Abstract
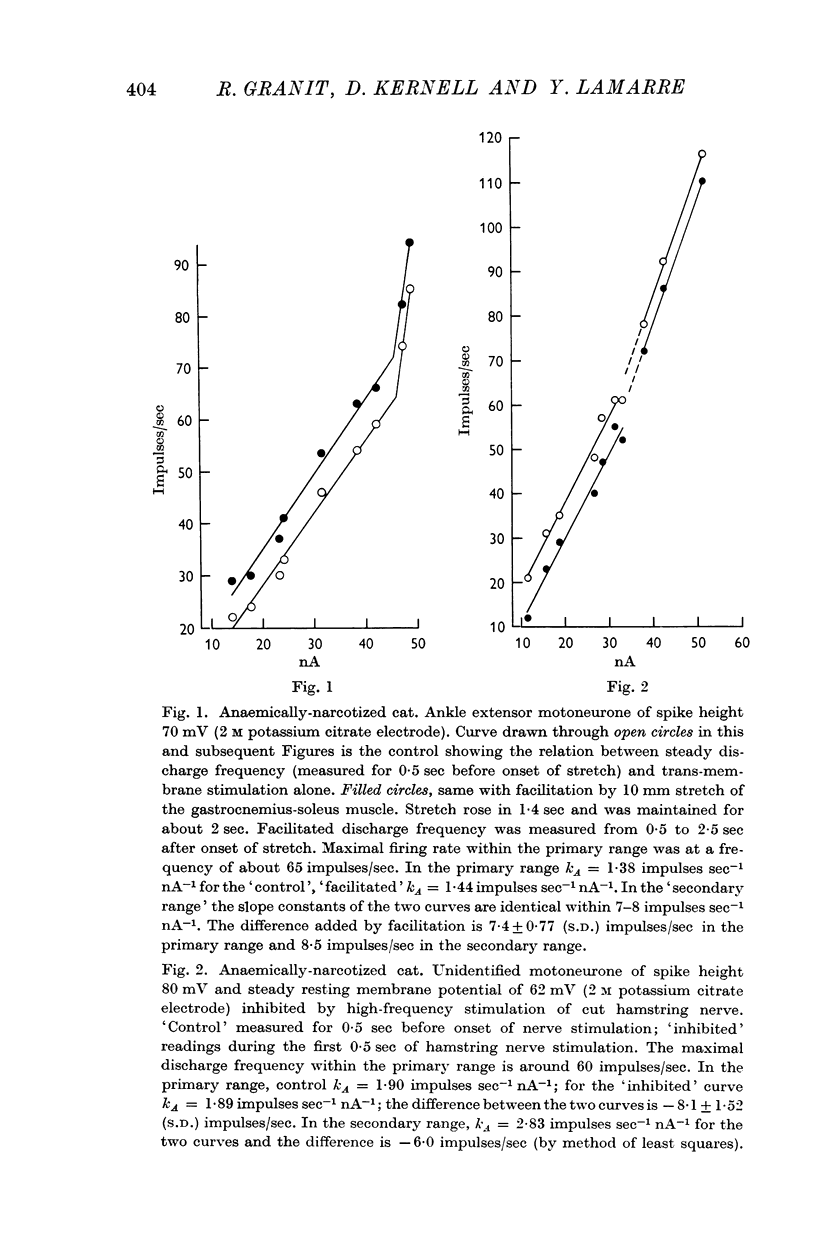
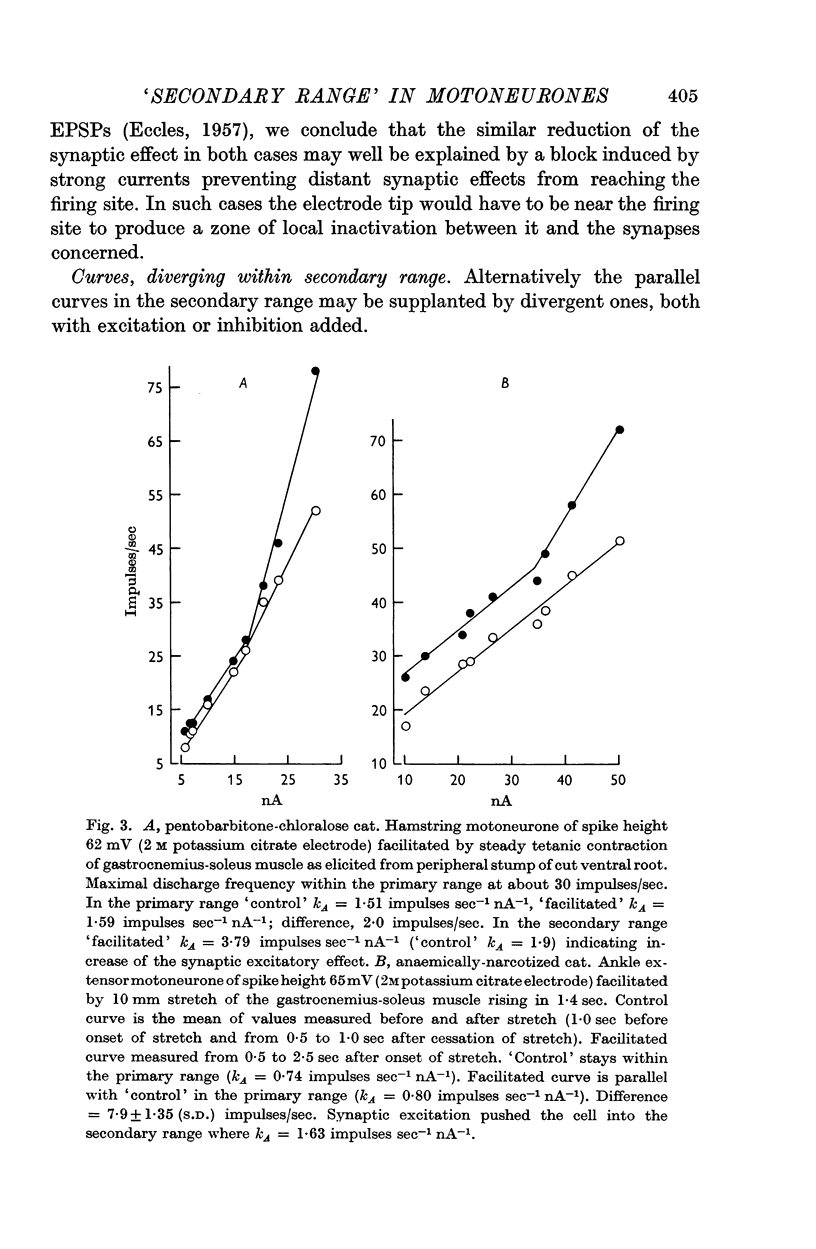
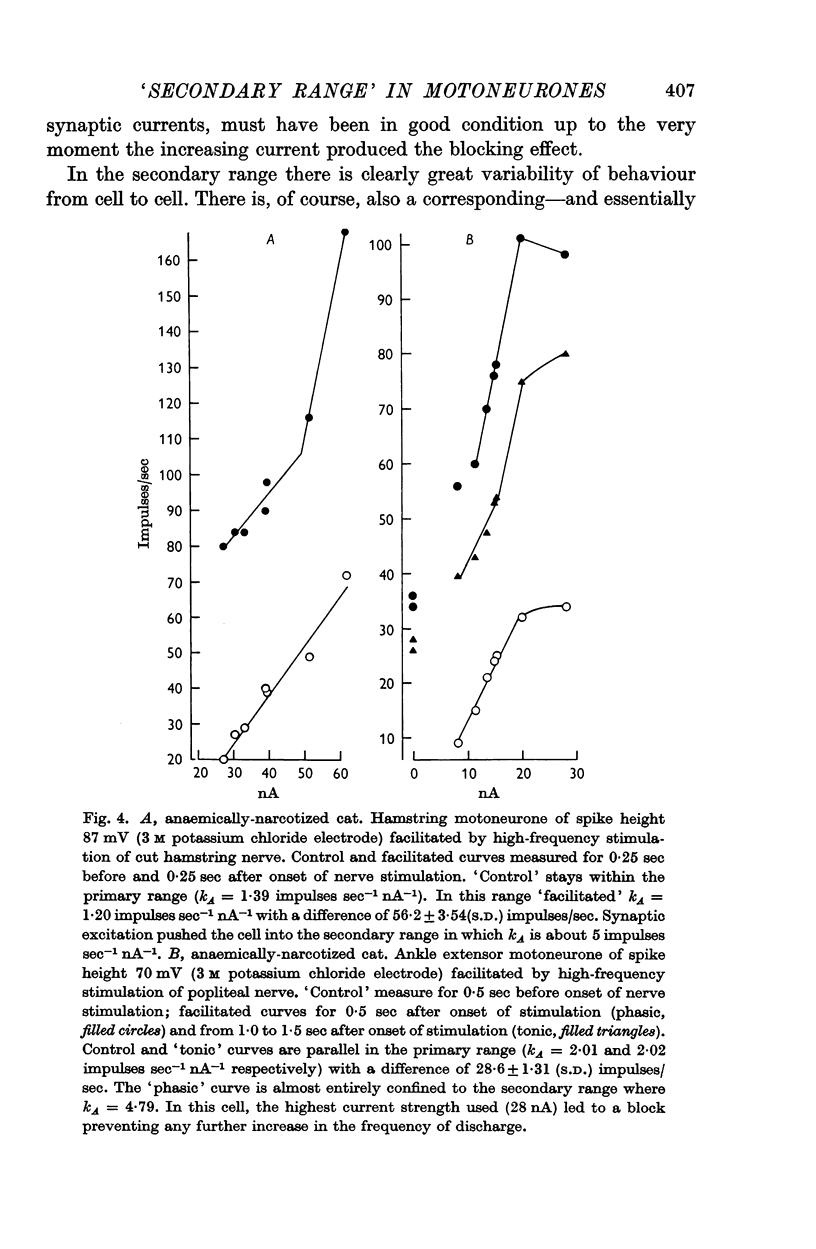
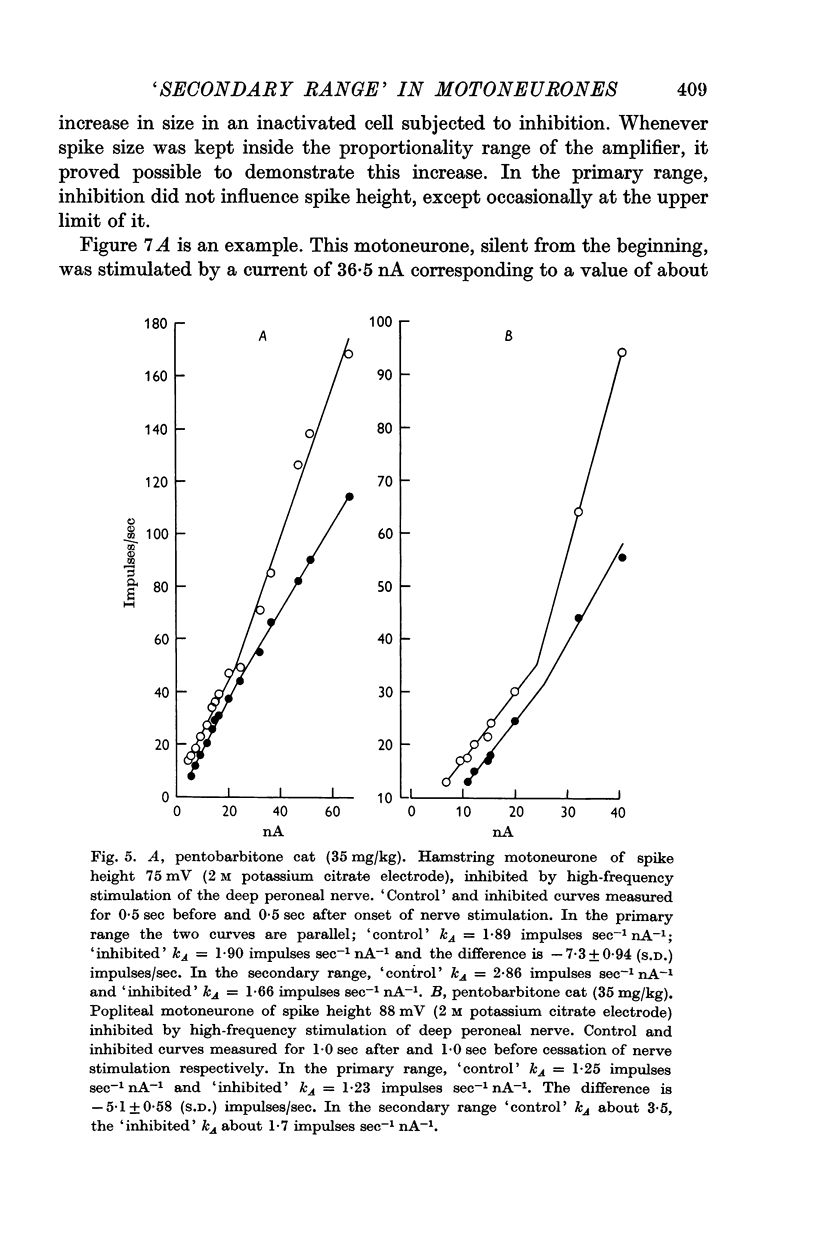
1. This paper extends the work on the `primary range' of firing (Granit, Kernell & Lamarre, 1966), in lumbar motoneurones to the `secondary range'. By definition the latter begins when, with stronger currents, the linear curve relating firing rate to injected current in the primary range undergoes a fairly sudden increase of slope.
2. It was shown that motoneurones firing at the higher frequencies of the secondary range were partially inactivated. Yet such firing rates were within the physiological range.
3. Algebraical summation of firing rates, when present in the secondary range, implied at the same time that the synaptic amount added was diminished by comparison with what it had been within the primary range.
