Abstract
1. The temperature dependence of the membrane potential of a molluscan giant neurone was examined under conditions which block the electrogenic activity of the Na—K exchange pump.
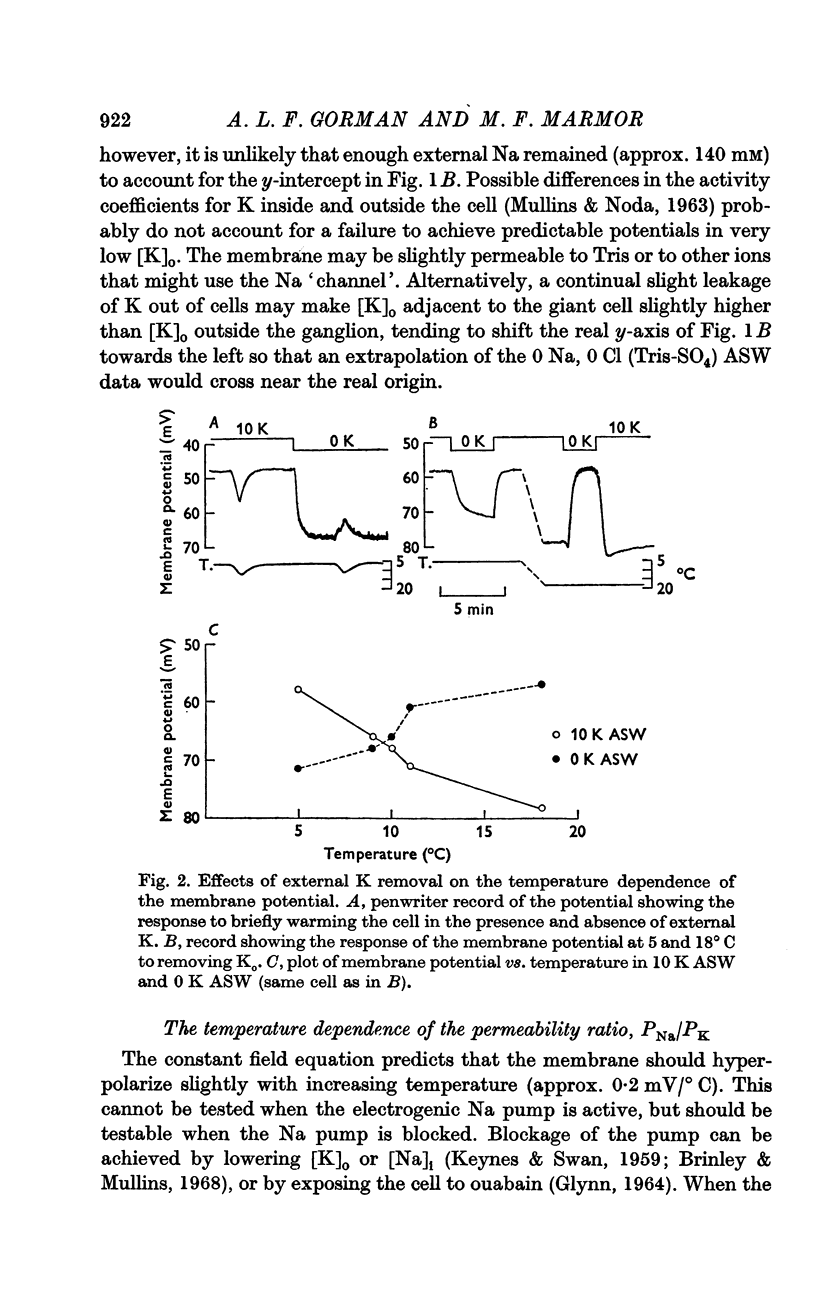
2. When the Na pump was blocked by ouabain or the removal of external K, the membrane potential depolarized as temperature was increased.
