Abstract
The mechanisms protecting nitrogenase in Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus from damage by oxygen were studied. Evidence is provided suggesting that in G. diazotrophicus these mechanisms include respiratory protection as well as conformational protection in which a putative FeSII Shethna protein is involved.
Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus (previously Acetobacter diazotrophicus) was originally isolated as an endosymbiont in sugarcane (4, 8) but has also been isolated from other agriculturally important plants (9, 17). In an earlier report, G. diazotrophicus was shown to play a major role in the supply of nitrogen to sugarcane (3), and this was confirmed by a recent study (25, 26).
Biological nitrogen fixation is catalyzed by nitrogenase, consisting of two proteins, dinitrogenase reductase (Fe protein) and dinitrogenase (MoFe protein) (24). Both of these metalloproteins are irreversibly inactivated by oxygen within minutes, with dinitrogenase reductase being the more sensitive. To protect nitrogenase from inactivation by oxygen, a variety of mechanisms operate in diazotrophs (7, 15, 21). In Azotobacter species, two major mechanisms are believed to contribute to the protection of nitrogenase, increased respiration and conformational protection. The increase in respiration of Azotobacter species under diazotrophic growth has been suggested to decrease the oxygen concentration around nitrogenase to a tolerable level (2, 18, 19, 22). Additional effects such as increased supplies of ATP and reductant have recently been proposed to play a major role in the protection (15). Conformational protection is due to the formation of a complex between the FeSII (Shethna) protein and nitrogenase under high intracellular oxygen concentrations. In this complex, nitrogenase is inactive but transiently protected from damage by oxygen (10, 13, 21). Additional studies have shown that the function of the FeSII protein is of major importance for cell viability under carbon and/or energy limitation but only when cells are grown diazotrophically (12, 14).
G. diazotrophicus can grow diazotrophically in an atmosphere of air (27), and diazotrophic conditions lead to an increase in respiration (5, 6) due to induction of a periplasmic, membrane-bound glucose dehydrogenase and a cytochrome ba oxidase (5, 6, 11). In addition to glucose, other carbon sources, e.g., gluconate and ethanol, have been shown to be oxidized primarily in the periplasm, whereas fructose is metabolized only through cytoplasmic reactions (1). Furthermore, diazotrophic growth increases with increased oxygen pressure provided that the proper carbon source is also present (5, 20, 27).
Recently, Pan and Vessey showed that subjecting diazotrophically grown G. diazotrophicus to stepwise increases in oxygen pressure led to inhibition of nitrogenase activity, which was rapidly recovered when the oxygen pressure was returned to the original level (16). In summary, these previous studies showed that the ability of G. diazotrophicus to fix nitrogen aerobically is not due to high respiratory capacity alone but that another mechanism is involved. To further identify the mechanisms protecting nitrogenase from oxygen inactivation, we have studied the influence of the carbon source on respiration as well as the possible operation of conformational protection in G. diazotrophicus.
In order to establish the relation between nitrogenase activity and the capacity of a carbon source to support respiration, respiratory rates with different carbon sources were determined for diazotrophically grown G. diazotrophicus PAL 5 (provided by J. Döbereiner, EMBRAPA, Seropédica, Brazil) (28). Cells in the late exponential phase were centrifuged, washed, and resuspended in fresh medium with or without a carbon source. Respiratory rates were determined using a Clark electrode, and the measurements (duplicates from two different cultures) were initiated by the addition of a carbon source to cells in air-saturated medium without a nitrogen source. The respiratory rates (μmol of O2 · min−1) were as follows: 220 ± 15 with glucose, 70 ± 1.4 with gluconate, 70 ± 2 with ethanol, 48 ± 5 with fructose, and 27 ± 1.4 with pyruvate. Glucose was by far the most efficient substrate for respiration, as has been reported previously (1, 5). Ethanol and gluconate were clearly better substrates than fructose and pyruvate. Based on these results, glucose and pyruvate were chosen as the efficient and less efficient respiratory substrates, respectively.
