Abstract
1. Two types of after-potentials in the stretch receptor neurone of crayfish are described.
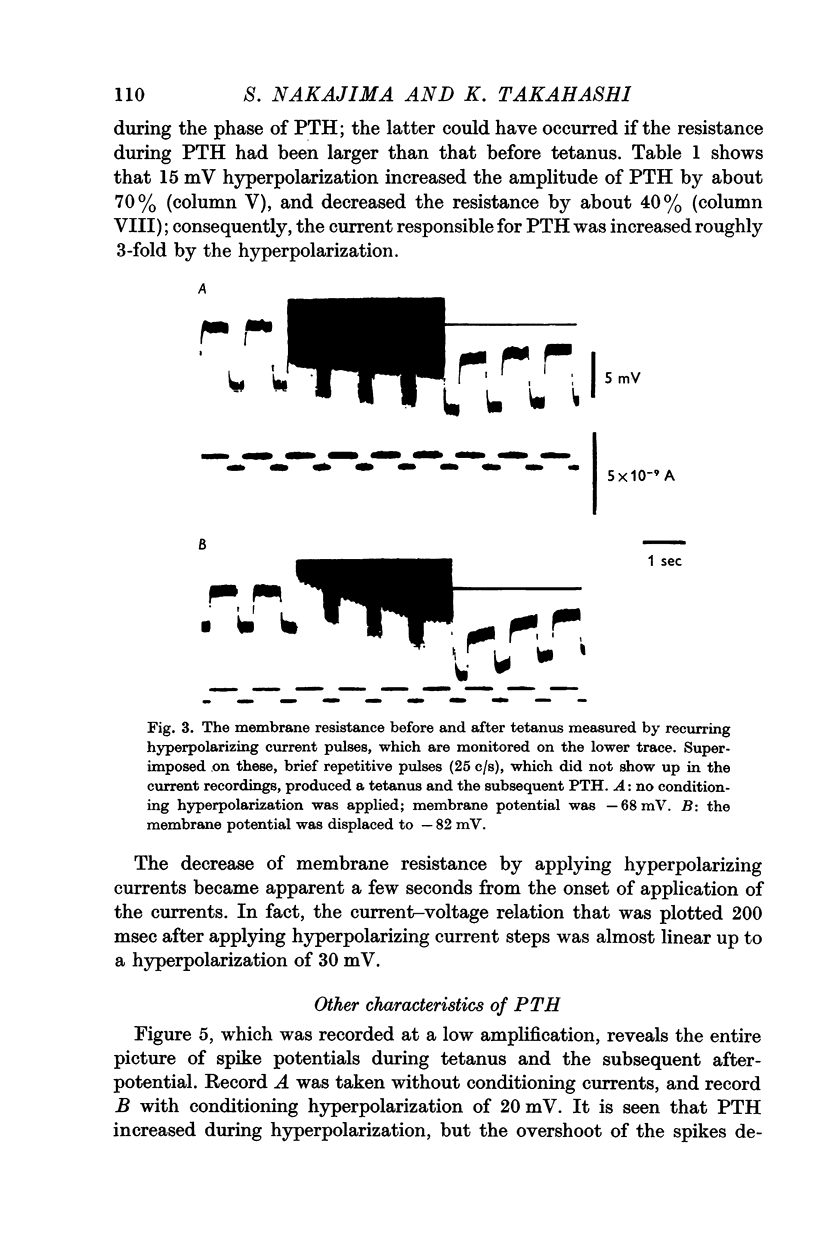
2. A short-duration after-hyperpolarization associated with a single spike or a few spikes is diminished and reversed on applying hyperpolarizing currents. However, a much longer-lasting post-tetanic hyperpolarization (PTH) is enhanced by conditioning hyperpolarization; thus, no reversal potential can be obtained.
3. No changes in membrane conductance occur during PTH.
4. Reducing K concentration in the bathing fluid diminishes PTH, while it shifts the reversal potential of the short after-potential toward greater negativity.
5. Replacement of Na with Li, or addition of 2,4-dinitrophenol in the bathing fluid suppresses PTH in a reversible manner.
6. Electrophoretic injection of Na into the cell induces a long-lasting hyperpolarization.
7. No change in K-equilibrium potential, as indicated by the reversal point of the short after-potential, is detected during PTH.
8. It is concluded that the short after-potential is caused by a permeability increase for potassium ion, whereas PTH is produced by an electrogenic Na-pump.
