Abstract
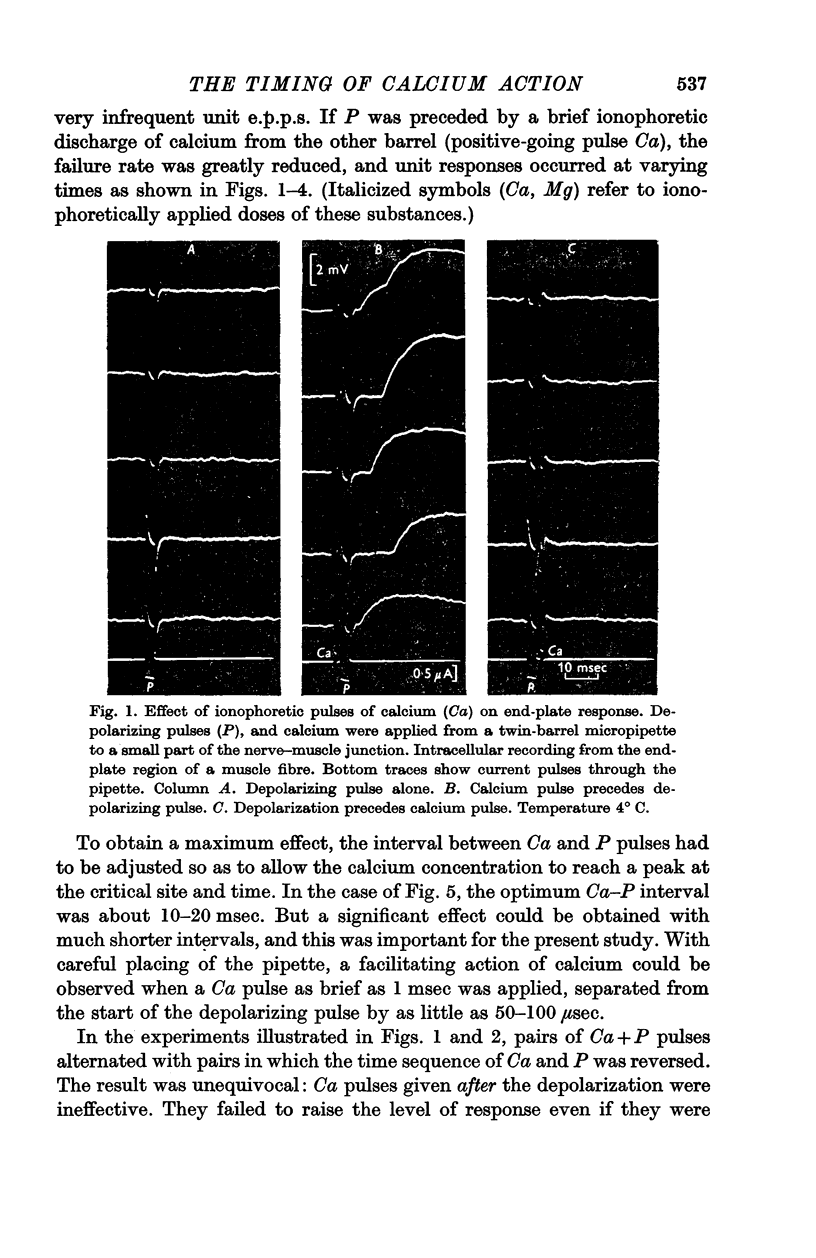
1. When a nerve—muscle preparation is paralysed by tetrodotoxin, brief depolarizing pulses applied to a motor nerve ending cause packets of acetylcholine to be released and evoke end-plate potentials (e.p.p.s), provided calcium ions are present in the extracellular fluid.
2. By ionophoretic discharge from a 1 M-CaCl2 pipette, it is possible to produce a sudden increase in the local calcium concentration at the myoneural junction, at varying times before or after the depolarizing pulse.
