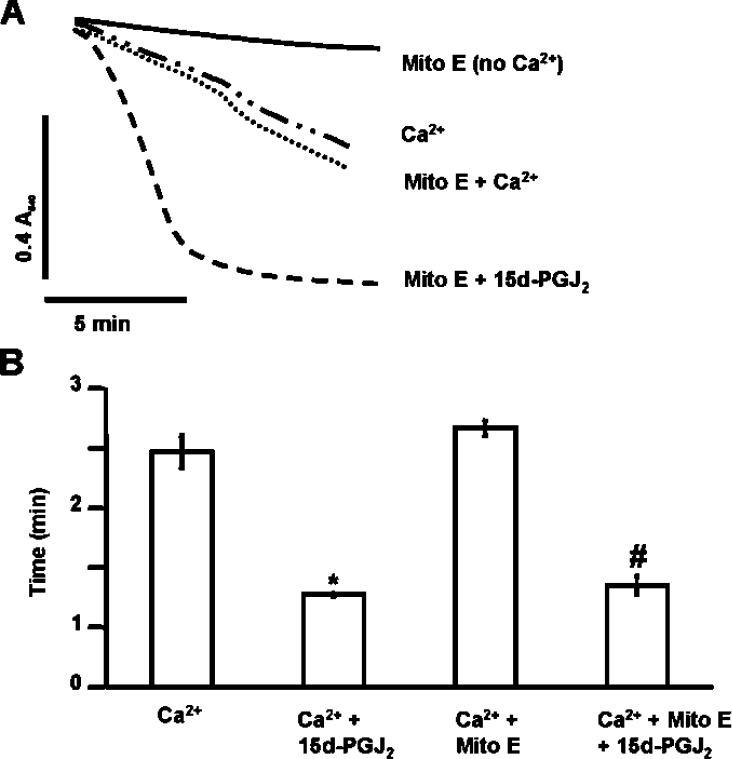
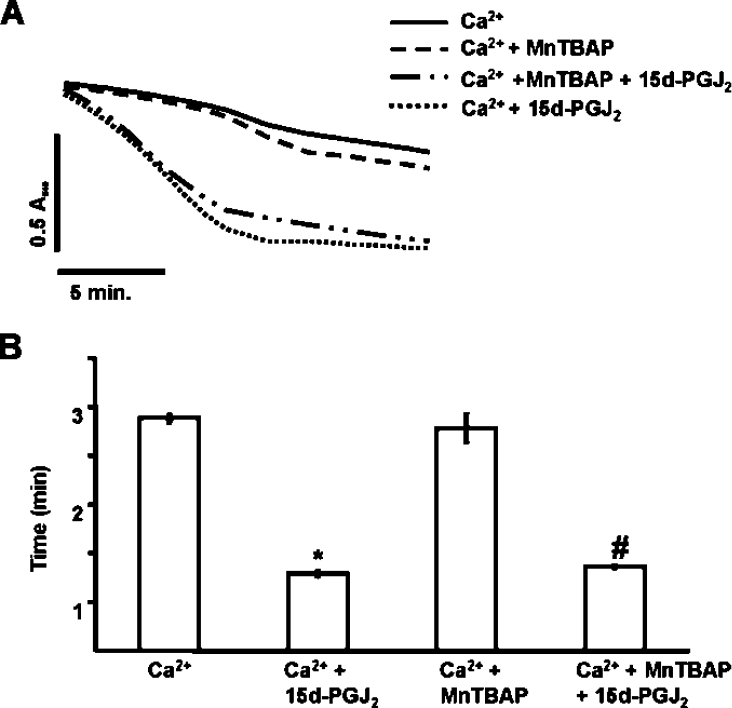
Since electrophilic lipids, such as 15d-PGJ2, can increase ROS, the effect of antioxidants on PT was investigated. In the first experiment, mitochondria were incubated with or without the mitochondrially targeted lipid radical scavenger Mito E (2 μM) for 1 min prior to the addition of 20 μM 15d-PGJ2. Figure 4 shows that Mito E had no significant effect on Ca2+-dependent PT potentiation mediated by 15d-PGJ2. These results demonstrate that the effects of 15d-PGJ2 on PT are not mediated by downstream mitochondrial lipid peroxidation products. Next, mitochondria were treated with or without 20 μM 15d-PGJ2 followed immediately by the addition of the superoxide scavenger, MnTBAP [Mn(III)tetrakis(4-benzoic acid)porphyrin chloride] (50 μM) and incubated for 2 min prior to the addition of Ca2+. The presence of MnTBAP did not significantly change PT potentiation by 15d-PGJ2, suggesting that ROS are not involved in potentiation of PT by 15d-PGJ2 (Figures 5A and 5B). We also monitored ROS formation with or without 15d-PGJ2 by assessing oxidative damage to mitochondrial proteins. For these experiments, mitochondria were treated with or without 20 μM 15d-PGJ2 for 2 min prior to addition of Ca2+. Mitochondria were allowed to swell, as shown in Figure 6(A), and then flash frozen to slow further swelling and ROS production. This time period was selected so that significant swelling occurred in the presence of 15d-PGJ2, but not for the Ca2+ control. Thus if 15d-PGJ2 was promoting oxidative protein modification, it should be evident from the comparison of these samples. Mitochondrial proteins were then assayed for protein carbonyl formation, a marker of ROS-mediated protein damage. Figure 6 shows there is no significant change in protein carbonyl formation in samples treated with 15d-PGJ2. Taken together, these data suggest that potentiation of PT by 15d-PGJ2 is not mediated by ROS production, downstream lipid peroxidation products or carbonyl formation on proteins.
Figure 4. Addition of Mito E has no effect on Ca2+-induced PT.
Mito E (2 μM) was added to mitochondria (1 mg/ml) in swelling buffer and incubation was carried out for 1 min. (A) 15d-PGJ2 (20 μM) was added after Mito E and allowed to react for an additional 2 min before the addition of Ca2+ (80 μM). Lag time (after the addition of Ca2+) was calculated as described in Figure 1. Data are single traces representative of three individual experiments. (B) The lag time before onset of swelling is indicated by the bar graph. Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. for at least three independent experiments. *, P<0.05 for Ca2++15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria compared with Ca2+-treated. #, P<0.05 for Ca2++Mito E+15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria compared with Ca2++Mito E-treated.
Figure 5. Ca2+-induced PT is not altered by the addition of the superoxide dismutase mimetic, MnTBAP.
