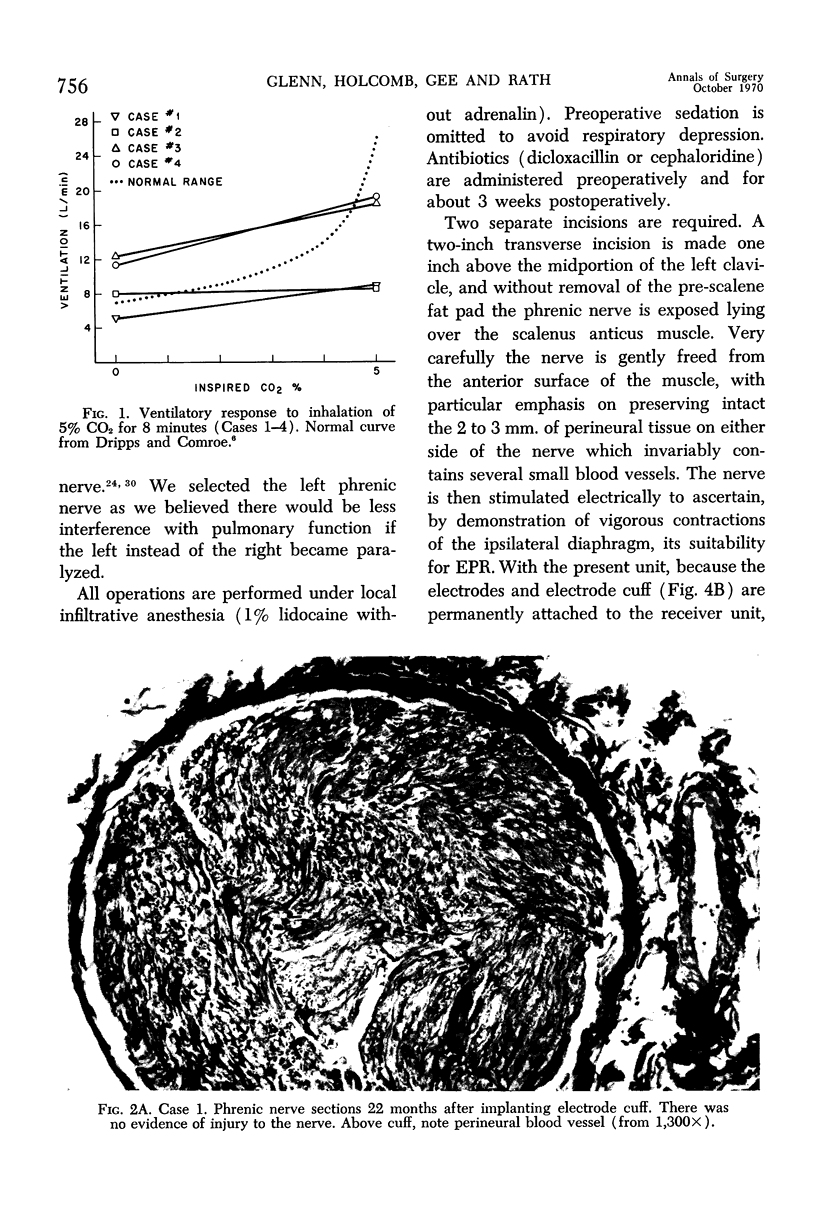
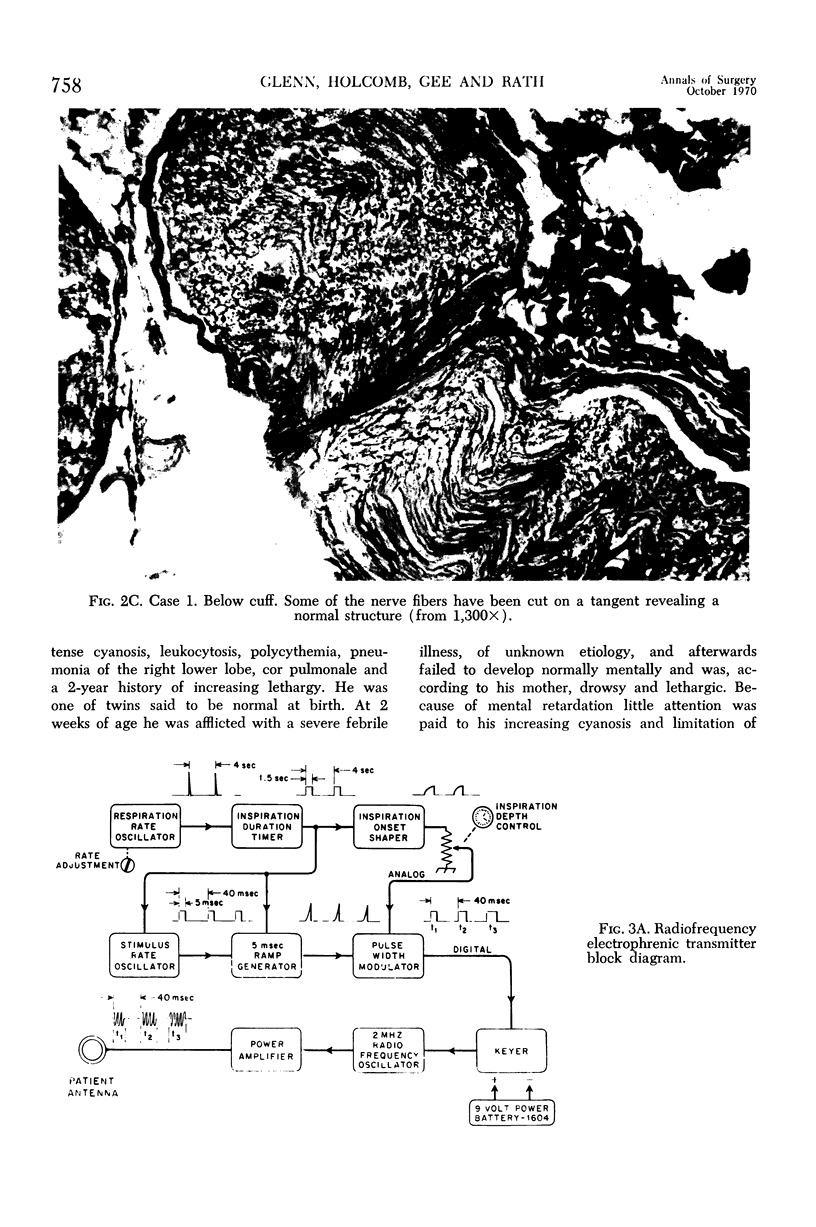
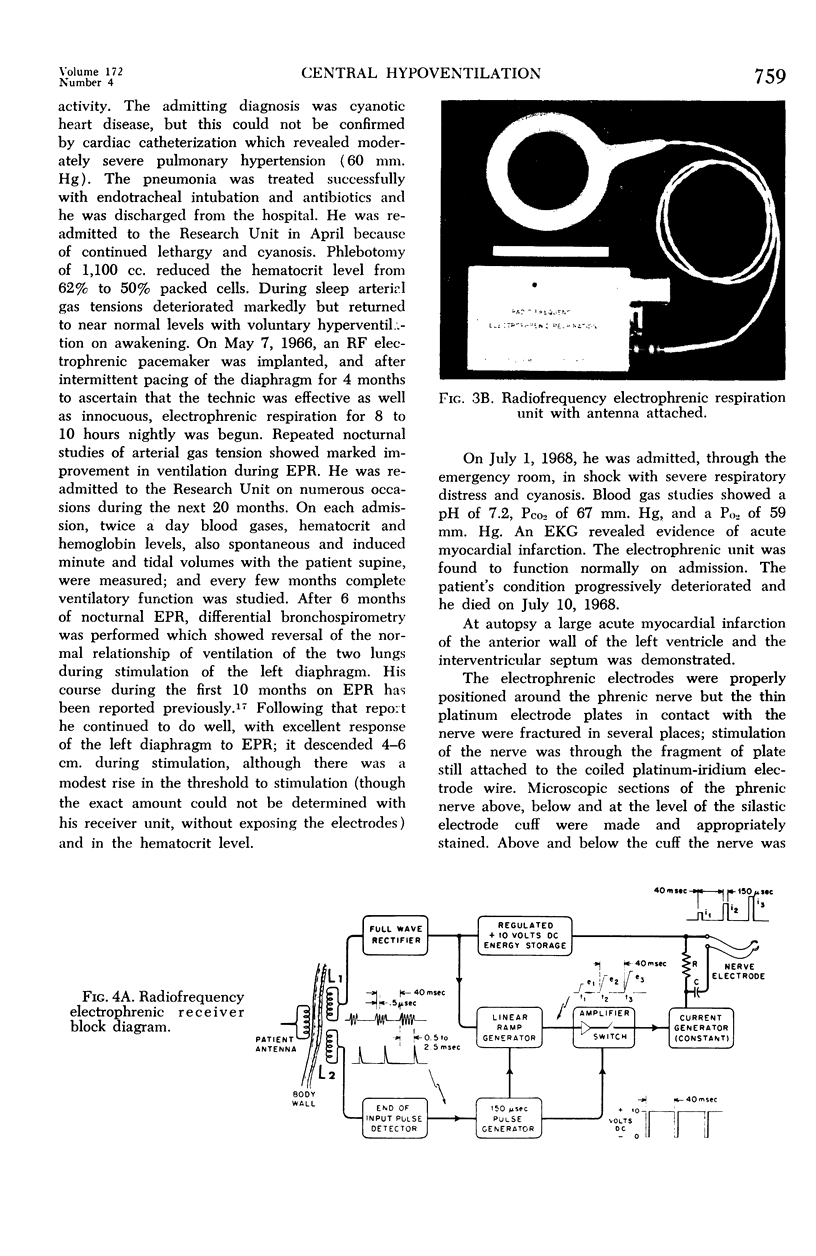
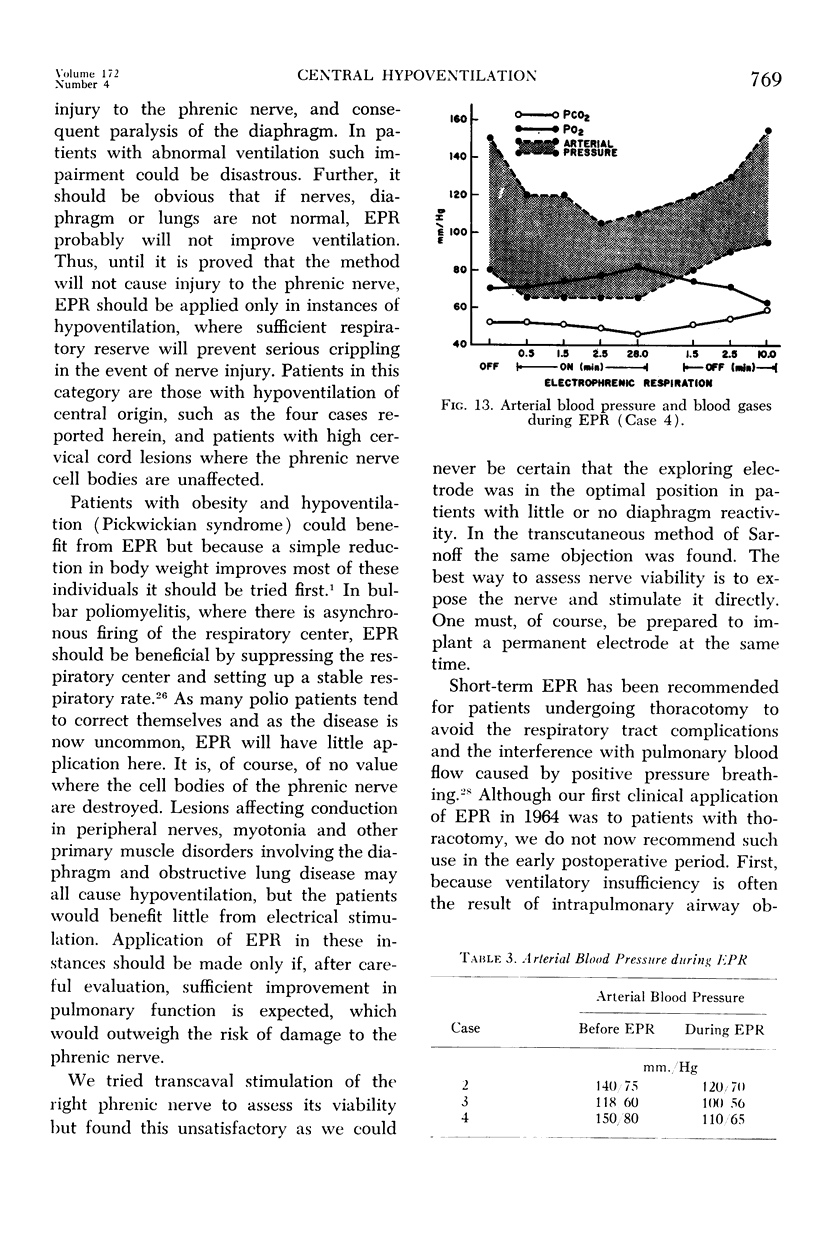
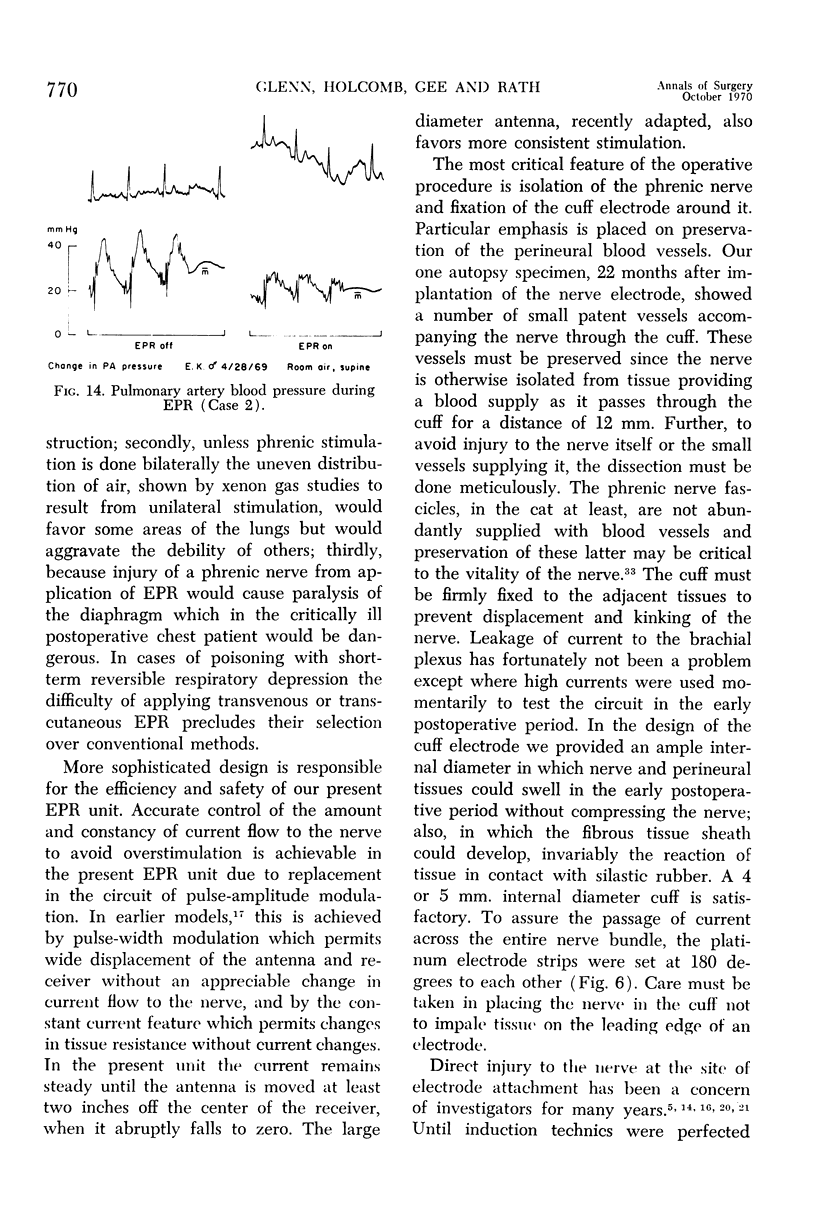
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON J. H., GAMPEL B., SLOME C., SCOTCH N., MAJOLA C. C. Age at menopause of urban Zulu women. Science. 1960 Aug 5;132(3423):356–357. doi: 10.1126/science.132.3423.356-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUCHINCLOSS J. H., Jr, GILBERT R. The cardiorespiratory syndrome related to obesity: clinical manifestations and pathologic physiology. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1959 May;1(4):423–434. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(59)80046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALL W. C., Jr, STEWART P. B., NEWSHAM L. G., BATES D. V. Regional pulmonary function studied with xenon 133. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:519–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI104505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN J. E., KUIDA H. Primary alveolar hypoventilation associated with Western equine encephalitis. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Apr;56:633–644. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-56-4-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagget W. M., Piccinini J. C., Austen W. G. Intravenous electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerve: a new technique for artificial respiration. Surg Forum. 1965;16:177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVilliers R., Nosé Y., Meier W., Kantrowitz A. Long-term, continuous electrostimulation of a peripheral nerve. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1964;10:357–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENBERG L., MAURO A., GLENN W. W., HAGEMAN J. H. RADIOFREQUENCY STIMULATION: A RESEARCH AND CLINICAL TOOL. Science. 1965 Feb 5;147(3658):578–582. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3658.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escher D. J., Furman S., Solomon N., Schwedel J. B. Transvenous pacing of the phrenic nerves. Am Heart J. 1966 Aug;72(2):283–284. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(66)90456-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENN W. W., HAGEMAN J. H., MAURO A., EISENBERG L., FLANIGAN S., HARVARD M. ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF EXCITABLE TISSUE BY RADIO-FREQUENCY TRANSMISSION. Ann Surg. 1964 Sep;160:338–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENN W. W., MAURO A., LONGO E., LAVIETES P. H., MACKAY F. J. Remote stimulation of the heart by radiofrequency transmission. Clinical application to a patient with Stokes-Adams syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1959 Nov 5;261:948–951. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195911052611905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greatbatch W., Piersma B., Shannon F. D., Calhoon S. W., Jr Polarization phenomena relating to physiological electrodes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 30;167(2):722–744. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb34133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman J., Flanigan S., Harvard B. M., Glenn W. W. Electromicturition by radiofrequency stimulation. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1966 Oct;123(4):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershberg P. I., Sohn D., Agrawal G. P., Kantrowitz A. Histologic changes in continuous, long-term electrical stimulation of a peripheral nerve. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1967 Apr;14(2):109–114. doi: 10.1109/tbme.1967.4502479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judson J. P., Glenn W. W. Radio-frequency electrophrenic respiration. Long-term application to a patient with primary hypoventilation. JAMA. 1968 Mar 18;203(12):1033–1037. doi: 10.1001/jama.203.12.