Abstract
Escherichia coli isolates causing urinary tract infection in 83 male infants younger than 90 days with and without bacteremia were compared for phylogenetic groups and the presence of 10 virulence factors. Our result suggest that the absence of both hemolysin and antigen K1 may be used as a negative predictive factor for bacteremia.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the major cause of bacterial infection in infants younger than 90 days. The estimated incidence of UTI in this age group is about 1% (22), and UTI is responsible for up to 10% of cases of fever (6, 14). UTI shows a marked male predominance during this period of age, and bacteremia occurs in one-quarter of cases, compared to less than 5% in older subjects (1, 7, 25). Although the proclivity for bloodstream infection in the very young is known, the mechanisms underlying the negative correlation between bacteremia and age in this setting are unknown. The decision to treat young infants with UTI with parenteral versus oral antibiotics is in part based on the risk of bacteremia. Indeed, the main complication of urosepsis in this young population is meningitis, which occurs in about 10% of bacteremic patients (1). However, the sensitivity of blood culture is low in this age group, mainly because only one sample of limited volume can be drawn each day. In addition, one-third of young infants with bacteremia have fewer than one pathogen per milliliter of blood (15). Several teams have attempted to identify factors that may be used to distinguish pediatric patients with and without bacteremia, in terms of clinical, biological, or radiological features and outcome (1, 8, 9, 21). The only significant difference so far identified is that patients with bacteremia are more likely to have anatomical or functional urinary tract disorders (1, 9).
Escherichia coli is the leading cause of bacterial UTI. Knowledge of the molecular pathogenicity of extraintestinal E. coli infections has improved markedly over the last decade (11). However, the possible relationship between the virulence genotype of infecting E. coli strains and the risk of bacteremia has not yet been studied in young infants with UTI. Here, we compared two collections of E. coli isolated from infants with bacteremic and nonbacteremic UTI, focusing on phenotypic and genetic determinants that might serve to predict bacteremia and to guide treatment.
To constitute the cohort of patients with bacteremia, we reviewed the records of all infants younger than 90 days hospitalized in our institution with community-acquired E. coli urosepsis between January 1992 and December 2002. The inclusion criteria were blood culture yielding E. coli and ≥105 CFU of E. coli per ml in a urine bag sample with at least 10 white blood cells per mm3. The patients without bacteremia were a part of a cohort described elsewhere (4). As UTI at this age affects mainly boys and in order to rule out confounding factors such as gender and urinary tract abnormalities, only isolates from boys with normal voiding cystourethrography or minor vesicoureteral reflux (grade I or II) were analyzed.
The urinary isolates were stored at −80°C until characterization. K1 antigen was detected by using antiserum to Neisseria meningitidis group B, as previously described (2). The phylogenetic groups of all the strains and the phylogenetic subgroups of strains belonging to group B2 were determined by PCR and ribotyping, respectively, as described elsewhere (3). A phylogenetic subgroup was assigned to each distinct ribotype pattern obtained with group B2 strains, using the same designation as Bingen-Bidois et al. (ribotypes I, II, III, IX, X, and XI). Nine putative virulence factor genes characteristic of extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (papC, P fimbriae; papGII, adhesin PapG class II; papGIII, adhesin PapG class III; sfa/foc, S fimbriae; hlyC, hemolysin; cnf1, cytotoxic necrotizing factor; iucC, iron uptake system [IUS] aerobactin; fyuA, IUS yersiniabactin; and iroN, IUS salmochelin) were identified by using a new multiplex PCR method adapted from our previous studies (3, 5). Briefly, PCR was carried out in a 50-μl volume with 25 μl of 2× QIAGEN Multiple PCR Master Mix (QIAGEN, Courtaboeuf, France), 5 μl of 5× Q-solution, 5 μl of a primer mix, 10 μl of distilled water, and 5 μl of bacterial lysate. The primers have been described elsewhere (3, 5), with the exception of those for iucC (aerplus.1, 5′-TGGACGCTGAAACCTGGCTTACGCAACTGT-3′; aerplus.2, 5′-CACGAAGTGACCCGTCTGCAAATCATGGAT-3′), which were slightly modified to obtain a product of 287 bp easily resolved from other amplicons by gel electrophoresis. Each primer was used at a final concentration of 1 μM, except for the hlyC, fyuA, and iroN primers (2 μM). PCR was performed with an iCycler thermal cycler (Bio-Rad, Marnes la Coquette, France) under the following conditions: DNA denaturation and polymerase activation for 15 min at 95°C; 30 cycles of 30 s at 94°C, 90 s at 55°C, and 90 s at 72°C; and a final extension step for 10 min at 72°C. Samples were electrophoresed in 3% Resophor gels (Eurobio, France) and then stained with ethidium bromide and photographed with UV transillumination. For each run of PCR a mixed bacterial lysate of strains RS218 and S88 was used as a positive control (5). The new multiplex PCR method was applied to all the strains, and its performance was compared with that of a monoplex standard PCR on the isolates from nonbacteremic patients (4). Hemolysin production was tested on sheep blood agar plates: strains producing a clear halo after overnight culture at 37°C were considered hemolysin positive. Fisher's exact test was used to identify significant differences (P < 0.05), with Bonferroni adjustment when required (18).