Mitochondria (1 mg/ml) were incubated in swelling buffer with succinate (5 mM) and rotenone (1 μM). (A) Ethanol or 15d-PGJ2 (20 μM) was added just prior to MnTBAP (50 μM) and allowed to incubate for 2 min before the addition of Ca2+ (130 μM). Lag time (after the addition of Ca2+) was calculated as described in Figure 1. Data are single traces representative of three individual experiments. (B) The lag time before onset of swelling is indicated in the histogram. Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. for at least three independent experiments. *, P<0.05 for Ca2++15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria compared with Ca2+-treated. #, P<0.05 for Ca2++MnTBAP+15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria compared with Ca2++MnTBAP-treated.
Figure 6. Detection of protein carbonyl formation on mitochondrial proteins after exposure to Ca2+ and 15d-PGJ2.
(A) Mitochondria (1 mg/ml) were incubated in swelling buffer with succinate (5 mM) and rotenone (1 μM) with or without 80 μM Ca2+ or 20 μM 15d-PGJ2 for the time period shown before samples were flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. (B) Carbonyl formation on mitochondrial proteins was detected after derivatization with DNPH followed by Western blot analysis, as indicated. The negative control (neg) was a sample of mitochondria in which the DNPH derivatization step was omitted. The positive control (pos) was prepared by incubating mitochondrial proteins with iron/ascorbate. Proteins separated on an identical gel were stained with Sypro Ruby (gel). (C) Quantitation of the Western blot in (B). Total density from each lane on the Western blot was normalized to the total density of the corresponding lane on the gel. Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. (n=3).
Modification of mitochondrial thiols By 15d-PGJ2
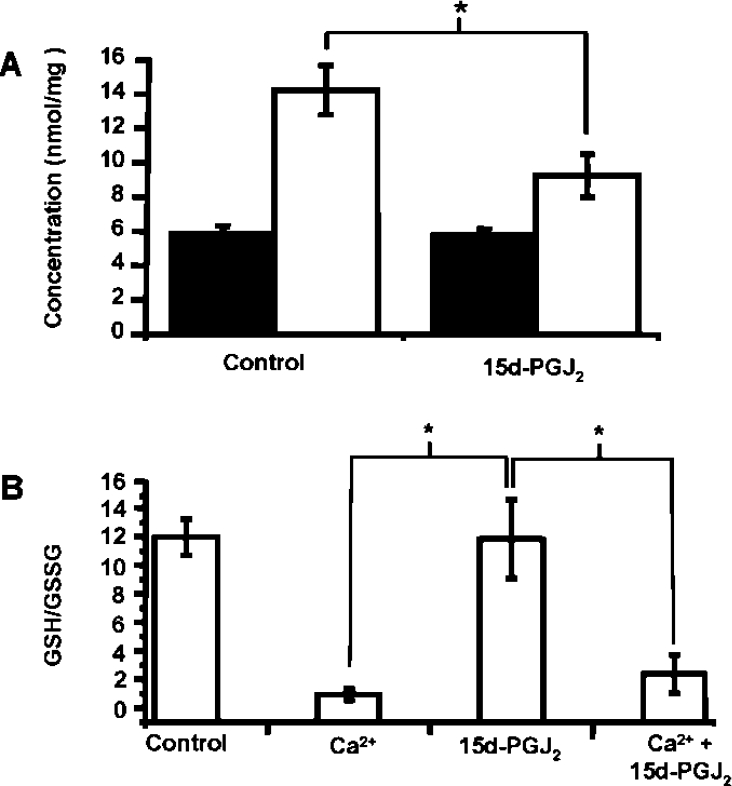
Electrophilic cyclopentenones, such as 15d-PGJ2, can covalently modify thiols by a Michael Addition reaction. As it is thought that depletion of the thiol antioxidant GSH may be one mechanism leading to PTP opening, GSH concentrations were measured in mitochondria 5 min after exposure to 15d-PGJ2. Figure 7(A) shows that in mitochondria that were treated with 15d-PGJ2 alone, levels of GSH (closed bars) were approx. 6 nmol/mg of protein and identical with untreated mitochondria. In contrast, exposure to 15d-PGJ2 resulted in a significant decrease in protein thiols (open bars). Furthermore, there was no significant difference in the GSH/GSSG ratio between the mitochondria treated with or without 15d-PGJ2. On addition of Ca2+ there was a substantial loss of GSH from the mitochondria, which is consistent with PTP opening and also oxidation, presumably due to the pore-associated production of ROS. Consistent with the lack of an effect of 15d-PGJ2 on GSH levels, there was no effect of the electrophile on the GSH/GSSG ratio with or without Ca2+.
Figure 7. Protein thiols, but not GSH, are depleted by 15d-PGJ2.
Mitochondria were incubated as described in the Experimental section for PT experiment. (A) Concentration of GSH (closed bars) and protein thiol (open bars) after incubation of mitochondria alone or with 15d-PGJ2 (10 μM). (B) At 20 min, the mitochondria were collected, centrifuged and derivatized for GSH and GSSG detection by HPLC. The GSH/GSSG ratio is shown for control mitochondria, 15d-PGJ2 (10 μM), Ca2+ (10 μM) and Ca2++15d-PGJ2. The results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. for at least three experiments. *, P<0.001.
