Abstract
Background
Circadian rhythms are endogenous, self-sustained oscillations with approximately 24-hr rhythmicity that are manifested in various physiological and metabolic processes. The circadian organization of these processes in mammals is governed by the master oscillator within the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) of the hypothalamus. Recent findings revealed that circadian oscillators exist in most organs, tissues, and even in immortalized cells, and that the oscillators in peripheral tissues are likely to be coordinated by SCN, the master oscillator. Some candidates for endogenous entrainment factors have sporadically been reported, however, their details remain mainly obscure.
Results
We developed the in vitro real-time oscillation monitoring system (IV-ROMS) by measuring the activity of luciferase coupled to the oscillatory gene promoter using photomultiplier tubes and applied this system to screen and identify factors able to influence circadian rhythmicity. Using this IV-ROMS as the primary screening of entrainment factors for circadian clocks, we identified 12 candidates as the potential entrainment factor in a total of 299 peptides and bioactive lipids. Among them, four candidates (endothelin-1, all-trans retinoic acid, 9-cis retinoic acid, and 13-cis retinoic acid) have already been reported as the entrainment factors in vivo and in vitro. We demonstrated that one of the novel candidates, 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2), a natural ligand of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ), triggers the rhythmic expression of endogenous clock genes in NIH3T3 cells. Furthermore, we showed that 15d-PGJ2 transiently induces Cry1, Cry2, and Rorα mRNA expressions and that 15d-PGJ2-induced entrainment signaling pathway is PPAR-γ – and MAPKs (ERK, JNK, p38MAPK)-independent.
Conclusion
Here, we identified 15d-PGJ2 as an entrainment factor in vitro. Using our developed IV-ROMS to screen 299 compounds, we found eight novel and four known molecules to be potential entrainment factors for circadian clocks, indicating that this assay system is a powerful and useful tool in initial screenings.
Background
Circadian rhythms are endogenous self-sustained oscillations with approximately 24-hr rhythmicity that are manifested in various physiological and metabolic processes [1,2] In mammals the circadian orchestration of these processes is governed by pacemaker cells located within the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) of the hypothalamus. It has also revealed that in mammals circadian oscillators exist not only in the SCN but also in peripheral tissues, and even in immortalized cells [3-5]. Because the periodicity of the circadian clock only approximates that of the environment, circadian clocks have to be adjusted to 24-h/day period by environmental time cues [6]. Circadian clocks are primarily synchronized with environmental time by the daylight cycle as an input signal to the SCN through the direct and indirect neural projections from retinal ganglion cells [6,7], however, other non-photic cues can also synchronize circadian clocks to 24-h/day [2].
The molecular mechanism of the circadian oscillator as a transcriptional-translational feedback loop has been unraveled by genetic analysis in Drosophila and mammals [8,9]. These molecular mechanisms based on the transcriptional-translational regulation are conserved among many species, including Arabidopsis, Neurospora, Drosophila, zebrafish, and mammals [9-11]. In mammals, principally two basic helix-loop-helix-PAS transcriptional factors, CLOCK and BMAL1, regulate gene expression by interacting with a promoter element termed E-box [12,13]. Target genes of these transcriptional factors include several repressor proteins, including PER1, PER2, PER3, CRY1, and CRY2, which function to inhibit the activity of CLOCK/BMAL1 complex by entering into the nucleus [14,15], thereby generating a circadian oscillation of their own transcription.
One of the molecular features of circadian clocks is rhythmic fluctuation of clock gene mRNA amounts. In situ hybridization and RNase protection assay are conventional techniques used to detect expression profiles of the clock and clock-controlled genes (for example, [4,16,17]). Quantitative real-time RT-PCR has recently become a popular method to investigate mRNA expression profiles (for example, [5,18]). The bioluminescent firefly luciferase protein has proven to be a useful reporter protein for monitoring the dynamics of gene activity in living cells [19]. Luminescence from luciferase expressed in transgenic plants, Drosophila, zebrafish and mammals has been used to monitor real-time dynamic change in gene transcription within the living organism [19-22]. Since this system is applied to transiently transfected cell cultures with clock gene promoters driving firefly luciferase gene expression [5,23], luciferase real-time monitoring system using photomultiplier tubes has become a powerful tool to investigate circadian clock mechanism, in particular to identify the critical elements for producing the circadian rhythmicity [24-26].
As described above, it has been thought that circadian clocks in peripheral tissues are regulated by the SCN via the secretion of hormones and/or the sympathetic/parasympathetic innervations from the SCN to peripheral tissues [27]. Recently, some potential "entrainment factors" have been reported [28-32], however, the mechanisms how the central SCN pacemaker clock orchestrates the peripheral clocks remains unclear. Here, we report systematic screening of various molecules in attempt to find entrainment factors by using our in vitro real-time oscillation monitoring system (IV-ROMS). In this study, we report eight novel candidates, including 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2), of entrainment factors for circadian clocks.