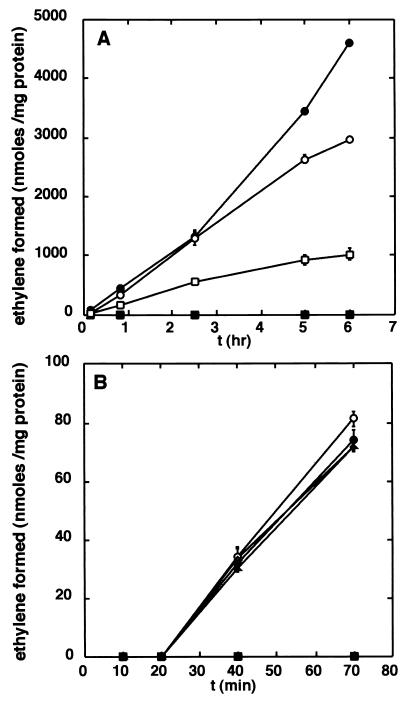
The capacity of G. diazotrophicus to catalyze nitrogen fixation, measured as acetylene reduction (28) in the presence of different oxygen concentrations with either glucose (100 mM) or pyruvate (180 mM), was determined. Nitrogenase activity was measured in an atmosphere with 20 or 5% oxygen in N2. As shown in Fig. 1A, the initial nitrogenase activity with glucose was independent of the oxygen concentration, whereas at a cell density corresponding to a turbidity (optical density) at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.6, pyruvate can only support nitrogenase activity under 5% oxygen. However, at an OD600 of 1.2, nitrogenase activity with pyruvate was demonstrated even under 20% oxygen at a rate similar to that seen with glucose as the substrate. At higher OD values, the activity was essentially the same, a phenomenon observed also with glucose at increasing OD values, probably due to production of a gradient of oxygen in the reaction mixture. These results clearly suggest that the total rate of respiration must be high enough to lower the concentration of oxygen to a level at which nitrogenase is not inactivated. With glucose as the reductant, the respiratory rate is high enough even at low cell densities, whereas the respiratory rate with pyruvate is insufficient to decrease the oxygen concentration at low cell densities. It can thus be concluded that respiratory protection is one mechanism operating in G. diazotrophicus and that its most important effect is to reduce the oxygen concentration. Other effects, such as an increase in the supply of ATP and/or reductant for nitrogenase, are probably less important judging from the difference between glucose and pyruvate at lower and higher cell densities.
FIG. 1.
Effect of different carbon sources and oxygen concentrations on nitrogenase activity. (A) Nitrogenase activity was determined as acetylene reduction with the following carbon sources and oxygen levels: glucose, 5% oxygen (○); glucose, 20% oxygen (•); pyruvate, 5% oxygen (□); pyruvate, 20% oxygen (▪). Cell density (OD600) = 0.6. Data shown are from four experiments with duplicates for each data point. (B) Reactivation of nitrogenase after inactivation under 20% oxygen. Samples were incubated with 20% oxygen in N2 for 1 h with pyruvate as the carbon source. After an additional 20 min, additions and changes were made. Glucose (○); glucose plus tetracycline (•); ethanol (▵); ethanol plus tetracycline (▴); change of atmosphere from 20 to 5% oxygen in N2 (▪). Data shown are samples run in duplicate from two different cultures. Cell density (OD600) = 0.6. The error bars in both panels show standard deviations.
In order to investigate whether nitrogenase in G. diazotrophicus is protected by additional mechanisms, cells (at an OD600 of 0.6) were subjected to 20% oxygen in N2 with pyruvate as the carbon source, leading to loss of nitrogenase activity. After 1 h under these conditions, glucose with or without tetracycline (15 μg/ml) or ethanol with or without tetracycline was added or the atmosphere was changed to 5% oxygen in N2. As shown in Fig. 1B, both glucose and ethanol supported rapid recovery of activity. Tetracycline, which inhibits protein synthesis in G. diazotrophicus (data not shown), produced no effect, indicating that the recovery was independent of protein synthesis. In contrast, pyruvate could not support the reactivation of nitrogenase, even at 5% oxygen, although pyruvate does support nitrogenase activity under this oxygen concentration (Fig. 1A). These results suggest that nitrogenase can be reversibly inactivated and that reactivation requires an efficient respiratory substrate and reductant, e.g., glucose.
