Abstract
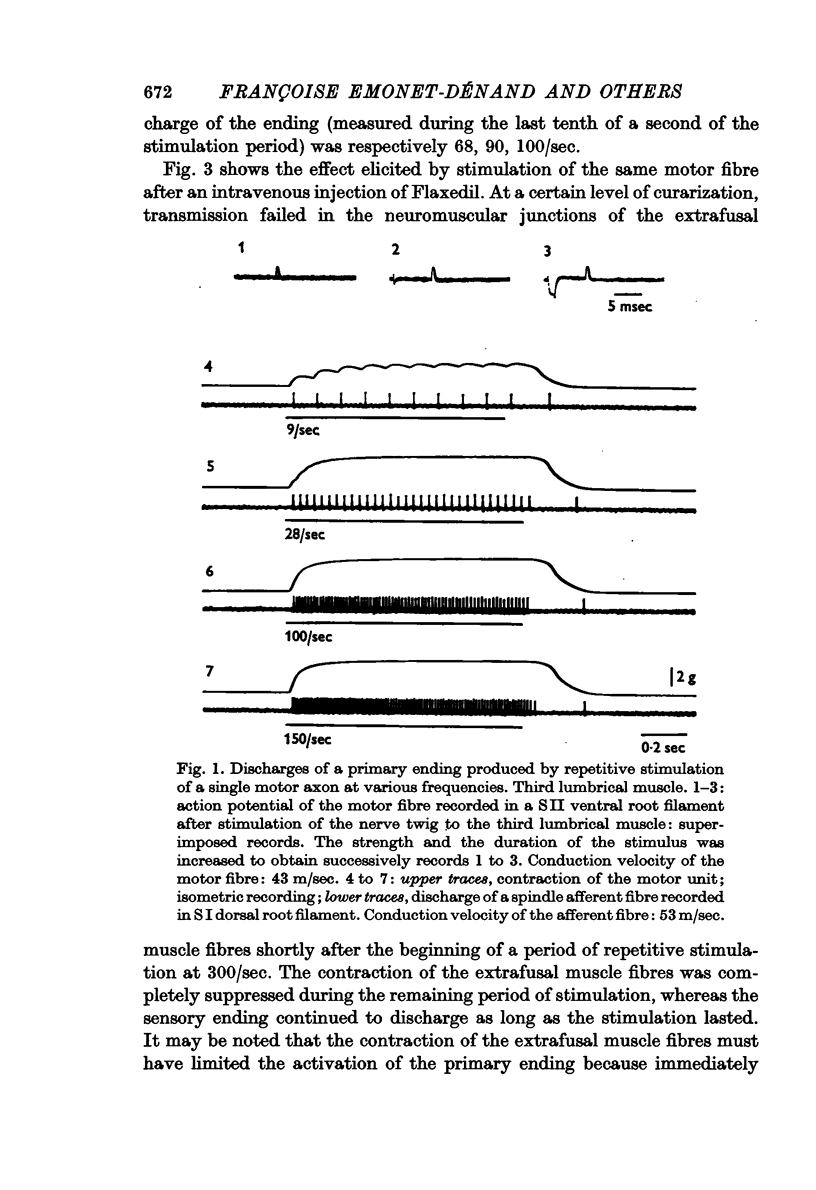
1. In rabbits, repetitive stimulation of single motor axons to lumbrical muscles elicits both a contraction of extrafusal muscle fibres and an increase in the discharge frequency of spindle primary endings.
