Abstract
1. The potency with which tubocurarine chloride (TC) and atropine sulphate (AS) influence the amplitude of the end-plate potentials was measured in the rat diaphragm. This effect was compared with the action of these drugs on brief depolarizations evoked by iontophoretic application of ACh to end-plate-free spots of the chronically denervated fibre.
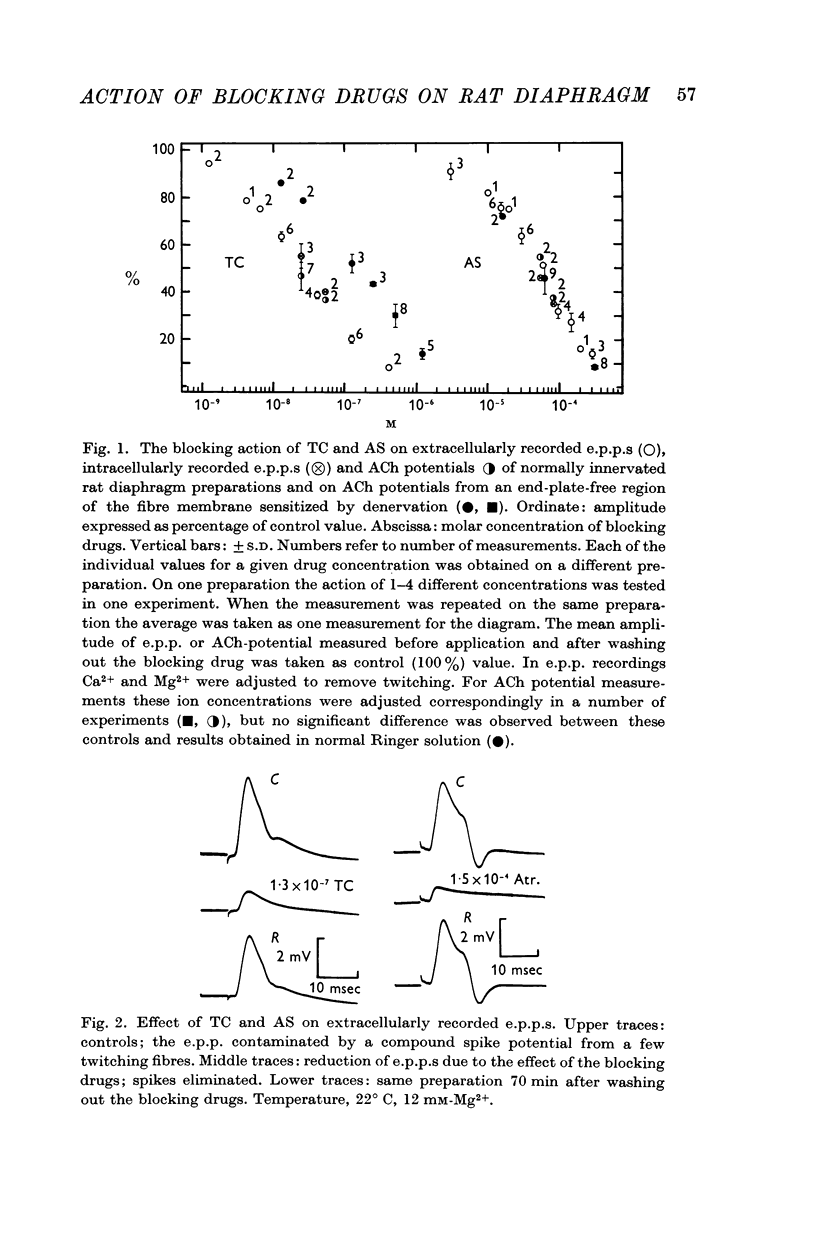
