Abstract
1. Measurements of the CO2 tensions in arterial blood, in blood from the superior sagittal sinus, in cisternal cerebrospinal fluid, and on the surface of the cerebral cortex were made in spontaneously breathing anaesthetized cats and rats after inhibition of carbonic anhydrase with acetazolamide in doses of 50-150 mg/kg.
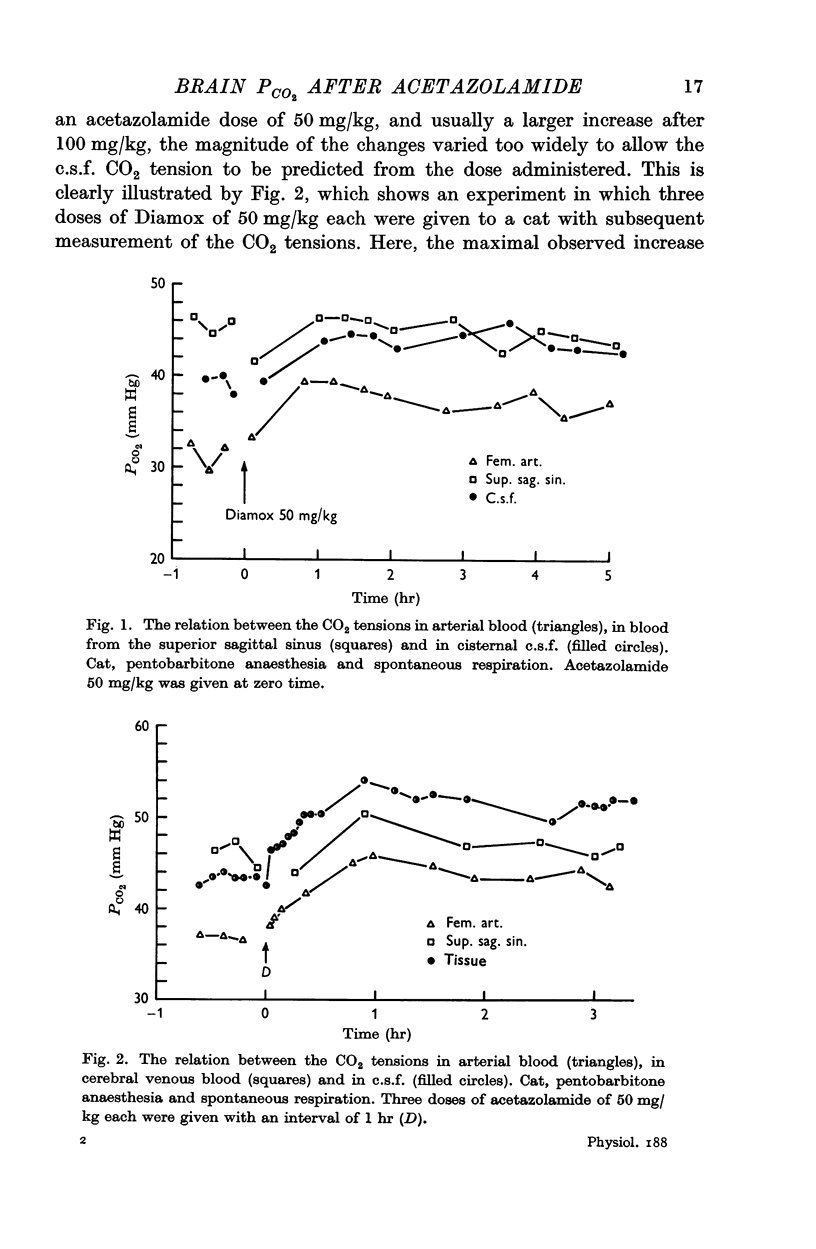
