Abstract
The dog with an end-to-side portacaval shunt (PCS) has been extensively used as a model to investigate hepatic encephalopathy (HE) as it demonstrates a plasma amino acid pattern similar to patients with chronic liver disease. In adult mongrel dogs, the effect of PCS on plasma and CSF amino acids, octopamine (OCT), phenylethanolamine (PEA) and CSF 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid (5-HIAA), were studied. Moreover, the effect of correction of plasma amino acids by infusional techniques was investigated.
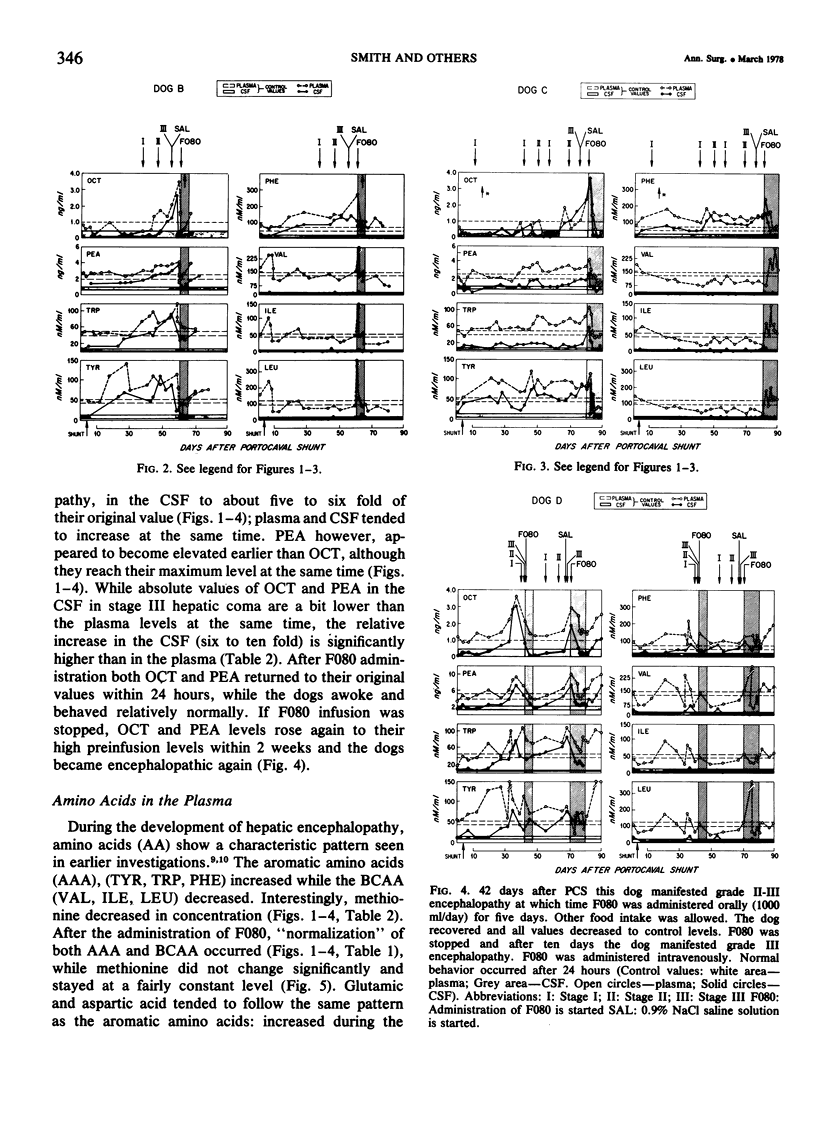
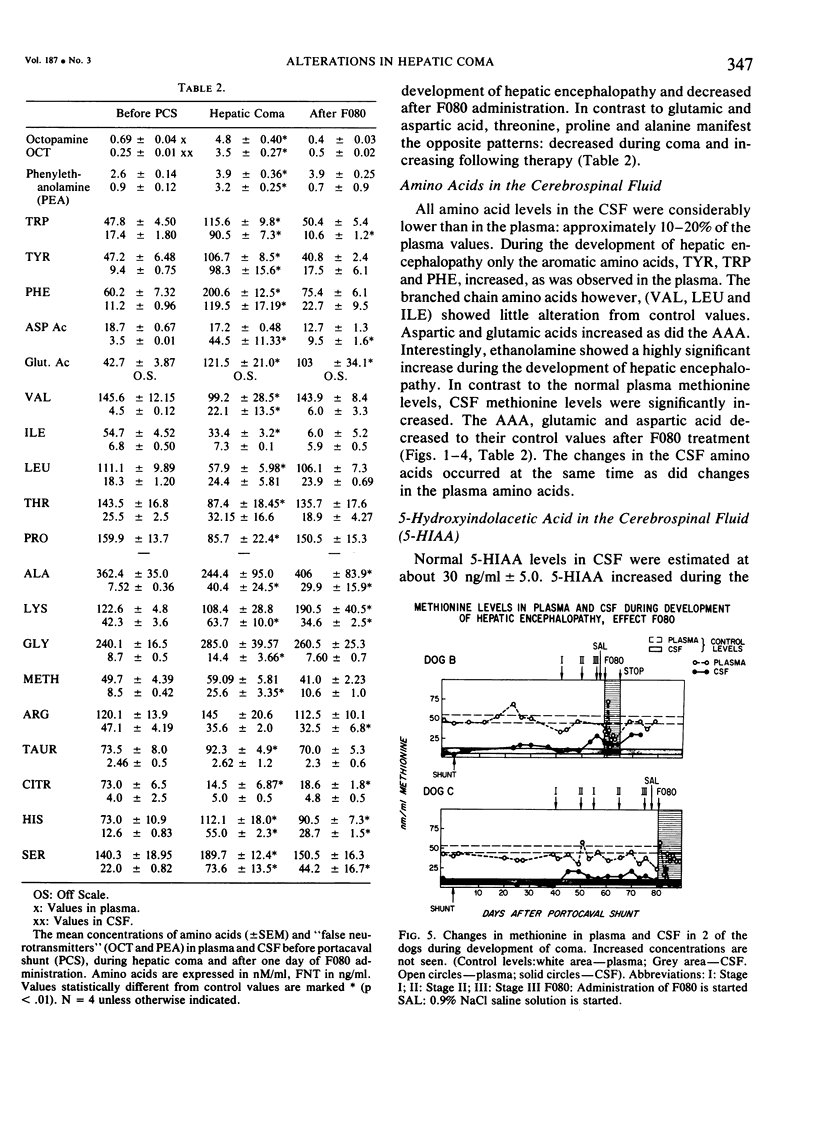
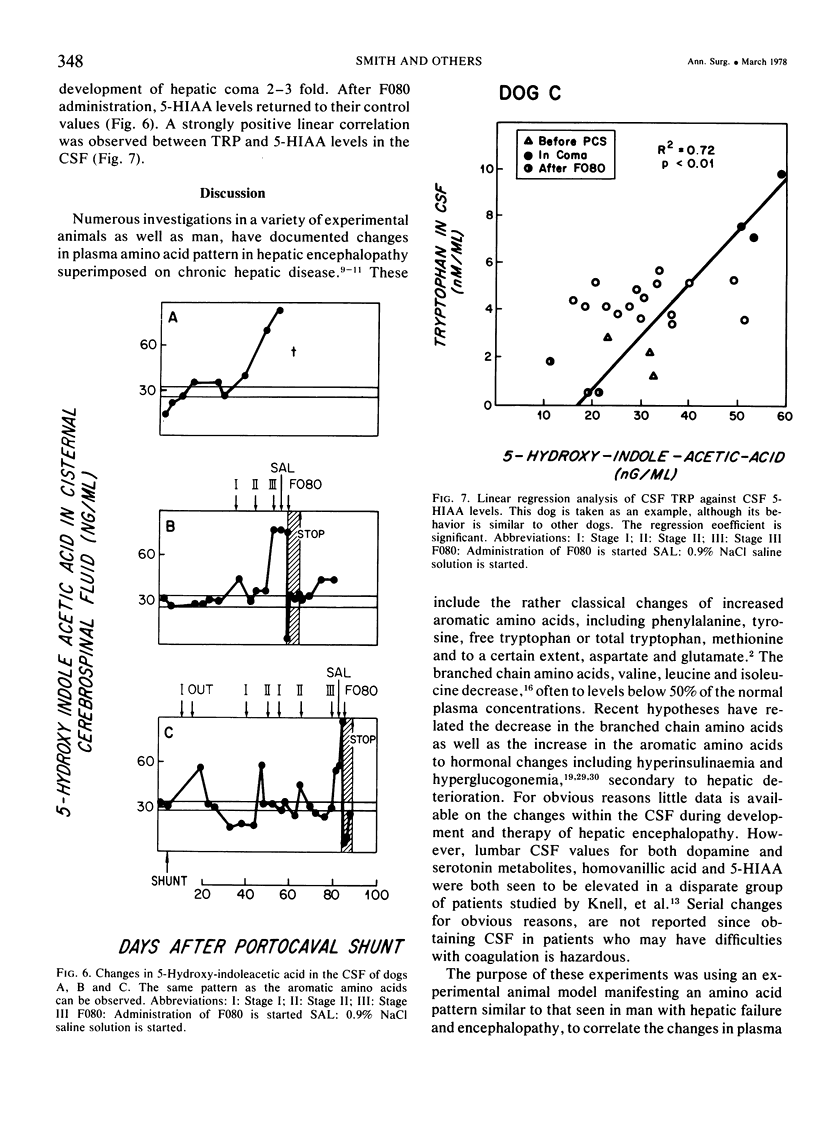
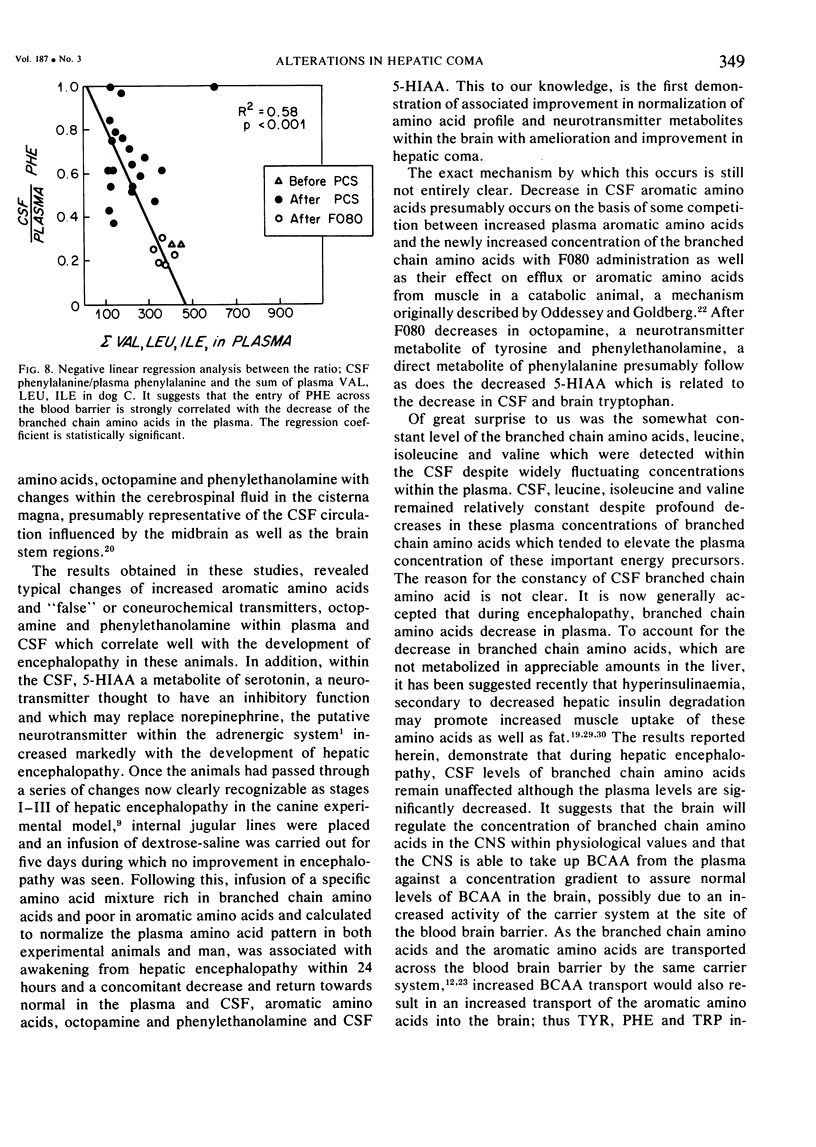
Tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine levels increased dramatically during the development of HE in plasma and CSF, while valine, leucine and isoleucine decreased in plasma only, but CSF levels remained stable. Plasma and CSF octopamine and phenylethanolamine and CSF 5-HIAA increased markedly as clinical features in the dogs' behavior, characteristic of hepatic encephalopathy occurred, including hypersalivation, ataxia, flapping tremor, somnolence and finally coma. Once in coma, the dogs were infused with an amino acid mixture (F080) calculated to normalize the plasma amino acid pattern. After one to eight hours, the dogs began to awake. Simultaneously, blood, and CSF aromatic amino acids returned to their control values, as did OCT, PEA and CSF 5-HIAA. If F080 infusion was stopped, biochemical alterations would appear within one week, again accompanied by clinical hepatic encephalopathy.
