Abstract
1 The antihypertensive efficacy of the new α1-adrenoceptor antagonist doxazosin is described, and its selectivity for α1-adrenoceptors is reported from both in vivo and in vitro studies.
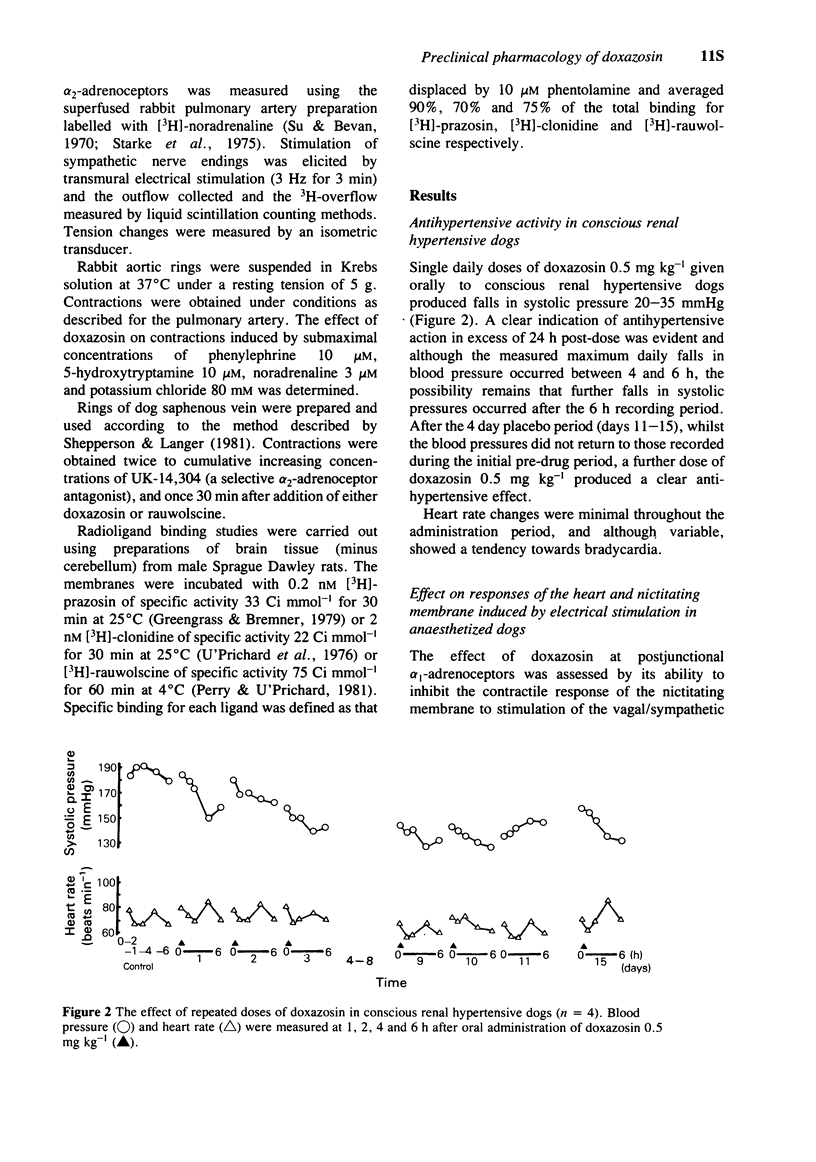
2 Groups of beagle dogs with chronic perinephritic hypertension were given doxazosin orally, and systolic blood pressure was recorded indirectly from an exteriorized carotid loop. Dogs given doxazosin 0.5 mg kg-1 daily for 10 days showed consistent daily falls in systolic pressure in addition to a progressive reduction in daily pre-dose pressures. A clear indication of antihypertensive action in excess of 24 h post dose was evident. Heart rate changes were minimal.
