Abstract
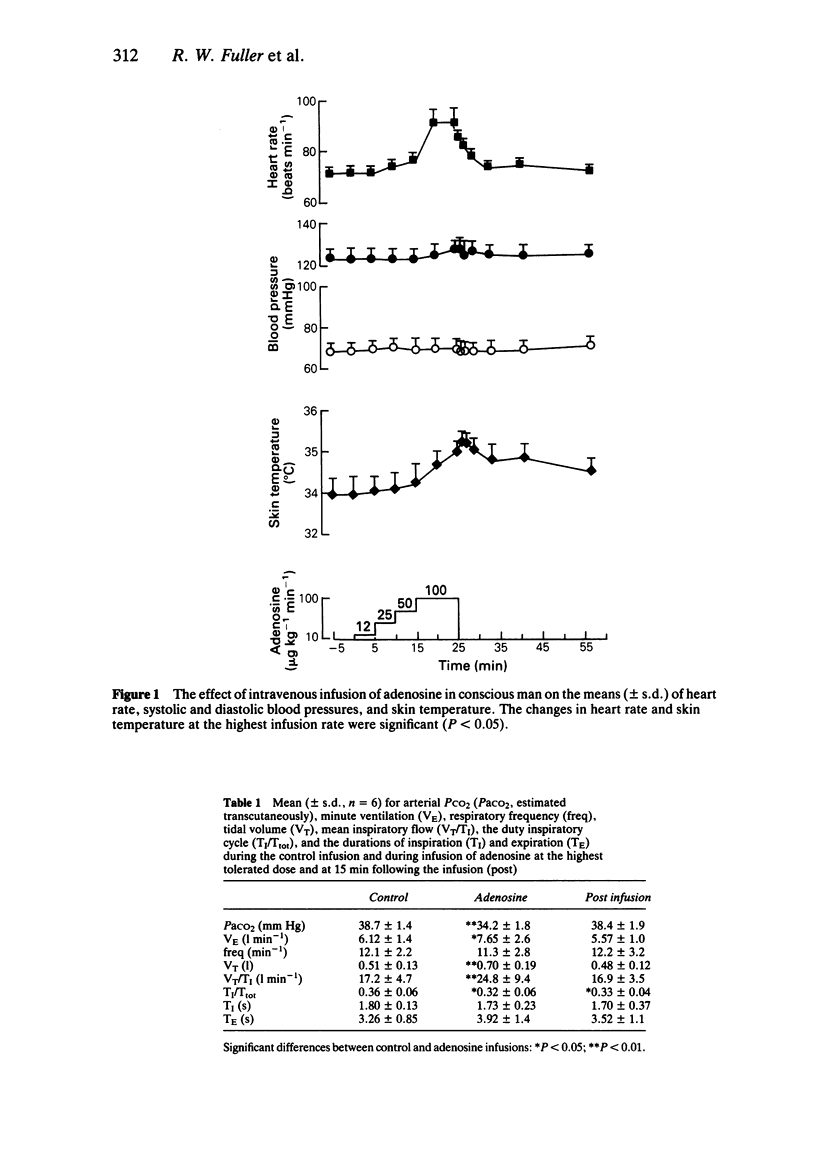
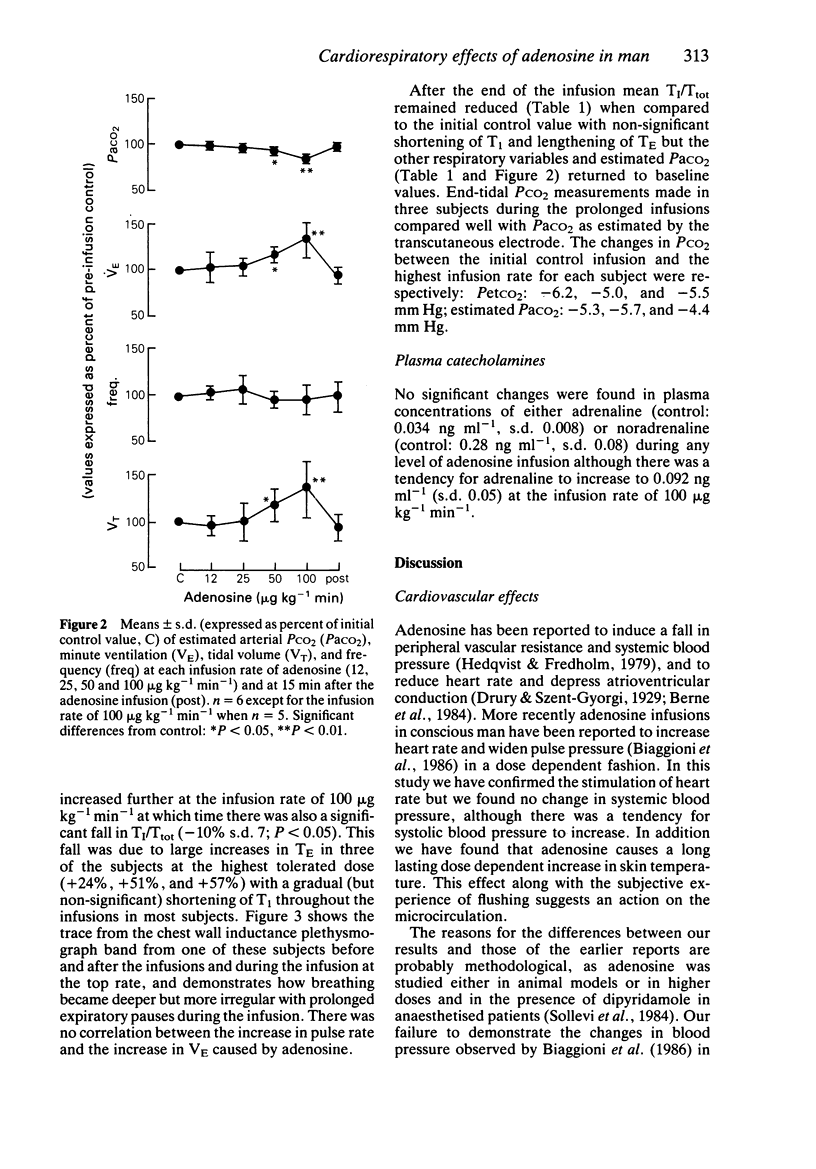
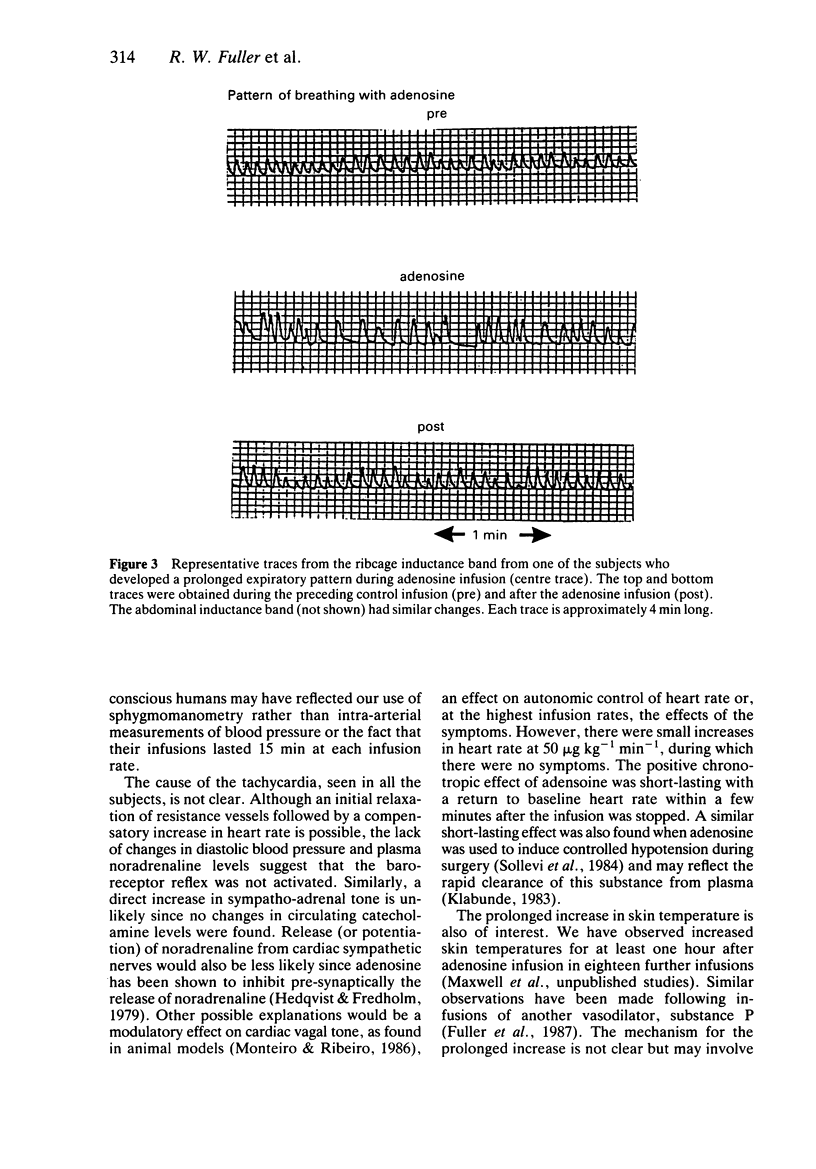
1. The nucleoside, adenosine, was infused into six conscious healthy male subjects at rates up to 100 micrograms kg-1 min-1. 2. Compared with a control 0.9% saline infusion, adenosine in all subjects caused dose dependent increases in heart rate, skin temperature and minute ventilation with corresponding falls in PaCO2, estimated transcutaneously. 3. There were no changes in systemic blood pressure, airways resistance (measured by forced partial expiratory manoeuvres), or plasma catecholamines. At the top infusion rates subjects experienced tolerable chest and abdominal discomfort. 4. These findings conflict with some previous studies in anaesthetised man and animals, in which higher doses of adenosine and its long acting analogues have caused hypotension and central respiratory depression. 5. Although some of these changes may have been due to symptoms, the cardiovascular changes may have been due to a vasodilator action and the respiratory stimulation may have been due to an action on peripheral chemoreceptors.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNE R. M. Cardiac nucleotides in hypoxia: possible role in regulation of coronary blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1963 Feb;204:317–322. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne R. M., DiMarco J. P., Belardinelli L. Dromotropic effects of adenosine and adenosine antagonists in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias involving the atrioventricular node. Circulation. 1984 Jun;69(6):1195–1197. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.69.6.1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biaggioni I., Onrot J., Hollister A. S., Robertson D. Cardiovascular effects of adenosine infusion in man and their modulation by dipyridamole. Life Sci. 1986 Dec 8;39(23):2229–2236. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. J., Jenner D. A. Novel double-isotope technique for enzymatic assay of catecholamines, permitting high precision, sensitivity and plasma sample capacity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Nov;61(5):591–598. doi: 10.1042/cs0610591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushley M. J., Tattersfield A. E., Holgate S. T. Inhaled adenosine and guanosine on airway resistance in normal and asthmatic subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;15(2):161–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derenne J. P., Couture J., Iscoe S., Whitelaw A., Milic-Emili J. Occlusion pressures in men rebreathing CO2 under methoxyflurane anesthesia. J Appl Physiol. 1976 May;40(5):805–814. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.40.5.