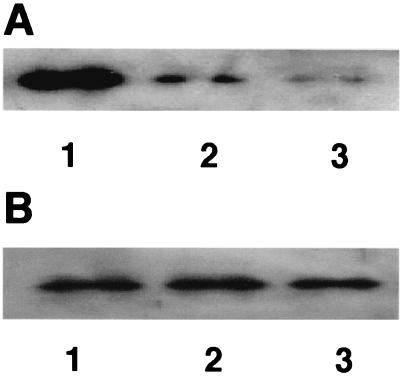
To investigate the effect on nitrogenase during inactivation, samples were taken at different times and analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) followed by Western blotting (28) using antibodies against dinitrogenase reductase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. As shown in Fig. 2A, dinitrogenase reductase was degraded when cells were kept under 20% oxygen in N2 with pyruvate as the carbon source, whereas in cells shifted to an atmosphere with 5% oxygen after 1 h under 20% oxygen, the amount of dinitrogenase reductase remained essentially at the original level (Fig. 2B). These results indicate that in addition to respiratory protection, conformational protection also safeguards G. diazotrophicus nitrogenase.
FIG. 2.
Stability of dinitrogenase reductase during oxygen treatment. Extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using antibodies against dinitrogenase reductase from R. rubrum. (A) Extracts were prepared from cells (OD600 = 0.6) incubated under 20% oxygen in N2 with pyruvate as the carbon source for 2 (lane 1), 4 (lane 2), and 6 (lane 3) h. (B) Extracts were prepared from cells (OD600 = 0.6) incubated with 20% oxygen in N2 with pyruvate as the carbon source for 1 h, after which the atmosphere was changed to 5% oxygen in N2. Samples were taken after incubation for another 2 (lane 1), 4 (lane 2), and 6 (lane 3) h. The same amount of total protein was loaded in all six lanes.
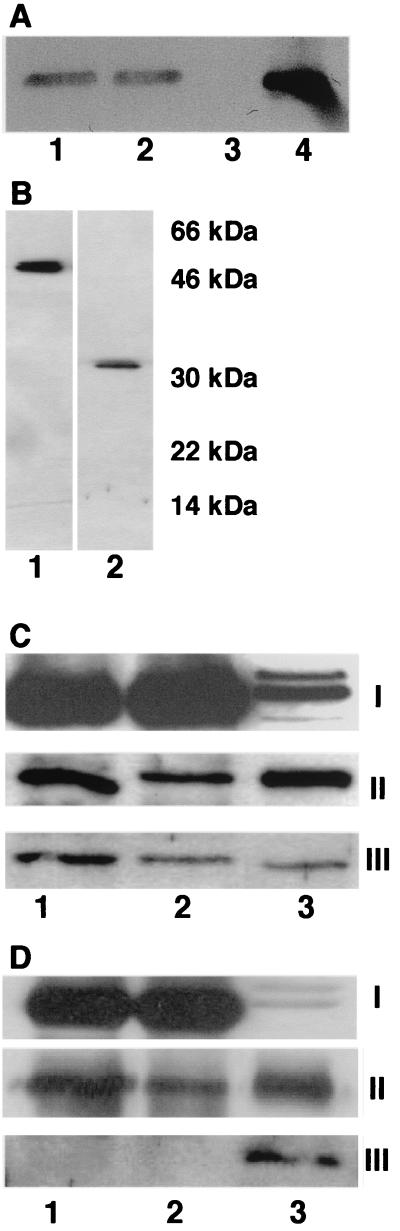
In Azotobacter species, conformational protection is due to the interaction of nitrogenase with the FeSII protein (23), leading to an inactive but protected nitrogenase. To investigate whether an FeSII protein is also present in G. diazotrophicus, Western blots were performed on extracts from G. diazotrophicus grown either diazotrophically or with ammonium chloride (30 mM). As shown in Fig. 3A, antibodies against the Azotobacter vinelandii FeSII protein (a gift from F. Moshiri) clearly identified a protein of the expected molecular mass (14 kDa) in extracts of cells under diazotrophic as well as nitrogen-sufficient growth conditions. The oxygen concentration did not influence the level of the putative FeSII protein in the extract (data not shown).