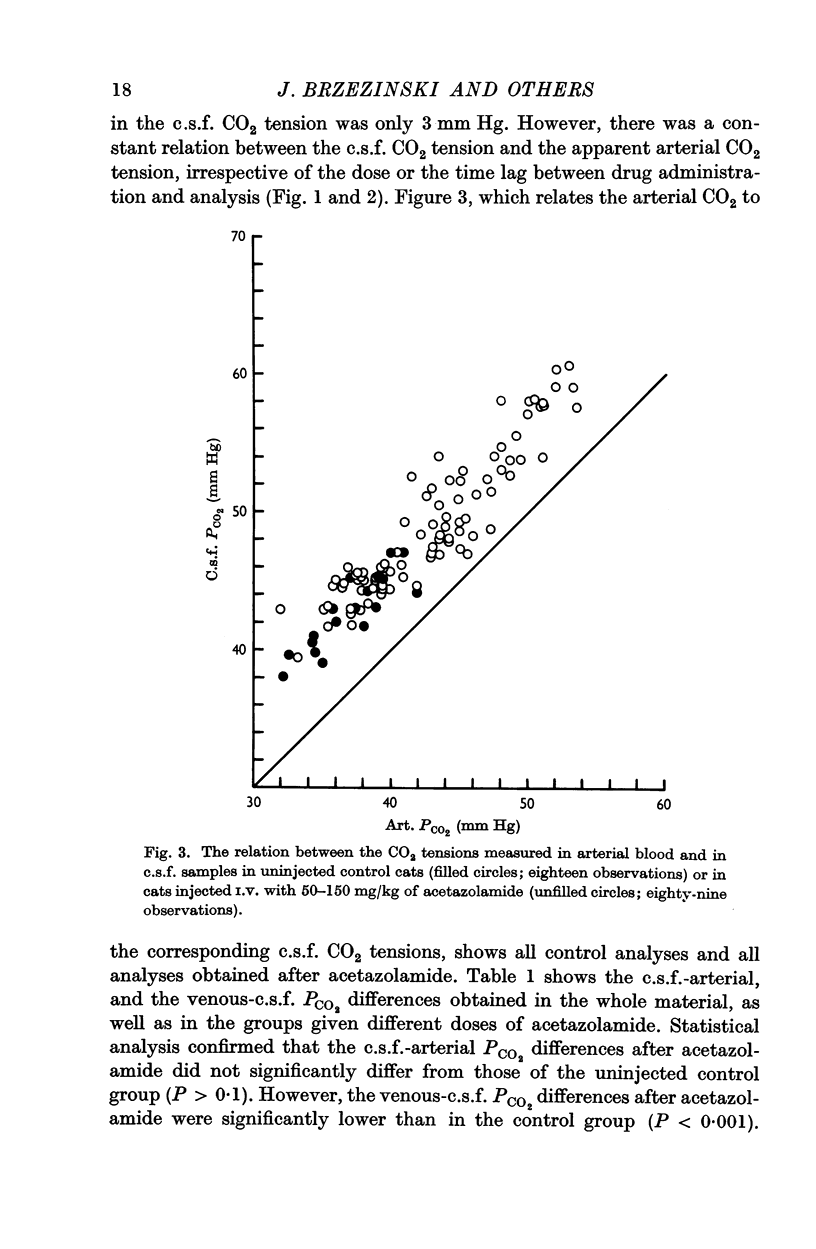
2. After an acetazolamide dose of 50 mg/kg in cats there was a mean increase in the c.s.f. CO2 tension of 8 mm Hg; after a dose of 100 mg/kg the corresponding mean increase was 13 mm Hg.
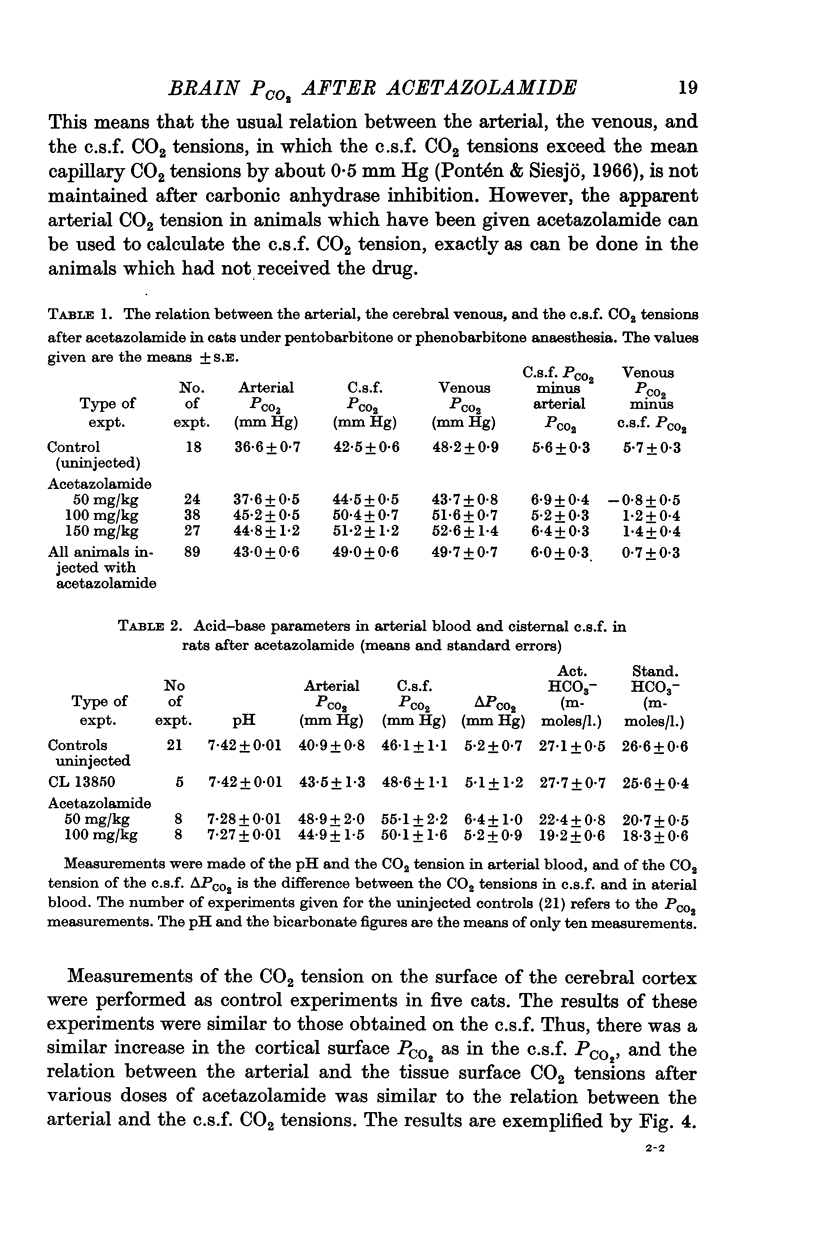
3. Since the CO2 tension measured in venous blood was only moderately influenced by the acetazolamide, the normal PCO2 difference between venous