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMarco J. P., Sellers T. D., Berne R. M., West G. A., Belardinelli L. Adenosine: electrophysiologic effects and therapeutic use for terminating paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Circulation. 1983 Dec;68(6):1254–1263. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.68.6.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drury A. N., Szent-Györgyi A. The physiological activity of adenine compounds with especial reference to their action upon the mammalian heart. J Physiol. 1929 Nov 25;68(3):213–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1929.sp002608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L., Millhorn D. E., Kiley J. P. Respiratory effects of a long-acting analog of adenosine. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 3;301(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox I. H., Kelley W. N. The role of adenosine and 2'-deoxyadenosine in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:655–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Maxwell D. L., Dixon C. M., McGregor G. P., Barnes V. F., Bloom S. R., Barnes P. J. Effect of substance P on cardiovascular and respiratory function in subjects. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Apr;62(4):1473–1479. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.4.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Fredholm B. B. Inhibitory effect of adenosine on adrenergic neuroeffector transmission in the rabbit heart. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Jan;105(1):120–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistad D., Abboud F. M., Mark A. L., Schmid P. G. Effect of baroreceptor activity on ventilatory response to chemoreceptor stimulation. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Sep;39(3):411–416. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.3.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klabunde R. E. Dipyridamole inhibition of adenosine metabolism in human blood. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 16;93(1-2):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz H., Yamamoto Y., Fredholm B. B., Prabhakar N. R., von Euler C. Adenosine analogues depress ventilation in rabbit neonates. Theophylline stimulation of respiration via adenosine receptors? Pediatr Res. 1984 Apr;18(4):387–390. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198404000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugliani R., Whipp B. J., Seard C., Wasserman K. Effect of bilateral carotid-body resection on ventilatory control at rest and during exercise in man. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov;285(20):1105–1111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111112852002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannix S. E., Bye P., Hughes J. M., Cover D., Davies E. E. Effect of posture on ventilatory response to steady-state hypoxia and hypercapnia. Respir Physiol. 