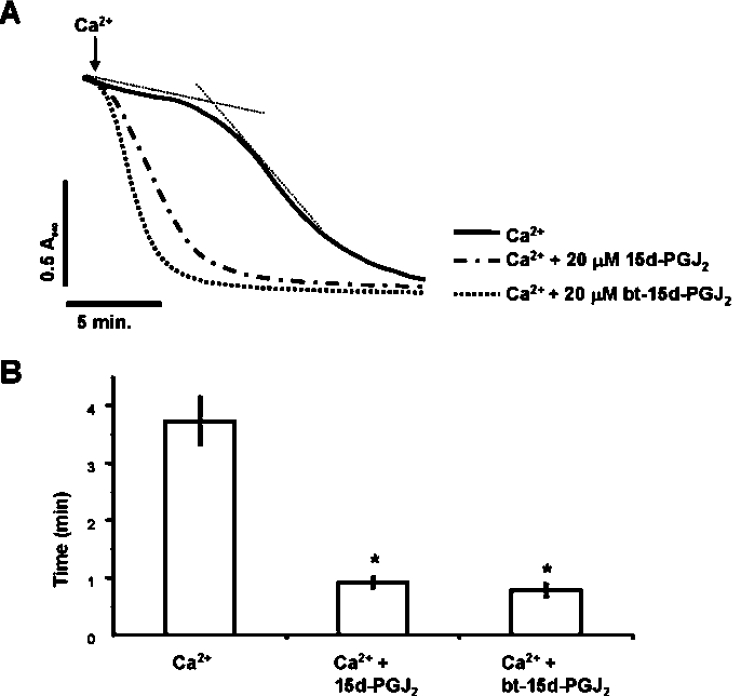
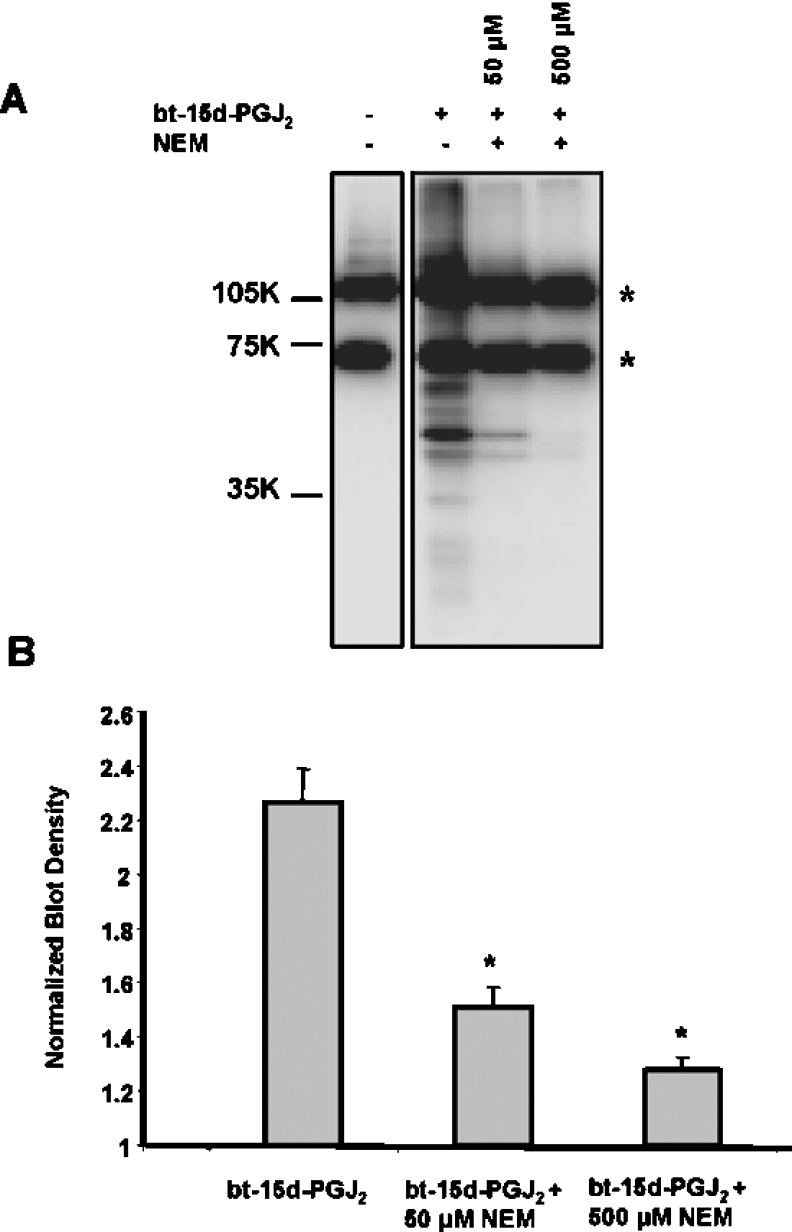
Using a biotin-tagged form of 15d-PGJ2 (bt-15d-PGJ2) we next investigated the role of protein thiol modification in PT potentiation by the electrophile. First, the ability of bt-15d-PGJ2 to act similarly to the native 15d-PGJ2 was tested by examining the effects on PT. As with the native lipid, bt-15d-PGJ2 (20 μM) promoted swelling in the presence of Ca2+ (Figures 8A and 8B), but not in the absence of Ca2+ (results not shown). Next, mitochondrial protein thiol modification was induced using NEM (N-ethylmaleimide) to alkylate potential protein thiol targets prior to treatment with bt-15d-PGJ2. In these experiments, isolated mitochondria were incubated with 50 or 500 μM NEM for 10 min, followed by treatment with 50 μM bt-15d-PGJ2 for 1 h. Mitochondrial proteins containing a biotin tag were then measured by Western blot analysis. Figure 9(A) shows that bt-15d-PGJ2 forms covalent adducts with mitochondrial proteins. The two bands showing a strong signal in the control not exposed to bt-15d-PGJ2 are the endogenous biotin-containing carboxylases in the mitochondria. The amounts of these proteins are constant relative to the signal resulting from biotinylated lipid–protein adducts and were used to normalize the loading of the samples for quantification purposes (Figure 9B). After treatment with NEM the majority of the biotin labelling is blocked, consistent with modification of thiols by the electrophilic lipid. Similar results were obtained using 20 μM bt-15d-PGJ2, however, the signal was proportionately lower.
Figure 8. Ca2+-induced PT is not modified by the biotin tagging of 15d-PGJ2.
Mitochondria (1 mg/ml) were incubated in the spectrophotometer in swelling buffer with succinate (5 mM) and rotenone (1 μM). (A) The same concentration (20 μM) of 15d-PGJ2 or bt-15d-PGJ2 was present from the beginning of the experiment and Ca2+ (80 μM) was added at 2 min. Lag time (after the addition of Ca2+) was calculated as described in Figure 1. Data are single traces representative of 3–6 individual experiments. (B) Data represent the mean times of maximum swelling±S.E.M. for 3–6 individual experiments. *, P<0.001 versus control (Ca2+ only).
Figure 9. Modification of mitochondrial proteins by bt-15d-PGJ2 is blocked by NEM.
(A) Mitochondria (1 mg/ml) in respiration buffer were incubated with NEM (0, 50 or 500 μM) for 10 min, followed by treatment with or without bt-15d-PGJ2 (50 μM) for 1 h. Protein adducts were detected by Western blot analysis. The asterisks mark the biotin-containing mitochondrial carboxylases. (B) Quantitation of density from (A) expressed as normalized blot density (total density of lane/density of carboxylase bands in that lane). Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. (n=3). *, P<0.01 versus bt-15d-PGJ2 only.