blood and c.s.f. was markedly reduced. The apparent arterial CO2 tension, i.e. the CO2 tension measured in vitro, always changed to the same extent as the c.s.f. CO2 tension.
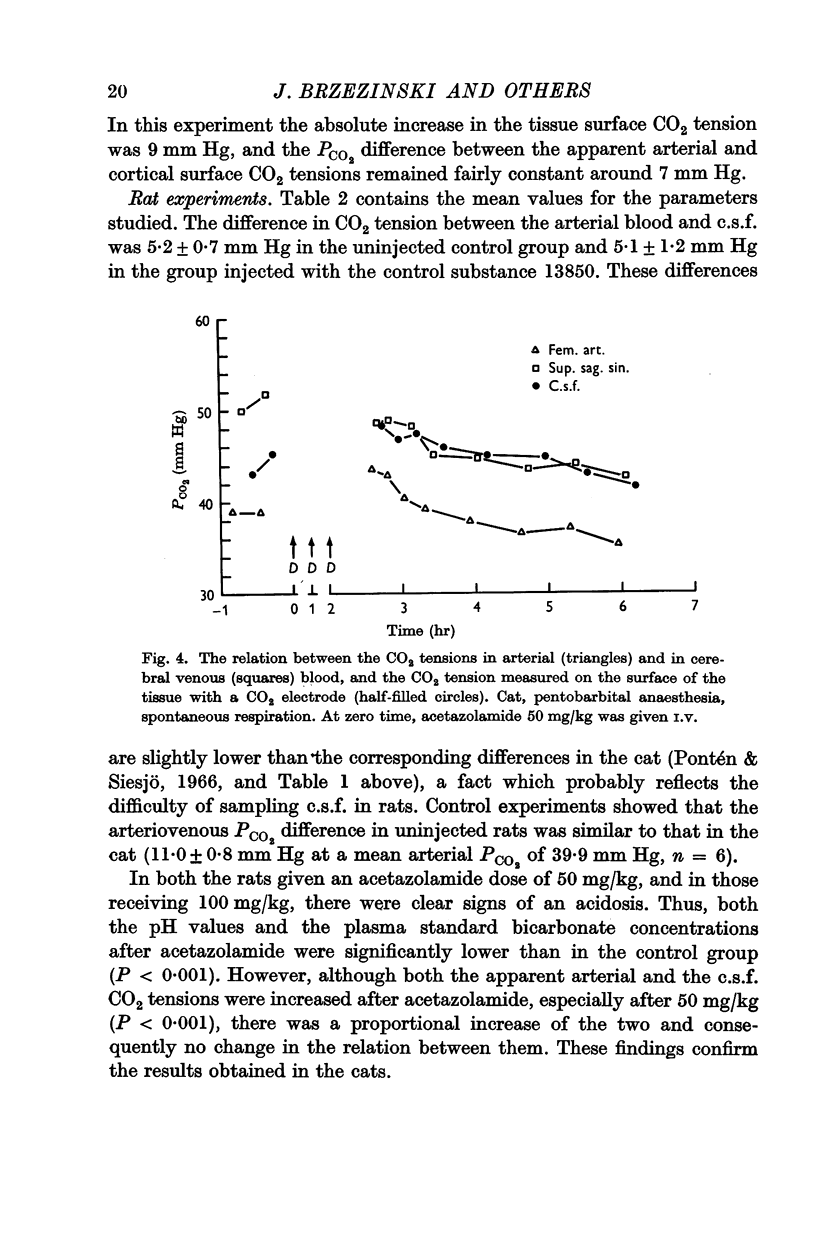
4. The findings were confirmed by measurements of the CO2 tension on the surface of the cerebral cortex, and by measurements of the blood and c.s.f. CO2 tensions in the rat.
