Abstract
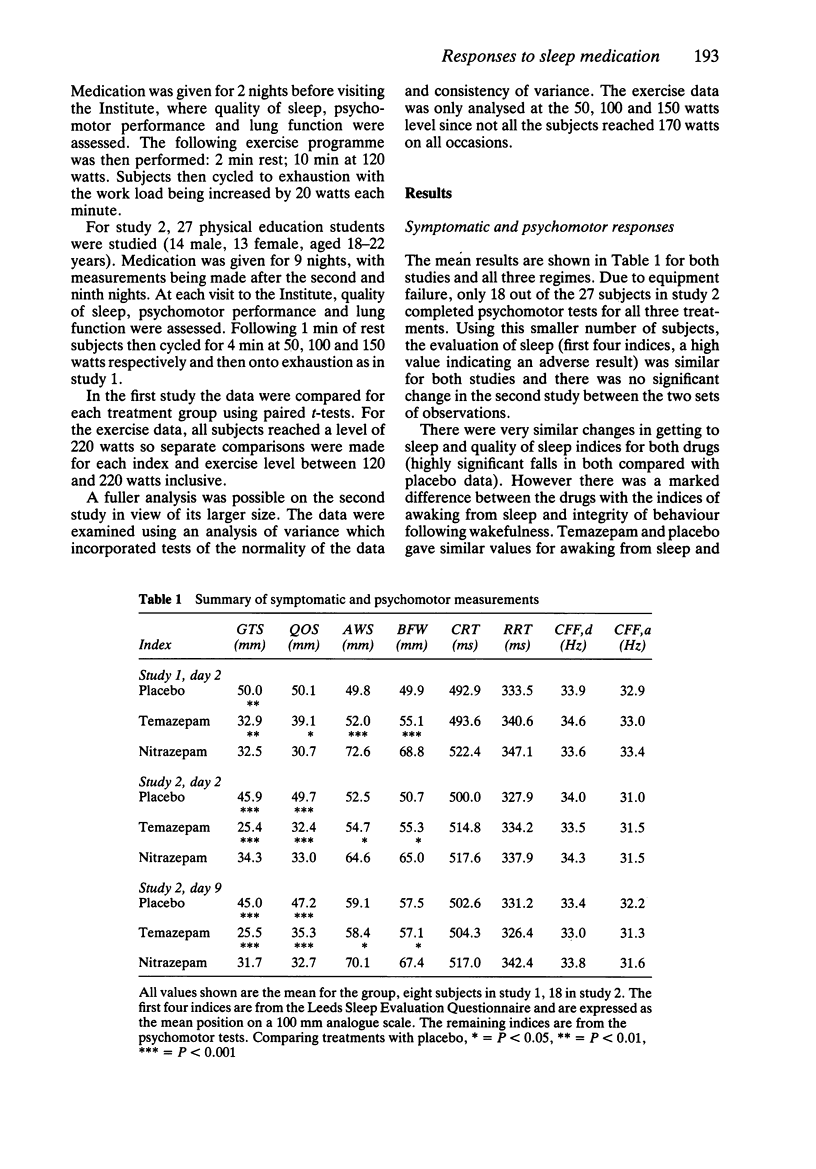
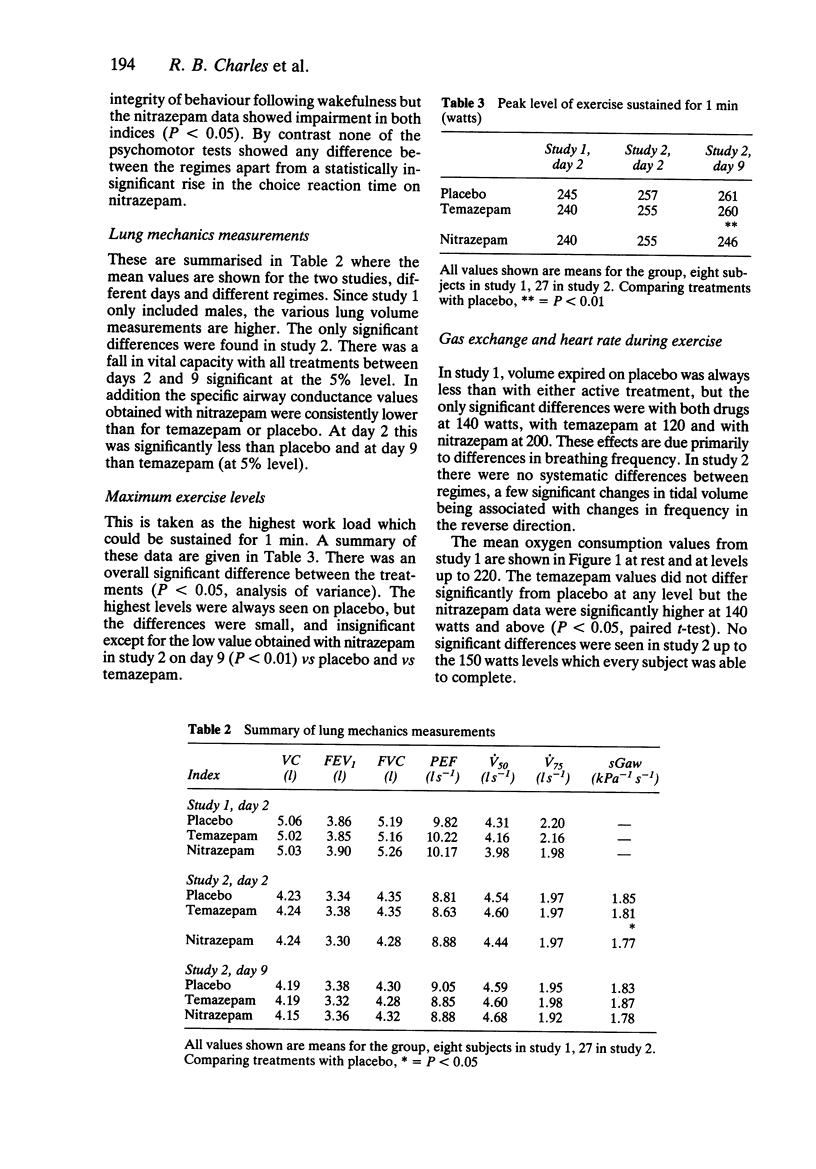
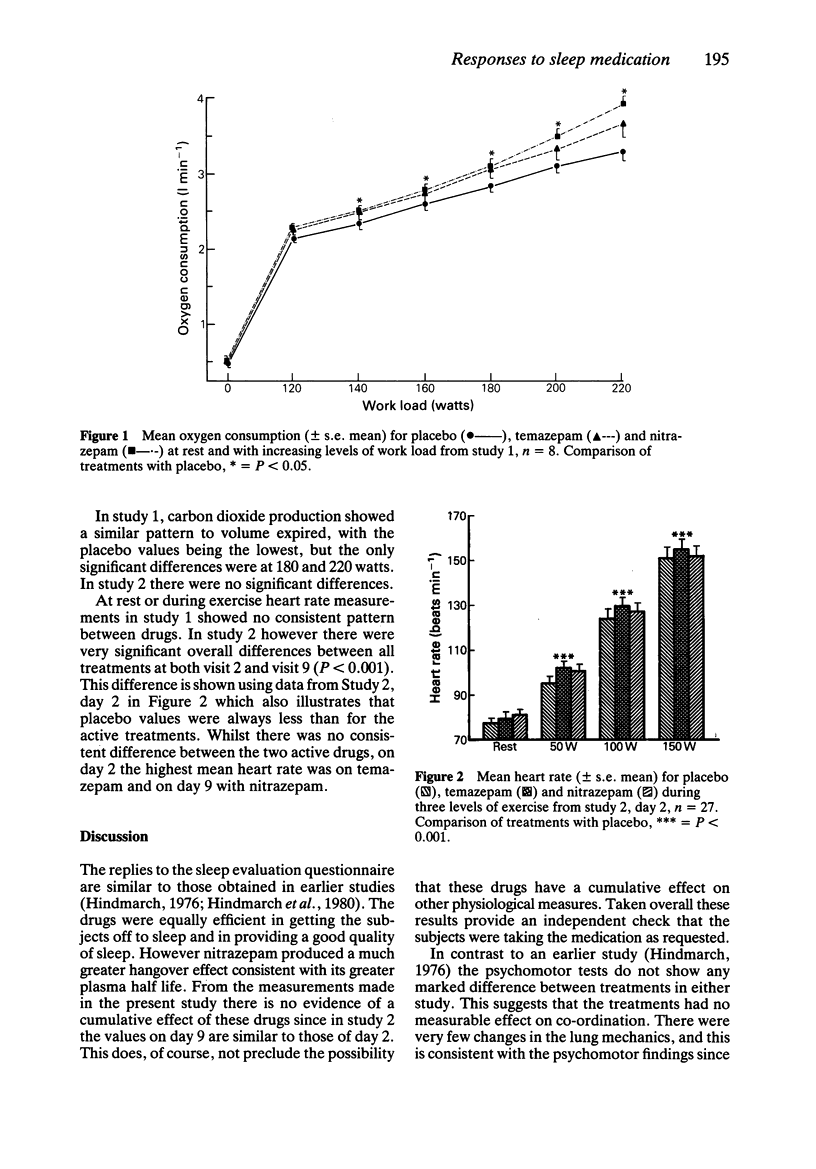
1 Athletes may use benzodiazepines before events to improve sleep, but these drugs may adversely affect performance. 2 Nitrazepam (10 mg) and temazepam (30 mg) were compared with placebo in 27 physical education students, (14 males, 13 females). Treatments were administered at night, using a double-blind, double dummy protocol, for 9 nights. Observations were made in the morning after night 2 and night 9. At least 2 weeks interval was allowed between each treatment. 3 At each examination lung mechanics were measured, a Leeds Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire completed, recognition reaction time, choice reaction time and the critical flicker fusion threshold test were used to assess psychomotor activity and an exercise test was performed. The subject exercised to exhaustion on a bicycle ergometer while ventilation, gas exchange and heart rate were recorded on an FM tape unit for off-line digital analysis. 4 The questionnaire indicated that both drugs were equally effective in promoting and maintaining sleep, but nitrazepam had a marked 'hangover' effect. The psychomotor activity and lung mechanics however seemed unaffected. On day 2, maximum exercise levels attained using either drug were comparable to placebo whilst on day 9 temazepam and placebo were significantly higher than nitrazepam. 5 Heart rate was significantly increased at each exercise level with both drugs. 6 Although there may be some effect of these drugs on athletic performance this is likely to be small especially with temazepam.