FIG. 3.
Identification of the FeSII protein in G. diazotrophicus and immunoprecipitation of the complex with nitrogenase. (A) Cell extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using antibodies raised against the FeSII protein from A. vinelandii. Lanes: 1, extract from G. diazotrophicus grown diazotrophically with 20% oxygen in N2; 2, extract from G. diazotrophicus grown nondiazotrophically with 20% oxygen in N2; 3, extract from Escherichia coli DH5α; 4, extract from E. coli DH5α containing plasmid pAVFeSII overexpressing the FeSII protein from A. vinelandii. (B) Extract from G. diazotrophicus analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against dinitrogenase from R. rubrum (lane 1) and against dinitrogenase reductase from R. rubrum (lane 2). (C and D) Immunoprecipita-tion of extracts prepared aerobically (C) and anaerobically (D). Lanes 1, immunoprecipitation with antibodies against dinitrogenase reductase from R. rubrum; lanes 2, immunoprecipitation with antibodies against dinitrogenase from R. rubrum; lanes 3, extract not immunoprecipitated. Panels I, antibodies against dinitrogenase from R. rubrum used for immunodetection; panels II, antibodies against dinitrogenase reductase from R. rubrum used for immunodetection; panels III, antibodies against the FeSII protein from A. vinelandii used for immunodetection.
To investigate the function of the putative FeSII protein, cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation using antibodies against R. rubrum dinitrogenase and dinitrogenase reductase. Cell extracts were prepared by passage of a cell suspension in buffer (25 mM HEPES [pH 7.8], 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 μg of leupeptin per ml, 0.1 mg of Pefablock per ml) through a Ribi cell fractionator followed by centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 60 min. For anaerobic extracts, cells were resuspended in degassed buffer containing 2 mM sodium dithionite. All manipulations were done under an atmosphere of oxygen-free nitrogen. Cells grown with glucose under 20% oxygen were used for both extracts. Extracts were diluted eight times in buffer (10 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 0.1% Triton, 0.1% bovine serum albumin) and immunoprecipitated. Protein A-Sepharose (Amersham Biosciences) was added and then centrifugation was performed to isolate precipitates, which were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using antibodies against R. rubrum nitrogenase and against the FeSII protein from A. vinelandii.
As shown in Fig. 3C, the immunoprecipitates from aerobic extracts contained both nitrogenase proteins as well as the putative FeSII protein, irrespective of which of the two antibodies was used in the immunoprecipitation. In contrast, the FeSII protein was not present in the precipitates from the anaerobic extract (Fig. 3D). It should be noted that the heavy chain of the antibodies migrate just ahead of the subunits of dinitrogenase, making quantitative evaluation of the amount of protein precipitated difficult. The amount of dinitrogenase reductase precipitated by the antibodies against dinitrogenase was much less than that in the precipitates from aerobic extracts. To rule out the possibility that the antibodies against nitrogenase cross-reacted with the FeSII protein, immunoprecipitation of extracts from cells grown nondiazotrophically was performed. No signal corresponding to the 14-kDa band could be detected on the Western blot (data not shown). Also, as shown in Fig. 3B, there was no cross-reaction between dinitrogenase and the antibodies directed against dinitrogenase reductase or vice versa. To further confirm protection by the formation of a complex, nitrogenase activity was measured in aerobically prepared extracts mixed with aerobic buffer. After 10 min, the activity had decreased to only 70% of that of the control extract incubated anaerobically with dithionite. This is in good agreement with results from similar experiments with Azotobacter extracts (14).