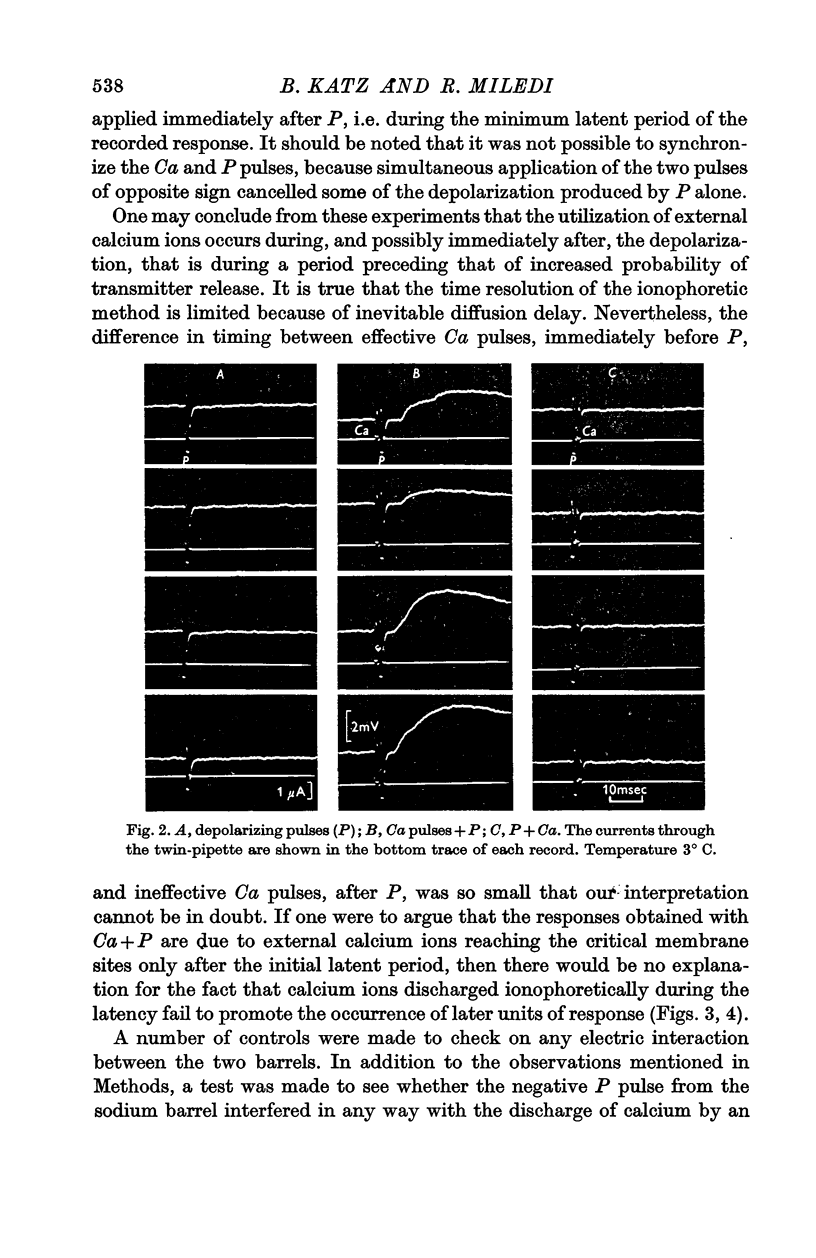
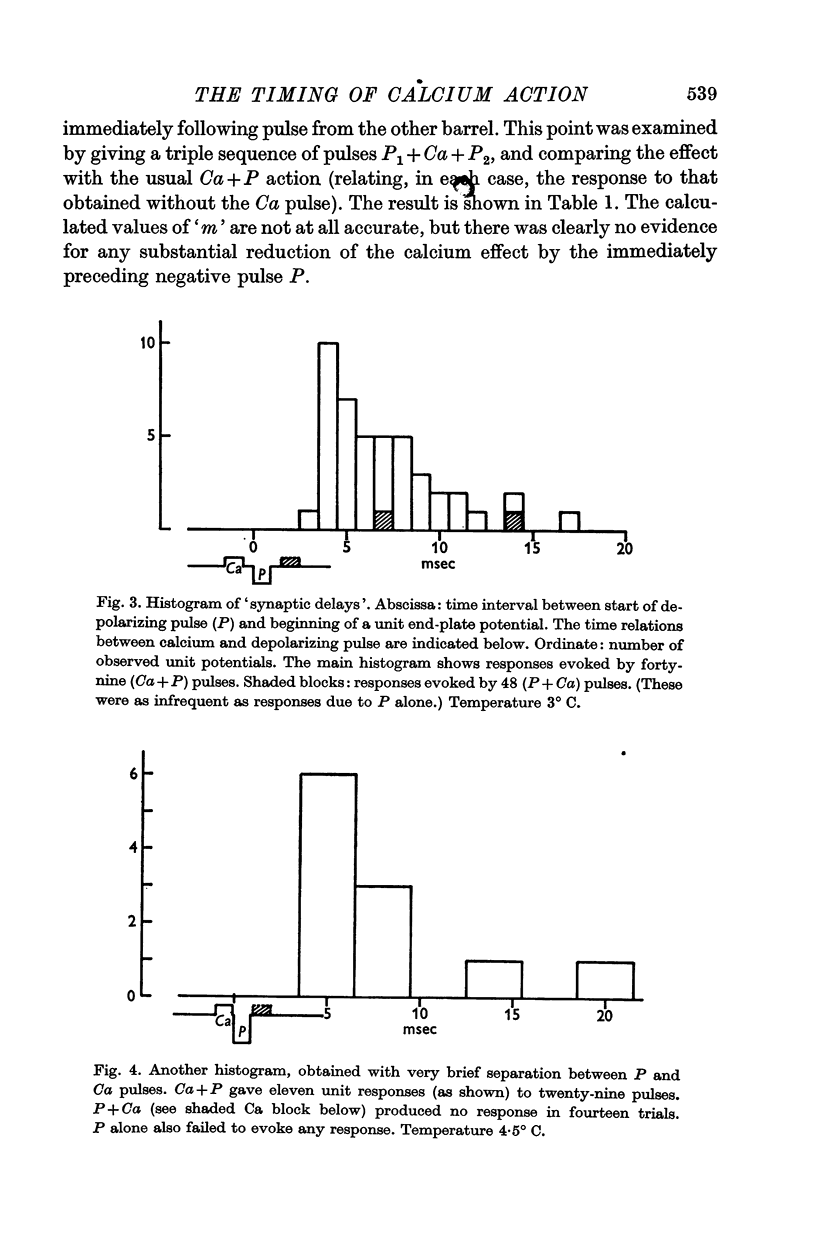
3. A brief application of calcium facilitates transmitter release if it occurs immediately before the depolarizing pulse. If the calcium pulse is applied a little later, during the period of the synaptic delay, it is ineffective.