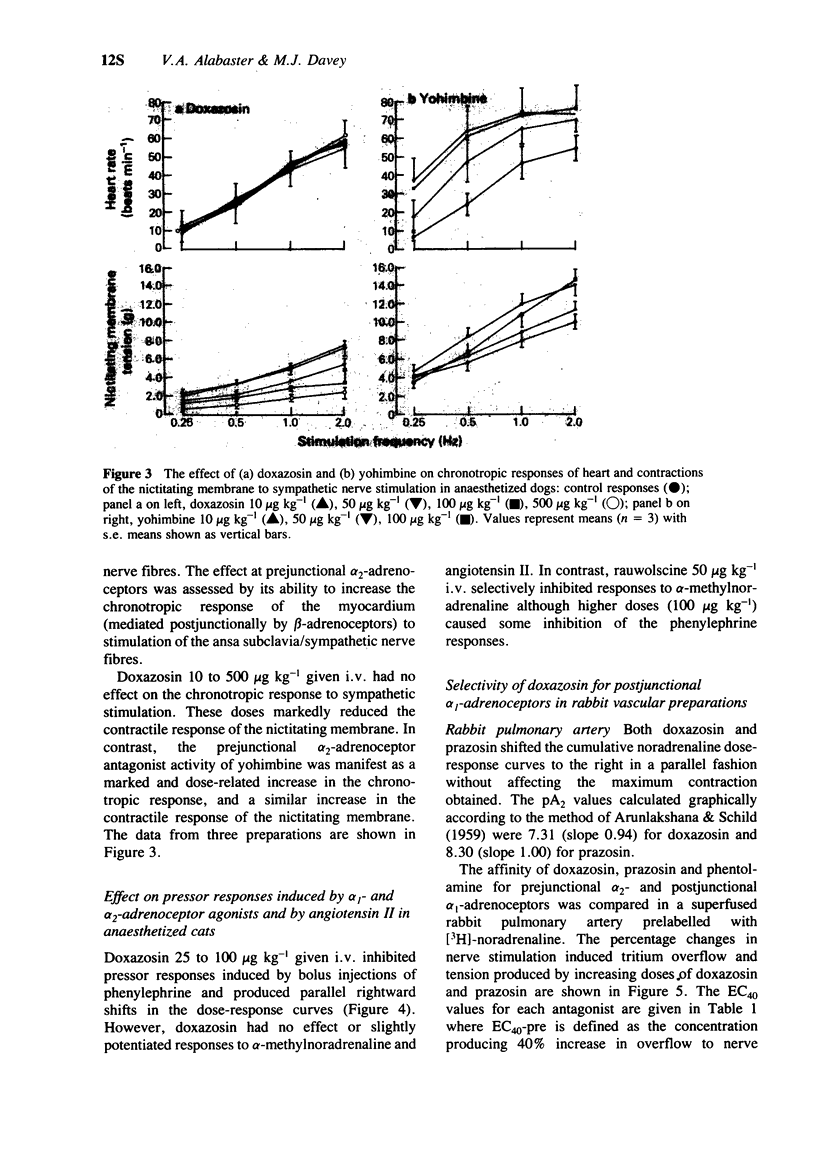
3 In pentobarbitone anaesthetized dogs pretreated with desimipramine, doxazosin 10-500 μg kg-1 i.v. reduced responses of the nictitating membrane to electrical stimulation of the vagosympathetic-depressor nerve trunk (an α1-adrenoceptor response) but had no effect on the chronotropic response of the heart to electrical stimulation of the ansa subclavia. In contrast, the prejunctional α2-adrenoceptor antagonist activity of yohimbine 10-100 μg kg-1 i.v. was manifest as a marked dose-related increase in both the heart rate and nictitating membrane responses.