Together, these results provide strong evidence for the protection of nitrogenase in G. diazotrophicus by a conformational mechanism involving a putative FeSII protein, which forms a complex with nitrogenase, rendering nitrogenase inactive but transiently protected from oxygen damage, similar to the situation in A. vinelandii. The specific signal leading to dissociation of the complex between nitrogenase and the FeSII protein has not been identified, although the redox status is believed to play a central role (14, 21). The fact that cells that were switched from an atmosphere with 20% to one with 5% oxygen in N2 with pyruvate did not regain activity indicates that pyruvate alone does not generate the signal for nitrogenase reactivation under these conditions, although dinitrogenase reductase is protected from degradation (Fig. 2B). The rapid reactivation produced by glucose indicates that the reducing power of pyruvate is sufficient to decrease oxygen concentration but not to support a sufficiently low redox state.
In conclusion, we have shown that the ability of G. diazotrophicus to catalyze nitrogen fixation under high oxygen concentrations is dependent on the capacity of the carbon source to support respiration at a rate sufficient to produce an oxygen concentration compatible with nitrogenase activity. It has been argued that the function of increased respiration in A. vinelandii is not primarily to lower the oxygen concentration, thus putting the role of respiratory protection into question (15). However, the result shown here in which pyruvate, a poor respiratory substrate, supports nitrogenase activity only when the cell density is high enough suggests that the main effect of the increased respiration in G. diazotrophicus under diazotrophic conditions (5) is in fact to lower the oxygen concentration. In addition, it has been shown that nitrogenase activity is only measurable when the oxygen concentration is lowered to nondetectable levels (5). As a complement, nitrogenase in G. diazotrophicus can also be protected, as described here, by a conformational mechanism involving a putative FeSII protein operating when cells are subjected to sudden increases in oxygen pressure, which has been shown in a recent study (16). This protective mechanism would enable cells to adjust to the new conditions without nitrogenase being damaged by oxygen. If the carbon source present supports a sufficiently high rate of respiration, then nitrogenase activity is regained; if not, then nitrogenase is degraded after a transient period of protection. The demonstration of an FeSII protein in G. diazotrophicus is the first report of the occurrence of this protein in a diazotroph not belonging to Azotobacter, opening the possibility that conformational protection of nitrogenase operates in other diazotrophs that grow and fix nitrogen under aerobic conditions.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to F. Moshiri for the gifts of antibodies against the FeSII protein from A. vinelandii and of the plasmid pAVFeSII for overexpression of this protein in Escherichia coli.
This investigation was supported by grants to S.N. from FORMAS and the Carl Trygger Foundation.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alvarez, B., and G. Martinez-Drets. 1995. Metabolic characterization of Acetobacter diazotrophicus. Can. J. Microbiol. 41:918-924. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bertsova, Y. U., A. V. Bogachev, and V. P. Skulachev. 2001. Noncoupled NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase of Azotobacter vinelandii is required for diazotrophic growth at high oxygen concentrations. J. Bacteriol. 183:6869-6874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boddey, R. M., S. Urquiaga, V. M. Reis, and J. Döbereiner. 1991. Biological nitrogen fixation associated with sugar cane. Plant Soil 137:111-117. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cavalcante, V. A., and J. Döbereiner. 1988. A new acid-tolerant nitrogen fixing bacterium associated with sugarcane. Plant Soil 108:23-31. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Flores-Encarnacion, M., M. Contreras-Zentella, L. Soto-Urzua, G. R. Aguilar, B. E. Baca, and J. E. Escamilla. 1999. The respiratory system and diazotrophic activity of Acetobacter diazotrophicus PAL5. J. Bacteriol. 181:6987-6995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Galar, M. L., and J. L. Boiardi. 1995. Evidence for a membrane-bound pyrroloquiniline quinone-linked glucose dehydrogenase in Acetobacter diazotrophicus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 43:713-716. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gallon, J. R. 1992. Reconciling the incompatible: nitrogen fixation and oxygen. New Phytologist 122:571-609. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gillis, M., K. Kersters, B. Hoste, D. Janssens, R. M. Kroppenstedt, M. P. Stephan, K. R. S. Teixeira, J. Döbereiner, and J. de Ley. 1989. Acetobacter diazotrophicus sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing acetic acid bacterium associated with sugarcane. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39:361-364. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jimenez-Salgado, T., L. E. Fuentes-Ramirez, A. Tapia-Hernandez, M. A. Mascarua-Esparza, E. Martinez-Romero, and J. Caballero-Mellado. 