Abstract
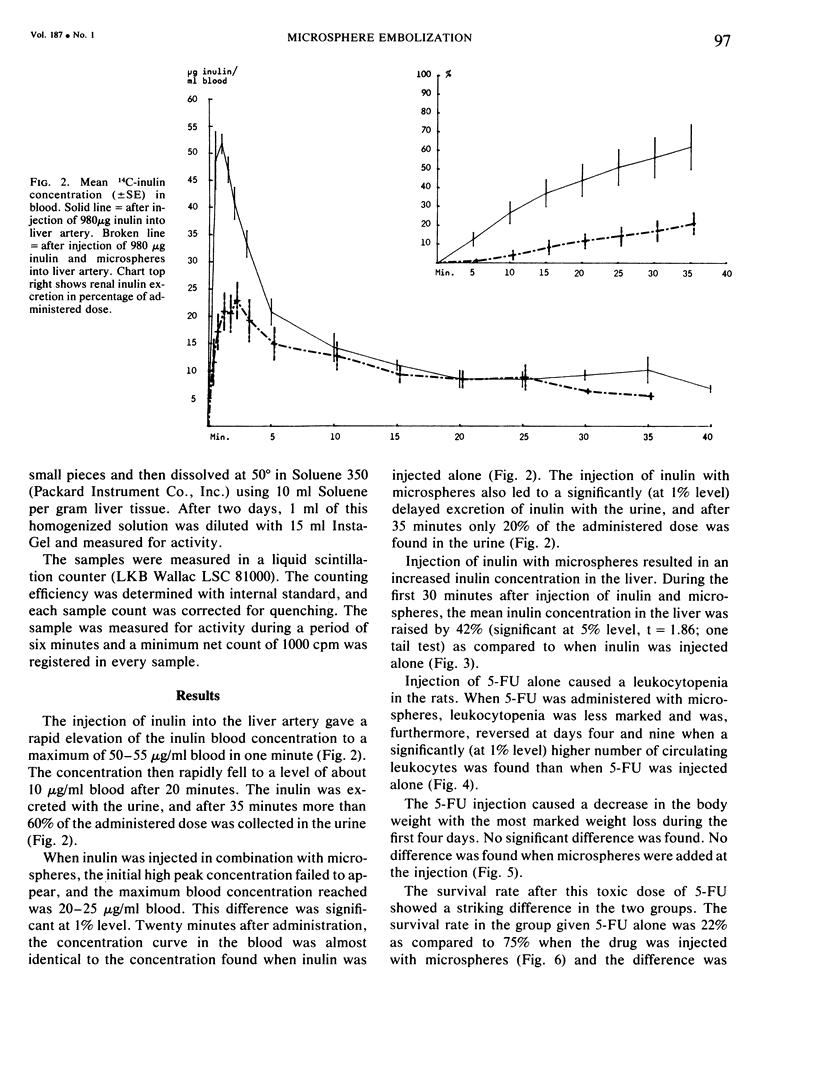
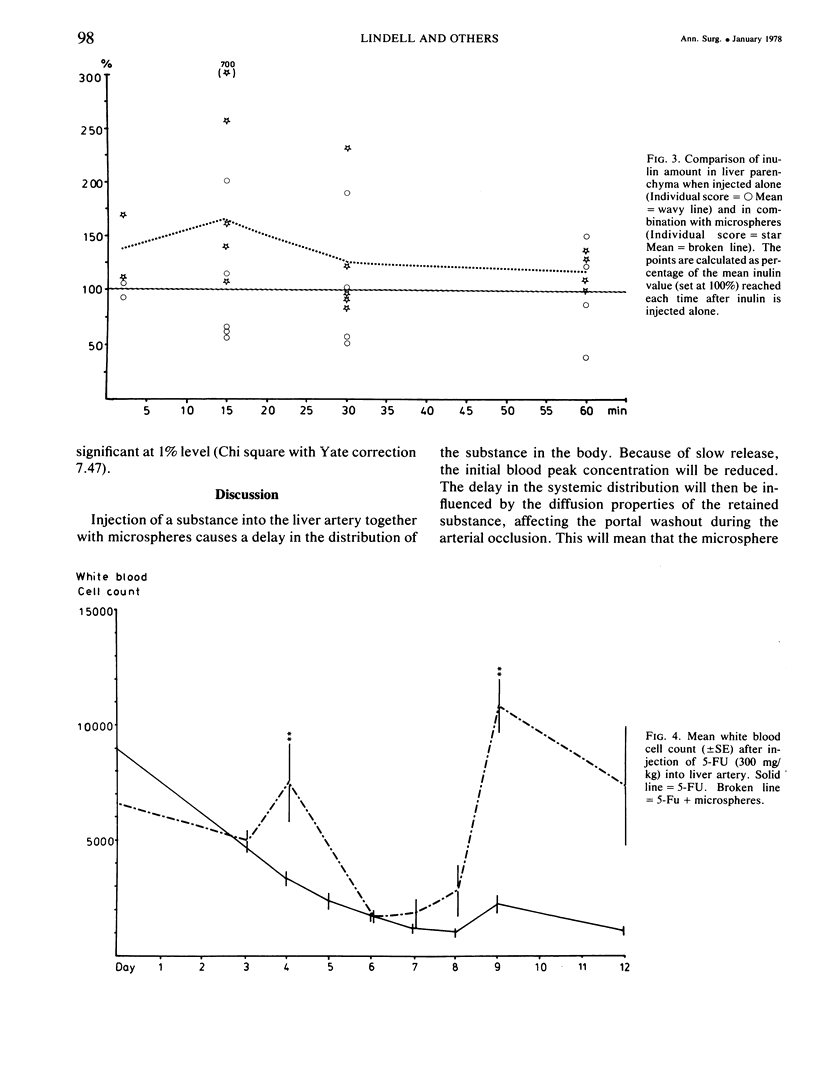
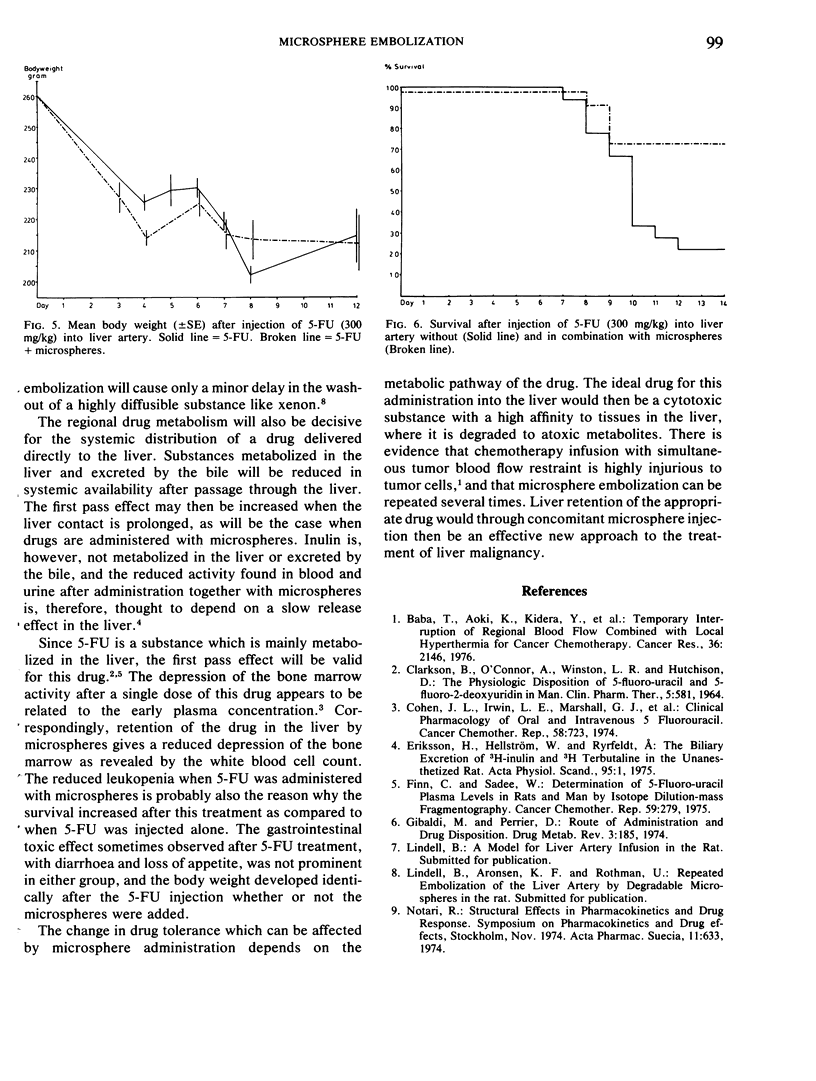
Earlier investigation has shown that a temporary arrest of arterial blood flow can be achieved by embolization with degradable microspheres. This study was made to investigate the change in pharmacokinetics, and drug tolerance which takes place when a substance is retained in the liver by a microsphere embolization. 14C-labelled inulin and 5-fluorouracil were studied. The administration of these substances with microspheres led to a delay in their systemic distribution. Furthermore there was an increased tolerance to 5-fluoro-uracil, probably due to a prolonged first pass effect when the substance was temporarily retained in the liver by a microsphere embolization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba T., Aoki K., Kidera Y., Kimura M., Kanematsu T. Temporary interruption of regional blood flow combined with local hyperthermia for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1976 Jul;36(7 Pt 1):2146–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKSON B., O'CONNOR A., WINSTON L., HUTCHISON D. THE PHYSIOLOGIC DISPOSITION OF 5-FLUOROURACIL AND 5-FLUORO-2'-DEOXYURIDINE IN MAN. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1964 Sep-Oct;5:581–610. doi: 10.1002/cpt196455581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. L., Irwin L. E., Marshall G. J., Darvey H., Bateman J. R. Clinical pharmacology of oral and intravenous 5-fluorouracil (NSC-19893). Cancer Chemother Rep. 1974 Sep-Oct;58(5 Pt 1):723–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson H., Hellström W., Ryrfeldt A. The biliary excretion of 3H-inulin and 3H-terbutaline in the unanesthetized rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Sep;95(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb10017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finj C., Sadée W. Determination of 5-fluorouracil (NSC-19893) plasma levels in rats and man by isotope dilution-mass fragmentography. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1975 Mar-Apr;59(2 Pt 1):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibaldi M., Perrier D. Route of administration and drug disposition. Drug Metab Rev. 1974;3(2):185–199. doi: 10.3109/03602537408993742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