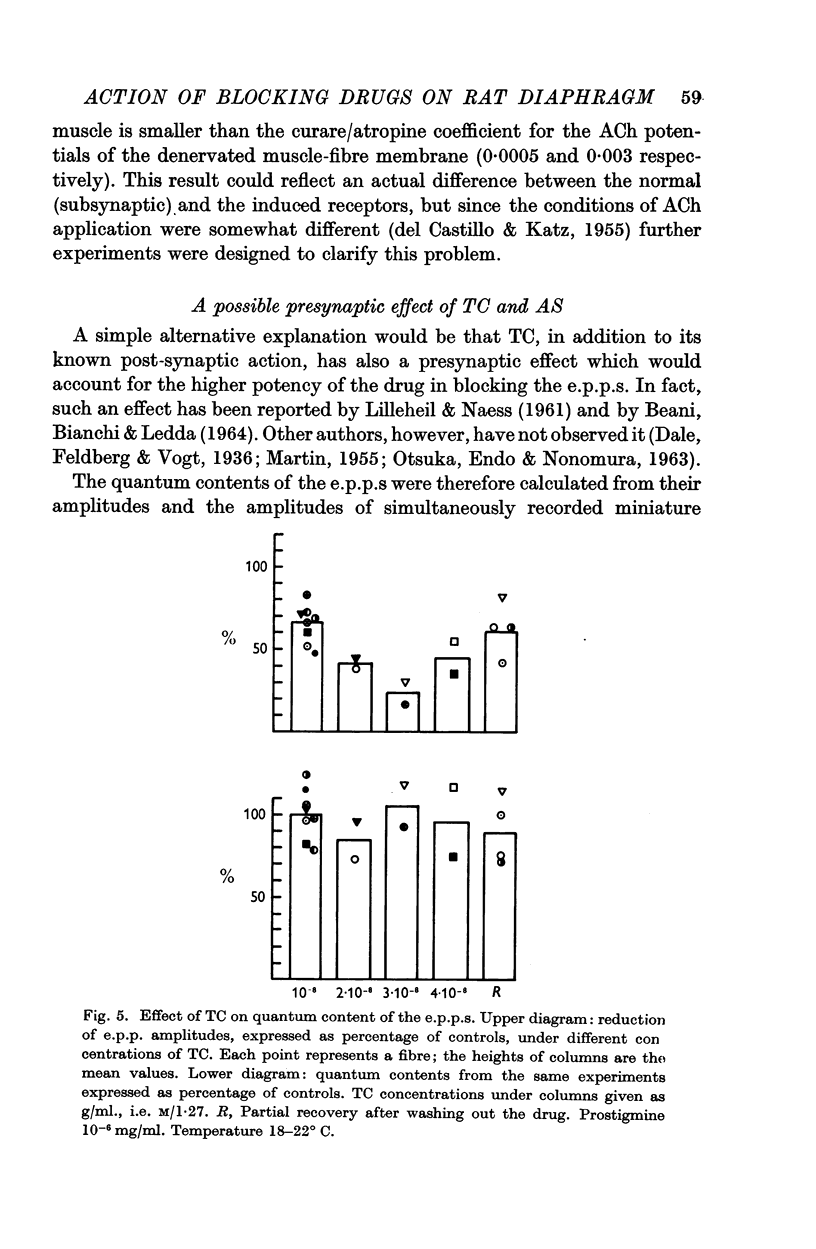
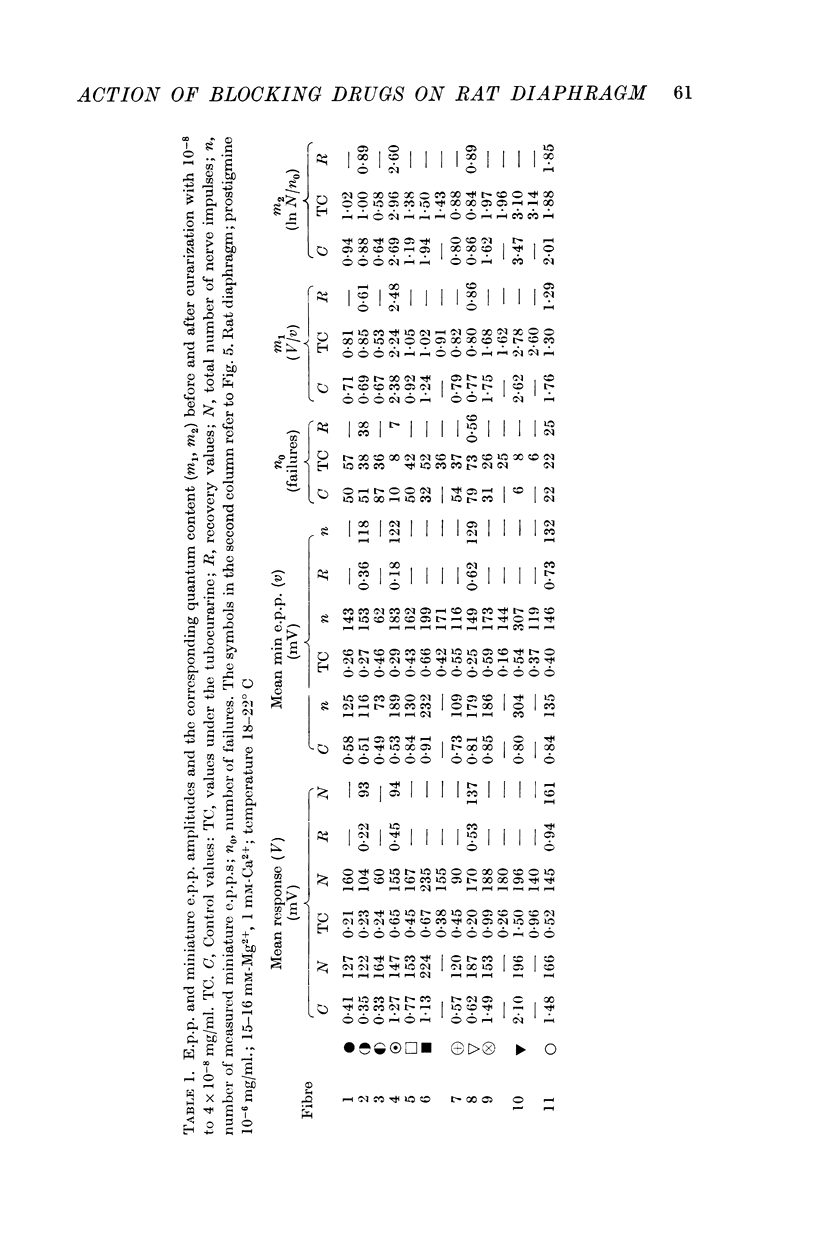
2. TC and AS act similarly on e.p.p.s, but the concentrations necessary to cause the same effect are 2000-times higher for AS.
