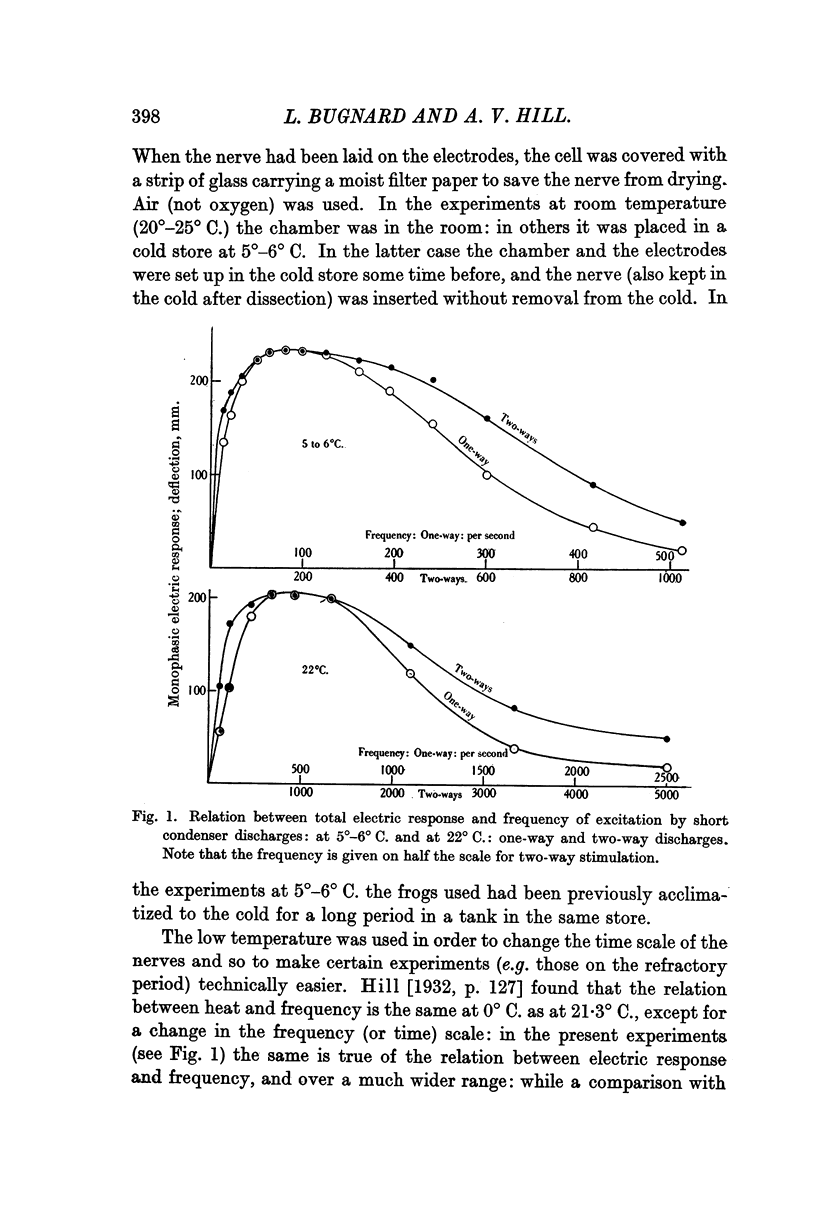
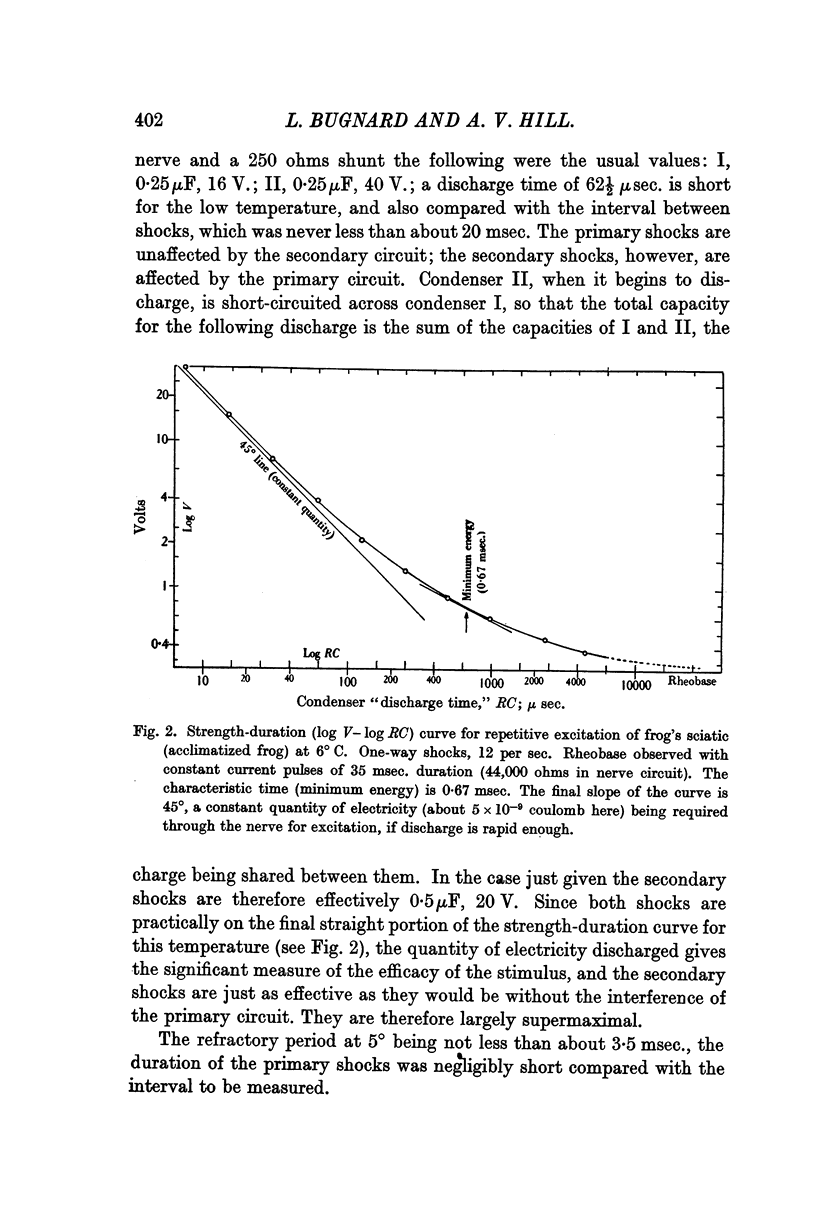
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogue J. Y., Rosenberg H. The rate of development and spread of electrotonus. J Physiol. 1934 Oct 17;82(3):353–368. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugnard L. "Inhibition" in medullated nerve. J Physiol. 1934 Feb 28;80(4):441–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. W., Hill A. V., Zotterman Y. The effect of frequency of stimulation on the heat production of nerve. J Physiol. 1927 Jul 7;63(2):130–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1927.sp002388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. Repetitive stimulation by commutator and condenser. J Physiol. 1934 Nov 12;82(4):423–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. Strength-duration curves for repetitive stimulation of medullated nerve. J Physiol. 1934 Oct 17;82(3):321–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