4. Superimposed synaptic excitatory stimuli did not (as in the `primary range') regularly add their effect algebraically on to the rate of firing achieved by injected currents alone. More commonly the synaptic effect of the constant input underwent a progressive increase throughout the secondary range.
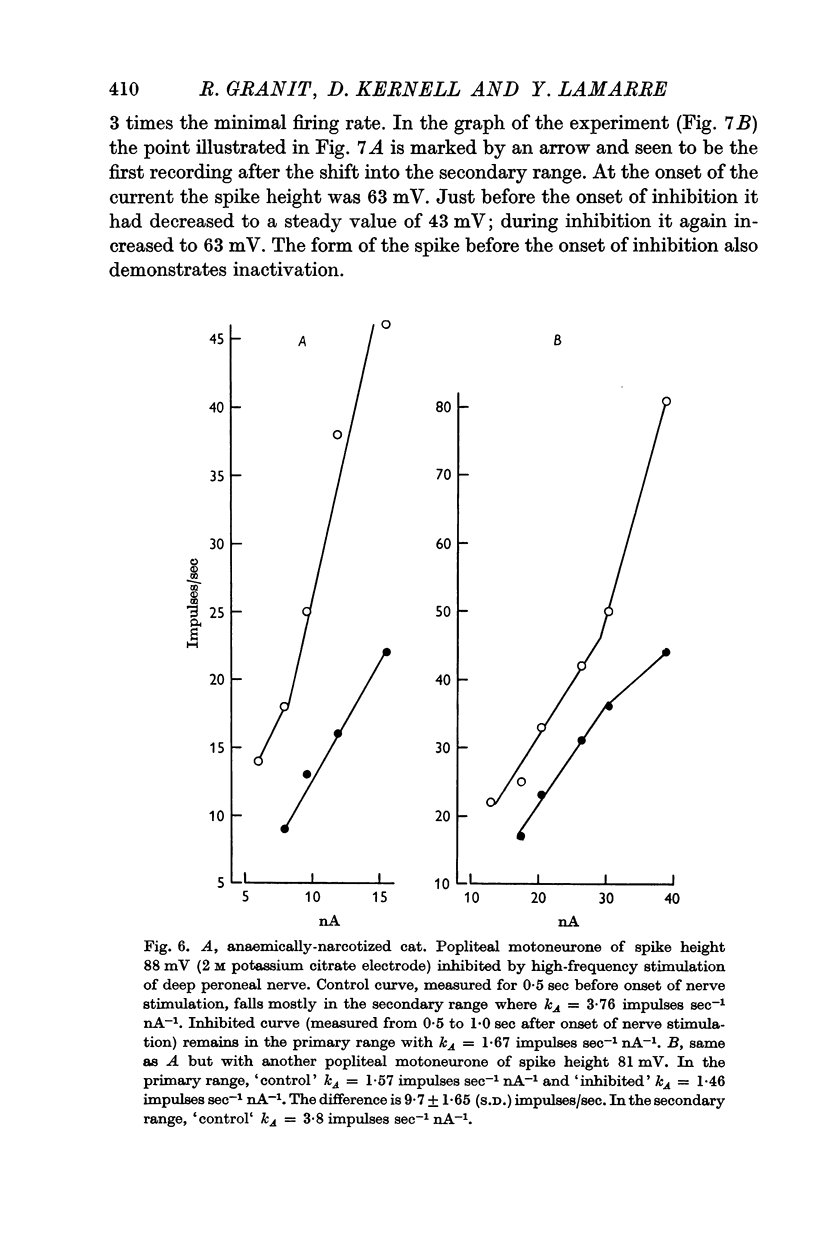
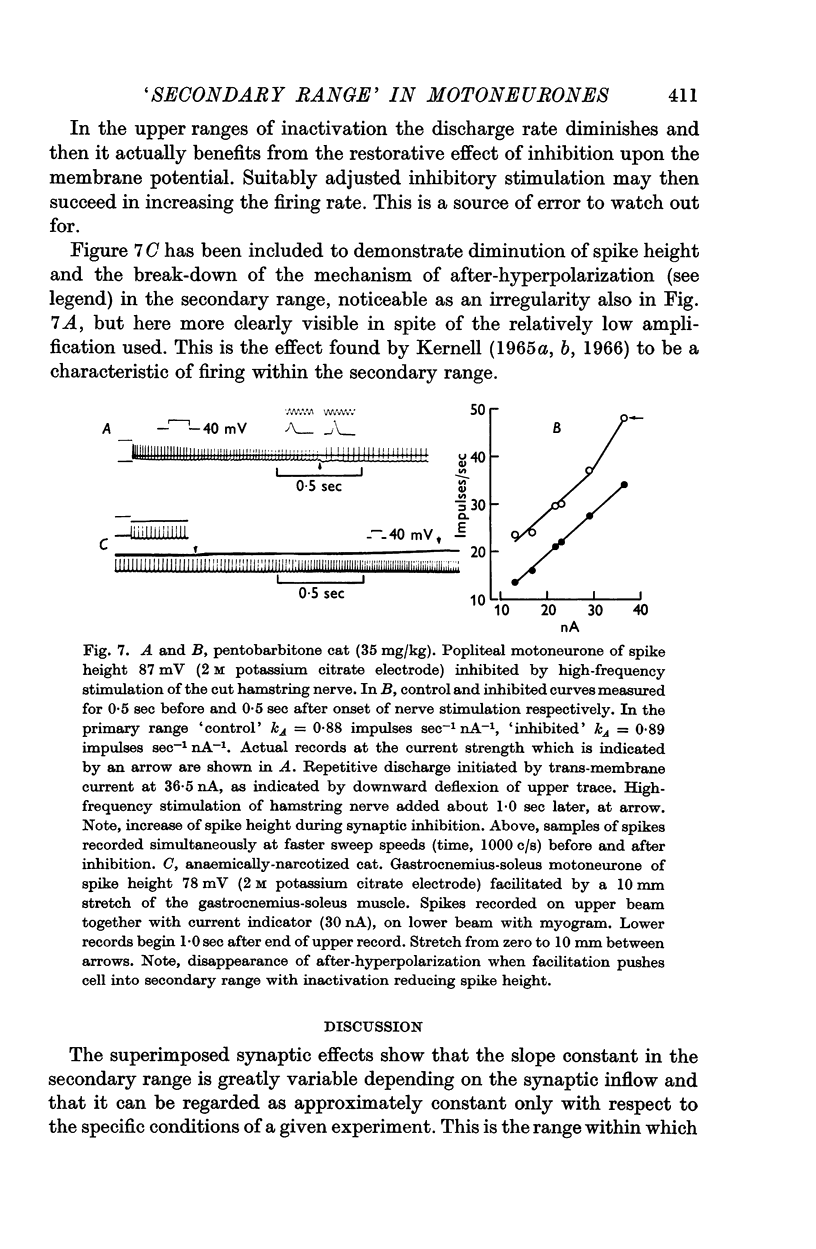
5. Superimposed inhibitory stimuli regularly reduced the slope constant as determined by trans-membrane current alone and, by counter-acting inactivation, made the motoneurone approach the mode of firing characteristic of the `primary range'.
6. The latter finding emphasizes the significance of analysing firing motoneurones with the aid of `slope constants' and provides inhibition with a new role in the integrative behaviour of motoneurones, as considered in the Discussion.