Abstract
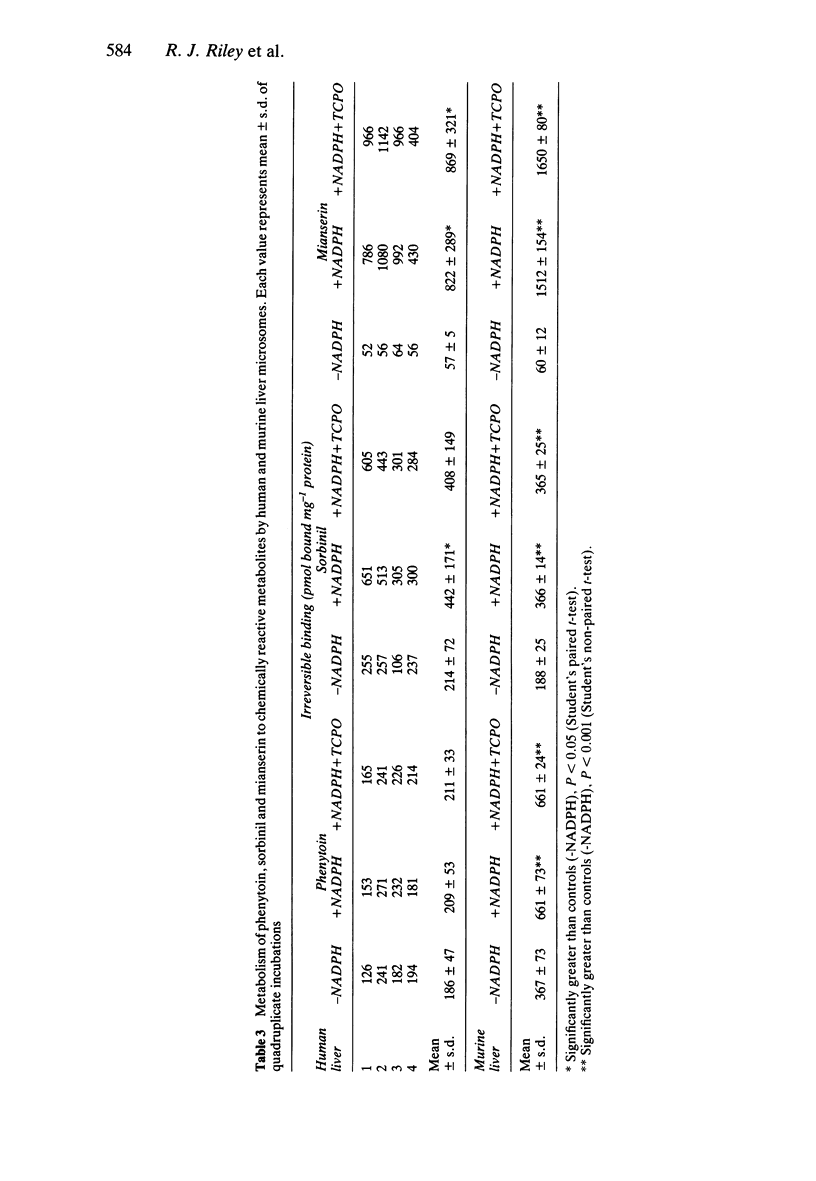
1. The cytotoxicity of metabolites generated from phenytoin, sorbinil and mianserin by human and mouse liver microsomes was assessed by co-incubation with human mononuclear leucocytes as target cells. Cytotoxicity was determined by trypan blue dye exclusion. 2. Phenytoin and sorbinil were metabolised by NADPH-dependent murine microsomal enzymes to cytotoxic metabolites. Cytotoxicity produced by both drugs was significantly enhanced by the epoxide hydrolase inhibitor trichloropropane oxide (TCPO). No significant cytotoxicity was observed in the presence of human liver microsomes. 3. Mianserin was metabolised by both human and mouse liver microsomes to a cytotoxin. Cytotoxicity was greater in the presence of human liver microsomes (13.7 +/- 2.2%; mean +/- s.d. for four livers, compared with 6.0 +/- 2.4%, mean +/- s.d., n = 4, with mouse liver microsomes), and was unaffected by pretreatment with TCPO. 4. Stable metabolites were quantified by radiometric high performance liquid chromatography. Phenytoin and sorbinil were metabolised to 5-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenyl-hydantoin (0.3-0.5% of incubated radioactivity) and 2-hydroxysorbinil (0.4-2.7% of incubated radioactivity), respectively, by both human and mouse liver microsomes. 5. Mianserin was metabolised to 8-hydroxymianserin and desmethylmianserin by both human and mouse liver microsomes. Desmethylmianserin was the major product in incubations with human liver microsomes (32.3 +/- 12%, mean +/- s.d. for four livers), whereas 8-hydroxymianserin was the predominant metabolite generated by mouse liver microsomes (25.9 +/- 1.5%, mean +/- s.d., n = 4). 6. Generation of electrophilic metabolites was assessed by determination of the amount of radiolabelled material which became irreversibly bound to protein. Only mouse liver microsomes activated phenytoin to a chemically reactive metabolite, whereas both mouse and human liver microsomes generated reactive metabolites from sorbinil and mianserin. 7. These studies show that drug cytotoxicity can be mediated by low concentrations (circa microM) of metabolites generated by NADPH-dependent hepatic microsomal enzymes; however demonstration of cytotoxicity in vitro has not been established as a means of predicting in vivo toxicity.
