Full text
PDF






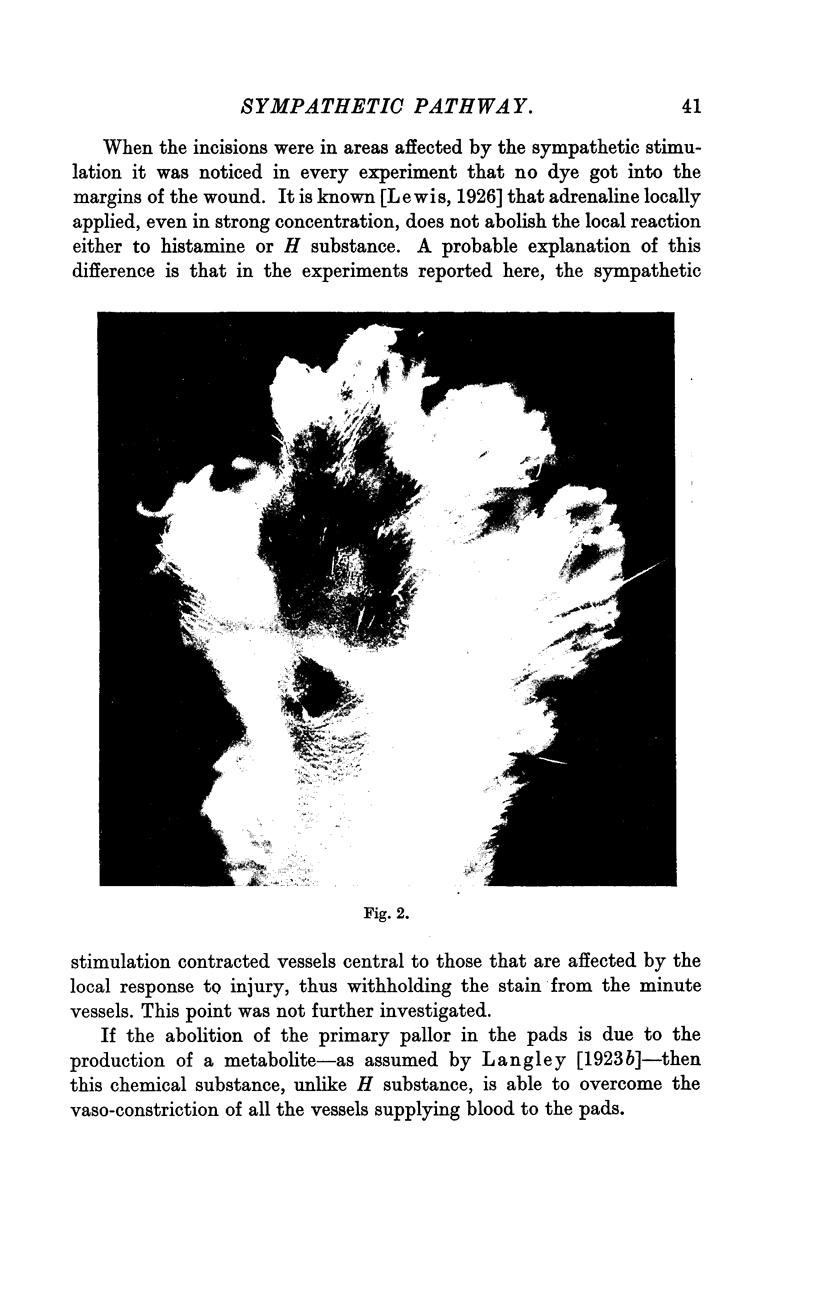


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Langley J. N. Antidromic action: Part II. Stimulation of the peripheral nerves of the cat's hind foot. J Physiol. 1923 Oct 22;58(1):49–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1923.sp002100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. N. The origin and course of the vaso-motor fibres of the frog's foot. J Physiol. 1911 Jan 27;41(6):483–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1911.sp001413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. N. The vascular dilatation caused by the sympathetic and the course of vaso-motor nerves. J Physiol. 1923 Oct 22;58(1):70–73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1923.sp002101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter W., Davies H. M. Experimental studies in the innervation of the skin. J Physiol. 1909 Feb 9;38(2-3):134–246.1. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1909.sp001299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]