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLIN A., BRILL N. Q., BROBERG P. J. Stimulation of irritable tissues by means of an alternating magnetic field. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:251–253. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILLY J. C., HUGHES J. R., ALVORD E. C., Jr, GALKIN T. W. Brief, noninjurious electric waveform for stimulation of the brain. Science. 1955 Apr 1;121(3144):468–469. doi: 10.1126/science.121.3144.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUCKS R. B., WEINBERG H., SMITH M. The erosion of electrodes by small currents. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1959 Nov;11:823–826. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(59)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield P. B. Myocardial stimulation: the electrochemistry of electrode-tissue coupling. Am J Physiol. 1967 Jun;212(6):1475–1488. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.6.1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARNOFF S. J., GAENSLER E. A., MALONEY J. V., Jr Electrophrenic respiration; IV. The effectiveness of contralateral ventilation during activity of one phrenic nerve. J Thorac Surg. 1950 Jun;19(6):929–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnoff S. J., Hardenbergh E., Whittenberger J. L. Electrophrenic Respiration. Science. 1948 Oct 29;108(2809):482–482. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2809.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemmer E. A., Crawford D. W., List J. W., Heber R. E., Connolly J. E. Diaphragmatic pacing in the treatment of hypoventilation syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1967 Nov;54(5):649–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWNSEND J. F., STOECKLE H., SCHUDER J. C. TISSUE AND ELECTRODE CHANGES IN CHRONIC CARDIAC PACING---AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1965;11:132–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heeckeren D. W., Glenn W. W. Electrophrenic respiration by radiofrequency induction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1966 Nov;52(5):655–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDMANN W. D., EISENBERG L., LEVITSKY S., MAURO A., GLENN W. W. VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION COMPLICATING ELECTRICAL PACEMAKING: A COMPARISON OF DIRECT CURRENT AND RADIO-FREQUENCY CARDIAC PACEMAKER STIMULATION. Surg Forum. 1963;14:260–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]