Abstract
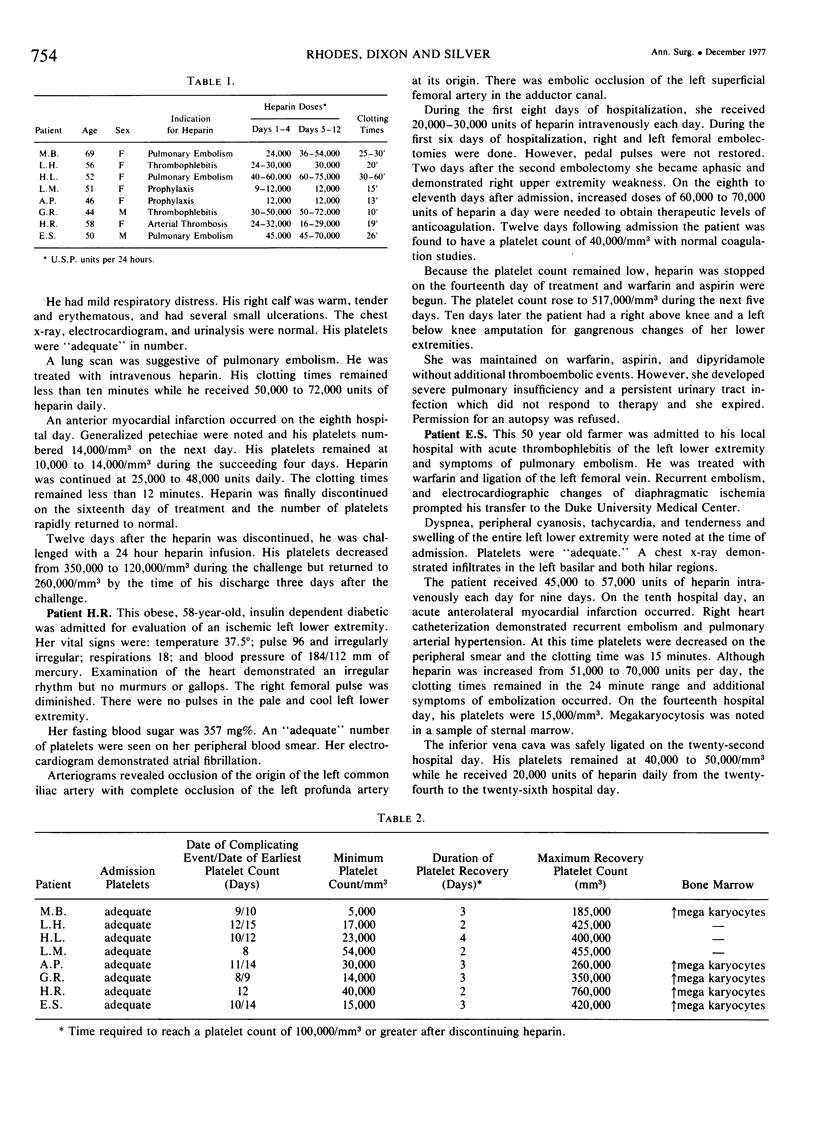
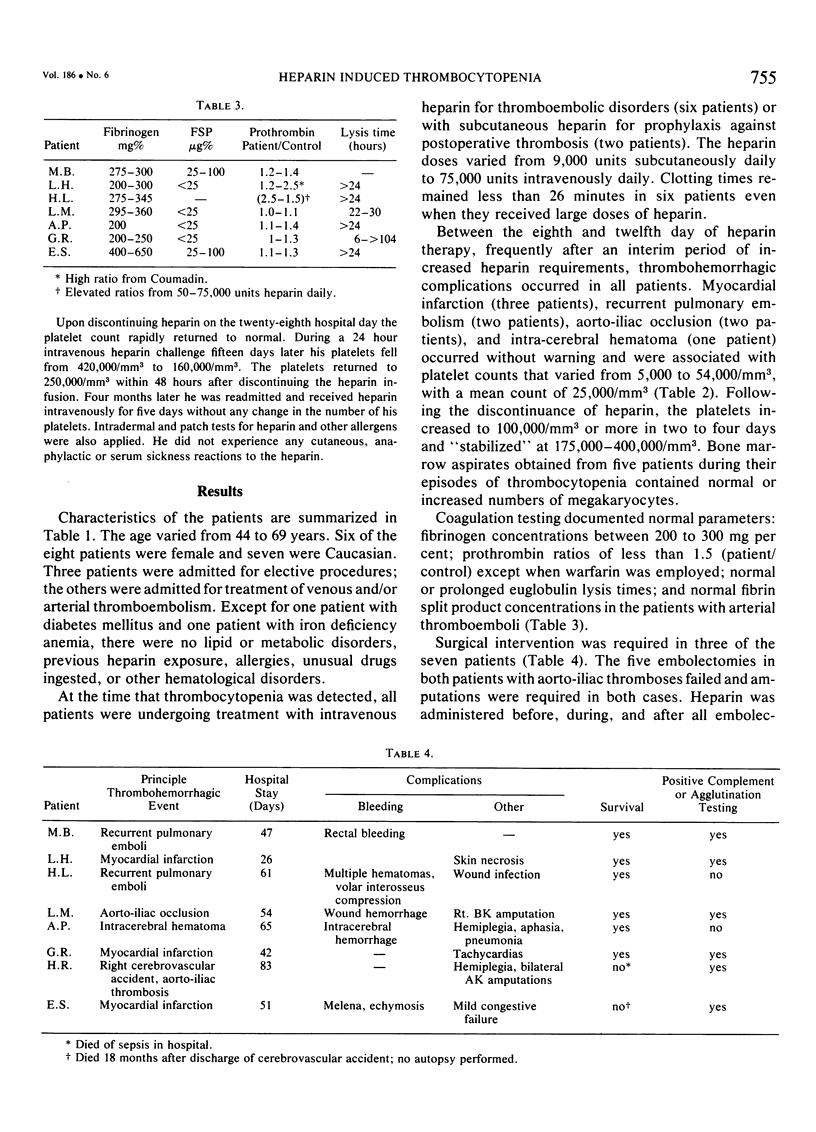
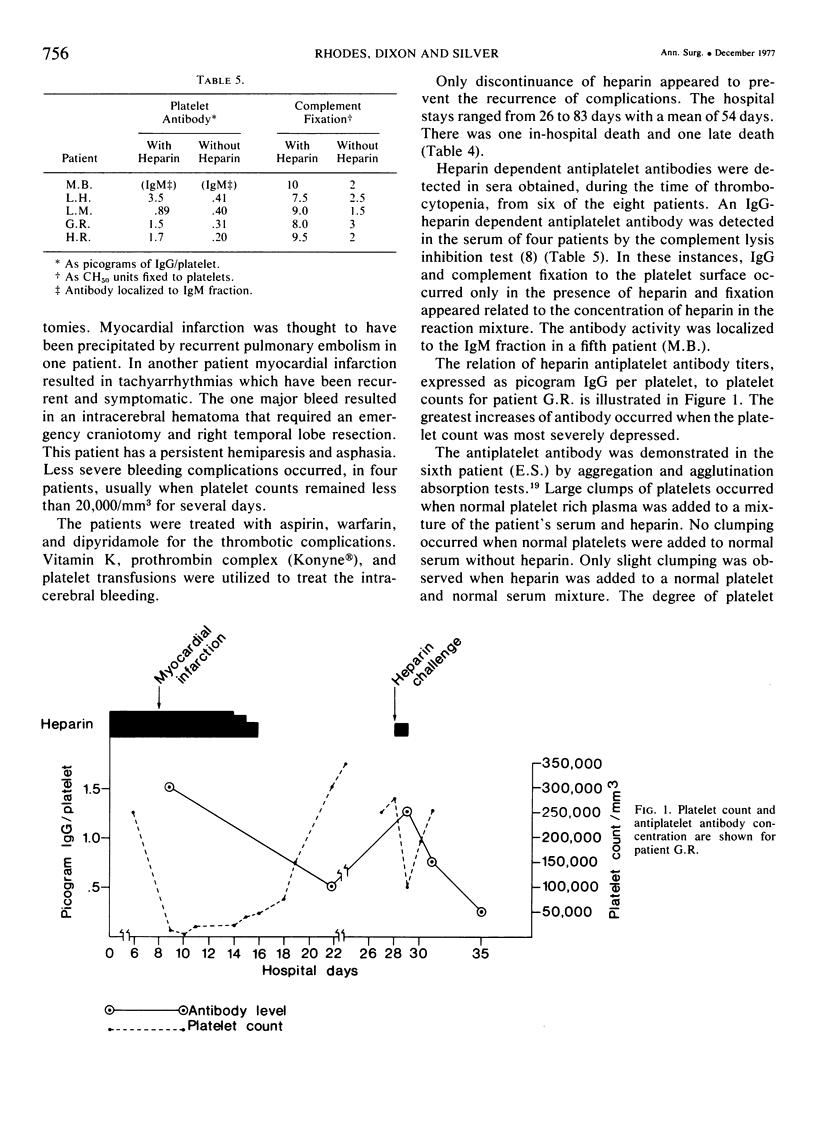
Increased heparin tolerance and recurrent thromboembolism which included myocardial infarction (3 patients), pulmonary embolism (2 patients) and complete aorto-iliac occlusion (2 patients), heralded the development of thrombocytopenia between the eighth and twelfth day of heparin therapy in six women and two men. The thrombocytopenia persisted until heparin was discontinued. Bleeding (cerebral hemorrhage) was the initial complication in one patients and occurred in conjunction with thrombotic complications in four other patients. Agglutination absorption testing in one and complement fixation testing in five patients suggested the presence of heparin dependent antiplatelet antibodies. After platelet recovery, four of the eight patients responded to parenteral heparin rechallenge with rapid decreases in their platelet counts. The early recognition of the syndrome with cessation of heparin therapy is imperative for the successful management of afflicted patients.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKROYD J. F. The immunological basis of purpura due to drug hypersensitivity. Proc R Soc Med. 1962 Jan;55:30–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN I. L. Anaphylaxis to heparin sodium; report of a case, with immunologic studies. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Aug 4;161(14):1379–1381. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.62970140005009b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECHER G., SCHNEIDERMAN M., CRONKITE E. P. The reproducibility and constancy of the platelet count. Am J Clin Pathol. 1953 Jan;23(1):15–26. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/23.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock R. B., Dumper C. W., Scharfman W. B. Heparin-induced immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jul 29;295(5):237–241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607292950501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNOFF A. I. Anaphylactic