Abstract
1. The action of ions which increase the nerve spike duration at Ranvier's node has been studied at the neuromuscular junction of the frog.
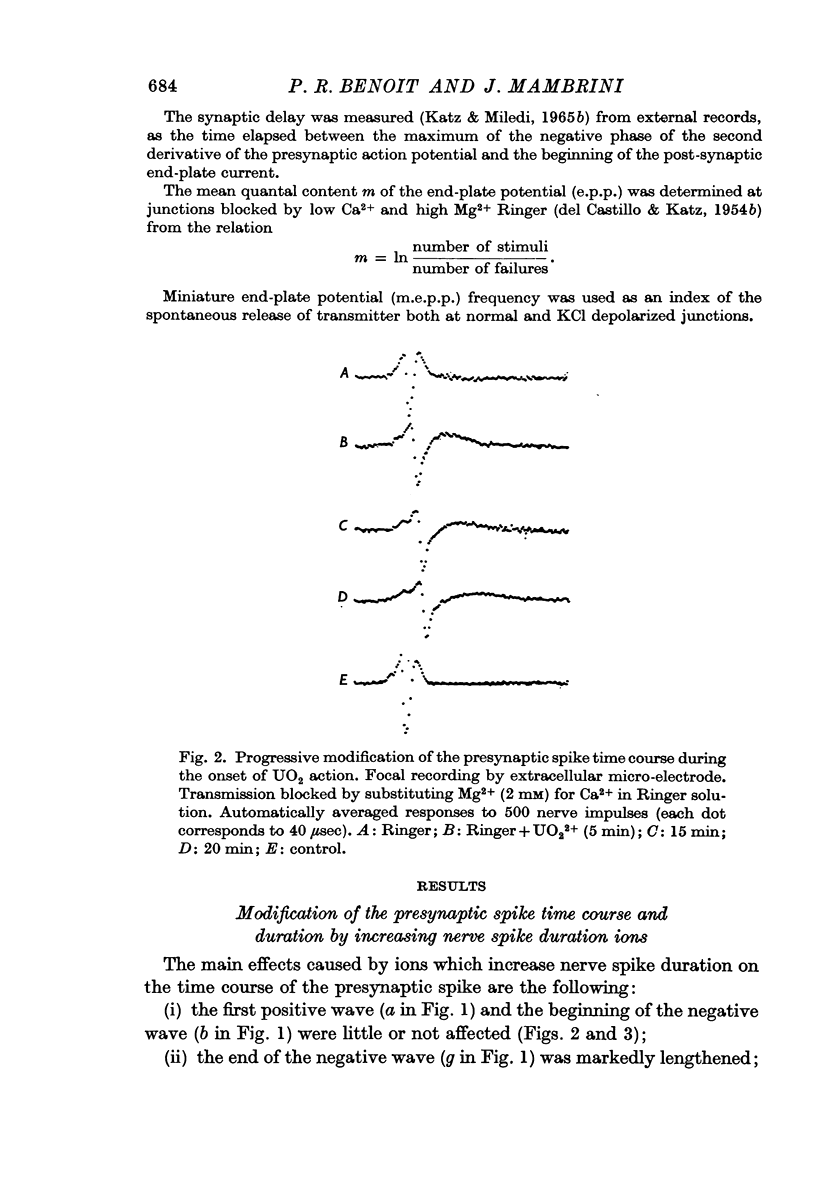
The duration of the presynaptic action potential is increased by UO2, Ni, Nz and TEA ions.