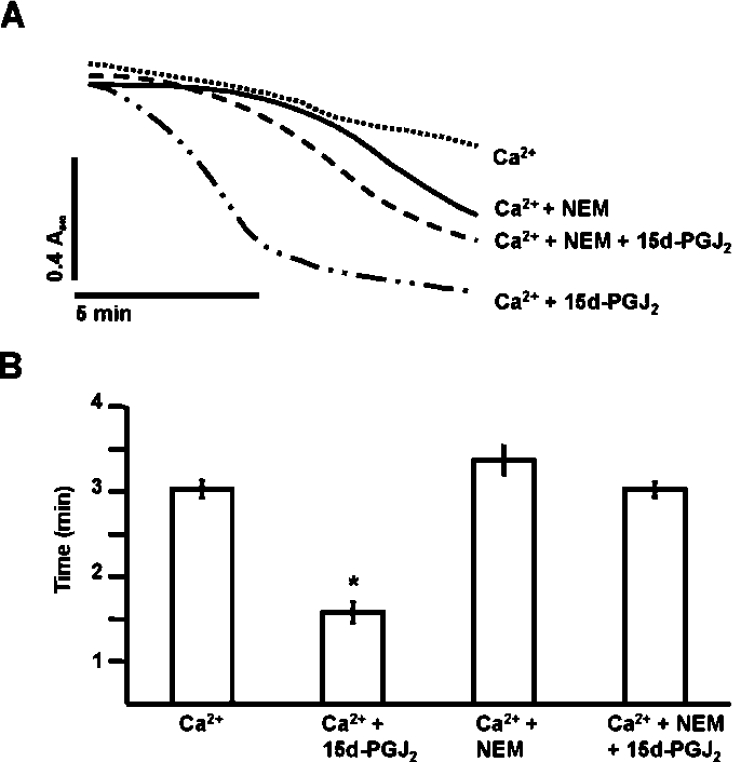
Next, we determined the effect of thiol alkylation on PT potentiation by 15d-PGJ2. Mitochondria were pre-treated with 50 μM NEM for 2 min prior to addition of 15d-PGJ2 to block potential thiol targets. Ca2+ was added 2 min after 15d-PGJ2, and swelling was monitored as described in Figure 1. Controls in which NEM or 15d-PGJ2 were added alone did not result in significant swelling (results not shown). NEM in the presence of Ca2+ also potentiates swelling, but blocks the ability of the electrophilic lipid to potentiate PT (Figures 10A and 10B). These data suggest that PT potentiation by 15d-PGJ2 is mediated by modification of mitochondrial protein thiols.
Figure 10. Blocking of the 15d-PGJ2-dependent potentiation of the PT by NEM.
NEM (50 μM) was added to mitochondria (1 mg/ml) in swelling buffer and allowed to incubate for 2 min. (A) 15d-PGJ2 (20 μM) was added after the NEM and allowed to react for an additional 2 min before the addition of Ca2+ (130 μM). Lag time (after the addition of Ca2+) was calculated as described in Figure 1. Data are single traces representative of three individual experiments. (B) The lag time before onset of swelling is indicated by the histogram. Results are expressed as the means±S.E.M. for at least three independent experiments. *, P<0.05 for Ca2++15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria compared with Ca2+-treated.
Identification of 15d-PGJ2 protein targets in isolated liver mitochondria
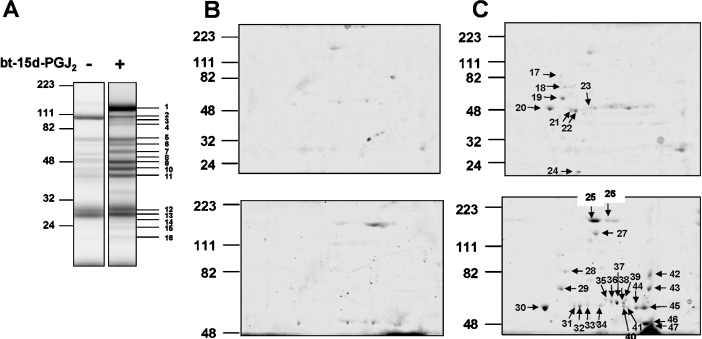
In the next series of experiments, a proteomic approach was used to identify proteins which have formed adducts with bt-15d-PGJ2. Attempts to separate proteins modified by bt-15d-PGJ2 directly by conventional 2D IEF resulted in the resolution of relatively few proteins (results not shown). This is likely to be due to a combination of factors, including problems with the separation of hydrophobic mitochondrial proteins by IEF and the low abundance of the proteins modified by the electrophilic lipids. To circumvent these limitations, we used an affinity precipitation method combined with 1D and 2D separation techniques. Mitochondria treated with 20 μM bt-15d-PGJ2 were affinity precipitated using neutravidin-coupled resin and then separated initially by 1D SDS/PAGE (Figure 11A). The control sample of untreated mitochondria revealed a number of faint bands, only three of which were significantly represented in the bt-15d-PGJ2-treated samples. As shown in Figure 11(A), 16 of 18 bands were of sufficient abundance to be identified by peptide mass fingerprinting (Table 1). In order to enhance the resolution from the 1D separation, a sample from the neutravidin pull-down was subjected to IEF, followed by resolution by SDS/PAGE (Figures 11B and 11C). The Coomassie Blue-stained gels in Figure 11(B) are the control pull-down samples from the untreated mitochondria and few proteins can be seen. Affinity-precipitated proteins from control and 20 μM bt-15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria were resolved on 12.5% acrylamide gels (Figure 11C, upper panel) and also stained for protein. From this gel, eight protein spots were identified by peptide mass fingerprinting (Table 1). However, several proteins migrating between 40–60 kDa were not resolved well and were too faint to be positively identified. Therefore, a second experiment was performed using affinity-purified proteins from control and 50 μM bt-15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria (Figure 11C, lower panel). Only the extent of adduct formation, and not the pattern of proteins at the higher concentration of the electrophile, was changed by this treatment. In addition, the proteins were separated for a longer time in order to optimize the resolution of the proteins between 40–60 kDa. From this experiment, an additional 23 protein spots were positively identified, and the different gel types used in the analysis are indicated in Table 1. Taken together, this approach resulted in a positive identification of essentially all the proteins detectable from the neutravidin pull-down from the bt-15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria. Some proteins, such as mitochondrial aldehyde and glutamate dehydrogenases (spots 31–34 and 35–38 respectively, Figure 11C), are represented as a family of spots with different pI on the 2D gel and therefore appear more than once in Table 1.
Figure 11. Identification of the mitochondrial electrophile-responsive proteome.
Isolated mitochondria were incubated in the presence or absence of 20 μM bt-15d-PGJ2 for 15 min at 25 °C, and labelled proteins were affinity precipitated with neutravidin, as described in the Experimental section, and visualized using 1D SDS/PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining (A). Affinity-precipitated proteins from untreated mitochondria (B) and from bt-15d-PGJ2-treated mitochondria (C) were also separated using 2D SDS/PAGE and stained for protein. Higher-molecular-mass proteins were optimally resolved using longer run times (B and C, lower panels).