Results and discussion
Establishment of IV-ROMS using mPer2-luc/Rat1 cell lines
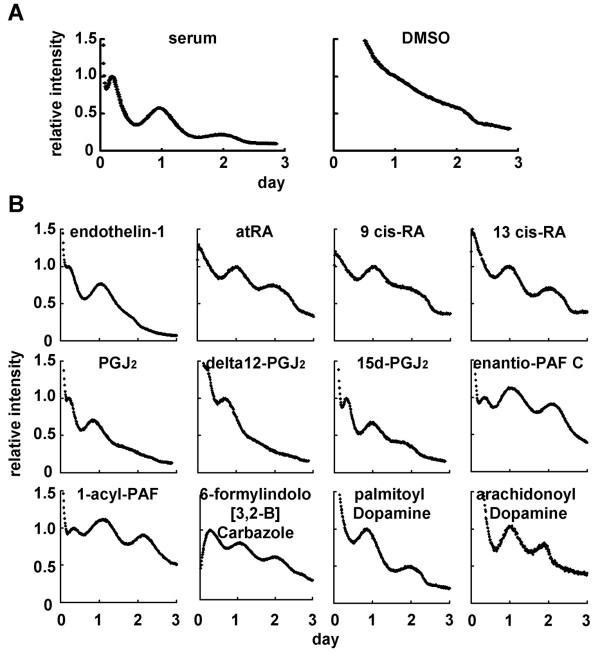
The photomultiplier tube detector system can detect bioluminescence of luciferase protein and can measure it every 15 min using a turntable (see Additional file 1). This system is maintained in an incubator at 5% CO2 and 35°C. We first established mPer2-luc/Rat1 fibroblast cell lines that stably express luciferase gene driven by mPer2 promoter. Per2 is considered to be one of the core molecule for molecular clocks since gene-knockout analysis revealed that mPer2 mutants display a shorted circadian period followed by a loss of circadian rhythmicity in constant darkness [33]. After stimulation with high concentration of serum for 1 h, rhythmicity of luciferase activity was monitored for duration of at least 2 or 3 days (Fig. 1A). In contrast to no oscillation in control (by DMSO treatment), rhythmic activity of luciferase was observed. Rhythmic phase of mPer2-luc/Rat1 cell lines was phenotypically the same as that in transiently transfected cells with mPer2-luc construct and was antiphase compared to transient transfected cells with hBmal1-luc construct [5]. These cell lines showed no abnormalities in their cell growth and morphology. In summary, these cell lines established here are suitable for the screening assay designed to identify entrainment factors for circadian clocks.
Figure 1.
Screening of entrainment factors by using IV-ROMS. mPer2-luc/Rat1 cells were monitored the luciferase intensity for duration of 3 days using IV-ROMS. Figure 1A shows luciferase activity after 1 h treatment with 50% serum (positive control, left panel) or DMSO (negative control, right panel). Figure 1B shows luciferase activity after 1 h treatment with 1 or 10 μM of each of the 12 possible circadian entrainment factors. A representative result was chosen out of three independent experiments. Abscissa presents "day", ordinate "relative luciferase intensity", respectively. The first peak was set to 1.
Screening of peptide and bioactive lipid libraries for circadian entrainment factors
The results of screening are shown in Figure 1B and Additional file 2 by using Peptide library (BAP96S, assayscript, Osaka, Japan) and Bioactive lipid library (Version 3, BIOMOL, PA, USA). Out of 299 compounds screened, 12 demonstrated the rhythmic expression of luciferase. Among them, four compounds (endothelin-1, all-trans retinoic acid, 9-cis retinoic acid, and 13-cis retinoic acid) have already been reported as resetting factors in vivo or in vitro [30,34]. By this assay, we newly identified eight candidates for circadian entrainment factors; prostaglandin J2 (PGJ2), Δ12-PGJ2, 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2), enantio-PAF C16, 1-acyl-PAF, 6-formylindolo [3,2-B] carbazole, palmitoyl dopamine, and arachidonoyl dopamine. These two libraries contain five known entrainment factors and we could identify all of them, except prostaglandin E2 [32], as an entrainment factor by this assay system (see Additional file 2), indicating that this assay system is reliable and suitable for screening of entrainment factors. We could not identify prostaglandin E2 because prostaglandin E2 receptor EP1, which is responsible for the entrainment of circadian clocks, was not expressed in Rat1 cells, but was expressed in NIH3T3 cells that Tsuchiya et al used [32] (see Additional file 3).
15d-PGJ2 triggers the rhythmic expression of endogenous clock genes in NIH3T3 cells
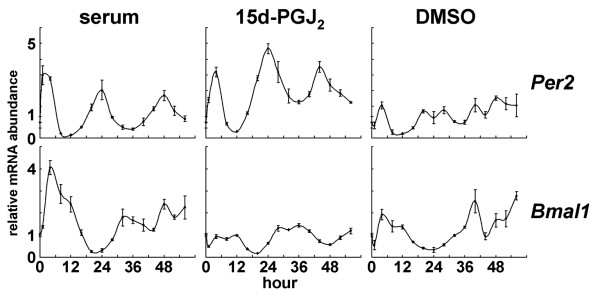
Among the eight novel candidates for entrainment factors, we focused on 15d-PGJ2, because cells stimulated by 15d-PGJ2 displayed the most robust effects on rhythmicity. 15d-PGJ2 has recently received increasing attention because it functions as a potential regulator of diverse processes including cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and inflammation [35]. In addition, 15d-PGJ2 is the dehydration end product of PGD2. Interestingly, PGD2 has been recognized as the most potent endogenous sleep-promoting substance [36]. Furthermore, the PGD2 concentration in rat cerebrospinal fluid shows a circadian shift coupled to the sleep-wake cycle [37]. To confirm whether 15d-PGJ2 is an authentic endogenous entrainment factor, we examined the expression profiles of clock genes in NIH3T3 fibroblast cells stimulated by 15d-PGJ2. Per2 and Bmal1 expression patterns were examined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR at 4-h intervals for duration of 56 h and rhythmic expressions were observed when treated for 1 h with 15d-PGJ2 and with high concentration serum, but not when treated with DMSO as a control (Fig. 2). Moreover, phases of Per2 and Bmal1 mRNA expression triggered by 15d-PGJ2 treatment were antiphasic with respect to each other, which is consistent with those triggered by serum and with previously reported expression profiles [5,38]. Taken together, these results demonstrate that 15d-PGJ2 can act as an in vitro entrainment factor for circadian clocks. PGD2 and other prostaglandins and prostanoids examined in this study showed no rhythmic fluctuation of luciferase activity (data not shown). The facts that 15d-PGJ2's precursor PGD2 has been recognized as the most potent endogenous sleep-promoting substance and that the PGD2 concentration in rat cerebrospinal fluid shows a circadian change coupled to the sleep-wake cycle, have led to the hypothesis that 15d-PGJ2 may act as an endogenous circadian entrainment factor in vivo. It would be interesting to see the effects of 15d-PGJ2 in vivo. However, it should be noted that the endogenous concentration of 15d-PGJ2 is extremely low [39], compared with the one used for the in vitro screening.
