Abstract
1 Verapamil is a racemic mixture of two optical isomers, the (-)-form being the more active component. Recent studies indicate a rapid hepatic transformation of (-)-verapamil, which results in different concentration-effect relationships after oral and intravenous administration. In practice the important pharmacokinetic properties of verapamil are low bioavailability (20%), predominant elimination by metabolism (> 95%) and a relatively short half-life (t½β is 3-5 h). After repeated dosing, the rate of hepatic drug clearance seems to decrease.
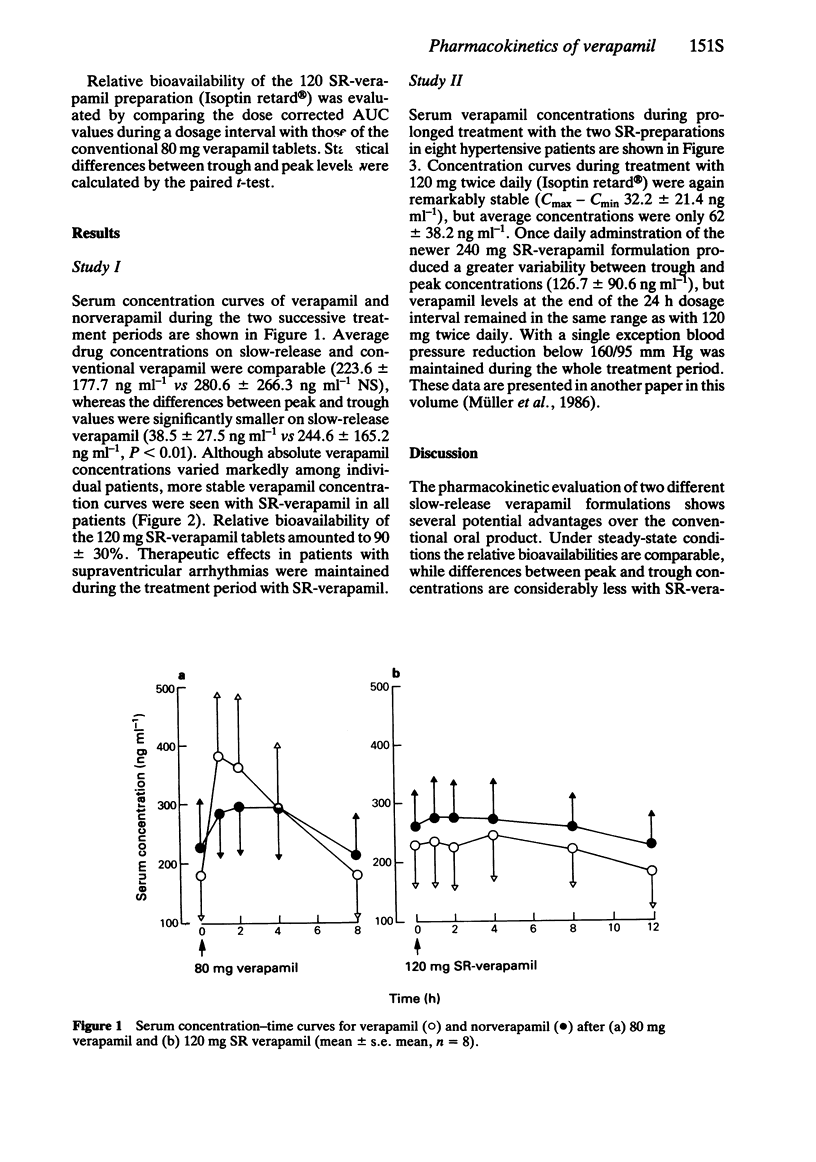
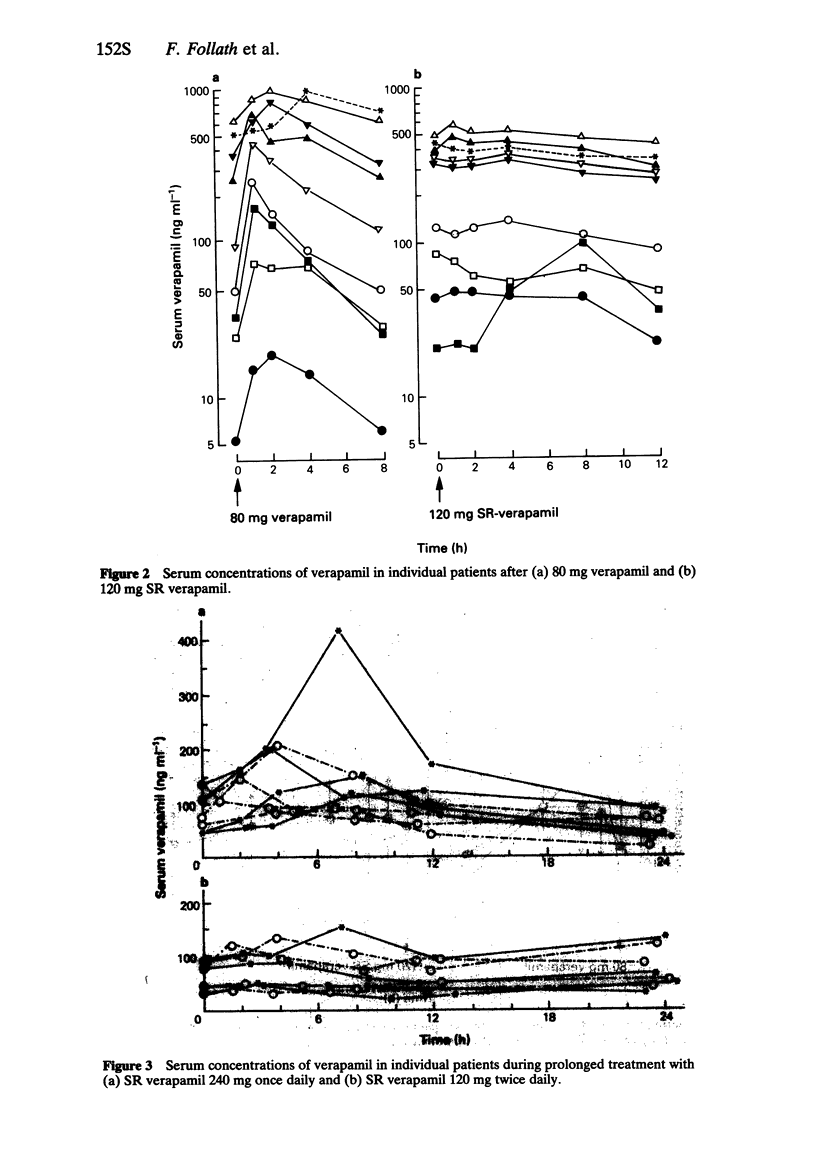
2 Slow release (SR) formulations of verapamil may offer certain therapeutic advantages during long-term treatment. A comparison of conventional (C) and SR tablets in a 1-week treatment of eight cardiac patients showed a relative bioavailability (AUCSR/AUCC) of 90 ± 30%. More stable serum drug levels were maintained by 12-hourly administration of SR verapamil.
3 A further study using a new 240 mg SR preparation in patients with arterial hypertension showed that even a single daily dose can be sufficient for adequate blood pressure control over 24 h.
Keywords: verapamil, slow release formulation, pharmacokinetics
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eichelbaum M., Birkel P., Grube E., Gütgemann U., Somogyi A. Effects of verapamil on P-R-intervals in relation to verapamil plasma levels following single I.V. and oral administration and during chronic treatment. Klin Wochenschr. 1980 Sep 15;58(18):919–925. doi: 10.1007/BF01477049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M., Somogyi A. Inter- and intra-subject variation in the first-pass elimination of highly cleared drugs during chronic dosing. Studies with deuterated verapamil. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;26(1):47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00546708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follath F., Fromer M., Meier P., Vozeh S. Pharmacodynamic comparison of oral and intravenous verapamil in atrial fibrillation. Clin Invest Med. 1980;3(1-2):49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. B., Richmond D. R., Ashley J. J., Kelly D. T. Verapamil kinetics in normal subjects and patients with coronary artery spasm. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Nov;30(5):644–652. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates R. E., Keefe D. L., Schwartz J., Harapat S., Kirsten E. B., Harrison D. C. Verapamil disposition kinetics in chronic atrial fibrillation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jul;30(1):44–51. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikler D. Verapamil in cardiology. Eur J Cardiol. 