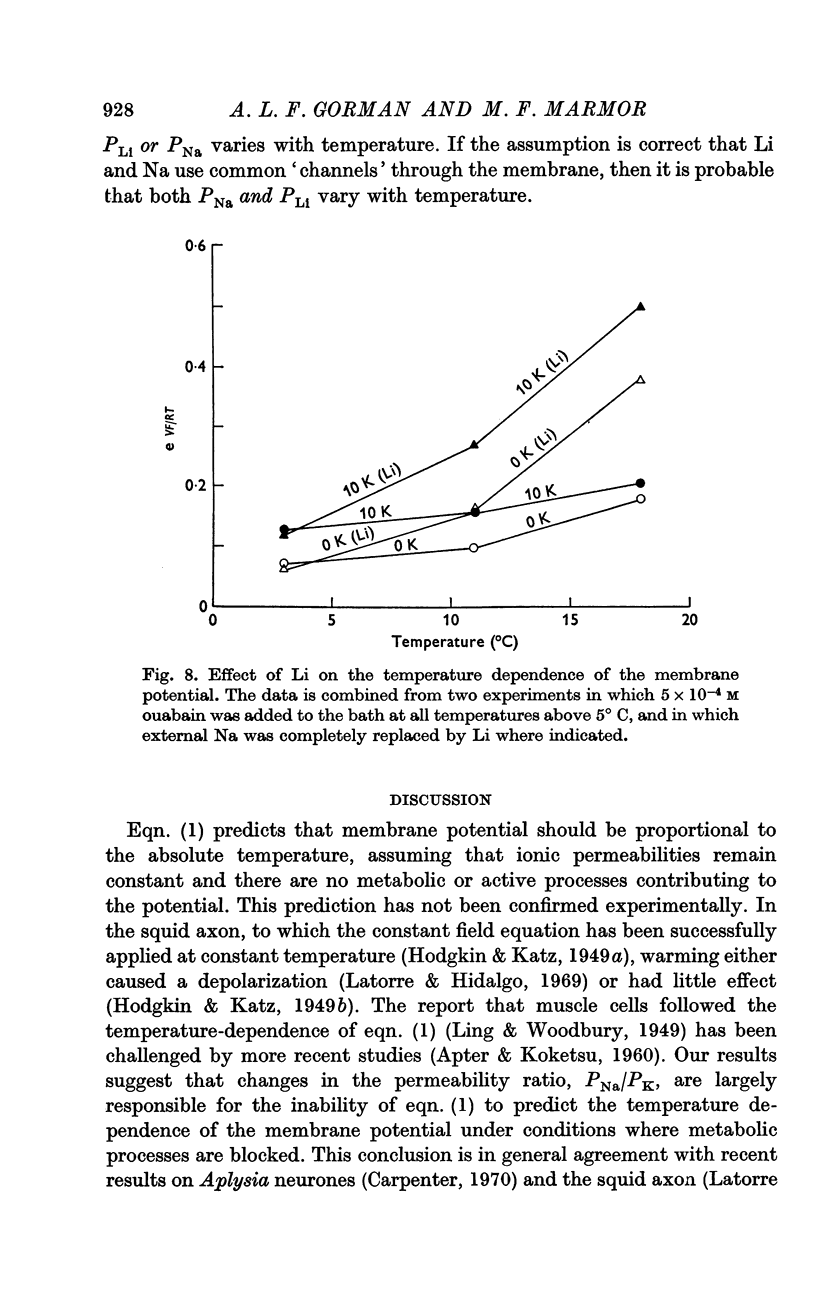
3. This depolarization was prevented by the replacement of external Na with impermeant cations, but was greater when Na was replaced with Li.