4. It is concluded that the utilization of external calcium ions at the neuromuscular junction is restricted to a brief period which barely outlasts the depolarization of the nerve ending, and which precedes the transmitter release itself.
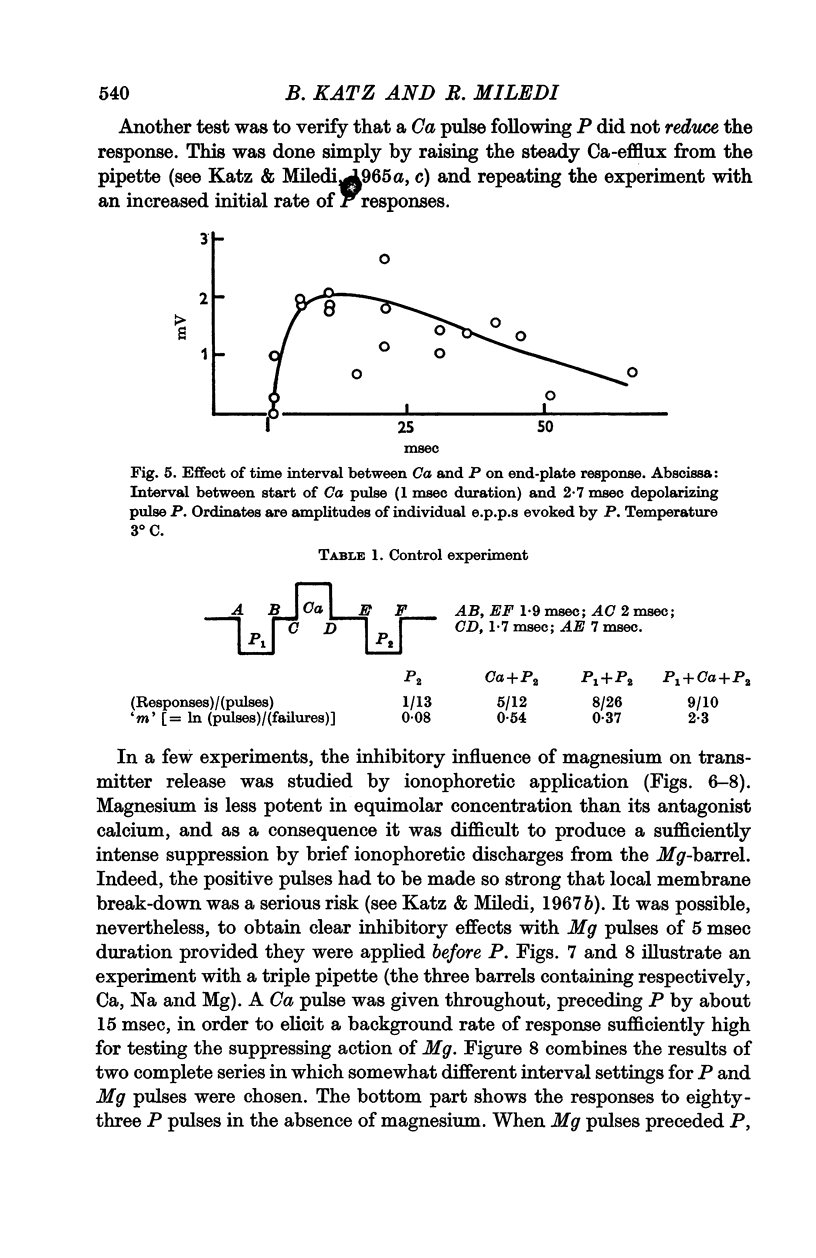
