Abstract
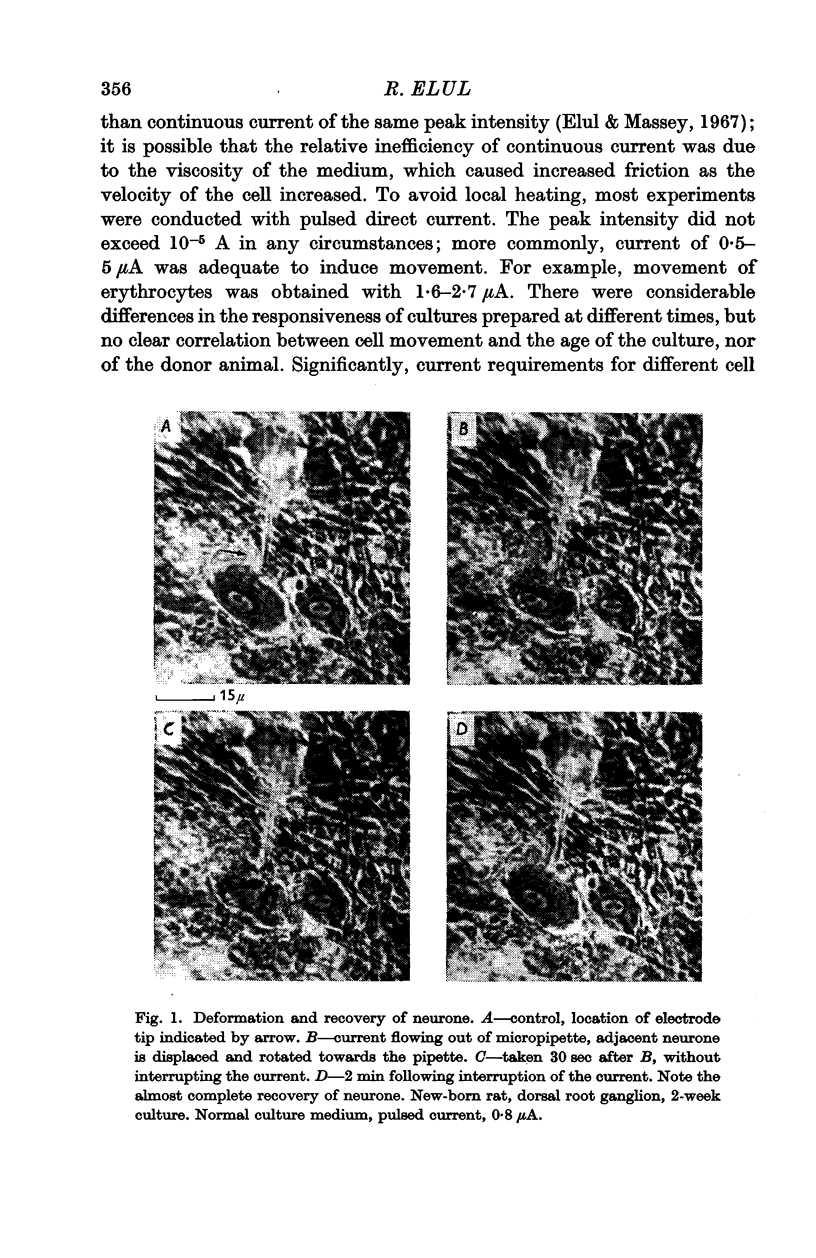
1. Focal electric field was generated by passing a current of 5 × 10-7 to 1 × 10-5 A from a micropipette into the culture medium. Movement of cells at a distance of 5-50 μ from the electrode tip was observed. In case of cells embedded in the culture only local deformation of the membrane was observed.
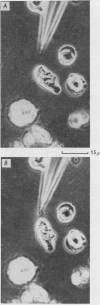
2. The cell species explored included neurones, glia, muscle fibres, connective cells, malignant cells and erythrocytes. All cells responded in a similar manner to the electric field, and the current required was in the same range.