1997. Coffea arabica L., a new host plant for Acetobacter diazotrophicus, and isolation of other nitrogen-fixing acetobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63:3676-3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lou, J., F. Moshiri, M. K. Johnson, M. E. Lafferty, D. L. Sorkin, A. Miller, and R. J. Maier. 1999. Mutagenesis studies of the FeSII protein of Azotobacter vinelandii: roles of histidine and lysine residues in the protection of nitrogenase from oxygen damage. Biochemistry 38:5563-5571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Luna, M. F., C. F. Mignone, and J. L. Boiardi. 2000. The carbon source influences the energetic efficiency of the respiratory chain of N2-fixing Acetobacter diazotrophicus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54:564-569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maier, R. J., and F. Moshiri. 2000. Role of the Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenase-protective Shethna protein in preventing oxygen-mediated cell death. J. Bacteriol. 182:3854-3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moshiri, F., B. R. Crouse, M. K. Johnson, and R. J. Maier. 1995. The “nitrogenase-protective” FeSII protein of Azotobacter vinelandii: overexpression, characterization, and crystallization. Biochemistry 34:12973-12982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Moshiri, F., J. W. Kim, C. Fu, and R. J. Maier. 1994. The FeSII protein of Azotobacter vinelandii is not essential for aerobic nitrogen fixation, but confers significant protection to oxygen-mediated inactivation of nitrogenase in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Microbiol. 14:101-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Oelze, J. 2000. Respiratory protection of nitrogenase in Azotobacter species: is a widely held hypothesis unequivocally supported by experimental evidence? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 24:321-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pan, B., and J. K. Vessey. 2001. Response of the endophytic diazotroph Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus on solid media to changes in atmospheric partial O2 pressure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:4694-4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Paula, M. A., S. Urquiaga, J. O. Siqueira, and J. Döbereiner. 1992. Synergistic effects of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and diazotrophic bacteria on nutrition and growth of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). Biol. Fertil. Soils 14:61-66. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Poole, R. K., and S. Hill. 1997. Respiratory protection of nitrogenase activity in Azotobacter vinelandii—roles of the terminal oxidases. Biosci. Rep. 17:303-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ramos, J. L., and R. L. Robson. 1985. Isolation and properties of mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii defective in aerobic nitrogen fixation. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131:1449-1458. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Reis, V. M., and J. Döbereiner. 1998. Effect of high sugar concentration on nitrogenase activity of Acetobacter diazotrophicus. Arch. Microbiol. 171:13-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Robson, R. L. 1979. Characterization of an oxygen-stable nitrogenase complex isolated from Azotobacter chroococcum. Biochem. J. 181:569-575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Robson, R. L., and J. R. Postgate. 1980. Oxygen and hydrogen in biological nitrogen fixation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 34:183-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Scherings, G., H. Haaker, H. Wassink, and C. Veeger. 1983. On the formation of an oxygen-tolerant three-component nitrogenase complex from Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur. J. Biochem. 135:591-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schindelin, H., C. Kisker, J. L. Schlessman, J. B. Howard, and D. C. Rees. 1997. Structure of ADP · AlF4−-stabilized nitrogenase complex and its implications for signal transduction. Nature 387:370-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sevilla, M., R. H. Burris, N. Gunapala, and C. Kennedy. 2001. Comparison of benefit to sugarcane plant growth and 15N2 incorporation following inoculation of sterile plants with Acetobacter diazotrophicus wild-type and Nif− mutants strains. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 14:358-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sevilla, M., A. de Oliveira, I. Baldani, and C. Kennedy. 1998. Contributions of the bacterial endophyte Acetobacter diazotrophicus to sugarcane nutrition: a preliminary study. Symbiosis 25:181-191. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stephan, M. P., M. Oliveira, K. R. S. Teixeira, G. Martinez-Drets, and J. Döbereiner. 1991. Physiology and dinitrogen fixation of Acetobacter diazotrophicus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 77:67-72. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ureta, A., and S. Nordlund. 2001. Glutamine synthetase from Acetobacter diazotrophicus: properties and regulation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 202:177-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]