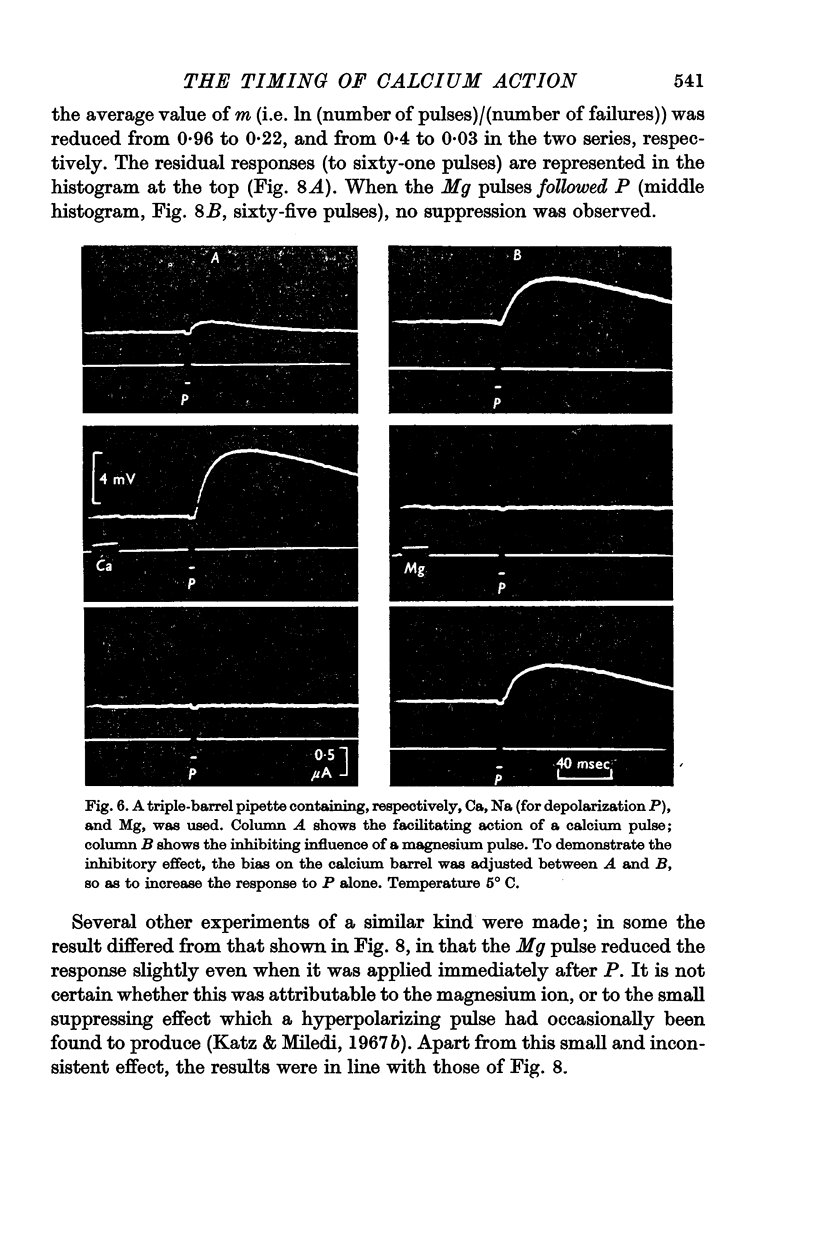
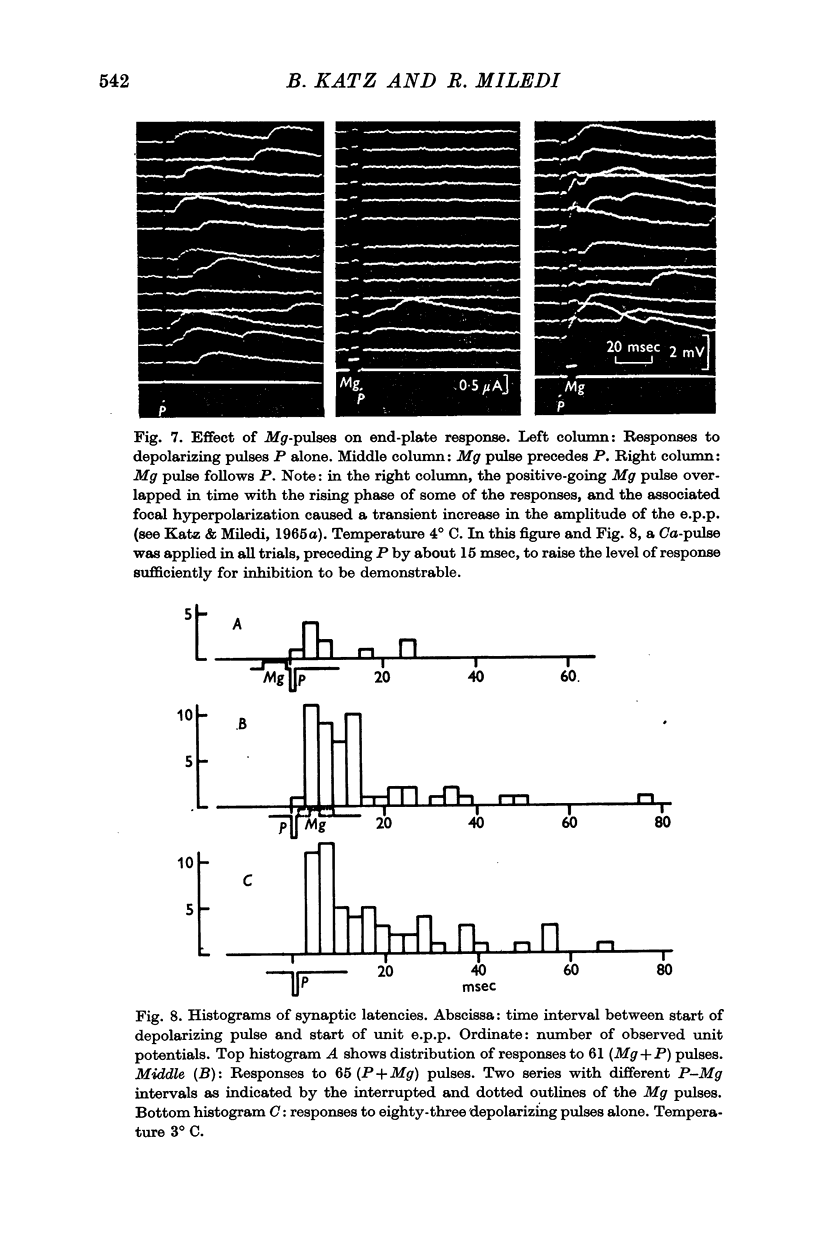
5. The suppressing effect of magnesium on transmitter release was studied by a similar method, with ionophoretic discharges from a 1 M-MgCl2-filled pipette. The results, though not quite as clear as with calcium, indicate that Mg pulses also are only effective if they precede the depolarizing pulses.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin and neuromuscular transmission. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):8–22. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