1974 Aug;2(1):3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F. B., Ha H. R., Hotz H., Schmidlin O., Follath F., Bühler F. R. Once a day verapamil in essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;21 (Suppl 2):143S–147S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer G. Comparative cardiovascular actions of verapamil and its major metabolites in the anaesthetised dog. Cardiovasc Res. 1978 Apr;12(4):247–254. doi: 10.1093/cvr/12.4.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschack M. Relationship of antiarrhythmic to inotropic activity and antiarrhythmic qualities of the optical isomers of verapamil. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;294(3):285–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00508397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter M. J., Shand D. G., Pritchett E. L. Comparison of intravenous and oral verapamil dosing. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Dec;32(6):711–720. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schomerus M., Spiegelhalder B., Stieren B., Eichelbaum M. Physiological disposition of verapamil in man. Cardiovasc Res. 1976 Sep;10(5):605–612. doi: 10.1093/cvr/10.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz E., Ha H. R., Bühler F. R., Follath F. Serum concentration and antihypertensive effect of slow-release verapamil. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982;4 (Suppl 3):S346–S349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Hammill S. C., Aanonsen L., Pritchett E. L. Reduced verapamil clearance during long-term oral administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Nov;30(5):701–706. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi A., Albrecht M., Kliems G., Schäfer K., Eichelbaum M. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability and ECG response of verapamil in patients with liver cirrhosis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;12(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelgesang B., Echizen H., Schmidt E., Eichelbaum M. Stereoselective first-pass metabolism of highly cleared drugs: studies of the bioavailability of L- and D-verapamil examined with a stable isotope technique. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;18(5):733–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock B. G., Rietbrock I., Vöhringer H. F., Rietbrock N. Verapamil disposition in liver disease and intensive-care patients: kinetics, clearance, and apparent blood flow relationships. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jan;29(1):27–34. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock B. G., Schulz W., Kober G., Rietbrock N. Direct determination of hepatic extraction of verapamil in cardiac patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jul;30(1):52–56. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


