Abstract
1. Recordings of transmembrane potentials have been made in vitro from the cells of the adrenal gland using glass micro-electrodes.
2. There was only a small species variation in the mean membrane potential of the cortical cells of the rabbit, rat and kitten; 66·2, 70·5, and 71·4 mV respectively.
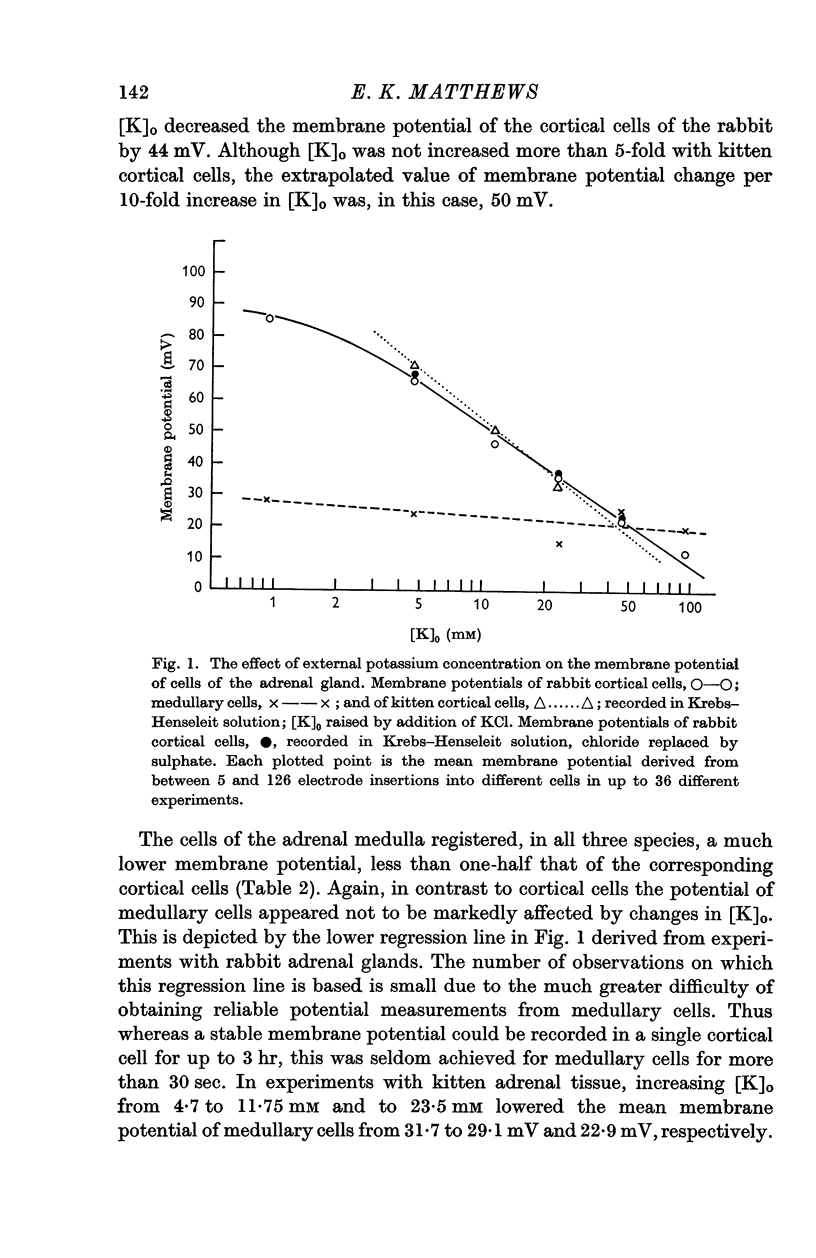
3. The membrane potential of cortical cells was dependent upon the external potassium concentration, [K]o. Raising [K]o above the normal concentration of 4·7 mM by addition of KCl decreased the membrane potential; lowering [K]o from normal increased it. The decrease in membrane potential was still evident when chloride was replaced by sulphate. Increasing [K]o 10-fold decreased the membrane potential of rabbit cortical cells by 44 mV and of kitten cortical cells by 50 mV.
4. The mean membrane potential measured in medullary chromaffin cells was for the rabbit 24·2 mV, rat 20 mV, and kitten 31·7 mV. The potentials of medullary cells were much less affected by changes in [K]o than were cortical cell potentials.
5. Age had little influence upon either cortical or medullary membrane potentials of adrenal glands, at least in early life.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. Potassium chloride movement and the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:154–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., KURIYAMA H. Effects of changes in the external sodium and calcium concentrations on spontaneous electrical activity in smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:29–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E. (ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE RAT ADRENAL MEDULLA. I. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION OF CHROMAFFIN CELLS IN THE NORMAL ADRENAL MEDULLA.) J Anat. 1965 Apr;99:231–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., POISNER A. M. On the mode of action of acetylcholine in evoking adrenal medullary secretion: increased uptake of calcium during the secretory response. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:385–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Poisner A. M., Rubin R. P. Efflux of adenine nucleotides from perfused adrenal glands exposed to nicotine and other chromaffin cell stimulants. J Physiol. 1965 Jul;179(1):130–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURIYAMA H. The influence of potassium, sodium and chloride on the membrane potential of the smooth muscle of taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:15–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVER J. D. Electron microscopic observations on the adrenal cortex. Am J Anat. 1955 Nov;97(3):409–429. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000970304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A. Electrophysiology of salivary glands. Physiol Rev. 1958 Jan;38(1):21–40. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Saffran M. Steroid production and membrane potential measurement in cells of the adrenal cortex. J Physiol. 1967 Mar;189(1):149–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanne O., Coraboeuf E. Potential and resistance measurements of rat liver cells in situ. Nature. 1966 Jun 25;210(5043):1390–1391. doi: 10.1038/2101390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. Cortical secretion of the isolated perfused adrenal. J Physiol. 1951 Apr;113(2-3):129–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M. The output of cortical hormone by the mammalian suprarenal. J Physiol. 1943 Dec 31;102(3):341–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODBURY D. M., WOODBURY J. W. CORRELATION OF MICRO-ELECTRODE POTENTIAL RECORDINGS WITH HISTOLOGY OF RAT AND GUINEA-PIG THYROID GLANDS. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:553–567. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