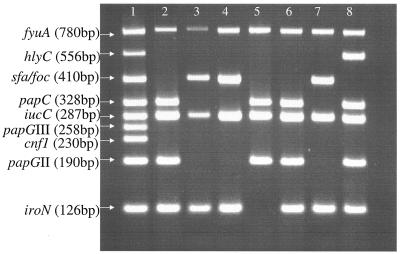
Thirty-two baby boys (mean age, 28 days; range, 8 to 80 days) with E. coli urosepsis and no major urinary tract abnormalities were identified from the hospital records. They were compared with a previously described cohort of 51 febrile baby boys (mean age, 38 days; range, 6 to 88 days) with nonbacteremic UTI and no major urinary tract abnormalities. Examples of results obtained with our new nonaplex PCR method are shown in Fig. 1 for seven different isolates. Overall, the results were in perfect agreement with our previously published results for the isolates from nonbacteremic patients. The phylogenetic group, subgroup, and virulence factor distributions in the two E. coli collections are shown in Table 1. The phylogenetic groups and subgroups were similarly distributed in the two collections. Overall, virulence factors were more frequent in bacteremic than nonbacteremic strains, but none of the differences for a given factor was statistically significant. As the differences in the frequencies of three virulence factors (antigen K1, hlyC, and iroN) exceeded 10%, we then examined the distributions of these three factors in a pairwise manner. Two pairs (hlyC and/or antigen K1; hlyC and/or iroN) had P values below 0.05 (Table 1), but only the pair hlyC and/or antigen K1 was significantly more frequent in bacteremic strains than in nonbacteremic strains after Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons (P = 0.005 × 3 = 0.015). The negative and positive predictive values for bacteremia of these two factors were 86% and 47%, respectively. The presence of the hlyC gene correlated with a hemolytic phenotype on blood agar (not shown).
FIG. 1.
Resophor gel showing multiplex PCR products corresponding to nine virulence genes. Lane 1, positive control DNA; lanes 2 to 8, amplification results of lysates of seven different UTI isolates.
TABLE 1.
Distribution of phylogenetic groups and subgroups, serogroups, and virulence factors in E. coli isolates from male infants with bacteremic and nonbacteremic UTI
| Variable | No. (%) of isolates
|
Pa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 83) | Bacteremic UTI (n = 32) | Nonbacteremic UTI (n = 51) | ||
| Phylogenetic groups and subgroupsb | ||||
| Group A | 3 (4) | 1 (3) | 2 (4) | 1 |
| Group B2 | 63 (76) | 27 (84) | 36 (71) | 0.15 |
| Subgroup II | 28 (34) | 12 (37) | 16 (31) | 0.56 |
| Subgroup I | 21 (25) | 11 (34) | 10 (19) | 0.13 |
| Subgroup III | 10 (12) | 4 (12) | 6 (12) | 1 |
| Subgroup IX | 2 (2) | 0 | 2 (4) | 0.52 |
| Subgroup UD | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (2) | 1 |
| Subgroup X | 1 (1) | 0 | 1 (2) | 1 |
| Group D | 17 (20) | 4 (12) | 13 (25) | 0.15 |
| Virulence factors | ||||
| Antigen K1 | 33 (40) | 15 (47) | 18 (35) | 0.29 |
| cnf1 | 21 (25) | 9 (28) | 12 (24) | 0.63 |
| hly | 35 (42) | 16 (50) | 19 (37) | 0.25 |
| papC | 72 (87) | 29 (90) | 43 (84) | 0.40 |
| papGII (without papGIII) | 56 (67) | 23 (72) | 33 (65) | 0.49 |
| papGIII (without papGII) | 5 (6) | 2 (6) | 3 (6) | 1 |
| papGII with papGIII | 11 (13) | 4 (12) | 7 (14) | |
| sfa/foc | 30 (36) | 12 (37) | 18 (35) | 0.83 |
| iutA | 70 (84) | 28 (87) | 42 (82) | 0.53 |
| iroN | 59 (71) | 25 (78) | 34 (67) | 0.26 |
| fyuA | 80 (96) | 31 (97) | 49 (96) | 1 |
| hly and/or antigen K1 | 61 (73) | 29 (90) | 32 (63) | 0.005 |
| hly and/or iroN | 62 (75) | 28 (87) | 34 (67) | 0.03 |
| Antigen K1 and/or iroN | 65 (78) | 28 (87) | 37 (73) | 0.72 |
P values (Fisher's exact test) for comparisons between bacteremic and nonbacteremic isolates.
