Abstract
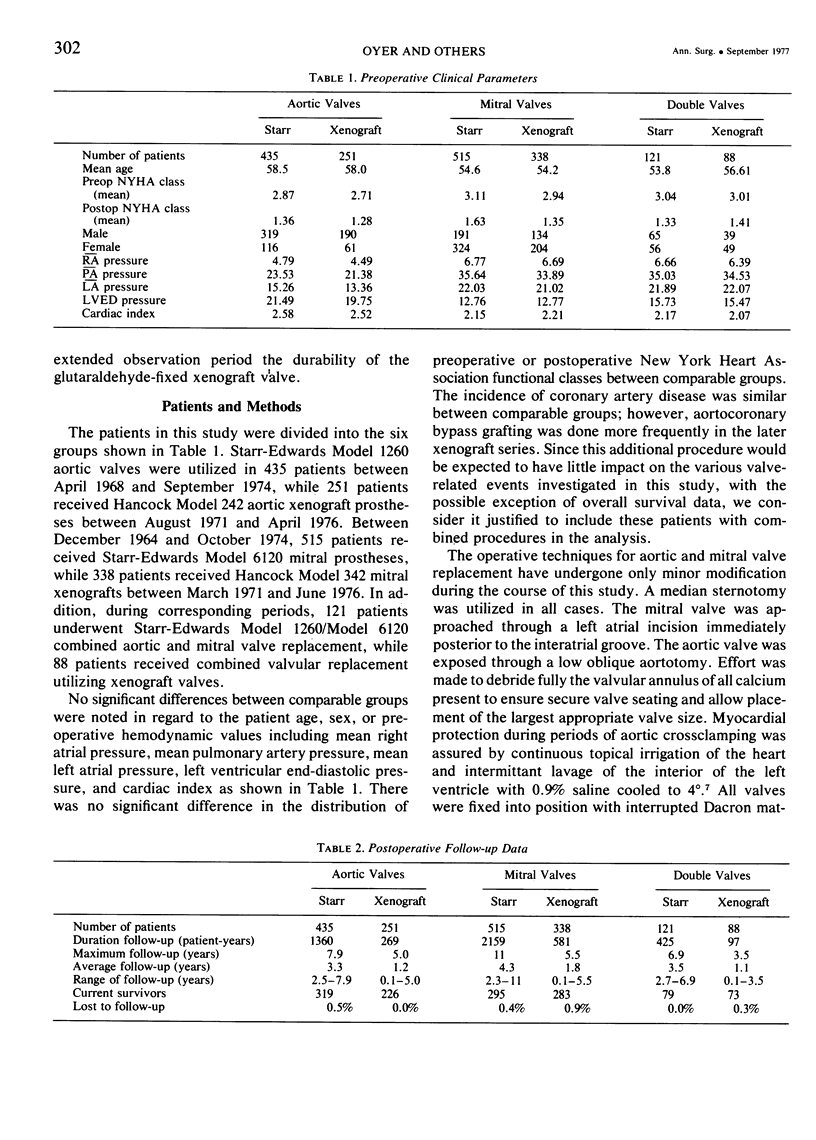
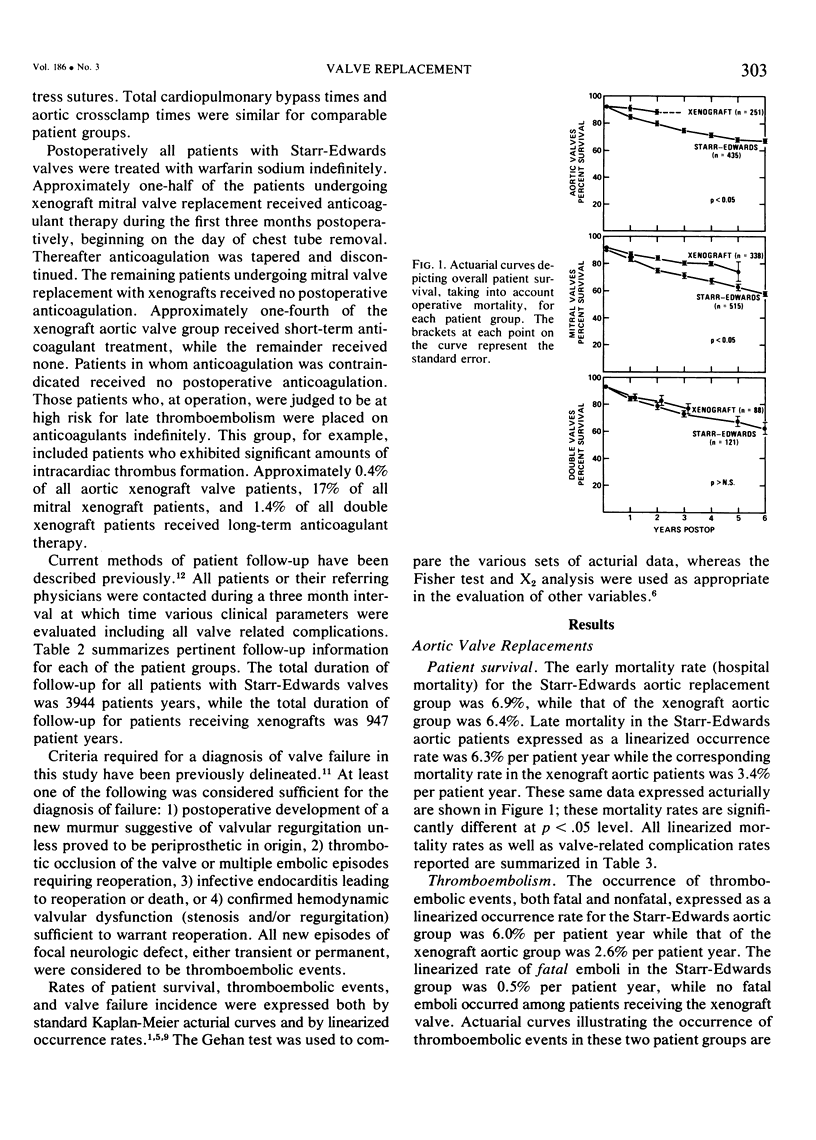
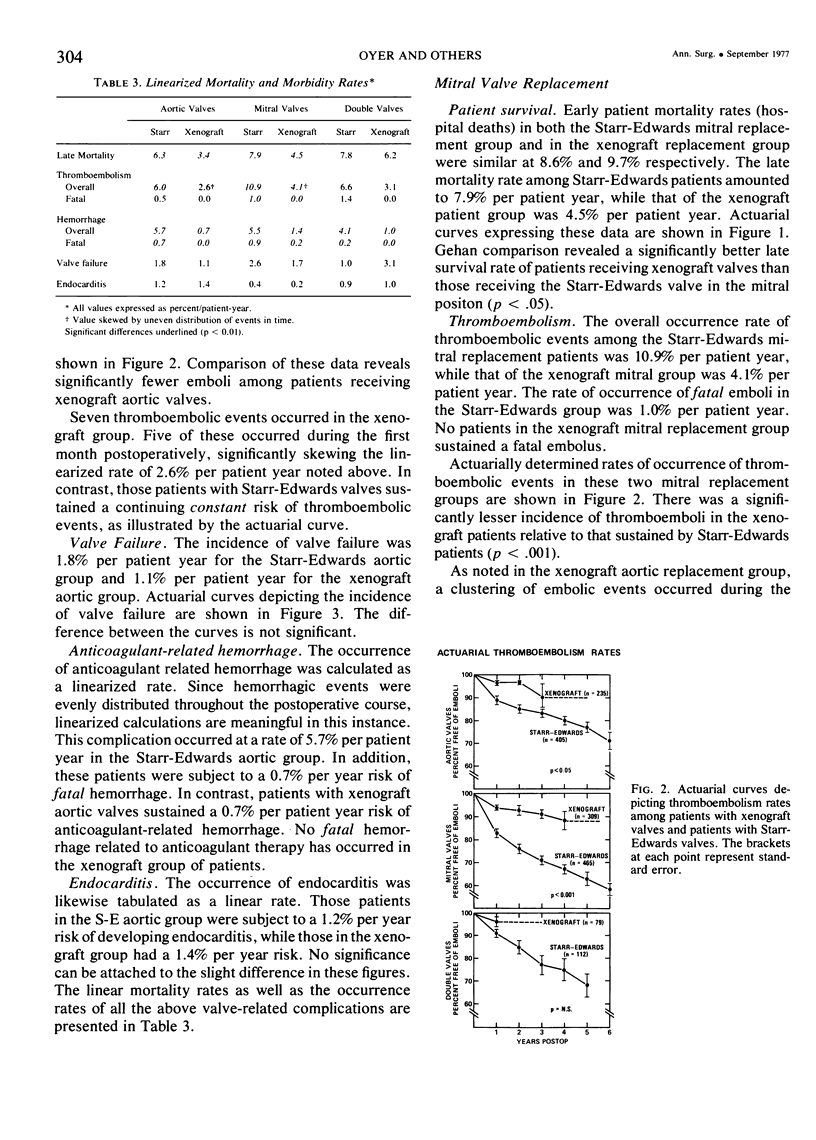
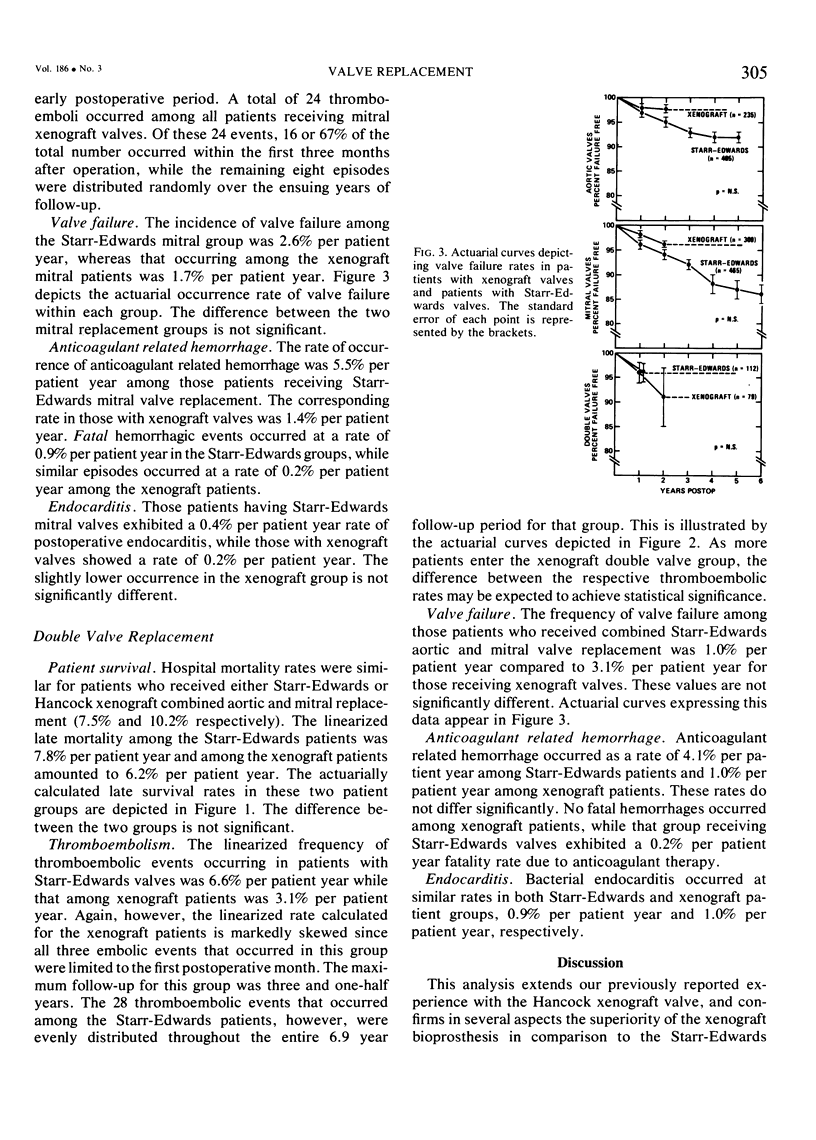
Although the Starr-Edwards caged-ball valve remains a standard of comparison for more recently introduced prostheses, a substantial incidence of thromboembolic and hemorrhagic complications prompted our evaluation of the Hancock glutaraldehyde-fixed porcine xenograft. We have compared the results of 435 aortic valve replacements using the Starr- Edwards valve (SE-AVR), 515 mitral valve replacements (SE-MVR), and 121 double-valve replacements (SE-AVRMVR) with 251 aortic valve replacements using the xenograft aortic valve (X-AVR), 338 mitral valve replacements (X-MVR), and 88 double-valve replacements (X-AVR-MVR). The Starr- Edwards valves were used during the period 1963 through 1973 and the xenograft valves between 1971 and 1976. No significant differences in patient age, sex, or preoperative hemodynamic data were noted between comparable groups. All patients with Starr-Edwards valves received long-term anticoagulation while anticoagulants