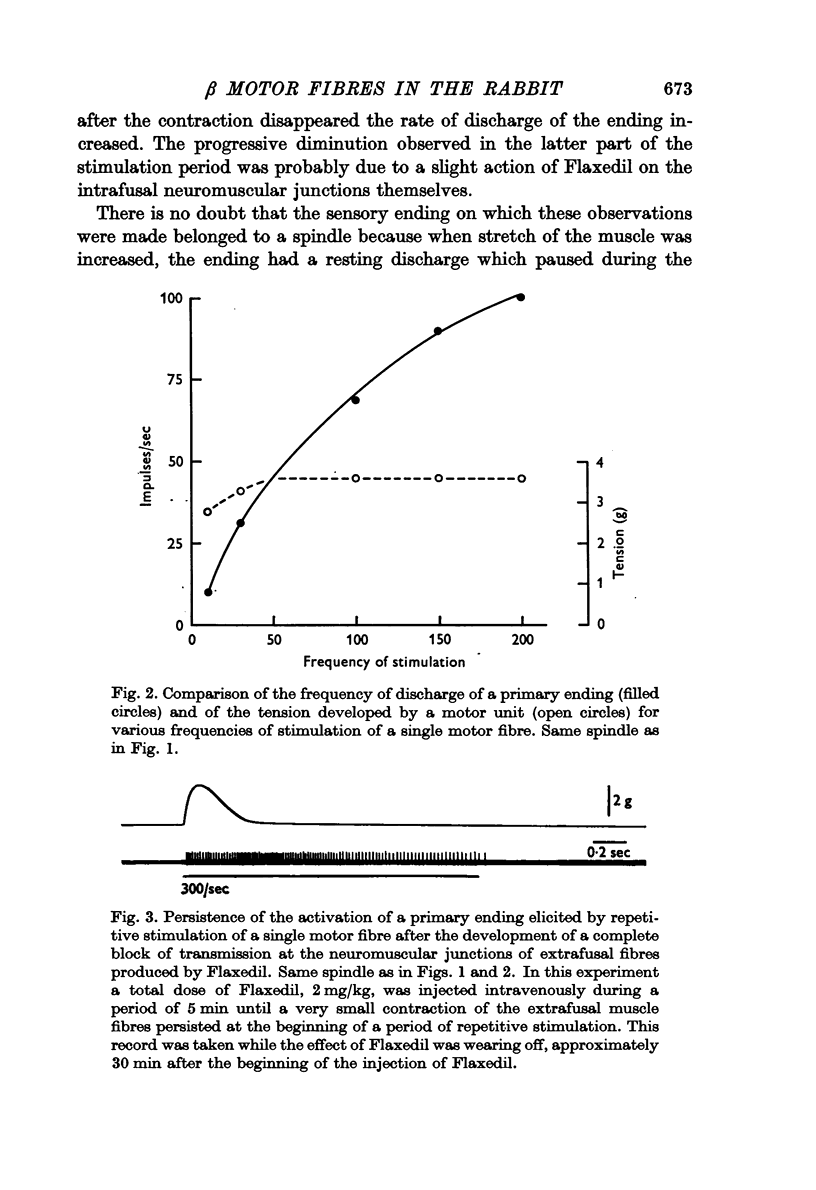
2. This activation of the sensory endings can be attributed to the contraction of intrafusal muscle fibres because it persists after the contraction of extrafusal muscle fibres has been suppressed by selective curarization of their neuromuscular junctions.
3. In non-curarized preparations the frequency of most of the afferent discharges continues to increase when rates of stimulation of motor fibres exceed the tetanic fusion frequency of the extrafusal muscle fibres.
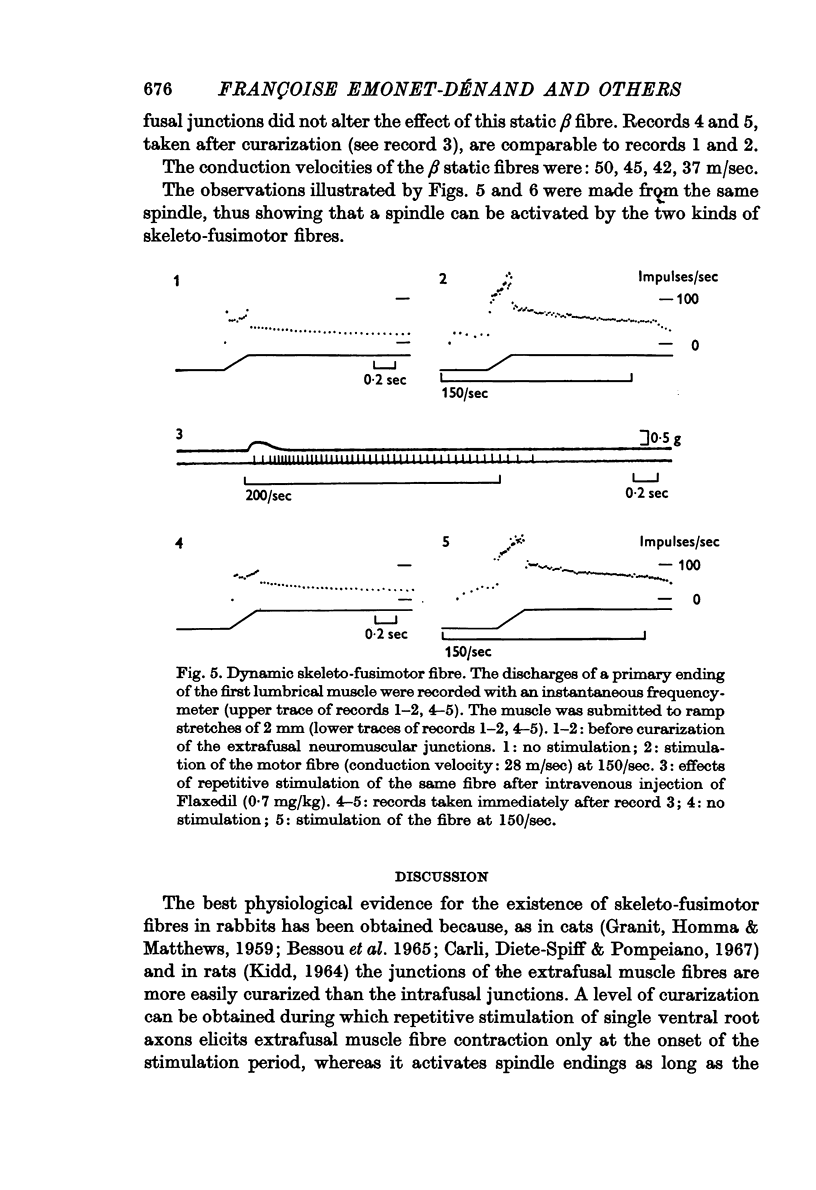
4. The effect of repetitive stimulation of motor fibres that supply extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibres was studied on the responses of primary endings to phasic stretch. Of twelve fibres, eight were found to exert a dynamic effect and four a static one.
5. Selective curarization of the extrafusal neuromuscular junctions does not modify the nature of the static and dynamic effects.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAL M. N., BARKER D. INTRAMUSCULAR BRANCHING OF FUSIMOTOR FIBRES. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:288–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKER D., HUNT J. P. MAMMALIAN INTRAFUSAL MUSCLE FIBRES. Nature. 1964 Sep 12;203:1193–1193. doi: 10.1038/2031193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN M. C., CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF THE TIBIALIS POSTERIOR MUSCLE OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:140–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. L'innervation motrice du muscle strié des vertébrés. Actual Neurophysiol (Paris) 1968;8:23–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Motor fibres innervating extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):649–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. THE EFFECTS OF STIMULATION OF STATIC AND DYNAMIC FUSIMOTOR FIBRES ON THE RESPONSE TO STRETCHING OF THE PRIMARY ENDINGS OF MUSCLE SPINDLES. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:109–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carli G., Diete-Spiff K., Pompeiano O. Mechanisms of muscle spindle ex- citation. Arch Ital Biol. 1967 Jun;105(2):273–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvaja N., Pompeiano O. The differentiation of two types of intrafusal fibres in rabbit muscle spindles. An electron microscopic study. Pflugers Arch. 1970;317(3):187–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00586503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Jankowska E., Laporte Y. Mise en évidence de fibres squeletto-fusimotrices (fibres beta) dans les muscles lombricaux du lapin. J Physiol (Paris) 1969;61 (Suppl 2):285–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Frequencygrams of rabbit spindle primary endings elicited by stimulation of fusimotor fibres. J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):673–684. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Pagès B. Fibres fusimotrices statiques et fibres fusimotrices dynamiques, chez le lapin. Arch Ital Biol. 1966 Jun;104(2):195–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HOMMA S., MATTHEWS P. B. Prolonged changes in the discharge of mammalian muscle spindles following tendon taps or muscle twitches. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Jun 24;46:185–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD G. L. EXCITATION OF PRIMARY MUSCLE SPINDLE ENDINGS BY BETA-AXON STIMULATION. Nature. 1964 Sep 19;203:1248–1251. doi: 10.1038/2031248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS P. B., WESTBURY D. R. SOME EFFECTS OF FAST AND SLOW MOTOR FIBRES ON MUSCLE SPINDLES OF THE FROG. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:178–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro A. J., Beilin R. L. Histochemical duality of rabbit intrafusal fibers. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 May;17(5):348–349. doi: 10.1177/17.5.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Düring M., Andres K. H. Zur Feinstruktur der Muskelspindel von Mammalia. Anat Anz. 1969;124(5):566–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