Phylogenetic groups and subgroups were determined by PCR and ribotyping, respectively. Each subgroup corresponds to a different ribotyping pattern, as described in reference 3, except for subgroup UD (“undescribed”).
To our knowledge, this is the first pediatric study of the role of E. coli virulence factors in bacteremic versus nonbacteremic UTI. Studies of adult patients (10, 19, 20) did not characterize the E. coli strains at the phylogenetic level or analyze such a large panel of genetic determinants. We used a new multiplex PCR method to detect nine common virulence genes. This is the most powerful multiplex PCR method described to date for molecular investigation of extraintestinal E. coli virulence, and it may facilitate the characterization of other strain collections.
The distribution of individual virulence determinants did not differ significantly between the bacteremic and nonbacteremic strains in our study. Likewise, Ikaheimo et al. found no significant differences in the distributions of P fimbria expression, hemolysin production, or the K serotype between E. coli isolates from bacteremic and nonbacteremic women with UTI (10). In contrast, Otto et al., in a similar study, investigated the distribution of P fimbriation, hemolysin production, serum resistance, and the K1 serotype and found a higher frequency of P fimbriation among urinary isolates from bacteremic women (19).
Interestingly, when we analyzed pairwise associations of the virulence factors, we found that K1 antigen and/or the hemolysin gene was significantly more frequent in bacteremic than nonbacteremic strains. Capsular antigen K1 is known to play a key role in E. coli survival in blood, as it is a major determinant of serum resistance (16, 17). Likewise, hemolysin is involved in the extraintestinal virulence of E. coli (24) and may damage human renal epithelial cells, facilitating passage of bacteria through the epithelial barrier (13, 23). However, among our 61 strains harboring K1 and/or hemolysin, only 7 (10%) harbored both factors (not shown). Although both determinants may play a key role in bacteremia, they tended to be mutually exclusive in our collection, suggesting mutual incompatibility. This apparent mutual exclusion is in accordance with the previous report of Johnson and Stell (12) and remains to be explained.
In conclusion, this study suggests that the absence of hemolysin and capsular antigen K1 has a negative predictive value for bacteremia in baby boys with E. coli urinary tract infection. Both factors can readily be screened for by using phenotypic methods; indeed, we observed a perfect correlation between hlyC gene detection and hemolysis on blood agar plates. Given the risk of bacteremia with UTI in young male infants and the inability to distinguish clinically patients with or without bacteremia, the finding of a K1- and hemolysin-negative E. coli isolate in urine may secure therapy and reduce the cost, permitting the earliest switch to oral antibiotic treatment and hospital discharge.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bachur, R., and G. L. Caputo. 1995. Bacteremia and meningitis among infants with urinary tract infections. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 11:280-284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bingen, E., B. Picard, N. Brahimi, S. Mathy, P. Desjardins, J. Elion, and E. Denamur. 1998. Phylogenetic analysis of Escherichia coli strains causing neonatal meningitis suggests horizontal gene transfer from a predominant pool of highly virulent B2 group strains. J. Infect. Dis. 177:642-650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bingen-Bidois, M., O. Clermont, S. Bonacorsi, M. Terki, N. Brahimi, C. Loukil, D. Barraud, and E. Bingen. 2002. Phylogenetic analysis and prevalence of urosepsis strains of Escherichia coli bearing pathogenicity island-like domains. Infect. Immun. 70:3216-3226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bonacorsi, S., S. Lefevre, O. Clermont, V. Houdouin, A. Bourrillon, C. Loirat, Y. Aujard, and E. Bingen. 2005. Escherichia coli strains causing urinary tract infection in uncircumcised infants resemble urosepsis-like adult strains. J. Urol. 173:195-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bonacorsi, S. P., O. Clermont, V. Houduoin, C. Cordevant, N. Brahimi, A. Marecat, C. Tinsley, X. Nassif, M. Lange, and E. Bingen. 2003. Molecular analysis and experimental virulence of French and North American Escherichia coli neonatal meningitis isolates; identification of new virulent clone. J. Infect. Dis. 187:1895-1906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Crain, E. F., and J. C. Gershel. 