1984 Oct;58(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell D. L., Fuller R. W., Nolop K. B., Dixon C. M., Hughes J. M. Effects of adenosine on ventilatory responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Nov;61(5):1762–1766. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.5.1762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S., Ribeiro J. A. Effect of adenosine on carotid chemoreceptor activity in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;74(1):129–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S., Ribeiro J. A. Pharmacological characterization of the receptor involved in chemoexcitation induced by adenosine. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;88(3):615–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10242.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P. G., Watt A. H., Routledge P. A., Smith A. P. Intravenous infusion of adenosine but not inosine stimulates respiration in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;23(3):331–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollevi A., Lagerkranser M., Irestedt L., Gordon E., Lindquist C. Controlled hypotension with adenosine in cerebral aneurysm surgery. Anesthesiology. 1984 Oct;61(4):400–405. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198410000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Barnes P., Pride N. B. The effects of almitrine on the ventilatory response to hypoxia and hypercapnia in normal subjects. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Oct;63(4):401–404. doi: 10.1042/cs0630401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradling J. R., Nicholl C. G., Cover D., Hughes J. M. Speed of response and accuracy of two transcutaneous carbon dioxide monitors. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Jul-Aug;19(4):407–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman K., Whipp B. J., Castagna J. Cardiodynamic hyperpnea: hyperpnea secondary to cardiac output increase. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Apr;36(4):457–464. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt A. H., Routledge P. A. Adenosine stimulates respiration in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;20(5):503–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb05108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessberg P., Hedner J., Hedner T., Persson B., Jonason J. Adenosine mechanisms in the regulation of breathing in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 30;106(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90678-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