Figure 2.
Endogenous clock gene expression profiles stimulated by 15d-PGJ2. NIT3T3 cells were stimulated by 50% serum (positive control; left column), DMSO (negative control; right column), or 10 μM 15d-PGJ2 (middle panel) for 1 h. Total RNAs were isolated at each time point. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using mPer2 (upper panels), mBmal1 (bottom panels), and 18S rRNA primers. Abscissa presents "hour", ordinate "mRNA amount", respectively. mRNA amount at time 0 was set to 1. The relative levels of each mRNA were normalized to the corresponding 18S rRNA levels.
15d-PGJ2 up-regulates Cry1, Cry2, and Rorα mRNA expressions
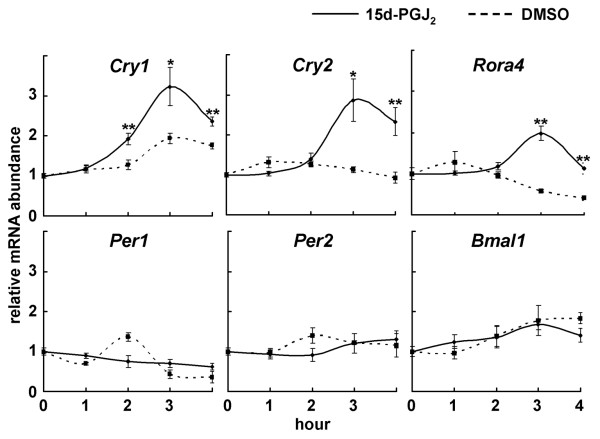
To examine which clock genes are induced by 15d-PGJ2 treatment, we systematically quantified the expression levels of the canonical clock genes. After the isolation of total RNA at 1-h intervals from NIH3T3 cells stimulated by 15d-PGJ2, quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using primers for Per1, Per2, Per3, Bmal1, Npas2, Cry1, Cry2, Dec1, Dec2, E4bp4, Dbp, and Rorα by using low-density arrays. Unexpectedly, stimulation with 15d-PGJ2 did not affect a transient Per1 and Per2 mRNA accumulation (Fig. 3), although both Per genes are known to be transiently accumulated by the various stimuli of entrainment [40]. On the other hand, we for the first time found that 15d-PGJ2 induced accumulation of Cry1 and Cry2 transcripts, as well as Rorα mRNA (Fig. 3), which is consistent with a previous report [41].
Figure 3.
15d-PGJ2 up-regulates Cry1, Cry2, and Rorα mRNA expression. NIH3T3 cells were stimulated by 10 μM 15d-PGJ2 (solid line) or DMSO (dotted line) for 1 h. Total RNAs were isolated at each time point. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using mCry1, mCry2, mRorα, mPer1, mPer2, mBmal1, and 18S rRNA primers. Abscissa presents "hour", ordinate "mRNA amount", respectively. Each mRNA amount at time point 0 was set to 1. Data are shown as the mean ± SE from three to five independent experiments. The relative levels of each mRNA were normalized to the corresponding 18S rRNA levels. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with relative control (Student's t-test).
Entrainment triggered by 15d-PGJ2 is independent of PPAR-γ signaling pathway
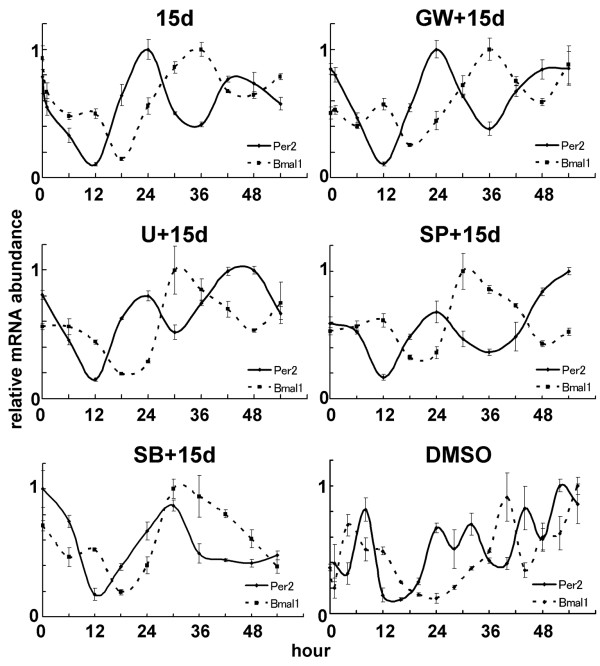
We next sought to identify entrainment signaling pathways triggered by 15d-PGJ2. Since 15d-PGJ2 has been known to be a natural ligand of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) [42], we assessed whether the clock gene expression triggered by 15d-PGJ2 is dependent on the PPAR-γ-mediated signaling pathway. NIH3T3 cells pretreated with DMSO or with a specific irreversible PPAR-γ antagonist GW9662 [43] were then stimulated with 15d-PGJ2, and harvested at every 6 h for duration of 54 h. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR using primers for Per2 and Bmal1 showed no different expression patterns between GW9662 and DMSO pretreated cells (Fig. 4). The same concentration (10 μM) of 15d-PGJ2 induced GADD45 and catalase mRNA, which are induced via PPAR-γ, in the same NIH3T3 cells, however, no stimulation of both mRNAs was seen in these cells pretreated with 10 μM GW9662 (see Additional file 4), indicating that these cells express PPAR-γ, that PPAR-γ was involved in our observation, and that the amount of GW9662 we used was enough for the system to work. These results suggest that the circadian entrainment triggered by 15d-PGJ2 is independent of the PPAR-γ signaling pathway. We further confirmed that other PPAR-γ ligands, Ciglitazone [44] and hexadecyl azelaoyl phosphatidlycholine (azPC) [45], did not lead to the circadian expression of the clock genes (see Additional file 5).