3. The dose—response curves for both inhibitors are unchanged by prostigmine.
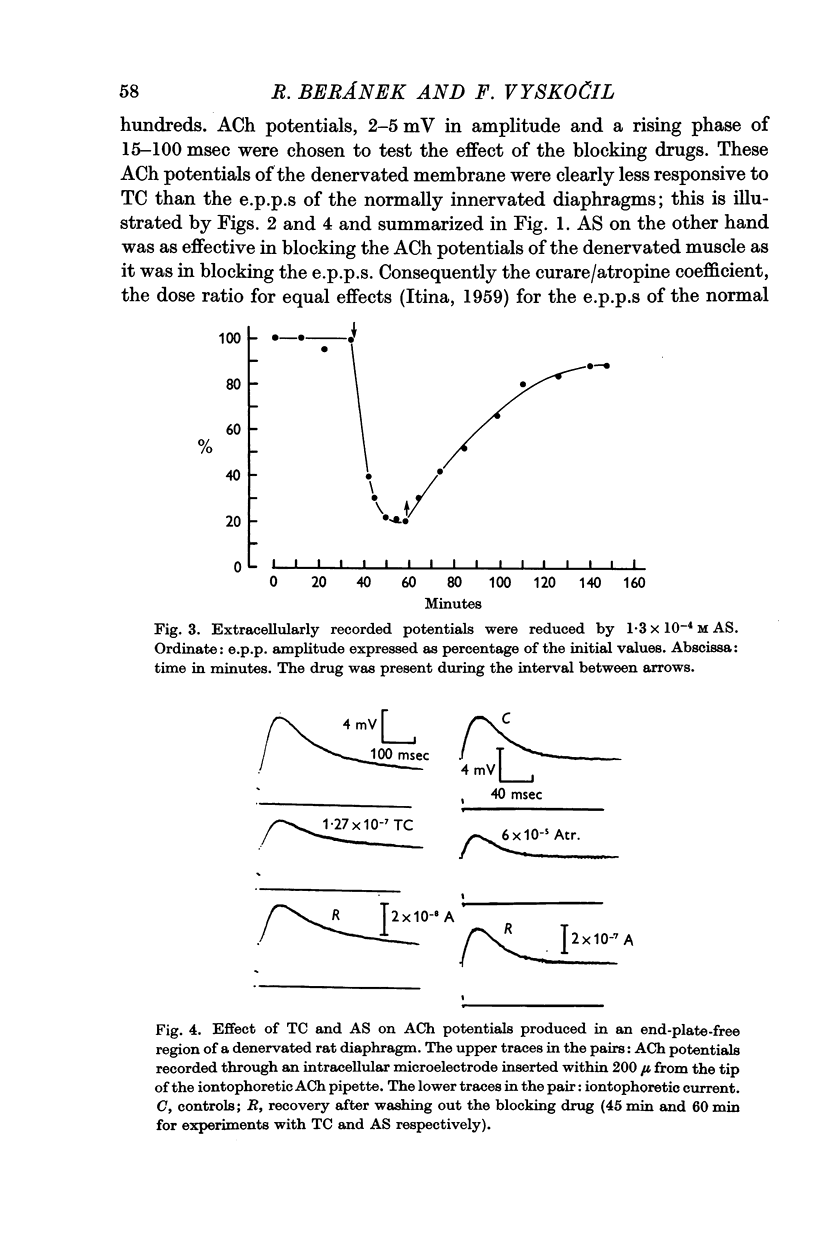
4. Ten to twenty-five days after denervation the ACh-potentials of the sensitized end-plate-free parts of the membrane are less responsive to curare than the normal e.p.p.s are. AS is as effective in blocking ACh potentials of denervated muscles as it is in blocking normal e.p.p.s. The curare/atropine coefficient (dose ratio for equal effect) is 0·0005 for e.p.p.s and 0·003 for ACh potentials of the denervated membrane.