The results indicate that the altered levels of aromatic and branched chain amino acids, octopamine and PEA in plasma and CSF correlate well with the development of HE and that correction of the plasma amino acid abnormalities improves encephalopathy simultaneously with correction of neurotransmitter derangements in CSF.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cummings M. G., Soeters P. B., James J. H., Kean J. M., Fischer J. E. Regional brain indoleamine metabolism following chronic portacaval anastomosis in the rat. J Neurochem. 1976 Aug;27(2):501–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb12274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Green A. R. Effects of immobilization on rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase and brain 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;37(3):689–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla W. D., Dewey H. K. The determination of tryptophan in plasma, liver, and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):160–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodsworth J. M., James J. H., Cummings M. C., Fischer J. F. Depletion of brain norepinephrine in acute hepatic coma. Surgery. 1974 Jun;75(6):811–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Brain serotonin content: physiological regulation by plasma neutral amino acids. Science. 1972 Oct 27;178(4059):414–416. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4059.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Baldessarini R. J. False neurotransmitters and hepatic failure. Lancet. 1971 Jul 10;2(7715):75–80. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Funovics J. M., Aguirre A., James J. H., Keane J. M., Wesdorp R. I., Yoshimura N., Westman T. The role of plasma amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. Surgery. 1975 Sep;78(3):276–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Rosen H. M., Ebeid A. M., James J. H., Keane J. M., Soeters P. B. The effect of normalization of plasma amino acids on hepatic encephalopathy in man. Surgery. 1976 Jul;80(1):77–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iob V., Mattson W. J., Jr, Sloan M., Coon W. W., Turcotte J. G., Child C. G., 3rd Alterations in plasma-free amino acids in dogs with hepatic insufficiency. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970 May;130(5):794–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. H., Hodgman J. M., Funovics J. M., Fischer J. E. Alterations in brain octopamine and brain tyrosine following portacaval anastomosis in rats. J Neurochem. 1976 Jul;27(1):223–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiely M., Sourkes T. L. Transport of L-tryptophan into slices of rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1972 Dec;19(12):2863–2872. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb03824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knell A. J., Davidson A. R., Williams R., Kantamaneni B. D., Curzon G. Dopamine and serotonin metabolism in hepatic encephalopathy. Br Med J. 1974 Mar 23;1(5907):549–551. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5907.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopin I. J. False adrenergic transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1968;8:377–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.08.040168.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. C., Tall A. R., Goldstein G. B., Mistilis S. P. Role of a false neurotransmitter, octopamine, in the pathogenesis of hepatic and renal encephalopathy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(6):465–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUTO Y., TAKAHASHI Y., KAWAMURA H. [EFFECT OF SHORT-CHAIN FATTY ACIDS ON THE ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF THE NEO-, PALEO-, AND ARCHICORTICAL SYSTEM]. No To Shinkei. 1964 Jul;16:601–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manghani K. K., Lunzer M. R., Billing B. H., Sherlock S. Urinary and serum octopamine in patients with portal-systemic encephalopathy. Lancet. 1975 Nov 15;2(7942):943–946. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. T. Interaction in the cerebral metabolism of the biogenic amines: effect of intravenous infusion of L-tryptophan on the metabolism of dopamine and 5-hydroxyindoles in brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;43(4):715–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Landsberg L., Axelrod J. An enzymatic assay for octopamine and other beta-hydroxylated phenylethylamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Dec;170(2):253–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Insulin, plasma aminoacid imbalance, and hepatic coma. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):722–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91632-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odessey R., Khairallah E. A., Goldberg A. L. Origin and possible significance of alanine production by skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7623–7629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Sessa G., Green J. P. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in brain capillaries: possible site of a blood-brain barrier for amino acids. Science. 1974 Apr 5;184(4132):66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4132.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHEAR E. A., RUEBNER B., SHERLOCK S., SUMMERSKILL W. H. Methionine toxicity in liver disease and its prevention by chlortetracycline. Clin Sci. 1956 Feb;15(1):93–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record C. O., Buxton B., Chase R. A., Curzon G., Murray-Lyon I. M., Williams R. Plasma and brain amino acids in fulminant hepatic failure and their relationship to hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep 10;6(5):387–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1976.tb00533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi-Fanelli F., Cangiano C., Attili A., Angelico M., Cascino A., Capocaccia L., Strom R., Crifó C. Octopamine plasma levels and hepatic encephalopathy: a re-appraisal of the problem. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Mar 15;67(3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90333-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R., Joshi P., Hendler R., Felig P., Conn H. O. Hyperglucagonemia in Laennec's cirrhosis. The role of portal-systemic shunting. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 31;290(5):239–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401312900502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeters P. B., Fischer J. E. Insulin, glucagon, aminoacid imbalance, and hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet. 1976 Oct 23;2(7991):880–882. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90541-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., Lal S., Sourkes T. L., Feldmuller F., Aronoff A., Martin J. B. Relationships between tryptophan in serum and CSF, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in CSF of man: effect of cirrhosis of liver and probenecid administration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Apr;38(4):322–330. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.4.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve L. Pathogenesis of hepatic coma. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Sep;118(3):211–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