Figure 4.
Rhythmic clock gene expression triggered by 15d-PGJ2 is independent of PPAR-γ-, MAPK-, JNK- and p38MAPK-signaling pathway. After 1 h pretreatment of DMSO (15d; upper left panel), 10 μM GW9662 (GW+15d; upper right panel), 10 μM U0126 (U+15d; middle left panel), 20 μM SP600125 (SP+15d; middle right panel), or 30 μM SB203580 (SB+15d; bottom left panel), NIH3T3 cells were stimulated by 10 μM 15d-PGJ2 for 1 h. As a negative control, NIH3T3 cells were pretreated by DMSO and stimulated by DMSO for 1 h (DMSO; bottom right panel). Total RNAs were isolated at each time point. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using mPer2 (solid line), mBmal1 (dotted line), and 18S rRNA primers. Abscissa presents "hour", ordinate "mRNA amount", respectively. The maximum mRNA amount was set to 1. The relative levels of each mRNA were normalized to the corresponding 18S rRNA levels.
We then explored which signaling pathways are involved in 15d-PGJ2-induced rhythmic clock gene expression. Recently, administration of 15d-PGJ2 was shown to activate ERK and JNK signaling pathways [42,46]. The known entrainment factors are thought to mainly act by activating ERK signaling pathway [47]. We thus examined whether these two MAPK signaling pathways can be linked with 15d-PGJ2-induced cyclic gene expression. Surprisingly, pretreatment of a specific JNK inhibitor SP600125 [48] and of a specific MEK inhibitor U0126 [49], both showed no effect on the entrainment of circadian clocks (Fig. 4). Although results of MAPK/ERK to entrainment in the different systems have been inconsistent [50], these results suggest that there exists an unknown entrainment pathway, independent of the ERK-mediated signaling pathway. Meanwhile, another pathway, the p38 MAPK signaling pathway was recently shown to be associated with circadian clocks by modulating their period lengths [51]. SB203580, a specific p38 inhibitor [52], slightly delayed the phase of Per2 rhythms but did not affect circadian expression of both Per2 and Bmal1 (Fig. 4), indicating that p38 MAPK signaling pathway is involved in modulation of period length, but not in the induction of clock gene expression by 15d-PGJ2.
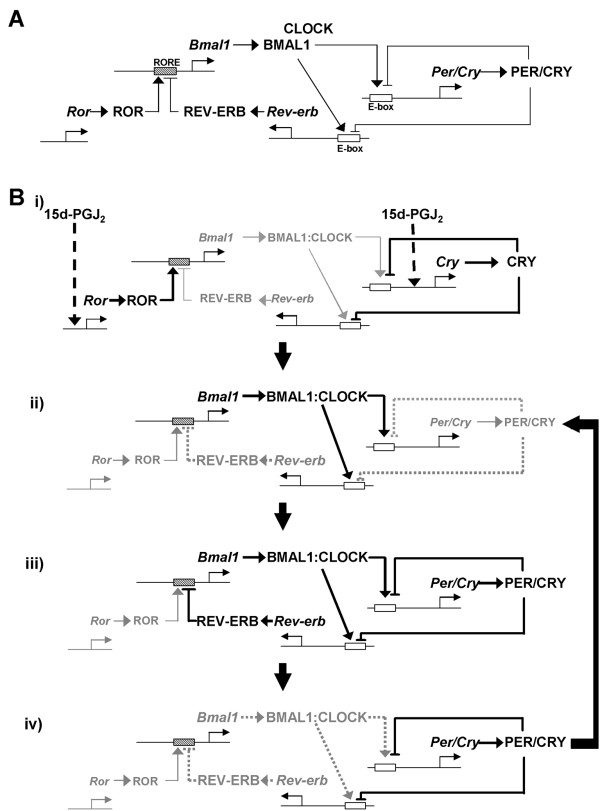
The interpretation of this study on the transcription-translation feedback loops of clock genes are summarized in Figure 5A. As shown in Figure 3, 15d-PGJ2 up-regulates transcription of Crys and Rorα (Fig. 5Bi). The translated RORα activates Bmal1 transcription [24,53,54], and translated BMAL1 binds to CLOCK forming a heterodimer which activates Per/Cry and Rev-erb transcriptions via E/E' elements (Fig. 5Bii; [12,13]). Translated PER/CRY and REV-ERB inhibit transcription of Per/Cry/Rev-erb and Bmal1 genes, respectively (Fig. 5Biii). The inhibition of Rev-erb transcription also reduces Bmal1 transcription (Fig. 5Biv; [55]). The reduced Per/Cry transcription and relatively increased RORα activity (by inhibition of REV-ERB) again up-regulate Bmal1 transcription and result in a completion of the "loop" (Fig. 5Biv -> 5Bii).
Figure 5.
Schema of the entrainment mechanism by 15d-PGJ2. 15d-PGJ2 up-regulates transcription of Crys and Rorα (Fig. 5Bi). The translated RORα activates Bmal1 transcription, and translated BMAL1 then binds to CLOCK and their heterodimers activate Per/Cry and Rev-erb transcriptions via E/E' box (Fig. 5Bii). Translated PER/CRY and REV-ERB inhibit Per/Cry/Rev-erb and Bmal1 transcription, respectively (Fig. 5Biii). The inhibition of Rev-erb transcription reduces Bmal1 transcription (Fig. 5Biv). The reduced Per/Cry transcription and relatively increased RORα activity (by inhibition of REV-ERB) again up-regulate Bmal1 transcription (Fig. 5Biv -> 5Bii).