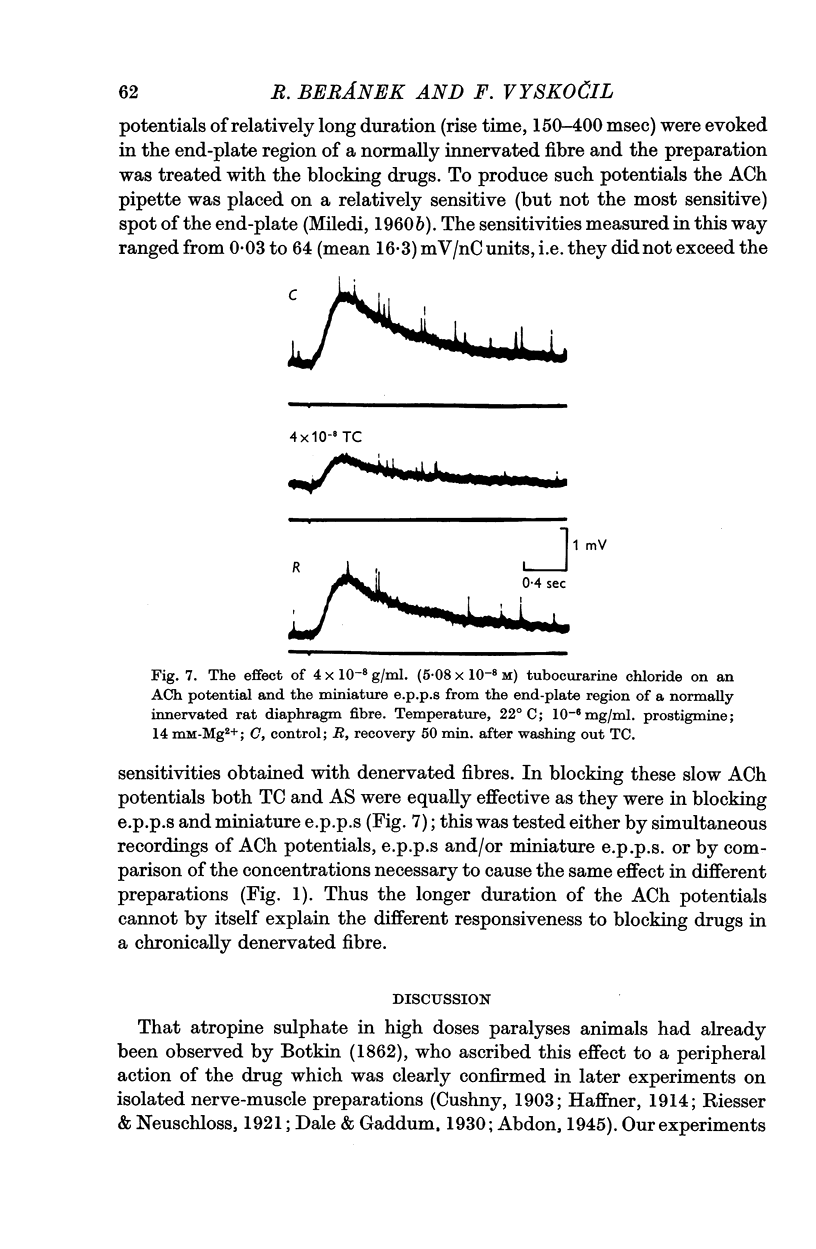
5. Both blocking drugs reduce the amplitude of ACh-potentials evoked in the end-plate region of normally innervated rat diaphragm fibres as effectively as they reduce the amplitude of e.p.p.s.
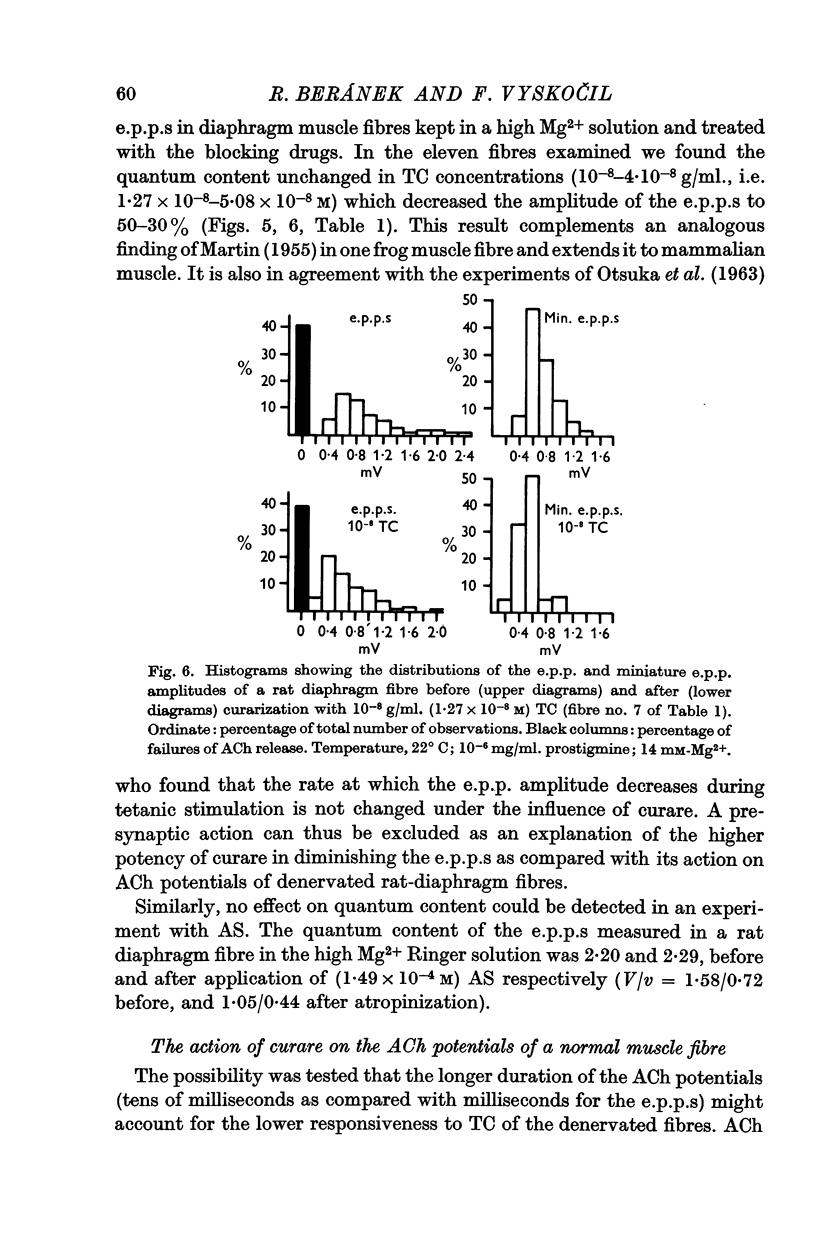
6. Neither TC nor AS have a presynaptic action in concentrations markedly reducing the e.p.p. amplitude.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. A study of supersensitivity in denervated mammalian skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):178–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEANI L., BIANCHI C., LEDDA F. THE EFFECT OF TUBOCURARINE ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:172–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. The end-plate potential in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):74–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE W. V. Structural variations of nerve endings in the striated muscles of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1957 Dec;108(3):445–463. doi: 10.1002/cne.901080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushny A. R. Atropine and the hyoscyamines-a study of the action of optical isomers. J Physiol. 1903 Nov 2;30(2):176–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1903.sp000988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. On the localization of acetylcholine receptors. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):157–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO L., KATZ B. A study of curare action with an electrical micromethod. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):339–356. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale H. H., Feldberg W., Vogt M. Release of acetylcholine at voluntary motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1936 May 4;86(4):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale H. H., Gaddum J. H. Reactions of denervated voluntary muscle, and their bearing on the mode of action of parasympathetic and related nerves. J Physiol. 1930 Sep 18;70(2):109–144. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., THESLEFF S. A study of acetylcholine induced contractures in denervated mammalian muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1960;17:84–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1960.tb01232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P. The electromotive action of acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):408–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The antagonism between tubocurarine and substances which depolarize the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCO J. V. THE TROPHIC EFFECT OF NEURONE ACTIVITY. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1963;13:124–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. N. On the reaction of cells and of nerve-endings to certain poisons, chiefly as regards the reaction of striated muscle to nicotine and to curari. J Physiol. 1905 Dec 30;33(4-5):374–413. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1905.sp001128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Junctional and extra-junctional acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:24–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA M., ENDO M., NONOMURA Y. Presynaptic nature of neuromuscular depression. Jpn J Physiol. 1962 Dec 15;12:573–584. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.12.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFF S., QUASTEL D. M. NEUROMUSCULAR PHARMACOLOGY. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1965;5:263–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.05.040165.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