5. It is concluded that the mean tissue CO2 tension of the brain can be estimated from the measured arterial CO2 tension, even under conditions of carbonic anhydrase inhibition.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHBY W., GARZOLI R. F., SCHUSTER E. M. Relative distribution patterns of three brain enzymes, carbonic anhydrase, choline esterase and acetyl phosphatase. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jul;170(1):116–120. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.170.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIN S. M., OTIS A. B. Carbon dioxide reention in anesthetized dogs after inhibition of carbonic anhydrase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Feb;103:439–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIN S. M., OTIS A. B. Effect of carbonic anhydrase inhibition on mixed venous carbon dioxide tension in anesthetized dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1960 May;15:390–392. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER E. T., CLARK R. T., Jr Respiratory effects of carbonic anhydrase inhibition in the trained unanesthetized dog. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Jul;13(1):42–46. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.13.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVSON H., LUCK C. P. The effect of acetazoleamide on the chemical composition of the aqueous humour and cerebrospinal fluid of some mammalian species and on the rate of turnover of 24Na in these fluids. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):279–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIACOBINI E. A cytochemical study of the localization of carbonic anhydrase in the nervous system. J Neurochem. 1962 Mar-Apr;9:169–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb11859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A., WOODBURY D. M. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition and brain electrolyte composition. Am J Physiol. 1960 Feb;198:434–440. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.2.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A. The number and distribution of capillaries in muscles with calculations of the oxygen pressure head necessary for supplying the tissue. J Physiol. 1919 May 20;52(6):409–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1919.sp001839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAREN T. H., ROBINSON B. The pharmacology of acetazolamide as related to cerebrospinal fluid and the treatment of hydrocephalus. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1960 Jan;106:1–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER J. S., GOTOH F. Interaction of cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism. Neurology. 1961 Apr;11(4):46–65. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.4_part_2.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITHOEFER J. C., DAVIS J. S. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase: effect on tissue gas tensions in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):797–801. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITHOEFER J. C. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase: its effect on carbon dioxide elimination by the lungs. J Appl Physiol. 1959 Jan;14(1):109–115. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1959.14.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontén U., Siesjö B. K. Gradients of CO2 tension in the brain. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jun;67(2):129–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAB M. [Acid-base equilibrium in arterial blood and cerebrospinal fluid in heart insufficiency and cor pulmonale and its control by carbonic anhydrase inhibition]. Klin Wochenschr. 1962 Dec 15;40:1233–1245. doi: 10.1007/BF01484389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSCHIRGI R. D., FROST R. W., TAYLOR J. L. Inhibition of cerebrospinal fluid formation by a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, 2-acetylamino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-5-sulfonamide (diamox). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Nov;87(2):373–376. doi: 10.3181/00379727-87-21386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISTRAND P., NECHAY B. R., MAREN T. H. Effects of carbonic anhydrase inhibition on cerebrospinal and intraocular fluids in the dog. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1961;17:315–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1961.tb01652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODBURY D. M., KARLER R. The role of carbon dioxide in the nervous system. Anesthesiology. 1960 Nov-Dec;21:686–703. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196011000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


