Abstract
1. Granular fractions of high purity consisting of subcellular kallikrein- and amylase-storing organelles have been isolated from homogenates of guinea-pig submaxillary gland.
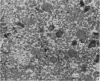
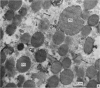
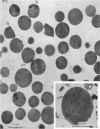
2. The isolated kallikrein- and amylase-containing granules closely resembled secretory granules observed in situ in serous acinar cells in intra-granular appearance, size and histochemical reaction.
3. The subcellular, histochemical and ultrastructural studies indicate that the serine protease, kallikrein, is like amylase an exocrine enzyme with a functional role in saliva.
Full text
PDF


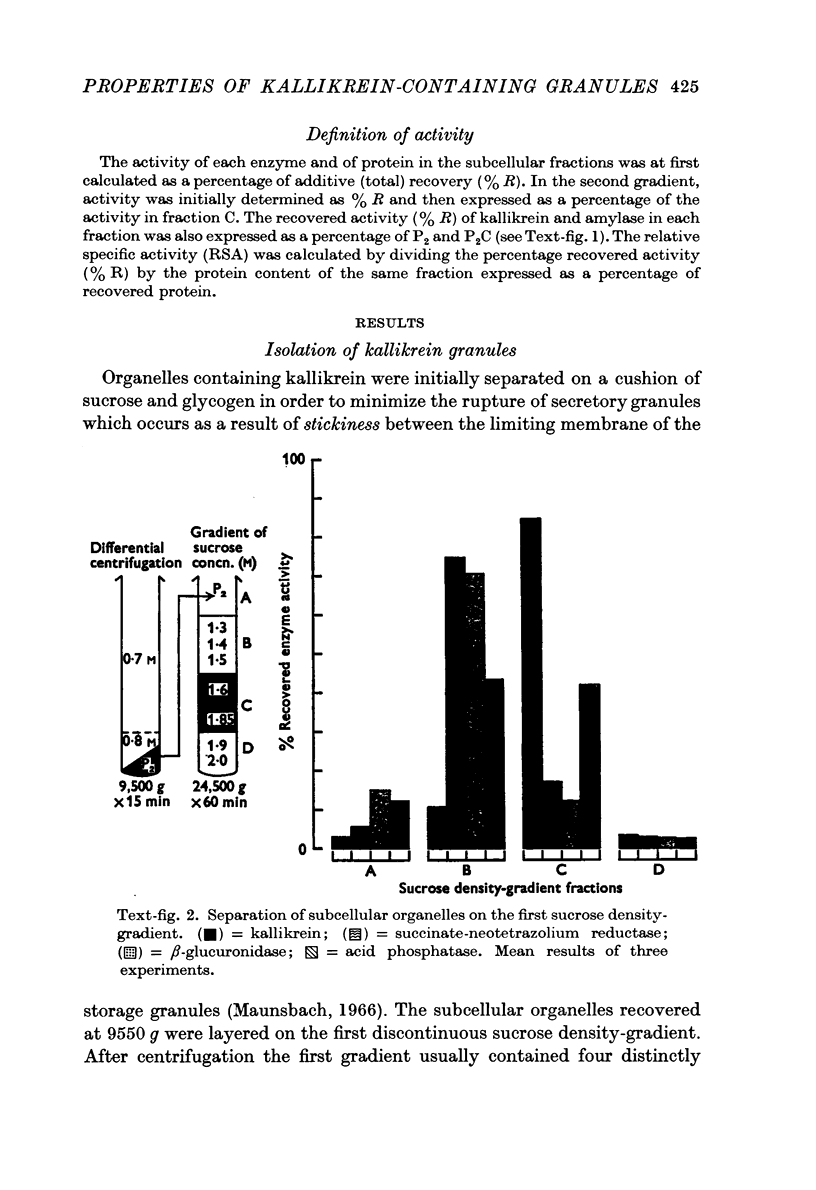
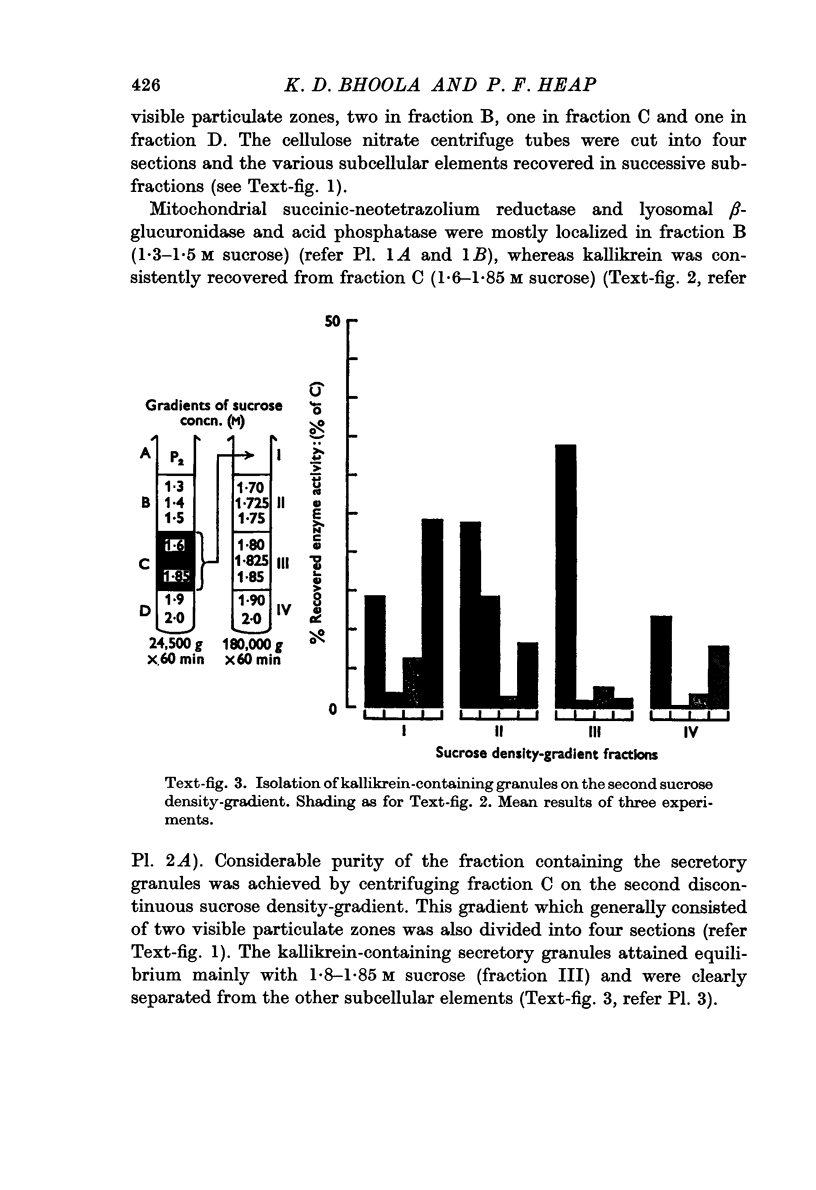

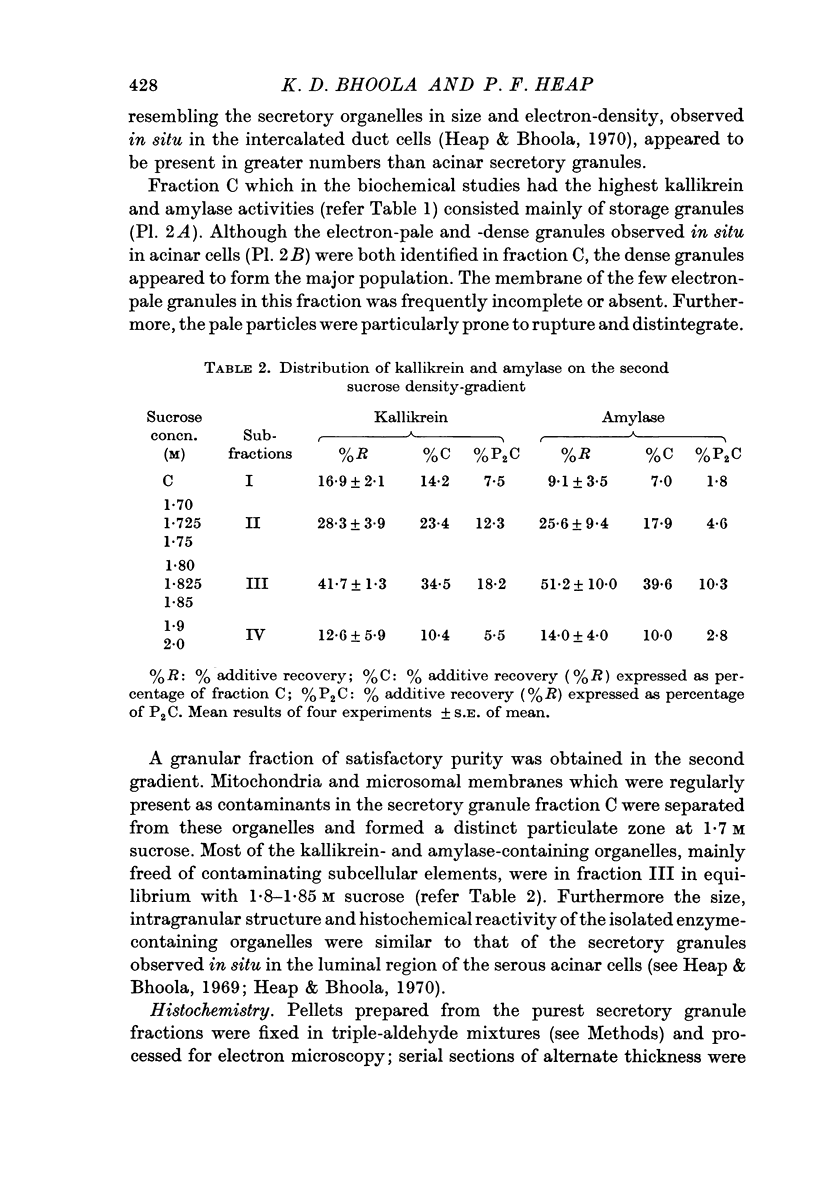




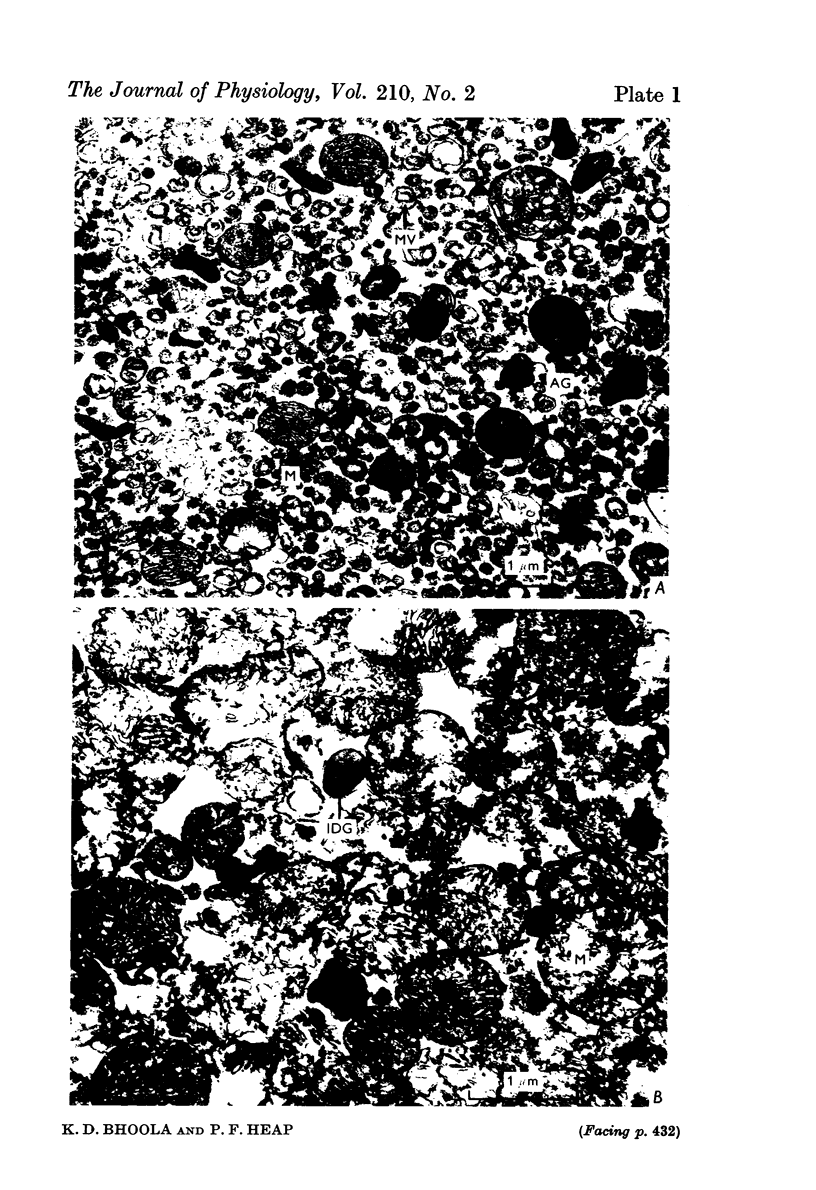
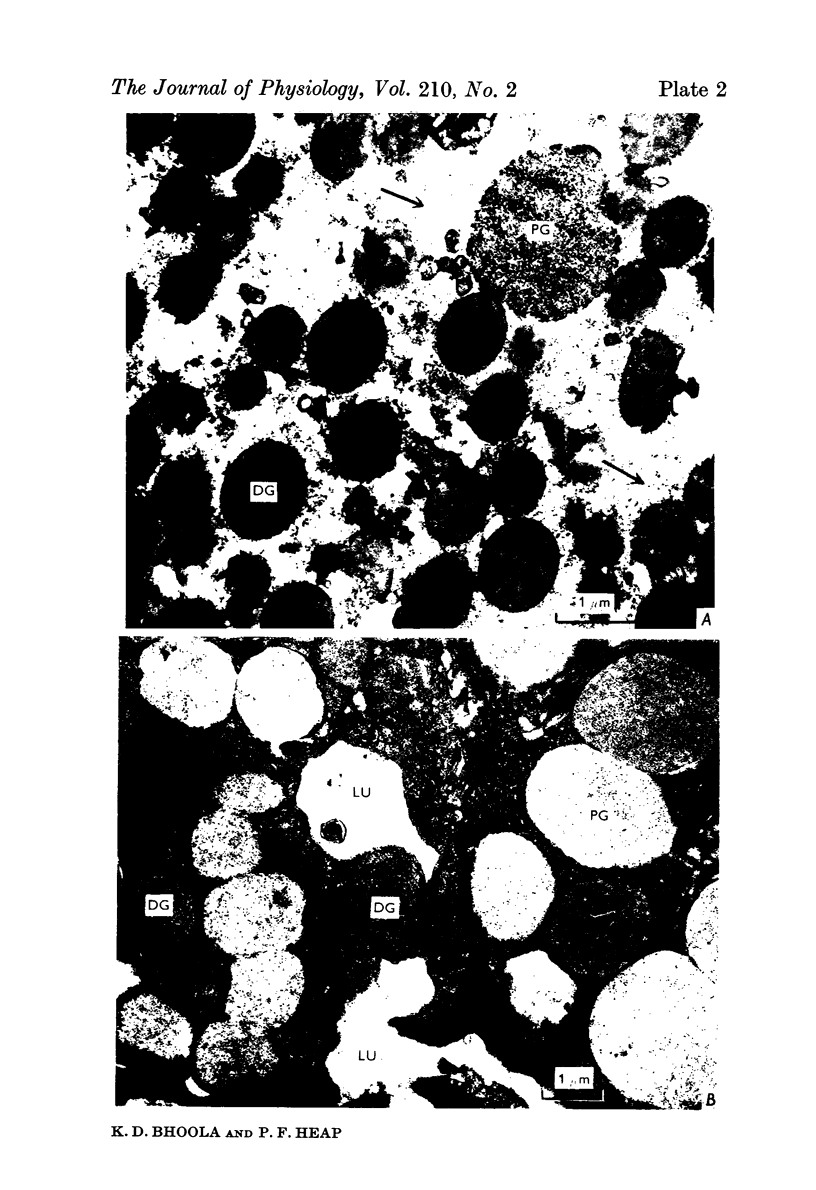
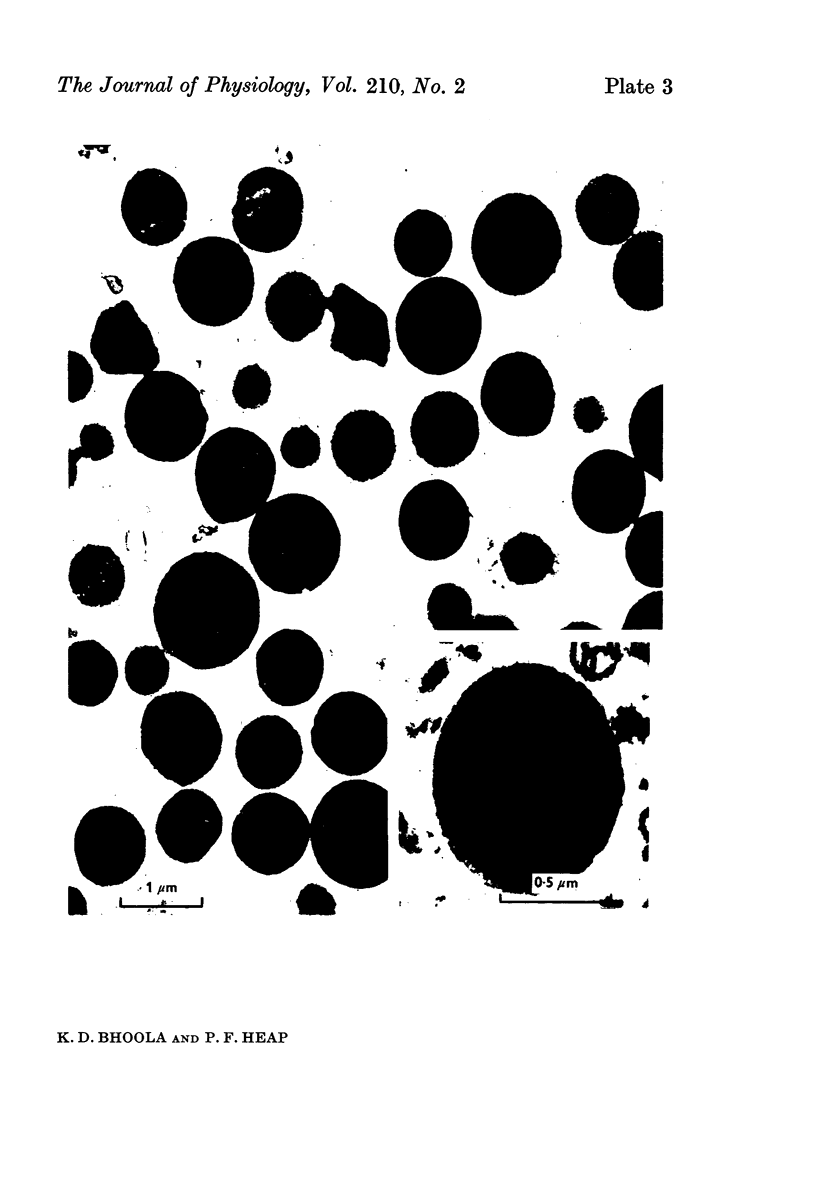
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhoola K. D., Heap P. F. Electron microscopy and histochemistry of isolated kallikrein granules. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;38(2):435P–436P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D. Intracellular distribution of submaxillary kallikrein. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(2):431–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhoola K. D., Ogle C. W. The subcellular localization of kallikrein, amylase and acetylcholine in the submaxillary gland of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(3):663–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekfors T. O., Hopsu-Havu V. K., Malniharju T. Increases vascular permeability caused by the trypsin-like enzymes purified from rat submandibular gland. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Jan-Feb;75(1):157–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Guimarāis J. A. Some observations on salivary secretion. J Physiol. 1935 Aug 22;85(1):15–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heap P. F., Bhoola K. D. Histochemical localization of kallikrein granules in the submaxillary gland of the guinea-pig. J Anat. 1969 Nov;105(Pt 3):525–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunsbach A. B. Isolation and purification of acid phosphatase-containing autofluorescent granules from homogenates of rat kidney cortex. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Sep;16(1):13–34. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P. J., Ekfors T. O., Hopsu V. K. Purification and characteristics of an alkaline protease from rat-submandibular gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 15;118(3):604–620. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER T. F., PLANTEROSE D. N. An assay procedure for a succinate-neotetrazolium-reductase system. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:591–596. doi: 10.1042/bj0740591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M. Kallikreins and kinins. Physiol Rev. 1969 Jul;49(3):509–547. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searcy R. L., Hayashi S., Hardy E. M., Berk J. E. The interaction of human serum protein fractions with the starch-iodine complex. Clin Chim Acta. 1965 Dec;12(6):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(65)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]