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fowler L. K. Temazepam (Euhypnos) as a hypnotic: a twelve-week trial in general practice. J Int Med Res. 1977;5(5):295–296. doi: 10.1177/030006057700500501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuccella L. M., Bolcioni G., Tamassia V., Ferrario L., Tognoni G. Human pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of temazepam administered in soft gelatin capsules. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Dec 16;12(5):383–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00562455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaddie J., Legge J. S., Palmer K. N., Petrie J. C., Wood R. A. Effect of nitrazepam in chronic obstructive bronchitis. Br Med J. 1972 Jun 17;2(5815):688–689. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5815.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes D. M., Rudolf M., Saunders K. B. Effect of nitrazepam and flurazepam on the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide. Thorax. 1976 Oct;31(5):548–551. doi: 10.1136/thx.31.5.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt A. R., Alpers J. H. Factors affecting airways conductance: a study of 752 working men. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Mar;24(3):310–316. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindmarch I. A 1,4-benzodiazepine, temazepam (K 3917), its effect on some psychological parameters of sleep and behaviour. Arzneimittelforschung. 1975 Nov;25(11):1836–1839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindmarch I. A sub-chronic study of the subjective quality of sleep and psychological measures of performance on the morning following night time medication with temazepam. Arzneimittelforschung. 1976;26(11):2113–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindmarch I. The effects of repeated doses of temazepam taken in conjunction with alcohol on aspects of psychomotor performance the morning following night time medication. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(12):2357–2360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleuvry B. J., Maddison S. E., Odeh R. B., Dodson M. E. Respiratory and psychological effects of oral temazepam in volunteers. Br J Anaesth. 1980 Sep;52(9):901–906. doi: 10.1093/bja/52.9.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S., Sherbaniuk R. W., Prasad K., Lee S. J., Sproule B. J. Cardiopulmonary effects of diazepam. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Mar-Apr;14(2):182–189. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973142182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolf M., Geddes D. M., Turner J. A., Saunders K. B. Depression of central respiratory drive by nitrazepam. Thorax. 1978 Feb;33(1):97–100. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard R. J., Allen C., Benade A. J., Davies C. T., Di Prampero P. E., Hedman R., Merriman J. E., Myhre K., Simmons R. The maximum oxygen intake. An international reference standard of cardiorespiratory fitness. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(5):757–764. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