Table 1. Affinity-precipitated proteins from liver mitochondria following treatment with bt-15dPGJ2.
Proteins identified by MS as being associated with modification by bt-15d-PGJ2 are listed together with their predicted molecular mass and MOWSE (molecular weight search) score. The first column identifies the spot or band number for each protein as indicated in Figure 11. The values for each MOWSE score are given in the order of the spot number. The accession number is reported in the final column. The numbers in the first column can be cross-referenced to the band numbers or spots in Figures 11(A) and 11(C).
| Band/spot no. | Protein | Predicted mass (kDa) | MOWSE score | Accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 25, 26 | Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 1 | 164.4 | 180, 105, 73 | NP_058768 |
| 2, 3, 27 | Pyruvate carboxylase | 129.7 | 235, 173, 109 | NP_036876 |
| 4, 7 | Similar to RIKEN cDNA D330038I09 (predicted) | 96.9 | 207, 112 | XP_235005 |
| 5 | Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 82.4 | 147 | NP_570839 |
| 6 | ANT | 74.2 | 153 | NP_056644 |
| 8 | Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 | 61.3 | 69 | NP_036702 |
| 9 | Heat-shock protein 1 (chaperonin) | 60.9 | 140 | NP_071565 |
| 10 | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 | 56.9 | 110 | NP_775117 |
| 11 | Acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 2 | 41.8 | 158 | NP_569117 |
| 12 | 3-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase | 38.3 | 159 | NP_446447 |
| 13 | Solute carrier family 25, member 5 | 32.9 | 107 | NP_476443 |
| 14 | 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type II | 27.2 | 122 | O70351 |
| 15 | Similar to aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B8 (predicted) | 29.6 | 82 | XP_220074 |
| 16 | Mitochondrial ATP synthase, O subunit | 23.3 | 89 | NP_620238 |
| 17 | Similar to mitochondrial inner membrane protein (mitofilin) (predicted) | 82.3 | 107 | XP_232055 |
| 18, 19 | Heat-shock protein 1 (chaperonin) | 60.9 | 91, 141 | NP_071565 |
| 20 | ATP synthase β subunit | 51.1 | 104 | AAB02288 |
| 21–23, 31–33 | Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase | 53.3 | 119, 103, 129, 111, 218, 116 | AAM94394 |
| 24 | ATP synthase, H+-transporting, mitochondrial F0 complex, subunit d | 18.7 | 89 | NP_062256 |
| 28 | Mortalin (MTHSP70) | 73.8 | 68 | P48721 |
| 29 | Heat-shock protein 1 (chaperonin) | 60.9 | 109 | NP_071565 |
| 30 | ATP synthase β subunit | 51.1 | 119 | AAB02288 |
| 34 | Propionyl-CoA carboxylase, β polypeptide | 58.6 | 127 | NP_058726 |
| 35–38 | Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 | 61.4 | 103, 145, 129, 127 | NP_036702 |
| 39 | Catalase | 59.7 | 132 | NP_036652 |
| 40, 44, 45 | ATP synthase α chain | 58.8 | 99, 128, 107 | P15999 |
| 41 | Methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (β) (predicted) | 66.1 | 140 | NP_001012177 |
| 42–43 | Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 82.5 | 129, 103 | NP_570839 |
| 46 | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 | 56.9 | 169 | NP_775117 |
| 47 | Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein II | 48.4 | 113 | NP_001006971 |
DISCUSSION
One of the processes through which mitochondria contribute to cell death is through the opening of the mitochondrial PTP [26–28]. The precise composition of the PTP remains unclear, but it is evident that it is a multi-subunit protein channel that spans the mitochondrial inner and outer membrane. Critical components appear to include the mitochondrial VDAC (voltage-dependent anion channel), the ANT (adenine nucleotide translocase), and cyclophilin D [16].
It is well established that reactive cyclopentenone electrophiles can induce apoptosis with a contribution from the mitochondrial pathway [7,8,23,29]. In the case of 15d-PGJ2, its impact on the PTP has not been examined. However, several lines of evidence suggest a mitochondrial interaction on addition of exogenous compound to cells. For example, evidence has been presented that addition of 15d-PGJ2 increases ROS formation from the mitochondrion and, as mentioned previously, high concentrations induce apoptosis [8]. It has also been demonstrated in a breast cancer cell line that apoptosis induced by 15d-PGJ2 is associated with a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential, enhanced ROS formation and inhibition of the respiratory chain [11]. In contrast, exposure of endothelial cells to non-toxic concentrations of 15d-PGJ2 induces the activity of complex I in the mitochondrion through a mechanism involving oxidant formation [13]. These data provide strong circumstantial evidence for an interaction of this electrophilic lipid with the organelle, but the impact on the mechanisms of PT in isolated mitochondria has not yet been examined.
In the present study with isolated rat liver mitochondria we have shown that electrophilic cyclopentenones alone do not induce cytochrome c release and the opening of the pore. However, in the presence of Ca2+, pre-treatment with 15d-PGJ2 potentiates the opening of the pore, as shown by an increased rate and extent of swelling, enhanced O2 consumption and greater cytochrome c release at early time points. This is similar to our recent findings with peroxynitrite in which PTP was only potentiated in the presence of Ca2+ and is an example of the ‘two-hit’ hypothesis, leading to opening of the pore [17,20]. In this model it is possible that the treatment of the mitochondria with the reactive electrophile causes conformational changes that increase the sensitivity of Ca2+-induced PTP. Interestingly, the promotion of pore opening in a similar manner has also been reported for other reactive lipid peroxidation products, including 4-hydroxyhexanal [30]. These data suggest that under conditions of pathological stress the exposure to reactive lipid peroxidation products reveals additional targets that lead to mitochondrial dependent cell death.
In addition to the potential for direct post-translational modification of proteins, electrophilic lipids can induce secondary formation of ROS that may be mitochondrially associated [11,12,15]. To test for a possible contribution to the 15d-PGJ2-dependent potentiation of the PT, the superoxide scavenger MnTBAP and the mitochondrially targeted lipid scavenger Mito E were tested for their effects on swelling. Neither antioxidant had any impact on the Ca2+-induced PT with or without the electrophilic lipid (Figures 4 and 5). As an additional test, the formation of protein carbonyls was also measured under conditions of the PT in the absence and presence of 15d-PGJ2, and again no significant change in protein modification was detected. Taken together, these data do not support the concept that secondary formation of mitochondrial ROS induced by exposure to the electrophile makes a significant contribution to potentiation of PT. However, it is important to note that these data do not rule out the possibility that in the intact cell mitochondrially derived ROS may play a role in cell signalling and thus influence pathways of cell death.