were used only for specific indications in patients with xenograft valves. Total follow up was 3944 patient years for the Starr-Edwards patients and 947 patient years for the xenograft patients. Hospital mortality was not significantly different for comparable groups: SE-AVR 6.9% vs. X-AVR 6.4%, SE-MVR 9.7% vs X-MVR 8.6%, and SE-AVR-MVR 7.5% vs. X-AVR-MVR 10.2%. Linearized mortality and morbidity data expressed as percent per patient- year are tabulated below. Pairs which differ significantly (p < .05) are italicized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. P., Bonchek L. I., Grunkemeier G. L., Lambert L. E., Starr A. The analysis and presentation of surgical results by actuarial methods. J Surg Res. 1974 Mar;16(3):224–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(74)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonchek L. I., Starr A. Ball valve prostheses: current appraisal of late results. Am J Cardiol. 1975 Jun;35(6):843–854. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(75)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTLER S. J., EDERER F. Maximum utilization of the life table method in analyzing survival. J Chronic Dis. 1958 Dec;8(6):699–712. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(58)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEHAN E. A. A GENERALIZED WILCOXON TEST FOR COMPARING ARBITRARILY SINGLY-CENSORED SAMPLES. Biometrika. 1965 Jun;52:203–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griepp R. B., Stinson E. B., Shumway N. E. Profound local hypothermia for myocardial protection during open-heart surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973 Nov;66(5):731–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis R. L., Hancock W. D., Yarbrough J. W., Glancy D. L., Morrow A. G. The flexible stent. A new concept in the fabrication of tissue heart valve prostheses. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1971 Nov;62(5):683–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson E. B., Griepp R. B., Oyer P. E., Shumway N. E. Long-term experience with porcine aortic valve xenografts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1977 Jan;73(1):54–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