Full text
PDF





















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASANO T., HURLBUT W. P. Effects of potassium, sodium, and azide on the ionic movements that accompany activity in frog nerves. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Jul 20;41(6):1187–1203. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.6.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., CARAVAGGIO L. L. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. V. Correlation of enzyme activity with cation flux in six tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Apr;101:37–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90531-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., KURIYAMA H. Effects of changes in ionic environment on the action of acetylcholine and adrenaline on the smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:59–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNSTOCK G. The action of adrenaline on excitability and membrane potential in the taenia coli of the guinea-pig and the effect of DNP on this action and on the action of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):183–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Phosphorus metabolism of intact crab nerve and its relation to the active transport of ions. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(2):383–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Shaw T. I. A comparison of the phosphorus metabolism of intact squid nerve with that of the isolated axoplasm and sheath. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(2):424–438. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALDWELL P. C., HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D., SHAW T. L. The effects of injecting 'energy-rich' phosphate compounds on the active transport of ions in the giant axons of Loligo. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:561–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J., ECCLES R. M., ITO M. EFFECTS PRODUCED ON INHIBITORY POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIALS BY THE COUPLED INJECTIONS OF CATIONS AND ANIONS INTO MOTONEURONS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 May 19;160:197–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C., KUFFLER S. W. Further study of soma, dendrite, and axon excitation in single neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Sep 20;39(1):121–153. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C., KUFFLER S. W. Processes of excitation in the dendrites and in the soma of single isolated sensory nerve cells of the lobster and crayfish. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Sep 20;39(1):87–119. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):341–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRUMENTO A. S. SODIUM PUMP: ITS ELECTRICAL EFFECTS IN SKELETAL MUSCLE. Science. 1965 Mar 19;147(3664):1442–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAGE P. W., HUBBARD J. I. IONIC CHANGES RESPONSIBLE FOR POST-TETANIC HYPERPOLARIZATION. Nature. 1964 Aug 8;203:653–654. doi: 10.1038/203653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD P., STRAUB R. W. After-potentials in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 30;144(3):442–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H., KAO C. Y., ALTAMIRANO M. Bioelectric effects of ions microinjected into the giant axon of Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):245–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J., MAIZELS M. The permeability of human erythrocytes to sodium. J Physiol. 1951 May;113(4):506–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Movements of Na and K in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):405–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Experiments on the injection of substances into squid giant axons by means of a microsyringe. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):592–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWICZ P., GERBER C. J. EFFECTS OF EXTERNAL POTASSIUM AND STROPHANTHIDIN ON SODIUM FLUXES IN FROG STRIATED MUSCLE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jan;48:489–514. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO M., OSHIMA T. THE ELECTROGENIC ACTION OF CATIONS ON CAT SPINAL MOTONEURONS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Nov 17;161:92–108. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B. Depolarization of sensory terminals and the initiation of impulses in the muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):261–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERKUT G. A., THOMAS R. C. AN ELECTROGENIC SODIUM PUMP IN SNAIL NERVE CELLS. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Jan;14:167–183. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNAN R. P. Membrane potential changes during sodium transport in frog sartorius muscle. Nature. 1962 Mar 10;193:986–987. doi: 10.1038/193986a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. CHLORIDE IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:690–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., LEWIS P. R. The sodium and potassium content of cephalopod nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Jun;114(1-2):151–182. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The permeability of frog muscle fibres to lithium ions. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:626–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWENSTEIN W. R., TERZUOLO C. A., WASHIZU Y. SEPARATION OF TRANSDUCER AND IMPULSE-GENERATING PROCESSES IN SENSORY RECEPTORS. Science. 1963 Nov 29;142(3596):1180–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3596.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., AWAD M. Z. THE CONTROL OF THE MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF MUSCLE FIBERS BY THE SODIUM PUMP. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:761–775. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., FRUMENTO A. S. The concentration dependence of sodium efflux from muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Mar;46:629–654. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAJIMA S. ADAPTATION IN STRETCH RECEPTOR NEURONS OF CRAYFISH. Science. 1964 Nov 27;146(3648):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3648.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAJIMA S., IWASAKI S., OBATA K. Delayed rectification and anomalous rectification in frog's skeletal muscle membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Sep;46:97–115. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., DEGUCHI T., URAKAWA N., OHKUBO Y. Stabilization and rectification of muscle fiber membrane by tetrodotoxin. Am J Physiol. 1960 May;198:934–938. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.5.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Kusano K. Behavior of delayed current under voltage clamp in the supramedullary neurons of puffer. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):613–628. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Takahashi K. Post-tetanic hyperpolarization in stretch receptor neurone of crayfish. Nature. 1966 Mar 19;209(5029):1220–1221. doi: 10.1038/2091220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Nakajima S., Grundfest H. The action of tetrodotoxin on electrogenic components of squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jul;48(6):975–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA M. Die Wirkung von Adrenalin auf Purkinje-Fasern von Säugetierherzen. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(5):512–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00362255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., STRAUB R. W. The hyperpolarization which follows activity in mammalian non-medullated fibres. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):80–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEN A. K., POST R. L. STOICHIOMETRY AND LOCALIZATION OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT IN THE ERYTHROCYTE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayman C. L. Electrical properties of Neurospora crassa. Respiration and the intracellular potential. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Sep;49(1):93–116. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTWEIN W., SCHMIDT R. F. [On the membrane effect of adrenalin on the myocardial fiber]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;271:715–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. Slow and fast groups of pyramidal tract cells and their respective membrane properties. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Sep;28(5):908–924. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.5.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