Several lines of evidence suggest that the mechanism of PT potentiation induced by 15d-PGJ2 involves the covalent modification of mitochondrial proteins at thiol residues. For example, the finding that the structurally similar, but non-electrophilic, lipid PGE2 did not enhance the PTP is consistent with the requirement for an electrophilic carbon to produce these effects. In support of this theory, 15d-PGJ2 decreased mitochondrial protein thiols and pre-treatment of the mitochondria with a thiol-reactive agent, NEM, potentiated the PT, but blocked the effects of 15d-PGJ2 (Figure 10). In a parallel experiment using a biotin-tagged electrophile it was found that NEM blocks most of the labelling of the mitochondrial proteins (Figure 9). Taken together, these data support the hypothesis that electrophilic lipids mediate their effects on the mitochondrial PT through the modification of a mitochondrial electrophile-responsive proteome composed of thiol-containing proteins.
To identify the members of this sub-proteome, proteomic analysis of the mitochondria revealed a number of proteins identified by affinity purification after treatment with bt-15d-PGJ2 (Tables 1 and 2). A highly stringent incubation buffer was used for these experiments containing high salt and Triton X-100. These conditions result in the dissociation of the mitochondrial multi-subunit complexes, and it is therefore likely that the proteins identified in the pull-down experiment have reacted with the electrophilic lipid. In support of this conclusion, only a single component of the multi-subunit electron transfer protein complex III (core protein II) was identified in the proteomic analysis. The carboxylase enzymes are endogenously biotinylated and therefore are likely false positives. Band 13 (solute carrier family 25, member 5) was also present in the control pull-down of mitochondria not treated with bt-15d-PGJ2 and will not be discussed further. It is interesting to note that proteins are modified which are present in both the matrix (e.g. glutamate dehydrogenase) and inner membrane (ATP synthase and complex III subunits) (Table 2). Furthermore, the protein subunits modified in both the ATP synthase and complex III are located predominantly on the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane [31,32]. These data confirm that the cyclopentenone electrophilic lipids can diffuse across the mitochondrial inner membrane, and can react with the proteins on the surface of the inner membrane and within the matrix.
Table 2. Characteristics of mitochondrial proteins labelled by bt-15d-PGJ2.
The mitochondrial proteins listed in Table 1 are summarized together with their location in the cell, if known. The carboxylases (*) are endogenously biotinylated and may not therefore have formed a stable adduct with bt-15d-PGJ2.
| Protein | Cellular location | Function/comment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Pyruvate carboxylase | Mitochondrial | Biotin containing | |
| *Propionyl-CoA carboxylase, β-polypeptide | Mitochondrial | Biotin containing | |
| *Methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (β) (predicted) | Mitochondrial | Biotin containing | |
| Glutamate dehydrogenase | Matrix | Glutamate metabolism | [43] |
| 3-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase | Mitochondrial membrane | Metabolism of ketone bodies | [44] |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase | Matrix | Detoxification of aldehydes | [45] |
| 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type II | Mitochondrial | Fatty acid β-oxidation | [46] |
| Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | Mitochondrial | Fatty acid β-oxidation | [47] |
| Acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 2 | Mitochondrial | Fatty acid β-oxidation | [48] |
| 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 | Mitochondrial | Synthesis of mevalonate | [49] |
| Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 1 | Matrix | Urea cycle | [50] |
| Catalase | Peroxisomes/matrix | Removal of hydrogen peroxide | [36] |
| ANT | Inner membrane | ATP/ADP translocation | [17] |
| ATP synthase subunits: α, β, FO complex subunit d, subunit o | Inner membrane | ATP synthesis | [51] |
| Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein II | Inner membrane | Electron transfer | [31] |
| Mortalin (MTHSP70) | Mitochondrial, endoplasmic reticulum, cytosol | Protein folding | [52] |
| Heat-shock protein 1 (chaperonin) | Mitochondria | Protein folding | [53] |
The classes of proteins which are modified include five dehydrogenases, four subunits of ATP synthase, ANT, a subunit of complex III, proteins associated with protein folding and several other metabolic proteins. Mortalin is predominantly localized to the mitochondrion and interacts with several proteins to control responses to stress, possibly by decreasing ROS formation [33,34]. It has been identified as a target for oxidative modification in mitochondria isolated from the brains of apolipoprotein E knock-out mice [35]. Metabolic enzymes acting as dehydrogenases or involving CoA are well represented as potential targets for modification by 15d-PGJ2. Whether a common structural motif renders these proteins more susceptible to modification is not clear at present. Another target, catalase, removes hydrogen peroxide, and has recently been shown to be present in rat liver mitochondria by a proteomic approach [36]. Since secondary production of ROS from the mitochondrion on exposure to lipid electrophiles has been reported, the potential modification of catalase could enhance the hydrogen peroxide available to modify the PTP. Modification of aldehyde dehydrogenase could decrease the availability of NADH and the formation of intra-mitochondrial ROS [37].
The precise targets within the proteins for modification by the cyclopentenone have not been identified, but, given the electrophilic nature of this compound, are likely to involve reactive nucleophiles, particularly cysteine residues. In support of this concept pre-treatment with a thiol-blocking agent, NEM, prior to the addition of 15d-PGJ2 prevented lipid electrophile-dependent promotion of Ca2+-dependent swelling. Not surprisingly many of the targets for modification by bt-15d-PGJ2 contain active site thiols, such as aldehyde dehydrogenase and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase [38,39].
Of particular note, with respect to the induction of the PTP, are the components of the ATP synthase and the ANT. Both proteins may be directly or indirectly involved with the formation and regulation of the PTP [17]. Previous studies have shown that oxidation of mitochondrial pyridine nucleotides and thiols are implicated in the potentiation of PT by oxidants, and thiol-specific antioxidants prevent opening of the pore [40,41]. It has been shown that a critical thiol group in ANT, Cys56, facilitates dimerization upon oxidative stress, which triggers the opening of PTP [42]. Other studies in which ANT was genetically inactivated in mouse liver suggest that ANT is not required for the PTP, but may play a regulatory role [18]. Furthermore, it has also been shown with mice without another component of the PTP, cyclophilin D, that PTP is important in Ca2+-mediated cell death, but not that regulated by Bcl2 [19]. It is interesting to speculate that modification by a lipid electrophile may change the interaction of the protein components of the PTP, leading to greater sensitivity to Ca2+-dependent induction of pore opening.