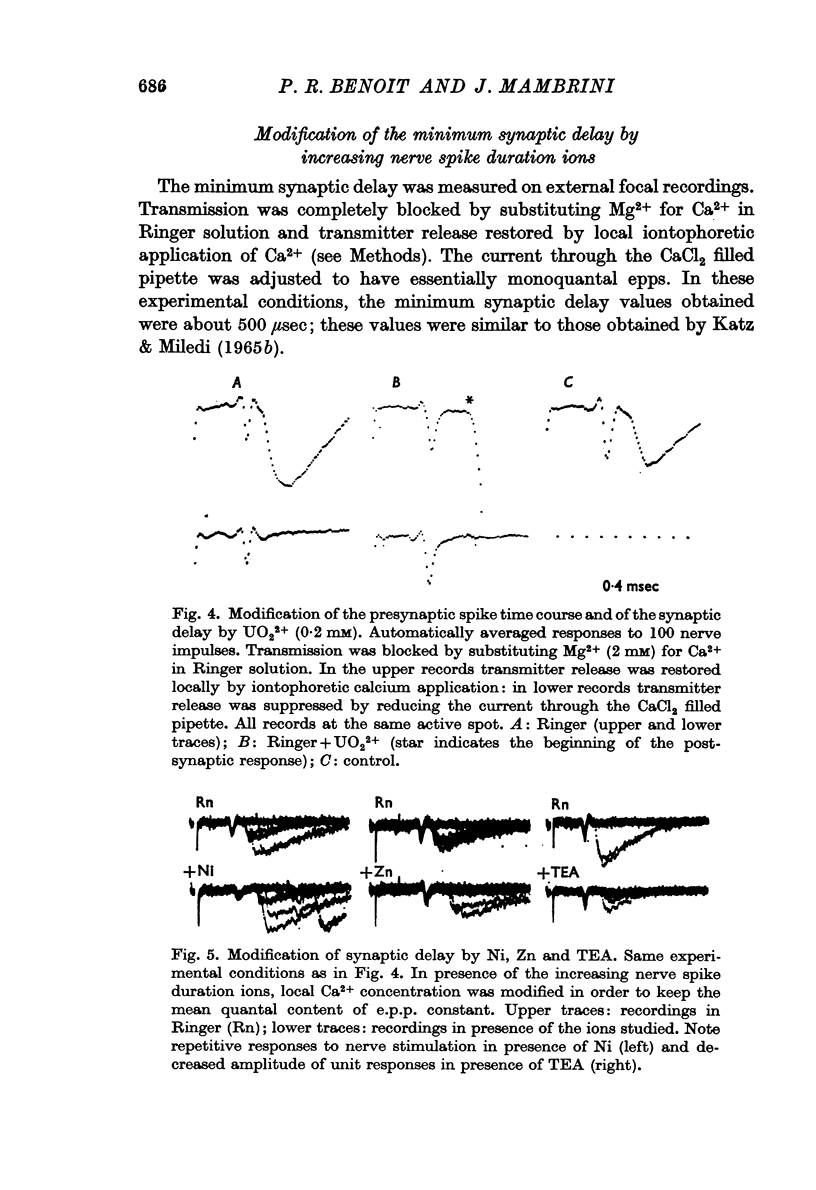
2. The release of transmitter after a nerve impulse is delayed and prolonged in the presence of the four ions, but the amount of evoked transmitter release estimated from the mean quantal content of e.p.p. is increased only by UO22+ and TEA. Both Ni2+ and Zn2+ decrease it.
3. The frequency of m.e.p.p.s is increased by UO22+ and decreased by Ni2+ and Zn2+ at KCl-depolarized junctions. It is not affected by TEA.
4. It has been concluded that the increased presynaptic spike duration is responsible for the delayed and prolonged transmitter release in the presence of ions which increase the nerve spike duration at Ranvier's node.
It is demonstrated that some `specific' effects possibly resulting from ionic competition for presynaptic sites between UO22+, Ni2+ or Zn2+ and other ions present in the Ringer may increase, interfere with, or hide the increased transmitter release that may be predicted from the lengthened presynaptic depolarization.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colomo F., Rahamimoff R. Interaction between sodium and calcium ions in the process of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(1):203–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Changes in end-plate activity produced by presynaptic polarization. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):586–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The effect of magnesium on the activity of motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):553–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Quastel D. M. Competition between sodium and calcium ions in transmitter release at mammalian neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):95–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Quastel D. M. Influence of sodium ions on transmitter release. Nature. 1965 Jun 5;206(988):1047–1048. doi: 10.1038/2061047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K. Action of tetraethylammonium chloride on neuromuscular transmission in frogs. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):213–218. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Modification of transmitter release by electrical interference with motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):1–7. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The effects of presynaptic polarization on the spontaneous activity at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):427–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEVES H. DIE WIRKUNG VON NICL2 AUF DEN ISOLIERTEN RANVIERSCHEN SCHNUERRING. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1963 Nov 11;278:273–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mambrini J., Benoit P. R. Action du nickel sur la libération du transmetteur à la jonction neuro-musculaire. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1967 Sep;161(3):524–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mambrini J., Benoit P. R. Modifications de la libération du médiateur à la jonction neuromusculaire sous l'action de l'ion uranyle. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Mar 11;266(11):1145–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Colomo F. Inhibitory action of sodium ions on transmitter release at the motor end-plate. Nature. 1967 Sep 9;215(5106):1174–1176. doi: 10.1038/2151174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPYROPOULOS C. S., BRADY R. O. Prolongation of response of node of Ranvier by metal ions. Science. 1959 May 15;129(3359):1366–1367. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3359.1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A., Isaacson A. Topochemical factors in potentiation of contraction by heavy metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):937–961. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Stämpfli R. Die Wirkung von Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid auf den einzelnen Ranvierschen Schnürring. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;287(4):311–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI H., MURAI T., SASAKI T. Some chemical aspect of plateau formation in the action current of the myelinated nerve fibre. Jpn J Physiol. 1960 Jun 29;10:280–291. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.10.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI H., USUDA S., EHARA S. Some factors influencing the plateau-formation in Co-treated or Nitreated single myelinated nerve fibres. Jpn J Physiol. 1962 Oct 15;12:545–559. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.12.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


