Abstract
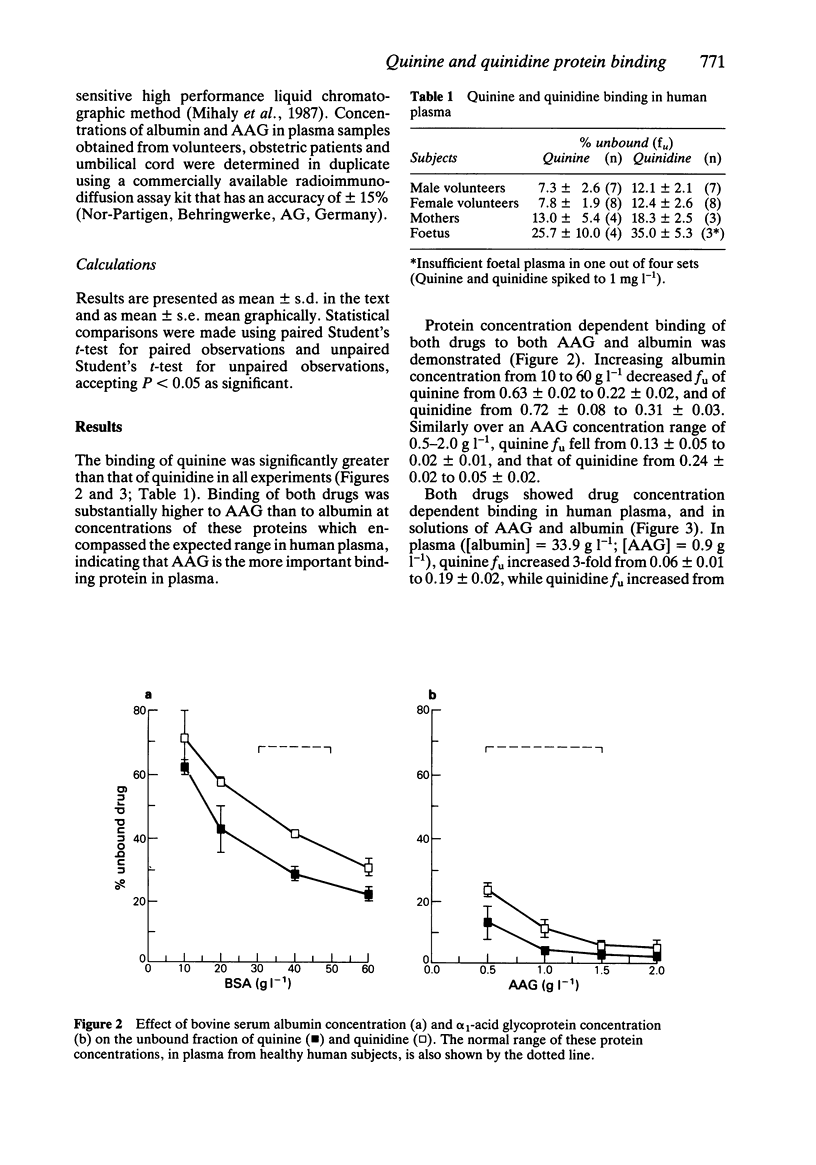
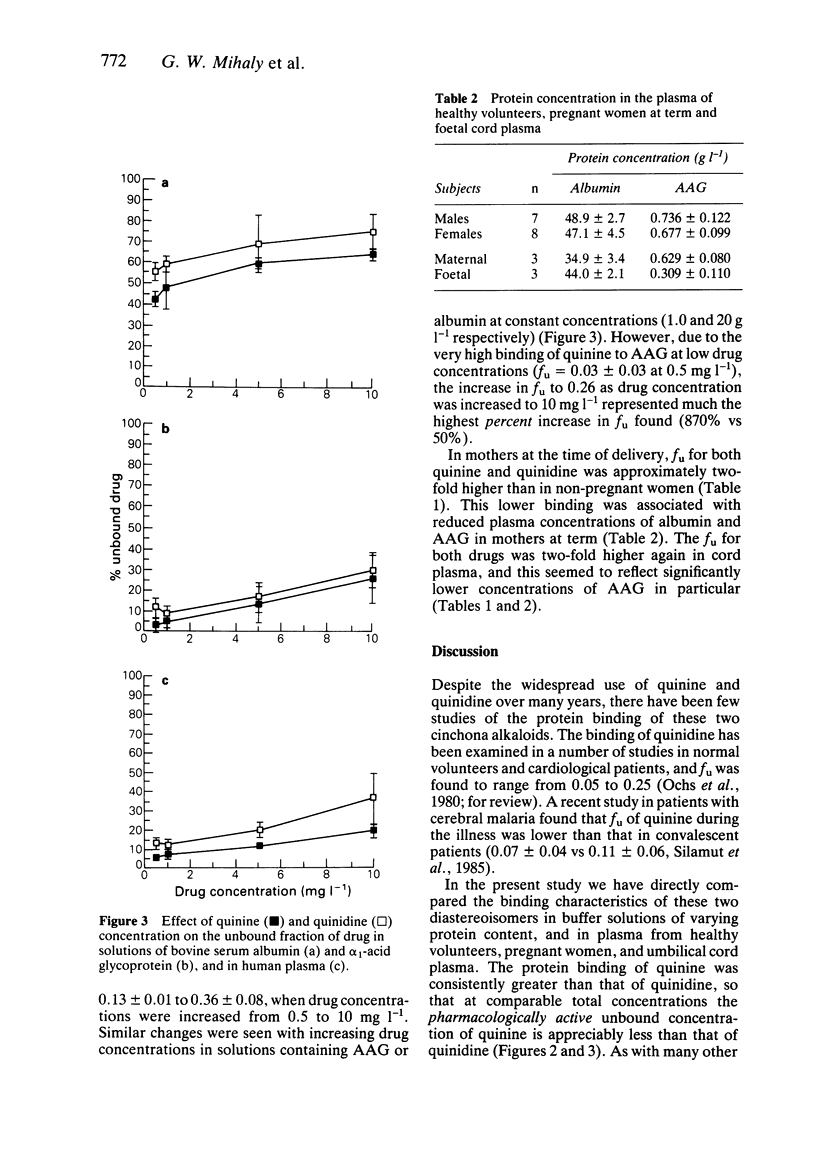
1. Little is known about the comparative plasma protein binding of the antimalarial agents quinine (QN) and its isomer quinidine (QD). We have examined the in vitro binding of QN and QD to albumin, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, normal human plasma, and maternal and foetal umbilical cord plasma. 2. QN was more avidly bound than QD, and binding of both drugs was substantially higher to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein than to albumin, indicating that alpha 1-acid glycoprotein is the more important binding protein. 3. Protein and drug concentration dependent binding was evident for both QN and QD. The unbound fraction of both drugs fell with increasing albumin (10 to 60 g l-1) and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (0.5 to 2.0 g l-1) concentration, and there was a marked increase in unbound fraction of QN (6 to 19%) and QD (13 to 36%) in human plasma when drug concentrations were increased over the antimalarial therapeutic range (0.5 to 10 mg l-1). 4. In human volunteer plasma, the unbound fractions of QN and QD were 7.5 +/- 2.2% and 12.3 +/- 2.3% respectively, whilst the unbound fractions for both drugs were significantly higher in maternal plasma (QN = 13.0 +/- 5.4%, QD = 18.3 +/- 2.5%) and significantly higher still in foetal umbilical cord plasma (QN = 25.7 +/- 10%, QD = 35 +/- 5.3%).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cummings A. J. A survey of pharmacokinetic data from pregnant women. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1983 Jul-Aug;8(4):344–354. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198308040-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Stock B., Patterson R. J., Levy G. Serum protein binding of drugs during and after pregnancy in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Aug;28(2):253–261. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edstein M., Stace J., Shann F. Quantification of quinine in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1983 Dec 9;278(2):445–451. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84807-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. J., Axelson J. E., Slaughter R. L., Elvin A. T., Lalka D. Factors affecting quinidine protein binding in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Sep;73(9):1264–1267. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Dangers of high-dose quinine and overhydration in severe malaria. Lancet. 1985 Jun 22;1(8443):1453–1454. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91885-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Dangers of high-dose quinine and overhydration in severe malaria. Lancet. 1985 Jun 22;1(8443):1453–1454. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91885-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herngren L., Ehrnebo M., Boréus L. O. Drug binding to plasma proteins during human pregnancy and in the perinatal period. Studies on cloxacillin and alprenolol. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1983;6(2):110–124. doi: 10.1159/000457284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looareesuwan S., Phillips R. E., White N. J., Kietinun S., Karbwang J., Rackow C., Turner R. C., Warrell D. A. Quinine and severe falciparum malaria in late pregnancy. Lancet. 1985 Jul 6;2(8445):4–8. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihaly G. W., Hyman K. M., Smallwood R. A., Hardy K. J. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of quinine and its diastereoisomer quinidine. J Chromatogr. 1987 Mar 20;415(1):177–182. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihaly G. W., Morgan D. J. Placental drug transfer: effects of gestational age and species. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;23(2):253–266. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. R., Greenblatt D. J., Woo E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of quinidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 Mar-Apr;5(2):150–168. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucca E., Crema A. Plasma protein binding of drugs in pregnancy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Jul-Aug;7(4):336–352. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207040-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. E., Looareesuwan S., White N. J., Silamut K., Kietinun S., Warrell D. A. Quinine pharmacokinetics and toxicity in pregnant and lactating women with falciparum malaria. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;21(6):677–683. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. E., Warrell D. A., White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Karbwang J. Intravenous quinidine for the treatment of severe falciparum malaria. Clinical and pharmacokinetic studies. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 16;312(20):1273–1278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505163122001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A. The plasma protein binding of basic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;22(5):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silamut K., White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Warrell D. A. Binding of quinine to plasma proteins in falciparum malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Jul;34(4):681–686. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of antimalarial drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1985 May-Jun;10(3):187–215. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198510030-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. J., Looareesuwan S., Warrell D. A., Warrell M. J., Bunnag D., Harinasuta T. Quinine pharmacokinetics and toxicity in cerebral and uncomplicated Falciparum malaria. Am J Med. 1982 Oct;73(4):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