In summary, we have shown that the model electrophilic cyclopentenone 15d-PGJ2 can potentiate the opening of the PTP and cytochrome c release from isolated liver mitochondria. The electrophile-responsive sub-proteome, which leads to these changes, probably involves the modification of multiple proteins, including components of the pore itself. These data suggest that under conditions of inflammatory stress, in which electrophilic lipid oxidation products can be formed, the mitochondrial pro-cell death pathways will be primed for activation by a secondary influx of Ca2+.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH (National Institutes of Health) grants ES10167, AA13395 and HL58031 (to V. D.-U.). We gratefully acknowledge the assistance from the MS core from Dr Stephen Barnes and Landon Wilson, and the contribution of Dr Paul Brookes (University of Rochester) and Ms Tess Hillson to these studies.
References
- 1.Dickinson D. A., Moellering D. R., Iles K. E., Patel R. P., Levonen A. L., Wigley A., Darley-Usmar V. M., Forman H. J. Cytoprotection against oxidative stress and the regulation of glutathione synthesis. Biol. Chem. 2003;384:527–537. doi: 10.1515/BC.2003.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Levonen A. L., Landar A., Ramachandran A., Ceaser E. K., Dickinson D. A., Zanoni G., Morrow J. D., Darley-Usmar V. M. Cellular mechanisms of redox cell signalling: role of cysteine modification in controlling antioxidant defences in response to electrophilic lipid oxidation products. Biochem. J. 2004;378:373–382. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ishii T., Itoh K., Ruiz E., Leake D. S., Unoki H., Yamamoto M., Mann G. E. Role of Nrf2 in the regulation of CD36 and stress protein expression in murine macrophages: activation by oxidatively modified LDL and 4-hydroxynonenal. Circ. Res. 2004;94:609–616. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000119171.44657.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Itoh K., Mochizuki M., Ishii Y., Ishii T., Shibata T., Kawamoto Y., Kelly V., Sekizawa K., Uchida K., Yamamoto M. Transcription factor Nrf2 regulates inflammation by mediating the effect of 15-deoxy-Δ(12,14)-prostaglandin J2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004;24:36–45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.1.36-45.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Go Y. M., Levonen A. L., Moellering D., Ramachandran A., Patel R. P., Jo H., Darley-Usmar V. M. Endothelial NOS-dependent activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase by oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001;281:H2705–H2713. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.281.6.H2705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mullally J. E., Moos P. J., Edes K., Fitzpatrick F. A. Cyclopentenone prostaglandins of the J series inhibit the ubiquitin isopeptidase activity of the proteasome pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:30366–30373. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102198200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Clay C. E., Monjazeb A., Thorburn J., Chilton F. H., High K. P. 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2-induced apoptosis does not require PPARγ in breast cancer cells. J. Lipid Res. 2002;43:1818–1828. doi: 10.1194/jlr.m200224-jlr200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kondo M., Shibata T., Kumagai T., Osawa T., Shibata N., Kobayashi M., Sasaki S., Iwata M., Noguchi N., Uchida K. 15-Deoxy-Δ (12,14)-prostaglandin J2: the endogenous electrophile that induces neuronal apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002;99:7367–7372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.112212599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Moos P. J., Edes K., Cassidy P., Massuda E., Fitzpatrick F. A. Electrophilic prostaglandins and lipid aldehydes repress redox sensitive transcription factors p53 and hypoxia-inducible factor by impairing the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:745–750. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211134200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shibata T., Yamada T., Ishii T., Kumazawa S., Nakamura H., Masutani H., Yodoi J., Uchida K. Thioredoxin as a molecular target of cyclopentenone prostaglandins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:26046–26054. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303690200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pignatelli M., Sanchez-Rodriguez J., Santos A., Perez-Castillo A. 15-Deoxy-Δ-12,14-prostaglandin J2 induces programmed cell death of breast cancer cells by a pleiotropic mechanism. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:81–92. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zmijewski J. W., Moellering D. R., Le Goffe C., Landar A., Ramachandran A., Darley-Usmar V. M. Oxidized LDL induces mitochondrially associated reactive oxygen/nitrogen species formation in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005;289:H852–H861. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00015.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ceaser E. K., Ramachandran A., Levonen A. L., Darley-Usmar V. M. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein and 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 increase mitochondrial complex I activity in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003;285:H2298–H2308. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00508.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Martinez B., Perez-Castillo A., Santos A. The mitochondrial respiratory complex I is a target for 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 action. J. Lipid Res. 2005;46:736–743. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M400392-JLR200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kondo M., Oya-Ito T., Kumagai T., Osawa T., Uchida K. Cyclopentenone prostaglandins as potential inducers of intracellular oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:12076–12083. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009630200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ichas F., Mazat J. P. From calcium signaling to cell death: two conformations for the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Switching from low- to high-conductance state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1366:33–50. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(98)00119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brookes P. S., Yoon Y., Robotham J. L., Anders M. W., Sheu S. S. Calcium, ATP, and ROS: a mitochondrial love–hate triangle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2004;287:C817–C833. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00139.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kokoszka J. E., Waymire K. G., Levy S. E., Sligh J. E., Cai J., Jones D. P., MacGregor G. R., Wallace D. C. The ADP/ATP translocator is not essential for the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Nature (London) 2004;427:461–465. doi: 10.1038/nature02229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Baines C. P., Kaiser R. A., Purcell N. H., Blair N. S., Osinska H., Hambleton M. A., Brunskill E. W., Sayen M. R., Gottlieb R. A., Dorn G. W., et al. Loss of cyclophilin D reveals a critical role for mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death. Nature (London) 2005;434:658–662. doi: 10.1038/nature03434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Brookes P. S., Darley-Usmar V. M. Role of calcium and superoxide dismutase in sensitizing mitochondria to peroxynitrite-induced permeability transition. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004;286:H39–H46. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00742.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brookes P. S., Salinas E. P., Darley-Usmar K., Eiserich J. P., Freeman B. A., Darley-Usmar V. M., Anderson P. G. Concentration-dependent effects of nitric oxide on mitochondrial permeability transition and cytochrome c release. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:20474–20479. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001077200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Picklo M. J., Zhang J., Nguyen V. Q., Graham D. G., Montine T. J. High-pressure liquid chromatography quantitation of cytochrome c using 393 nm detection. Anal. Biochem. 1999;276:166–170. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Levonen A. L., Dickinson D. A., Moellering D. R., Mulcahy R. T., Forman H. J., Darley-Usmar V. M. Biphasic effects of 15-deoxy-Δ(12,14)-prostaglandin J2 on glutathione induction and apoptosis in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001;21:1846–1851. doi: 10.1161/hq1101.098488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Davies S. M., Poljak A., Duncan M. W., Smythe G. A., Murphy M. P. Measurements of protein carbonyls, ortho- and meta-tyrosine and oxidative phosphorylation complex activity in mitochondria from young and old rats. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2001;31:181–190. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(01)00576-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Venkatraman A., Landar A., Davis A. J., Chamlee L., Sanderson T., Kim H., Page G., Pompilius M., Ballinger S., Darley-Usmar V., Bailey S. M. Modification of the mitochondrial proteome in response to the stress of ethanol-dependent hepatotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:22092–22101. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402245200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bratton S. B., Cohen G. M. Apoptotic death sensor: an organelle's alter ego? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001;22:306–315. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)01718-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Crompton M. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem. J. 1999;341:233–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Crompton M., Barksby E., Johnson N., Capano M. Mitochondrial intermembrane junctional complexes and their involvement in cell death. Biochimie. 2002;84:143–152. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(02)01368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Clay C. E., Atsumi G. I., High K. P., Chilton F. H. Early de novo gene expression is required for 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:47131–47135. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100339200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kristal B. S., Park B. K., Yu B. P. 4-Hydroxyhexenal is a potent inducer of the mitochondrial permeability transition. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:6033–6038. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.11.6033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dudkina N. V., Eubel H., Keegstra W., Boekema E. J., Braun H. P. Structure of a mitochondrial supercomplex formed by respiratory-chain complexes I and III. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:3225–3229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408870102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cross R. L., Muller V. The evolution of A-, F-, and V-type ATP synthases and ATPases: reversals in function and changes in the H+/ATP coupling ratio. FEBS Lett. 2004;576:1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.08.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wadhwa R., Takano S., Kaur K., Aida S., Yaguchi T., Kaul Z., Hirano T., Taira K., Kaul S. C. Identification and characterization of molecular interactions between mortalin/mtHsp70 and HSP60. Biochem. J. 2005;391:185–190. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu Y., Liu W., Song X. D., Zuo J. Effect of GRP75/mtHsp70/PBP74/mortalin overexpression on intracellular ATP level, mitochondrial membrane potential and ROS accumulation following glucose deprivation in PC12 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005;268:45–51. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-2996-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Choi J., Forster M. J., McDonald S. R., Weintraub S. T., Carroll C. A., Gracy R. W. Proteomic identification of specific oxidized proteins in ApoE-knockout mice: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2004;36:1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jiang X. S., Dai J., Sheng Q. H., Zhang L., Xia Q. C., Wu J. R., Zeng R. A comparative proteomic strategy for subcellular proteome research: ICAT approach coupled with bioinformatics prediction to ascertain rat liver mitochondrial proteins and indication of mitochondrial localization for catalase. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2005;4:12–34. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M400079-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Irwin W. A., Gaspers L. D., Thomas J. A. Inhibition of the mitochondrial permeability transition by aldehydes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;291:215–219. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Thoden J. B., Huang X., Kim J., Raushel F. M., Holden H. M. Long-range allosteric transitions in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Protein Sci. 2004;13:2398–2405. doi: 10.1110/ps.04822704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Venkatraman A., Landar A., Davis A. J., Ulasova E., Page G., Murphy M. P., Darley-Usmar V., Bailey S. M. Oxidative modification of hepatic mitochondria protein thiols: effect of chronic alcohol consumption. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G521–G527. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00399.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kowaltowski A. J., Netto L. E., Vercesi A. E. The thiol-specific antioxidant enzyme prevents mitochondrial permeability transition. Evidence for the participation of reactive oxygen species in this mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:12766–12769. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.21.12766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Halestrap A. P., Woodfield K. Y., Connern C. P. Oxidative stress, thiol reagents, and membrane potential modulate the mitochondrial permeability transition by affecting nucleotide binding to the adenine nucleotide translocase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:3346–3354. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.6.3346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.McStay G. P., Clarke S. J., Halestrap A. P. Role of critical thiol groups on the matrix surface of the adenine nucleotide translocase in the mechanism of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Biochem. J. 2002;367:541–548. doi: 10.1042/BJ20011672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Herrero-Yraola A., Bakhit S. M., Franke P., Weise C., Schweiger M., Jorcke D., Ziegler M. Regulation of glutamate dehydrogenase by reversible ADP-ribosylation in mitochondria. EMBO J. 2001;20:2404–2412. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.10.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nasser B., Morpain C., Zirkel J., Seiter M., Laude B., Trommer W. E., Latruffe N. Labeling of the mitochondrial membrane D-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (BDH) with new bifunctional phospholipid analogues. J. Lipid Mediat. 1993;7:169–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Venkatraman A., Shiva S., Davis A. J., Bailey S. M., Brookes P. S., Darley-Usmar V. M. Chronic alcohol consumption increases the sensitivity of rat liver mitochondrial respiration to inhibition by nitric oxide. Hepatology. 2003;38:141–147. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Frackowiak J., Mazur-Kolecka B., Kaczmarski W., Dickson D. Deposition of Alzheimer's vascular amyloid-β is associated with decreased expression of brain L-3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase (ERAB) Brain Res. 2001;907:44–53. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02497-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kobayashi A., Jiang L. L., Hashimoto T. Two mitochondrial 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenases in bovine liver. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1996;119:775–782. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hiltunen J. K., Qin Y. β-Oxidation–strategies for the metabolism of a wide variety of acyl-CoA esters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1484:117–128. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hegardt F. G. Mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase: a control enzyme in ketogenesis. Biochem. J. 1999;338:569–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Martinez-Ramon A., Knecht E., Rubio V., Grisolia S. Levels of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I in livers of young and old rats assessed by activity and immunoassays and by electron microscopic immunogold procedures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1990;38:371–376. doi: 10.1177/38.3.2303702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gilkerson R. W., Selker J. M., Capaldi R. A. The cristal membrane of mitochondria is the principal site of oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:355–358. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00633-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wadhwa R., Taira K., Kaul S. C. An Hsp70 family chaperone, mortalin/mtHsp70/PBP74/Grp75: what, when, and where? Cell Stress Chaperones. 2002;7:309–316. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(2002)007<0309:ahfcmm>2.0.co;2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Barral J. M., Broadley S. A., Schaffar G., Hartl F. U. Roles of molecular chaperones in protein misfolding diseases. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2004;15:17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]