Full text
PDF



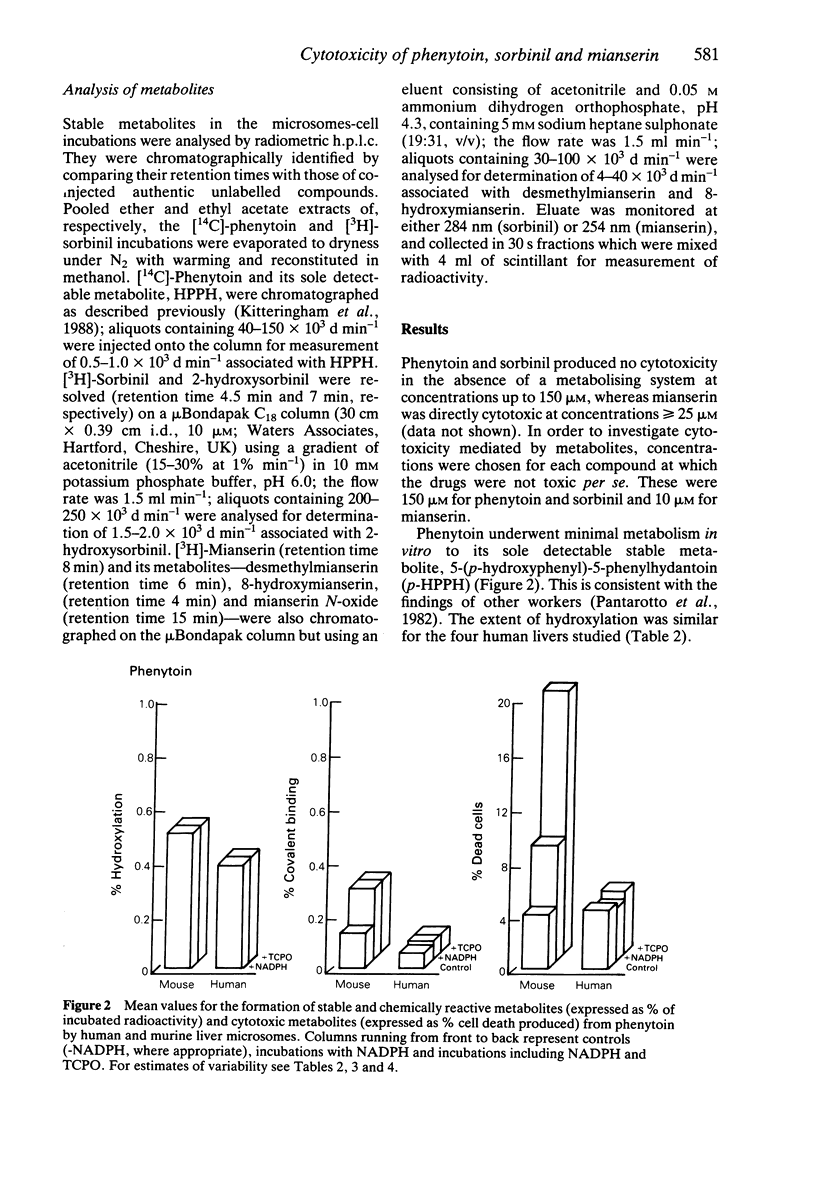



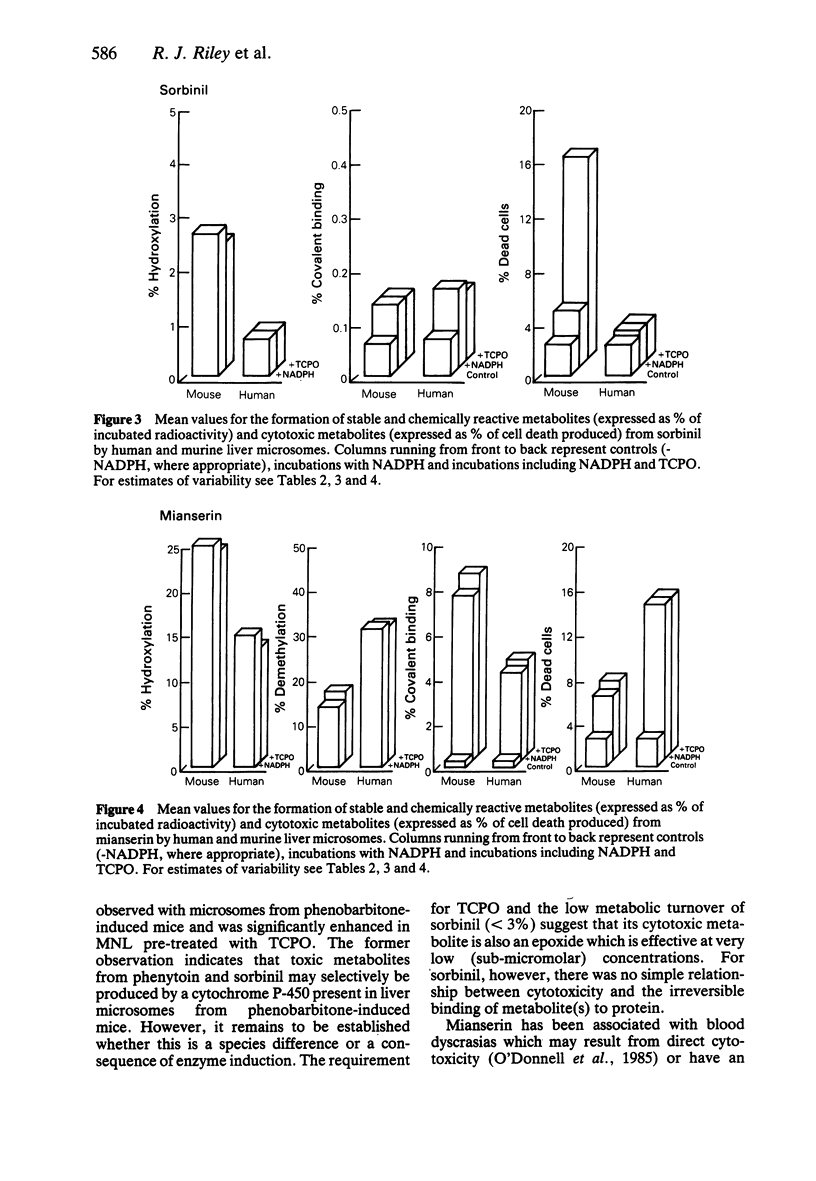


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acosta D., Mitchell D. B. Metabolic activation and cytotoxicity of cyclophosphamide in primary cultures of postnatal rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 1;30(23):3225–3230. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90522-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albano E., Rundgren M., Harvison P. J., Nelson S. D., Moldéus P. Mechanisms of N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine cytotoxicity. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;28(3):306–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billings R. E., Fischer L. J. Oxygen-18 incorporation studies of the metabolism of phenytoin to the catechol. Drug Metab Dispos. 1985 May-Jun;13(3):312–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges J. W., Benford D. J., Hubbard S. A. Mechanisms of toxic injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;407:42–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb47813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin S. Bone marrow depression due to mianserin, phenylbutazone, oxyphenbutazone, and chloramphenicol--Part I. Adverse Drug React Acute Poisoning Rev. 1986 Summer;5(2):97–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Fischer L. J. Phenytoin metabolism in mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982 Mar-Apr;10(2):156–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesen M., Moustafa M. A., Adline J., Vandervorst D., Poupaert J. H. Evidence for an arene oxide-NIH shift pathway in the metabolic conversion of phenytoin to 5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenylhydantoin in the rat and in man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982 Nov-Dec;10(6):667–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devalia J. L., Ogilvie R. C., McLean A. E. Dissociation of cell death from covalent binding of paracetamol by flavones in a hepatocyte system. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 1;31(23):3745–3749. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar G. J., Pierach C. A., Ahamed P. N., Howard R. B. Diphenylhydantoin--induced hepatic necrosis. Postgrad Med. 1974 Jul;56(1):128–134. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1974.11713808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostal L. A., Aitio A., Harris C., Bhatia A. V., Hernandez O., Bend J. R. Cytosolic glutathione S-transferases in various rat tissues differ in stereoselectivity with polycyclic arene and alkene oxide substrates. Drug Metab Dispos. 1986 May-Jun;14(3):303–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. J., Herold G. E. Immunological abnormalities and hydantoins. Br Med J. 1972 Jun 3;2(5813):561–563. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5813.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Liebler D. C. Enzymatic activation of chemicals to toxic metabolites. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1985;14(3):259–307. doi: 10.3109/10408448509037460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammock B. D., Hasagawa L. S. Differential substrate selectivity of murine hepatic cytosolic and microsomal epoxide hydrolases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 1;32(7):1155–1164. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner S. A., Fry J. R., Clothier R. H., Balls M. The detection of cytotoxicity produced by short-lived reactive intermediates: a study with bromobenzene. Xenobiotica. 1987 Jun;17(6):777–782. doi: 10.3109/00498258709043985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspan J. Pharmacological inhibition of aldose reductase in human diabetic neuropathy. Drugs. 1986;32 (Suppl 2):23–29. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198600322-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitteringham N. R., Lambert C., Maggs J. L., Colbert J., Park B. K. A comparative study of the formation of chemically reactive drug metabolites by human liver microsomes. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;26(1):13–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggs J. L., Park B. K. Drug-protein conjugates--XVI. Studies of sorbinil metabolism: formation of 2-hydroxysorbinil and unstable protein conjugates. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 15;37(4):743–748. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz F., Failinger C., 3rd, Blake D. A. Phenytoin teratogenesis: correlation between embryopathic effect and covalent binding of putative arene oxide metabolite in gestational tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Oct;203(1):231–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell J. L., Sharman J. R., Begg E. J., Colls B. M., Moller P. W. Possible mechanism for mianserin induced neutropenia associated with saturable elimination kinetics. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Nov 16;291(6506):1375–1376. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6506.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch F., Kaubisch N., Jerina D. M., Daly J. W. Hepatic epoxide hydrase. Structure-activity relationships for substrates and inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4858–4866. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantarotto C., Arboix M., Sezzano P., Abbruzzi R. Studies on 5,5-diphenylhydantoin irreversible binding to rat liver microsomal proteins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 15;31(8):1501–1507. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. K. Metabolic basis of adverse drug reactions. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1986 Jul;20(3):195–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke D. V. Activation mechanisms to chemical toxicity. Arch Toxicol. 1987;60(1-3):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00296939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purba H. S., Maggs J. L., Orme M. L., Back D. J., Park B. K. The metabolism of 17 alpha-ethinyloestradiol by human liver microsomes: formation of catechol and chemically reactive metabolites. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;23(4):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., DePierre J. W., Pero R. W. Measurement and characterization of membrane-bound and soluble epoxide hydrolase activities in resting mononuclear leukocytes from human blood. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):3654–3660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Guthenberg C., Pero R. W., Mannervik B. The trans-stilbene oxide-active glutathione transferase in human mononuclear leucocytes is identical with the hepatic glutathione transferase mu. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):783–785. doi: 10.1042/bj2460783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielberg S. P. Acetaminophen toxicity in human lymphocytes in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 May;213(2):395–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielberg S. P., Gordon G. B., Blake D. A., Goldstein D. A., Herlong H. F. Predisposition to phenytoin hepatotoxicity assessed in vitro. N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 24;305(13):722–727. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109243051302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielberg S. P. In vitro assessment of pharmacogenetic susceptibility to toxic drug metabolites in humans. Fed Proc. 1984 May 15;43(8):2308–2313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner E., Alván G., Garle M., Maguire J. H., Lind M., Nilson S. O., Tomson T., McClanahan J. S., Sjöqvist F. The debrisoquin hydroxylation phenotype does not predict the metabolism of phenytoin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1987 Sep;42(3):326–333. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1987.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter A. J., Bjorge S. M., Axworthy D. B., Nelson S. D., Baillie T. A. The microsomal metabolism and site of covalent binding to protein of 3'-hydroxyacetanilide, a nonhepatotoxic positional isomer of acetaminophen. Drug Metab Dispos. 1984 Sep-Oct;12(5):565–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampaglione N., Jollow D. J., Mitchell J. R., Stripp B., Hamrick M., Gillette J. R. Role of detoxifying enzymes in bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Oct;187(1):218–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jongh G. D., van den Wildenberg H. M., Nieuwenhuyse H., van der Veen F. The metabolism of mianserin in women, rabbits, and rats: identification of the major urinary metabolites. Drug Metab Dispos. 1981 Jan-Feb;9(1):48–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr C., Groth C. G., Jansson H., Lundgren G., Lind M., Glaumann H. Drug metabolism in human liver in vitro: establishment of a human liver bank. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Jun;27(6):711–725. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