In vitro real-time oscillation monitoring system (IV-ROMS)
IV-ROMS can be applied to identify molecules which are involved in other mechanisms pertaining to circadian clock system; transcriptional-translational feedback loops of circadian mechanism and input signaling pathway mechanism, for example, by using RNAi, inhibitor, and other libraries. We can also apply this system to other research fields. Further modification and development of this system will be needed in order to be applied for more systematic and high-throughput screenings.
Conclusion
Here we present the in vitro real-time oscillation monitoring system (IV-ROMS). Indeed, we newly found eight candidates out of 299 compounds as circadian entrainment factors (Fig. 1 and Additional file 2). We further confirmed that one of the candidates, 15d-PGJ2, triggers the rhythmic expression of endogenous circadian clocks by inducing Crys and Rorα, but not Pers, in NIH3T3 cells (Fig. 2), indicating that this assay system is a powerful and useful tool for the initial screening procedure. This system can also be applied not only to find new intracellular molecules involved in circadian clocks; new transcription factors, new signaling and degradation pathways, but also to investigate other cellular mechanisms like cell-cycle or oncogenesis.
Methods
Cell culture
Rat1 and NIH3T3 fibroblast cells were grown at 37°C and 5% CO2. Rat1 and NIH3T3 cells were grown in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (1.0 g/L glucose) with L-Gln and sodium pyruvate (DMEM, Nacalai tesque, Kyoto, Japan) supplemented with 5 and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), respectively, and antibiotics.
Establishment of mPer2-luciferase-stably-expressing Rat1 cell line
A bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone (pBeloBac11 24484) containing the complete genomic sequence of the mouse Per2 (mPer2) gene was purchased from BACPAC Resource Center at Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute. The mPer2 promoter region was isolated and cloned in the pGL3 Basic vector (Promega). The mPer2 region spans from -2811 to +110 (+1 indicates the putative transcriptional start site). Rat1 cells were cotransfected with linearized mPer2 promoter/pGL3 and pcDNA3, which contains neomycin resistant gene. Transfection was carried out by using Polyfect Transfection Reagent (QIAGEN) according to the manufacture's instructions. The cells were cultured in 10% FBS/DMEM containing 500 μg/ml geneticin (SIGMA) for 1 to 2 weeks. Cells were then individually isolated, and 24 clones were established as mPer2-luc/Rat1 cells. After screening for the luciferase activity by using IV-ROMS, we established two independent clones with clear rhythmic activity.
Real-time luciferase activity monitoring in living cells
mPer2-luc/Rat1 cells were seeded in a 35 mm-dish at density of 2 × 105 cells and incubated for 2 days. The medium was then exchanged for serum-free medium supplemented with a compound to be screened. Compound was diluted to a final concentration of 1 μM for peptide and 1 or 10 μM for bioactive lipid, respectively. One hour later the medium was replaced with 1% FBS/DMEM supplemented with 0.1 mM luciferin/10 mM HEPES (pH 7.2). Light emission was measured and integrated for 1 min at intervals of 15 min with a photomultiplier tube (Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu, Japan). Data were analyzed by LM2400 software (Hamamatsu Photonics).
Real-time quantitative RT-PCR
TaqMan® Low Density Array (Applied Biosystems), which contained mPer1, mPer2, mPer3, mArntl (mBmal1), mNpas2, mCry1, mCry2, mBhlhb2 (mDec1), mBhlhb3 (mDec2), mDbp, and mNfil3 (mE4bp4) as clock genes and 18S rRNA as an internal control, was examined by using an ABI PRISM 7900HT Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems) as described previously [56]. For one port of the TaqMan Low Density Array, 100 ng cDNA template was mixed with 50 μl of 2 × TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) and filled up to 100 μl with distilled water. The reaction was first incubated at 50°C for 2 min, then at 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 1 min.
Each real-time quantitative RT-PCR was performed by using an ABI PRISM 7900HT Sequence Detection System as described previously [5]. Briefly, DNase-treated total RNA (1 μg) was reverse-transcribed by using a random hexamer primer and Superscript reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen). The cDNA equivalent to 50 ng total RNA was PCR-amplified. The PCR primers and TaqMan probes (5' FAM and 3' TAMRA) used are as follows:
mPer2 FW: CGC CTA GAA TCC CTC CTG AGA,
mPer2 RV: CCA CCG GCC TGT AGG ATC T,
mPer2 TaqMan probe: AGG CTG TGG ATG AAA GGG CGG TC,
mBmal1 FW: GCA GTG CCA CTG ACT ACC AAG A,
mBmal1 RV: TCC TGG ACA TTG CAT TGC AT,
mBmal1 TaqMan probe: ATC AAG AAT GCA AGG GAG GCC CAC A,
18S rRNA FW: CGC CGC TAG AGG TGA AAT TC,
18S rRNA RV: CGA ACC TCC GAC TTT CGT TCT,
18S rRNA TaqMan probe: CCG GCG CAA GAC GGA CCA GA.
The PCR primers for mCry1, mCry2, and mRorα were described previously [5,24]. Values are reported as mean ± SE. Statistical differences were determined by a Student's t test. Statistical significance is displayed as * (p < 0.05) or ** (p < 0.01).