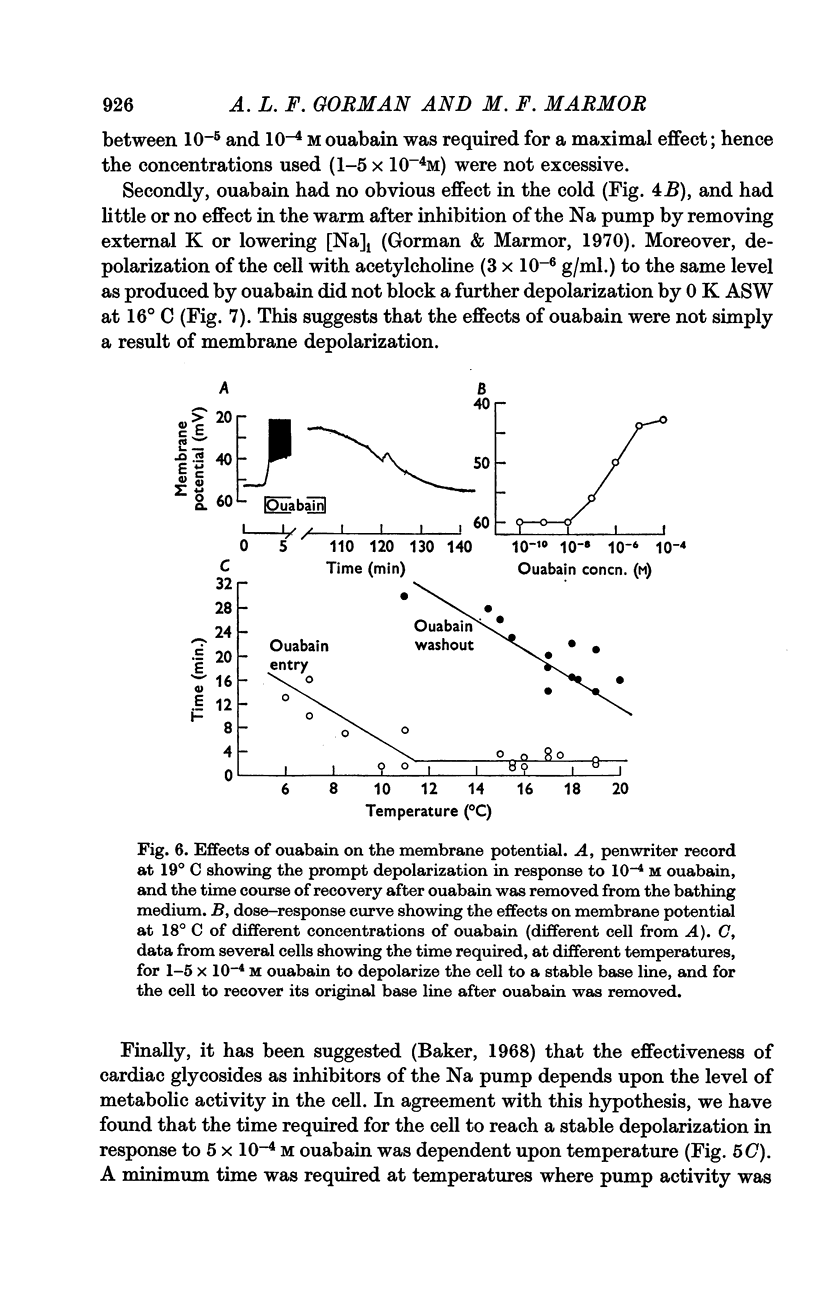
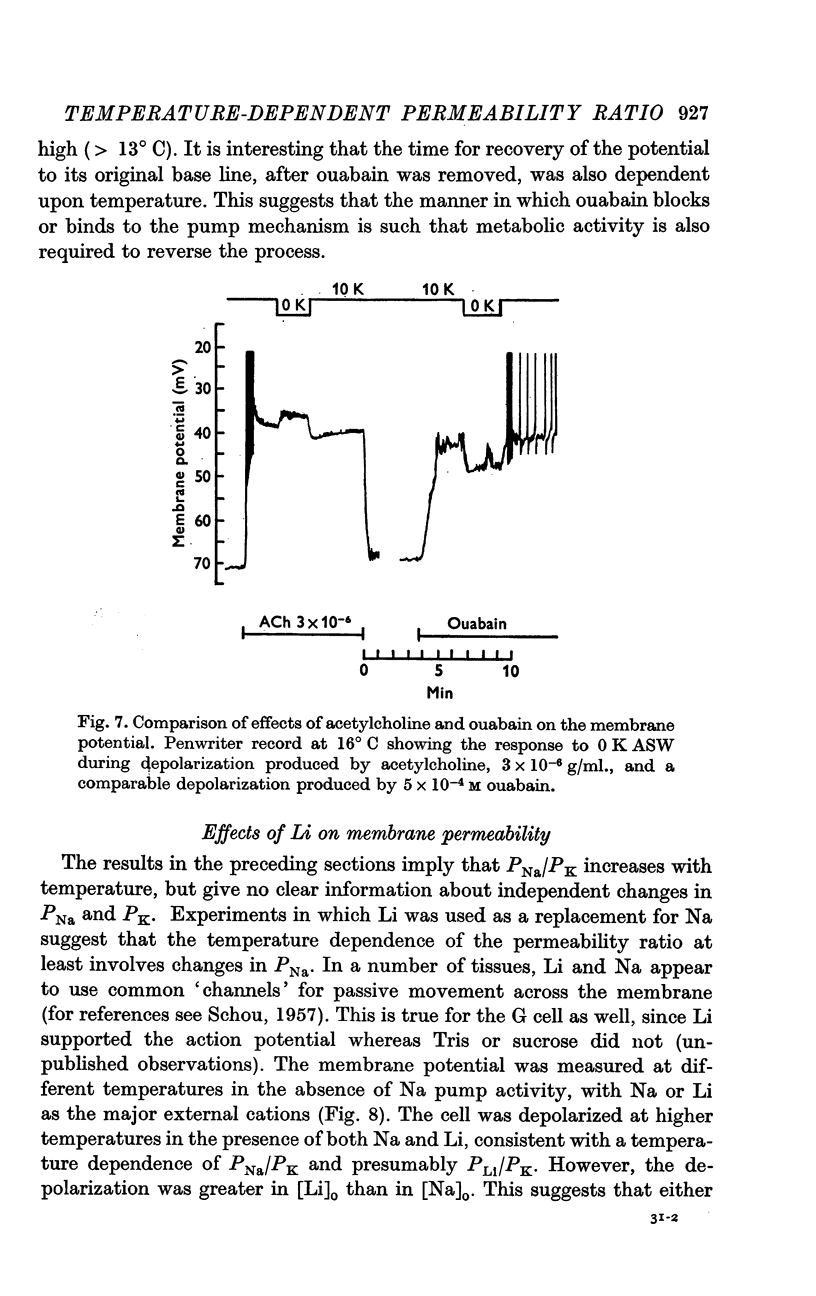
4. All observed effects of ouabain were attributable to inhibition of the Na pump. The depolarization in response to ouabain at warmer temperatures was completely reversible, and the rate of both onset and reversibility of the ouabain effect was dependent upon temperature.
5. Using a modified form of the constant field equation, the internal K concentration and the Na—K permeability ratio, PNa/PK, were calculated from the experimental data.
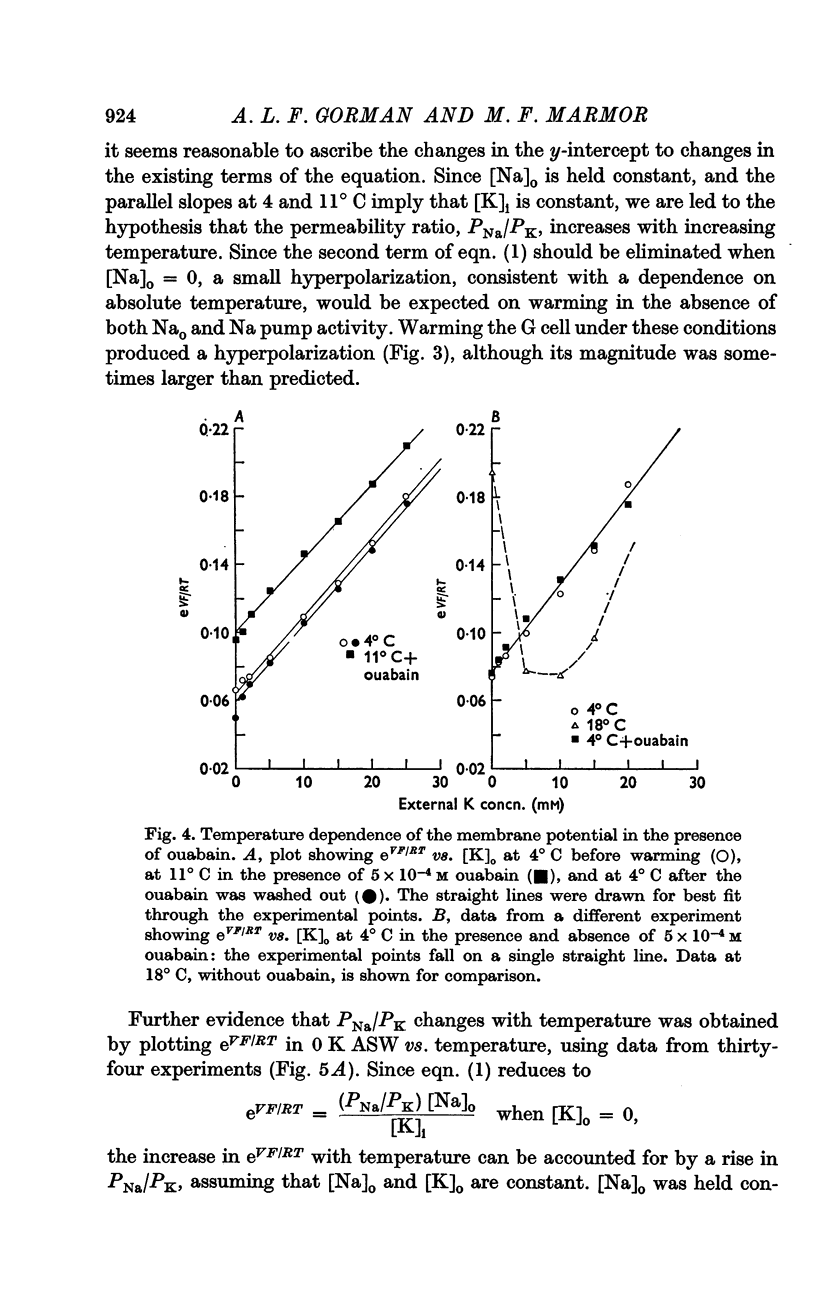
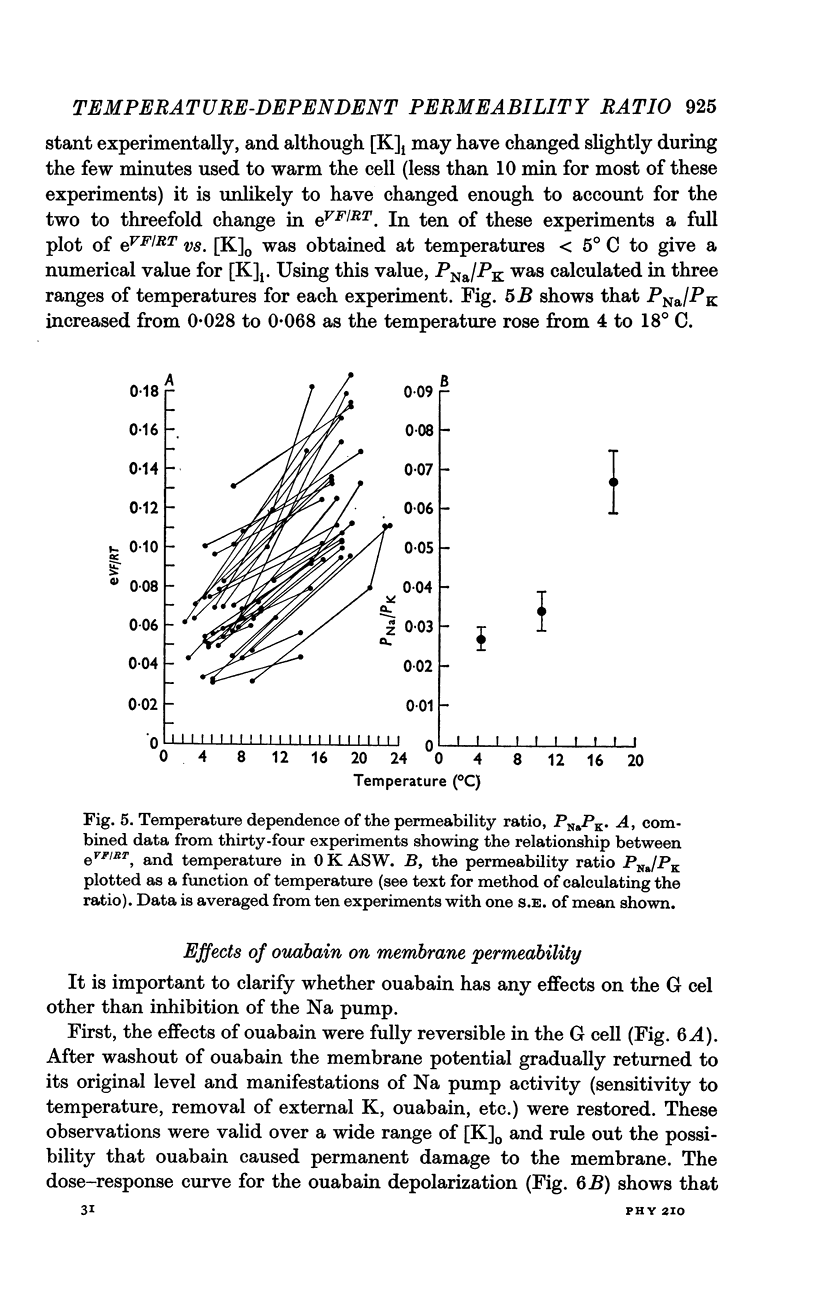
6. PNa/PK was found to increase from 0·028 at 4° C to 0·068 at 18° C. It is suggested that this increase is due primarily to a change in PNa.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APTER J. T., KOKETSU K. Temperature studies implicating calcium in regulation of muscle membrane potential. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Dec;56:123–127. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030560302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A., Bülbring E., Tomita T. The effect of temperature on the membrane conductance of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Sodium fluxes in internally dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Aug;52(2):181–211. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Marmor M. F. Contributions of the sodium pump and ionic gradients to the membrane potential of a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;210(4):897–917. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L. Ionic movements and electrical activity in giant nerve fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):1–37. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of temperature on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):240–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERKUT G. A., THOMAS R. C. AN ELECTROGENIC SODIUM PUMP IN SNAIL NERVE CELLS. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Jan;14:167–183. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNAN R. P. Membrane potential changes during sodium transport in frog sartorius muscle. Nature. 1962 Mar 10;193:986–987. doi: 10.1038/193986a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING G., WOODBURY J. W. Effect of temperature on the membrane potential of frog muscle fibers. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Dec;34(3):407–412. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Hidalgo M. C. Effect of temperature on resting potential in giant axons of squid. Nature. 1969 Mar 8;221(5184):962–963. doi: 10.1038/221962a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., NODA K. THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM-FREE SOLUTIONS ON THE MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF FROG MUSCLE FIBERS. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Sep;47:117–132. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J. The macromolecular properties of excitable membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Sep 6;94:390–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreton R. B. An application of the constant-field theory to the behaviour of giant neurones of the snail, Helix aspersa. J Exp Biol. 1968 Jun;48(3):611–623. doi: 10.1242/jeb.48.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATLAK C. S. Derivation of an equation for the diffusion potential. Nature. 1960 Dec 10;188:944–945. doi: 10.1038/188944b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOU M. Biology and pharmacology of the lithium ion. Pharmacol Rev. 1957 Mar;9(1):17–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Austin G. M., Yai H. Increase in permeability of the postsynaptic membrane to potassium produced by 'nembutal'. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1506–1508. doi: 10.1038/2151506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N. Changes in conductances of frog sartorius fibers produced by CO2, ReO4-, and temperature. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):1069–1075. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Membrane current and intracellular sodium changes in a snail neurone during extrusion of injected sodium. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):495–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