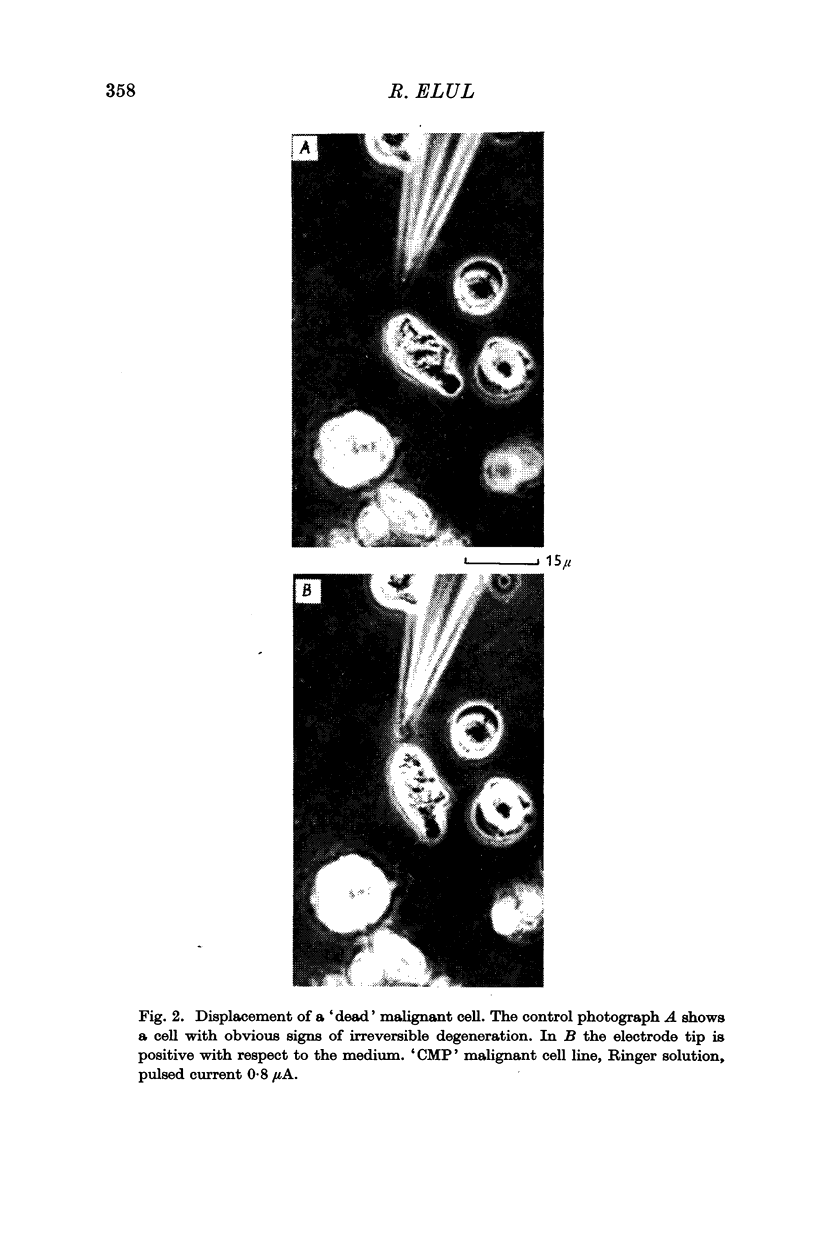
3. Cells were attracted to a positive micropipette and repelled from a negative one: the only exception was observed in certain malignant cells which moved in the opposite direction.
4. Movement and membrane deformation could be obtained with electrodes filled with various concentrated and isotonic solutions. The composition of the culture medium also had no qualitative influence on these effects.
5. Metabolic poisons or rupture of the cell membrane had no effect on the movement. Isolated membrane fragments showed movement similar to that of intact cells.
6. The possibility of artifacts due to proximity of the focal electrode is considered. It is shown that electro-osmosis cannot account for the present observations. Some other artifacts are also excluded.
7. It is proposed that the most satisfactory way to account for the present observations is by a membrane carrying negative fixed charge of the order of 2·5 × 103 e.s.u./cm2. Some physiological consequences of presence of negative charge in the membrane are briefly discussed.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., PETHICA B. A., SEAMAN G. V. The charged groups at the interface of some blood cells. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):12–19. doi: 10.1042/bj0690012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG J. J., HILD W. Contractile responses to electrical stimulation of glial cells from the mammalian central nervous system cultivated in vitro. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1959 Feb;53:139–144. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030530112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elul R. Dependence of synaptic transmission on protein metabolism of nerve cells: a possible electrokinetic mechanism of learning? Nature. 1966 Jun 11;210(5041):1127–1131. doi: 10.1038/2101127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARD D. H., SEAMAN G. V. The influence of pH and ionic strength on the electrokinetic stability of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:635–654. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILD W., TASAKI I. Morphological and physiological properties of neurons and glial cells in tissue culture. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Mar;25:277–304. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES A. M. The electrochemistry of the bacterial surface. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;8:95–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POMERAT C. M. Pulsatile activity of cells from the human brain in tissue culture. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1951 Nov;114(5):430–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONDER E., PONDER R. V. The electrophoretic velocity of human red cells, of their ghosts and mechanically produced fragments, and of certain lipid complexes. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:503–508. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiborn C. W., Jr, Massey J. F. Dialyzing membrane for improved spinal cord maintenance in roller tube cultures. Stain Technol. 1965 Sep;40(5):293–294. doi: 10.3109/10520296509116429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON T. E., McLEES B. D. An electrophoretic study of suspensions of intact mitochondria and fragments of mitochondrial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 24;50:213–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]