List of abbreviations used
SCN, suprachiasmatic nuclei; IV-ROMS, in vitro real-time oscillation monitoring system; 15d-PGJ2, 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-γ; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; DMEM; Dulbecco's modified eagle medium; FBS, Fetal bovine serum
Authors' contributions
YN carried out most of experiments and drafted the manuscript. MA designed the system. DT carried out the molecular biology studies and proofread the manuscript. AY participated in the coordination and provided financial support. TT is the PI and has participated in its design and coordination, and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Schema of IV-ROMS. Two photomultiplier tubes are installed within the lid and the light emission is integrated for 1 min per sample at intervals of 15 min. 24 samples are able to be detected at once. Data are analyzed by LM2400 software (Hamamatsu Photonics).
Compound libraries used in this assay. Peptide library (BAP96S, assayscript, Osaka, Japan) and Bioactive lipid library (Version 3, BIOMOL, Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA) were used in this screening assay. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of known entrainment factors.
EP1 mRNA is expressed in NIH3T3 cells, but not in Rat1 cells. Total RNAs were isolated from NIH3T3 and Rat1 cells and semi-quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using prostaglandin E2 receptor EP1 and G3PDH primers. G3PDH mRNA was used as an internal control. For EP1 and G3PDH, the cDNA equivalent to 50 ng and 0.5 ng of total RNA respectively, were PCR-amplified by 30 cycles each.
Pretreatment of PPAR-γ antagonist, GW9662, repressed 15d-PGJ2-induced PPAR-γ-mediated gene expressions. The effect of GW9662 on PPARγ-mediated GADD45 (A) and catalase (B) mRNA expressions was evaluated by using a quantitative real-time PCR. 1 h GW9662 (GW: +) or DMSO (GW: -) pretreated-NH3T3 cells were stimulated by 15d-PGJ2 (15d: +) or DMSO (15d: -). mRNA amounts after 1 h stimulation by15d-PGJ2 or DMSO were measured. The mRNA amount of GW: -, 15d: - condition was set to 1. The relative levels of each mRNA were normalized to the corresponding 18S rRNA levels. Data are shown as the mean ± SE from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with the condition 'GW: -, 15d: +'. (Student's t-test).
15d-PGJ2-induced entrainment mechanism for circadian clocks is independent of PPAR-γ-signaling pathway. After 1 h pretreatment with (middle right panel) or without (middle left panel) PPAR-γ antagonist, GW96662, mPer2-luc/Rat1 cells were stimulated by 15d-PGJ2 for 1 h and the luciferase intensity was monitored by using IV-ROMS. mPer2-luc/Rat1 cells stimulated for 1 h by PPAR-γ agonists, azPC (bottom left panel) or ciglitazone (bottom right panel) were monitored by using IV-ROMS. A representative result was chosen out of at least three independent experiments. Abscissa presents "day", ordinate "relative luciferase intensity", respectively.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Setsuko Tsuboi, Chiaki Matsubara, and Yoko Sakakida for their technical assistance. Also thank Yoshihiro Urade for discussion and Yasufumi Shigeyoshi for Rat1 cells. This work was supported in part by research grants from the MEXT and Takeda Science Foundation.
Contributor Information
Yasukazu Nakahata, Email: yasu_nakahata@yahoo.co.jp.
Makoto Akashi, Email: akashima@med.saga-u.ac.jp.
Daniel Trcka, Email: dtrcka@hotmail.com.
Akio Yasuda, Email: yasuda@sony.de.
Toru Takumi, Email: takumi@obi.or.jp.
References
- Cermakian N, Sassone-Corsi P. Multilevel regulation of the circadian clock. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:59–67. doi: 10.1038/35036078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U, Sassone-Corsi P. A web of circadian pacemakers. Cell. 2002;111:919–922. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsalobre A, Damiola F, Schibler U. A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells. Cell. 1998;93:929–937. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81199-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi M, Nishida E. Involvement of the MAP kinase cascade in resetting of the mammalian circadian clock. Genes Dev. 2000;14:645–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T, Nakahata Y, Soma H, Akashi M, Mamine T, Takumi T. Transcriptional oscillation of canonical clock genes in mouse peripheral tissues. BMC Mol Biol. 2004;5:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menaker M. Circadian rhythms. Circadian photoreception. Science. 2003;299:213–214. doi: 10.1126/science.1081112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reppert SM, Weaver DR. Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 2002;418:935–941. doi: 10.1038/nature00965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey PL, Takahashi JS. Mammalian circadian biology: elucidating genome-wide levels of temporal organization. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2004;5:407–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.5.061903.175925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young MW, Kay SA. Time zones: a comparative genetics of circadian clocks. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:702–715. doi: 10.1038/35088576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pando MP, Sassone-Corsi P. Unraveling the mechanisms of the vertebrate circadian clock: zebrafish may light the way. Bioessays. 2002;24:419–426. doi: 10.1002/bies.10091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D, Cassone VM, Earnest DJ, Golden SS, Hardin PE, Thomas TL, Zoran MJ. Circadian rhythms from multiple oscillators: lessons from diverse organisms. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:544–556. doi: 10.1038/nrg1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekakis N, Staknis D, Nguyen HB, Davis FC, Wilsbacher LD, King DP, Takahashi JS, Weitz CJ. Role of the CLOCK protein in the mammalian circadian mechanism. Science. 1998;280:1564–1569. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5369.1564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogenesch JB, Gu YZ, Jain S, Bradfield CA. The basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS orphan MOP3 forms transcriptionally active complexes with circadian and hypoxia factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:5474–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.10.5474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K, Zylka MJ, Sriram S, Shearman LP, Weaver DR, Jin X, Maywood ES, Hastings MH, Reppert SM. mCRY1 and mCRY2 are essential components of the negative limb of the circadian clock feedback loop. Cell. 1999;98:193–205. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakida Y, Miyamoto Y, Nagoshi E, Akashi M, Nakamura TJ, Mamine T, Kasahara M, Minami Y, Yoneda Y, Takumi T. Importin alpha/beta mediates nuclear transport of a mammalian circadian clock component, mCRY2, together with mPER2, through a bipartite nuclear localization signal. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:13272–13278. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413236200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T, Matsubara C, Shigeyoshi Y, Taguchi K, Yagita K, Maebayashi Y, Sakakida Y, Okumura K, Takashima N, Okamura H. A new mammalian period gene predominantly expressed in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes Cells. 1998;3:167–176. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1998.00178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T, Taguchi K, Miyake S, Sakakida Y, Takashima N, Matsubara C, Maebayashi Y, Okumura K, Takekida S, Yamamoto S, Yagita K, Yan L, Young MW, Okamura H. A light-independent oscillatory gene mPer3 in mouse SCN and OVLT. Embo J. 1998;17:4753–4759. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.16.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T, Nagamine Y, Miyake S, Matsubara C, Taguchi K, Takekida S, Sakakida Y, Nishikawa K, Kishimoto T, Niwa S, Okumura K, Okamura H. A mammalian ortholog of Drosophila timeless, highly expressed in SCN and retina, forms a complex with mPER1. Genes Cells. 1999;4:67–75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geusz ME, Fletcher C, Block GD, Straume M, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Kay SA, Day RN. Long-term monitoring of circadian rhythms in c-fos gene expression from suprachiasmatic nucleus cultures. Curr Biol. 1997;7:758–766. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plautz JD, Kaneko M, Hall JC, Kay SA. Independent photoreceptive circadian clocks throughout Drosophila. Science. 1997;278:1632–1635. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5343.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki S, Numano R, Abe M, Hida A, Takahashi R, Ueda M, Block GD, Sakaki Y, Menaker M, Tei H. Resetting central and peripheral circadian oscillators in transgenic rats. Science. 2000;288:682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5466.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokkan KA, Yamazaki S, Tei H, Sakaki Y, Menaker M. Entrainment of the circadian clock in the liver by feeding. Science. 2001;291:490–493. doi: 10.1126/science.291.5503.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda HR, Chen W, Adachi A, Wakamatsu H, Hayashi S, Takasugi T, Nagano M, Nakahama K, Suzuki Y, Sugano S, Iino M, Shigeyoshi Y, Hashimoto S. A transcription factor response element for gene expression during circadian night. Nature. 2002;418:534–539. doi: 10.1038/nature00906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi M, Takumi T. The orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha regulates circadian transcription of the mammalian core-clock Bmal1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12:441–448. doi: 10.1038/nsmb925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda HR, Hayashi S, Chen W, Sano M, Machida M, Shigeyoshi Y, Iino M, Hashimoto S. System-level identification of transcriptional circuits underlying mammalian circadian clocks. Nat Genet. 2005;37:187–192. doi: 10.1038/ng1504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi M, Ichise T, Mamine T, Takumi T. Molecular mechanism of cell-autonomous circadian gene expression of Period2, a crucial regulator of the mammalian circadian clock. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:555–565. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-05-0396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida N, Kaneko M, Allada R. Biological clocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:8819–8820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.16.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsalobre A, Brown SA, Marcacci L, Tronche F, Kellendonk C, Reichardt HM, Schutz G, Schibler U. Resetting of circadian time in peripheral tissues by glucocorticoid signaling. Science. 2000;289:2344–2347. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5488.2344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer A, Yang FC, Snodgrass P, Li X, Scammell TE, Davis FC, Weitz CJ. Regulation of daily locomotor activity and sleep by hypothalamic EGF receptor signaling. Science. 2001;294:2511–2515. doi: 10.1126/science.1067716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P, Seo SP, Rudic RD, Sehgal A, Chakravarti D, FitzGerald GA. Regulation of CLOCK and MOP4 by nuclear hormone receptors in the vasculature: a humoral mechanism to reset a peripheral clock. Cell. 2001;105:877–889. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng MY, Bullock CM, Li C, Lee AG, Bermak JC, Belluzzi J, Weaver DR, Leslie FM, Zhou QY. Prokineticin 2 transmits the behavioural circadian rhythm of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nature. 2002;417:405–410. doi: 10.1038/417405a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya Y, Minami I, Kadotani H, Nishida E. Resetting of peripheral circadian clock by prostaglandin E2. EMBO Rep. 2005;6:256–261. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B, Larkin DW, Albrecht U, Sun ZS, Sage M, Eichele G, Lee CC, Bradley A. The mPer2 gene encodes a functional component of the mammalian circadian clock. Nature. 1999;400:169–173. doi: 10.1038/22659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagita K, Tamanini F, van Der Horst GT, Okamura H. Molecular mechanisms of the biological clock in cultured fibroblasts. Science. 2001;292:278–281. doi: 10.1126/science.1059542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen ZY, Tseng CC. 15-deoxy-Delta12,14 prostaglandin J2 up-regulates Kruppel-like factor 4 expression independently of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma by activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signal transduction pathway in HT-29 colon cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;68:1203–1213. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.014944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O, Urade Y. Prostaglandin D2 in sleep-wake regulation: recent progress and perspectives. Neuroscientist. 2002;8:12–15. doi: 10.1177/107385840200800105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey HP, Ram A, Matsumura H, Satoh S, Hayaishi O. Circadian variations of prostaglandins D2, E2, and F2 alpha in the cerebrospinal fluid of anesthetized rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;213:625–629. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C, Etchegaray JP, Cagampang FR, Loudon AS, Reppert SM. Posttranslational mechanisms regulate the mammalian circadian clock. Cell. 2001;107:855–867. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00610-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Parikh LC, Ide T, Lawson JA, McNamara P, Reilly M, FitzGerald GA. Biosynthesis of 15-deoxy-delta12,14-PGJ2 and the ligation of PPARgamma. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI200318012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsalobre A, Marcacci L, Schibler U. Multiple signaling pathways elicit circadian gene expression in cultured Rat-1 fibroblasts. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1291–1294. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00758-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migita H, Morser J. 