1990. Urinary tract infections in febrile infants younger than 8 weeks of age. Pediatrics 86:363-367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ginsburg, C. M., and G. H. McCracken, Jr. 1982. Urinary tract infections in young infants. Pediatrics 69:409-412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hoberman, A., E. R. Wald, R. W. Hickey, M. Baskin, M. Charron, M. Majd, D. H. Kearney, E. A. Reynolds, J. Ruley, and J. E. Janosky. 1999. Oral versus initial intravenous therapy for urinary tract infections in young febrile children. Pediatrics 104:79-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Honkinen, O., T. Jahnukainen, J. Mertsola, J. Eskola, and O. Ruuskanen. 2000. Bacteremic urinary tract infection in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 19:630-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ikaheimo, R., A. Siitonen, U. Karkkainen, J. Mustonen, T. Heiskanen, and P. H. Makela. 1994. Community-acquired pyelonephritis in adults: characteristics of E. coli isolates in bacteremic and non-bacteremic patients. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 26:289-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Johnson, J. R., and T. A. Russo. 2002. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: “the other bad E coli.” J. Lab. Clin. Med. 139:155-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Johnson, J. R., and A. L. Stell. 2000. Extended virulence genotypes of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urosepsis in relation to phylogeny and host compromise. J. Infect. Dis. 181:261-272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kaper, J. B., J. P. Nataro, and H. L. Mobley. 2004. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:123-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kaplan, R. L., M. B. Harper, M. N. Baskin, A. B. Macone, and K. D. Mandl. 2000. Time to detection of positive cultures in 28- to 90-day-old febrile infants. Pediatrics 106:E74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kellogg, J. A., F. L. Ferrentino, M. H. Goodstein, J. Liss, S. L. Shapiro, and D. A. Bankert. 1997. Frequency of low level bacteremia in infants from birth to two months of age. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 16:381-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kim, K. S., H. Itabashi, P. Gemski, J. Sadoff, R. L. Warren, and A. S. Cross. 1992. The K1 capsule is the critical determinant in the development of Escherichia coli meningitis in the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 90:897-905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Leying, H., S. Suerbaum, H. P. Kroll, D. Stahl, and W. Opferkuch. 1990. The capsular polysaccharide is a major determinant of serum resistance in K-1-positive blood culture isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 58:222-227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Olsen, C. H. 2003. Review of the use of statistics in infection and immunity. Infect. Immun. 71:6689-6692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Otto, G., M. Magnusson, M. Svensson, J. Braconier, and C. Svanborg. 2001. pap genotype and P fimbrial expression in Escherichia coli causing bacteremic and nonbacteremic febrile urinary tract infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32:1523-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Otto, G., T. Sandberg, B. I. Marklund, P. Ulleryd, and C. Svanborg. 1993. Virulence factors and pap genotype in Escherichia coli isolates from women with acute pyelonephritis, with or without bacteremia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 17:448-456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pitetti, R. D., and S. Choi. 2002. Utility of blood cultures in febrile children with UTI. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 20:271-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rushton, H. G. 1997. Urinary tract infections in children. Epidemiology, evaluation, and management. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 44:1133-1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Trifillis, A. L., M. S. Donnenberg, X. Cui, R. G. Russell, S. J. Utsalo, H. L. Mobley, and J. W. Warren. 1994. Binding to and killing of human renal epithelial cells by hemolytic P-fimbriated E. coli. Kidney Int. 46:1083-1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Welch, R. A., E. P. Dellinger, B. Minshew, and S. Falkow. 1981. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal Escherichia coli infections. Nature 294:665-667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wiswell, T. E., and W. E. Hachey. 1993. Urinary tract infections and the uncircumcised state: an update. Clin. Pediatr. 32:130-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]