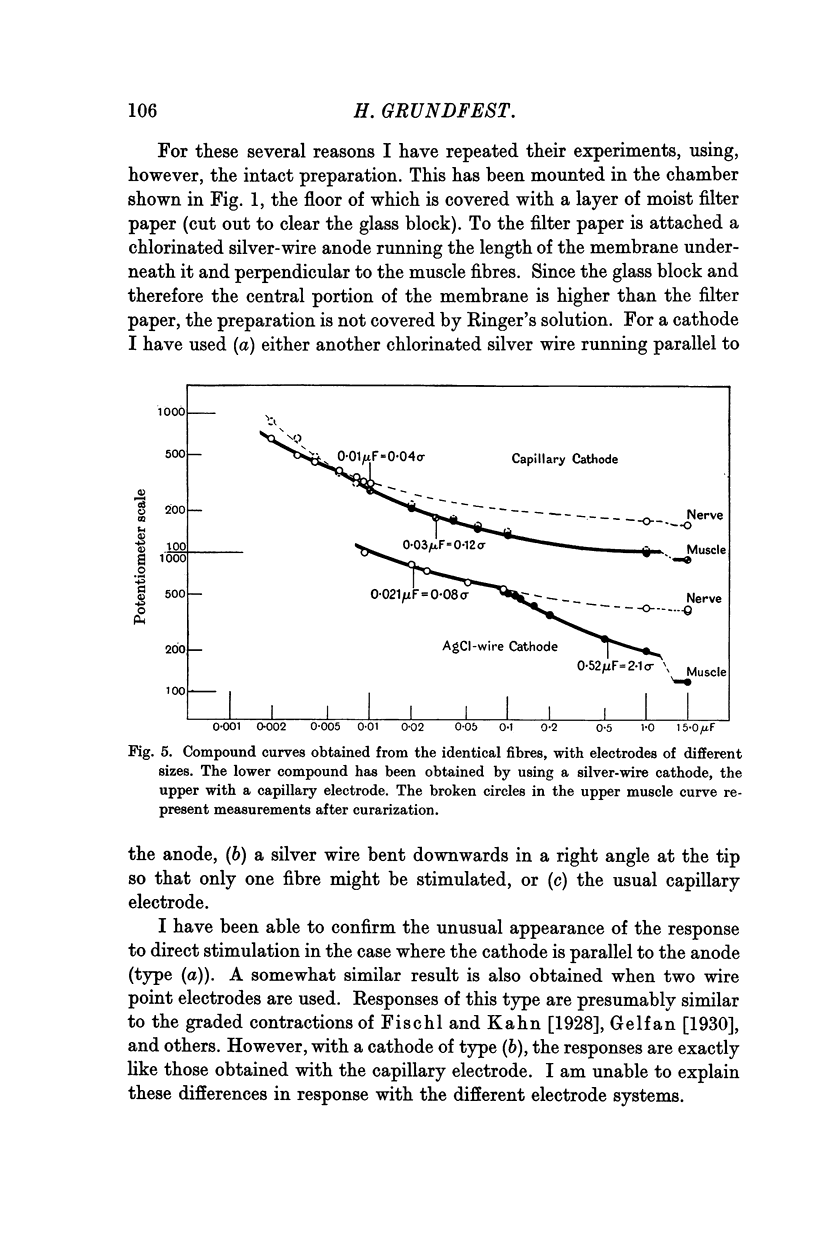
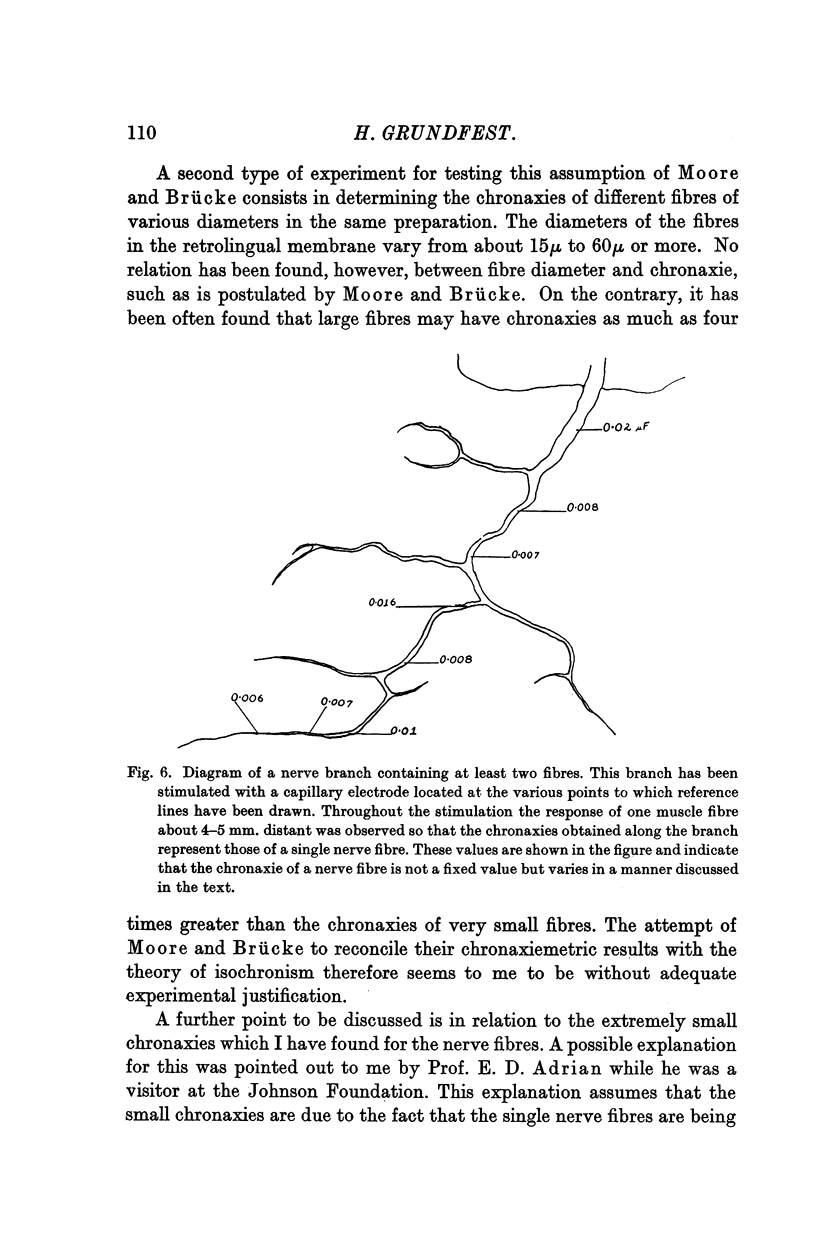
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lapicque L. On electric stimulation of muscle through ringer's solution. J Physiol. 1931 Nov 14;73(3):219–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas K. The excitable substances of amphibian muscle. J Physiol. 1907 Nov 29;36(2-3):113–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1907.sp001222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt F. H., Reid M. A. A METHOD FOR WORKING ON THE TERMINAL NERVE-MUSCLE UNIT. Science. 1930 Oct 24;72(1869):431–433. doi: 10.1126/science.72.1869.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton W. A. Excitable substances in the nerve-muscle complex. J Physiol. 1930 Dec 4;70(4):317–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton W. A. Identification of Lucas's alpha excitability. J Physiol. 1932 Aug 10;75(4):445–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1932.sp002903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton W. A. Lapicque's canonical strength duration curve. J Physiol. 1932 Apr 26;74(4):424–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1932.sp002859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton W. A. The normal presence of alpha and gamma excitabilities in the nerve-muscle complex. J Physiol. 1931 Jul 6;72(3):265–287. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts C. F. The effect of curari and denervation upon the electrical excitability of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1924 Oct 9;59(2-3):143–152. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1924.sp002171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