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Bronk D. W. The discharge of impulses in motor nerve fibres: Part II. The frequency of discharge in reflex and voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1929 Mar 20;67(2):i3–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. INACTIVATION OF THE SODIUM-CARRYING MECHANISM IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:445–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., VALLBO A. B. ACCOMMODATION IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS AS COMPUTED ON THE BASIS OF VOLTAGE CLAMP DATA. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jan-Feb;63:1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SHORTESS G. K. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF REPETITIVE FIRING OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES, CAUSED BY INJECTED CURRENTS. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:911–931. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SMITH R. S. DELAYED DEPOLARIZATION AND THE REPETITIVE RESPONSE TO INTRACELLULAR STIMULATION OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:890–910. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grampp W. Multiple-spike discharge evoking after-depolarizations in the slowly adapting stretch receptor neuron of the lobster. II. The slow after-depolarization. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 May;67(1):100–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R., Kernell D., Lamarre Y. Algebraical summation in synaptic activation of motoneurones firing within the 'primary range' to injected currents. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(2):379–399. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell A. D. A study of the interaction between motoneurones in the frog spinal cord. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):612–648. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNELL D. THE DELAYED DEPOLARIZATION IN CAT AND RAT MOTONEURONES. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:42–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60616-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON P. G., FRANK K. ORTHODROMICALLY PRODUCED CHANGES IN MOTONEURONAL EXTRACELLULAR FIELDS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Sep;27:928–941. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.5.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERL E. R. Observations on the discharge of flexor motoneurones. J Physiol. 1962 Dec;164:450–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURPURA D. P., MCMURTRY J. G. INTRACELLULAR ACTIVITIES AND EVOKED POTENTIAL CHANGES DURING POLARIZATION OF MOTOR CORTEX. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Jan;28:166–185. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.1.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLBO A. B. ACCOMMODATION RELATED TO INACTIVATION OF THE SODIUM PERMEABILITY IN SINGLE MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:429–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J., TALBOT W. H. PATTERN OF DISCHARGE OF FLEXOR MOTONEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 May;27:451–463. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