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) signals through retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor-alpha but not peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in human vascular endothelial cells: the effect of 15d-PGJ2 on tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:710–716. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000156482.76228.d1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosjean O, Boutin JA. Natural ligands of PPARgamma: are prostaglandin J(2) derivatives really playing the part? Cell Signal. 2002;14:573–583. doi: 10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang JT, Welch JS, Ricote M, Binder CJ, Willson TM, Kelly C, Witztum JL, Funk CD, Conrad D, Glass CK. Interleukin-4-dependent production of PPAR-gamma ligands in macrophages by 12/15-lipoxygenase. Nature. 1999;400:378–382. doi: 10.1038/22572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Wilkison WO, Willson TM, Kliewer SA. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) J Biol Chem. 1995;270:12953–12956. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.50.30221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies SS, Pontsler AV, Marathe GK, Harrison KA, Murphy RC, Hinshaw JC, Prestwich GD, Hilaire AS, Prescott SM, Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM. Oxidized alkyl phospholipids are specific, high affinity peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands and agonists. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16015–16023. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100878200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher JU, Pillinger MH. 15d-PGJ2: the anti-inflammatory prostaglandin? Clin Immunol. 2005;114:100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2004.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cermakian N, Sassone-Corsi P. Environmental stimulus perception and control of circadian clocks. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12:359–365. doi: 10.1016/S0959-4388(02)00347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O'Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, Bhagwat SS, Manning AM, Anderson DW. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:13681–13686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.251194298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, Feeser WS, Van Dyk DE, Pitts WJ, Earl RA, Hobbs F, Copeland RA, Magolda RL, Scherle PA, Trzaskos JM. Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:18623–18632. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.29.18623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav G, Straume M, Heath J, Zatz M. Are changes in MAPK/ERK necessary or sufficient for entrainment in chick pineal cells? J Neurosci. 2003;23:10021–10031. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-31-10021.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y, Sanada K, Hirota T, Shimizu F, Fukada Y. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates oscillation of chick pineal circadian clock. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:25166–25171. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212726200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuenda A, Rouse J, Doza YN, Meier R, Cohen P, Gallagher TF, Young PR, Lee JC. SB 203580 is a specific inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 1995;364:229–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00357-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato TK, Panda S, Miraglia LJ, Reyes TM, Rudic RD, McNamara P, Naik KA, FitzGerald GA, Kay SA, Hogenesch JB. A functional genomics strategy reveals Rora as a component of the mammalian circadian clock. Neuron. 2004;43:527–537. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y, Ikeda M, Kimura T, Honma S, Ohmiya Y, Honma K. Bidirectional role of orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha in clock gene transcriptions demonstrated by a novel reporter assay system. FEBS Lett. 2004;565:122–126. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.03.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preitner N, Damiola F, Lopez-Molina L, Zakany J, Duboule D, Albrecht U, Schibler U. The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell. 2002;110:251–260. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00825-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T, Nakahata Y, Tanaka M, Yoshida M, Soma H, Shinohara K, Yasuda A, Mamine T, Takumi T. Acute physical stress elevates mouse period1 mRNA expression in mouse peripheral tissues via a glucocorticoid-responsive element. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:42036–42043. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509600200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Schema of IV-ROMS. Two photomultiplier tubes are installed within the lid and the light emission is integrated for 1 min per sample at intervals of 15 min. 24 samples are able to be detected at once. Data are analyzed by LM2400 software (Hamamatsu Photonics).
Compound libraries used in this assay. Peptide library (BAP96S, assayscript, Osaka, Japan) and Bioactive lipid library (Version 3, BIOMOL, Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA) were used in this screening assay. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of known entrainment factors.
EP1 mRNA is expressed in NIH3T3 cells, but not in Rat1 cells. Total RNAs were isolated from NIH3T3 and Rat1 cells and semi-quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using prostaglandin E2 receptor EP1 and G3PDH primers. G3PDH mRNA was used as an internal control. For EP1 and G3PDH, the cDNA equivalent to 50 ng and 0.5 ng of total RNA respectively, were PCR-amplified by 30 cycles each.
Pretreatment of PPAR-γ antagonist, GW9662, repressed 15d-PGJ2-induced PPAR-γ-mediated gene expressions. The effect of GW9662 on PPARγ-mediated GADD45 (A) and catalase (B) mRNA expressions was evaluated by using a quantitative real-time PCR. 1 h GW9662 (GW: +) or DMSO (GW: -) pretreated-NH3T3 cells were stimulated by 15d-PGJ2 (15d: +) or DMSO (15d: -). mRNA amounts after 1 h stimulation by15d-PGJ2 or DMSO were measured. The mRNA amount of GW: -, 15d: - condition was set to 1. The relative levels of each mRNA were normalized to the corresponding 18S rRNA levels. Data are shown as the mean ± SE from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with the condition 'GW: -, 15d: +'. (Student's t-test).
15d-PGJ2-induced entrainment mechanism for circadian clocks is independent of PPAR-γ-signaling pathway. After 1 h pretreatment with (middle right panel) or without (middle left panel) PPAR-γ antagonist, GW96662, mPer2-luc/Rat1 cells were stimulated by 15d-PGJ2 for 1 h and the luciferase intensity was monitored by using IV-ROMS. mPer2-luc/Rat1 cells stimulated for 1 h by PPAR-γ agonists, azPC (bottom left panel) or ciglitazone (bottom right panel) were monitored by using IV-ROMS. A representative result was chosen out of at least three independent experiments. Abscissa presents "day", ordinate "relative luciferase intensity", respectively.