reaction following injection of heparin. N Engl J Med. 1950 Mar 2;242(9):315–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195003022420902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft J. D., Jr, Swisher S. N., Jr, Gilliland B. C., Bakemeier R. F., Leddy J. P., Weed R. I. Coombs'-test positivity induced by drugs. Mechanisms of immunologic reactions and red cell destruction. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jan;68(1):176–187. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-1-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry N., Bardana E. J., Pirofsky B. Heparin sensitivity. Report of a case. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Nov;132(5):744–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Rosse W., Ebbert L. Quantitative determination of antibody in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Correlation of serum and platelet-bound antibody with clinical response. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 30;292(5):230–236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501302920503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratantoni J. C., Pollet R., Gralnick H. R. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: confirmation of diagnosis with in vitro methods. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLLUB S., ULIN A. W. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Mar;59:430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTZ A. Severe spontaneous hypersensitivity to heparin. Ann Intern Med. 1951 Oct;35(4):919–922. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-35-4-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurewich V., Hume M., Patrick M. The laboratory diagnosis of venous thromboembolic disease by measurement of fibrinogen-fibrin degradation products and fibrin monomer. Chest. 1973 Nov;64(5):585–590. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.5.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. G., Bell W. R. Disseminated intravascular coagulation during heparin therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Apr;80(4):477–481. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-4-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Lalezari P., Johnson A. J. A rapid, simple, sensitive method for measuring fibrinolytic split products in human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):871–875. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natelson E. A., Lynch E. C., Alfrey C. P., Jr, Gross J. B. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. An unexpected response to treatment of consumption coagulopathy. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Dec;71(6):1121–1125. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-6-1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole R. D. Letter: Heparin: adverse reaction. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):759–759. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-759_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS B., ROSATO F. E., ROSATO E. F. HEPARIN--A CAUSE OF ARTERIAL EMBOLI? Surgery. 1964 Jun;55:803–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G. R., Dixon R. H., Silver D. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia with thrombotic and hemorrhagic manifestations. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1973 Mar;136(3):409–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickman F. D., Handin R., Howe J. P., Alpert J. S., Dexter L., Dalen J. E. Fibrin split products in acute pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):664–668. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN N. R. Immunoreactions involving platelets. I. A steric and kinetic model for formation of a complex from a human antibody, quinidine as a haptene, and platelets; and for fixation of complement by the complex. J Exp Med. 1958 May 1;107(5):665–690. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISMANN R. E., TOBIN R. W. Arterial embolism occurring during systemic heparin therapy. AMA Arch Surg. 1958 Feb;76(2):219–227. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1958.01280200041005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