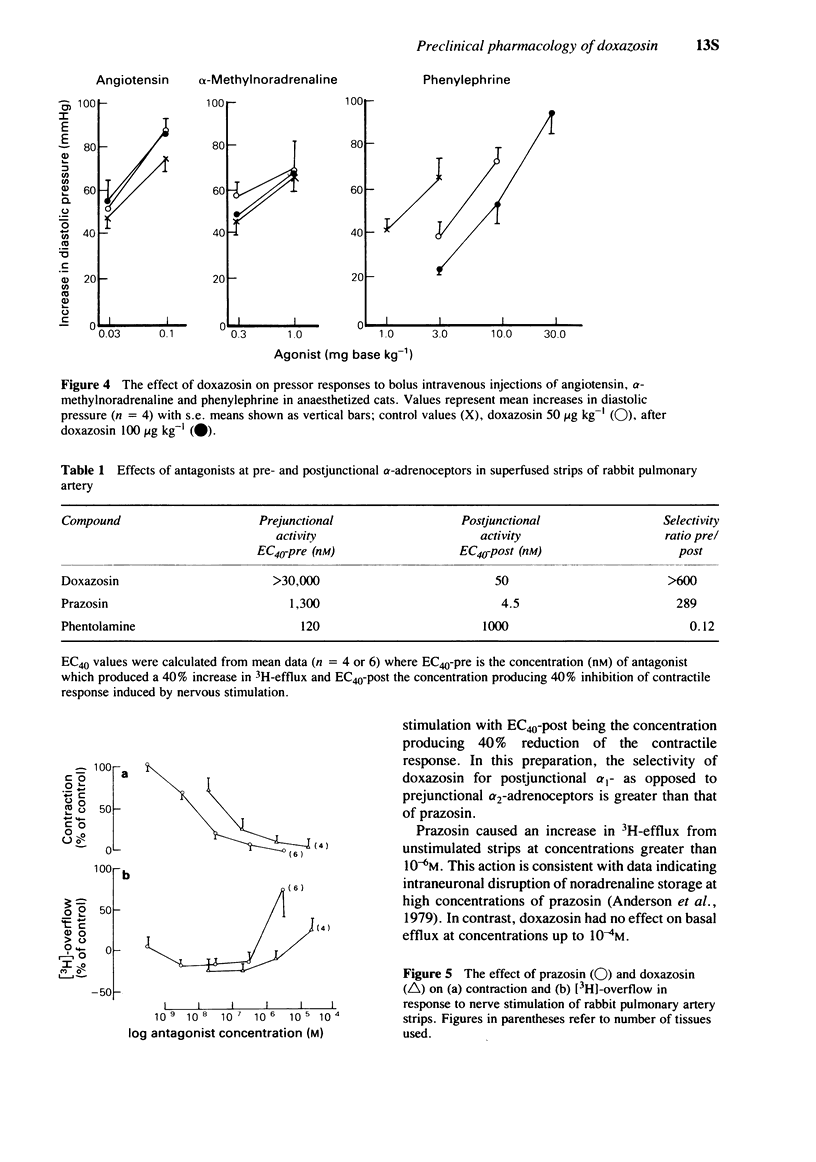
4 The lack of effect of doxazosin on postjunctional α2-adrenoceptors in vivo was demonstrated in the anaesthetized cat. Doxazosin at 50 and 100 μg kg-1 i.v. inhibited pressor responses to injected phenylephrine (an α1-adrenoceptor agonist) but had no effect on pressor responses to either α-methylnoradrenaline (an α2-adrenoceptor agonist) or angiotensin II.
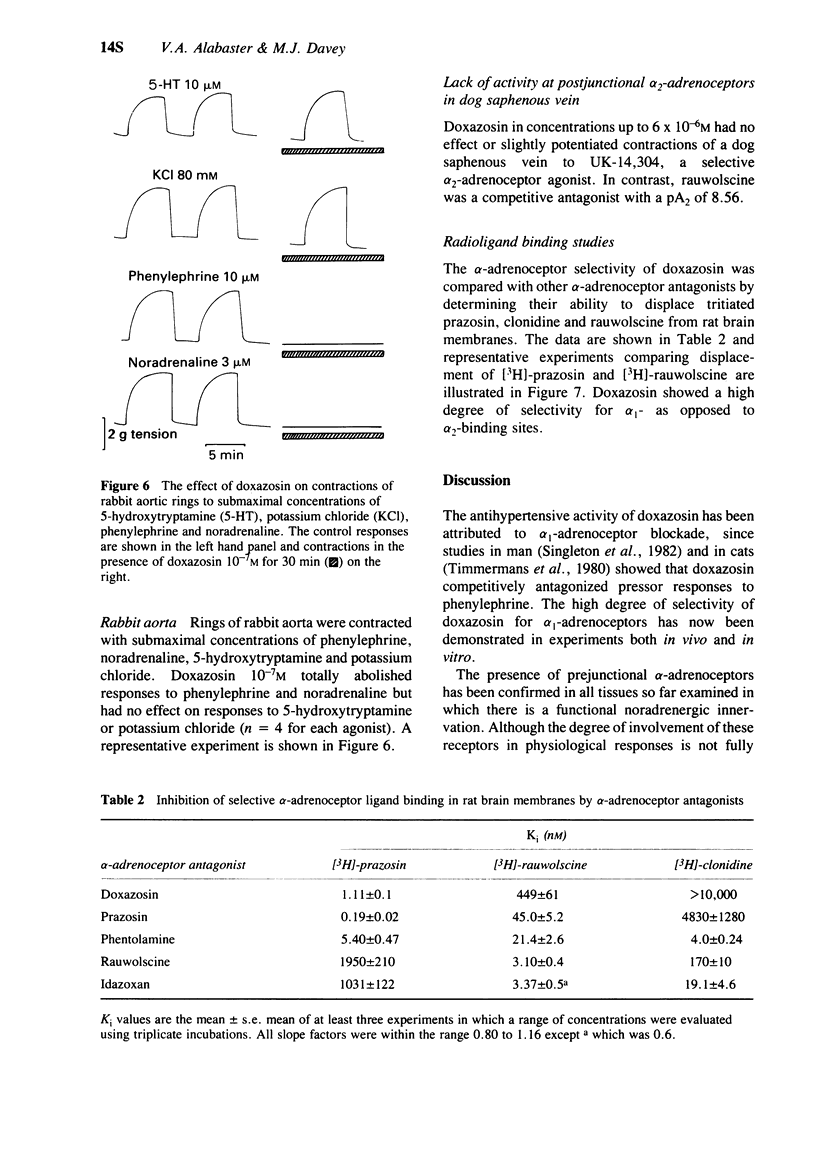
5 Studies in isolated tissues, for example the rabbit pulmonary artery and the dog saphenous vein, have also shown the lack of activity of doxazosin at pre- and postjunctional α2-adrenoceptors.
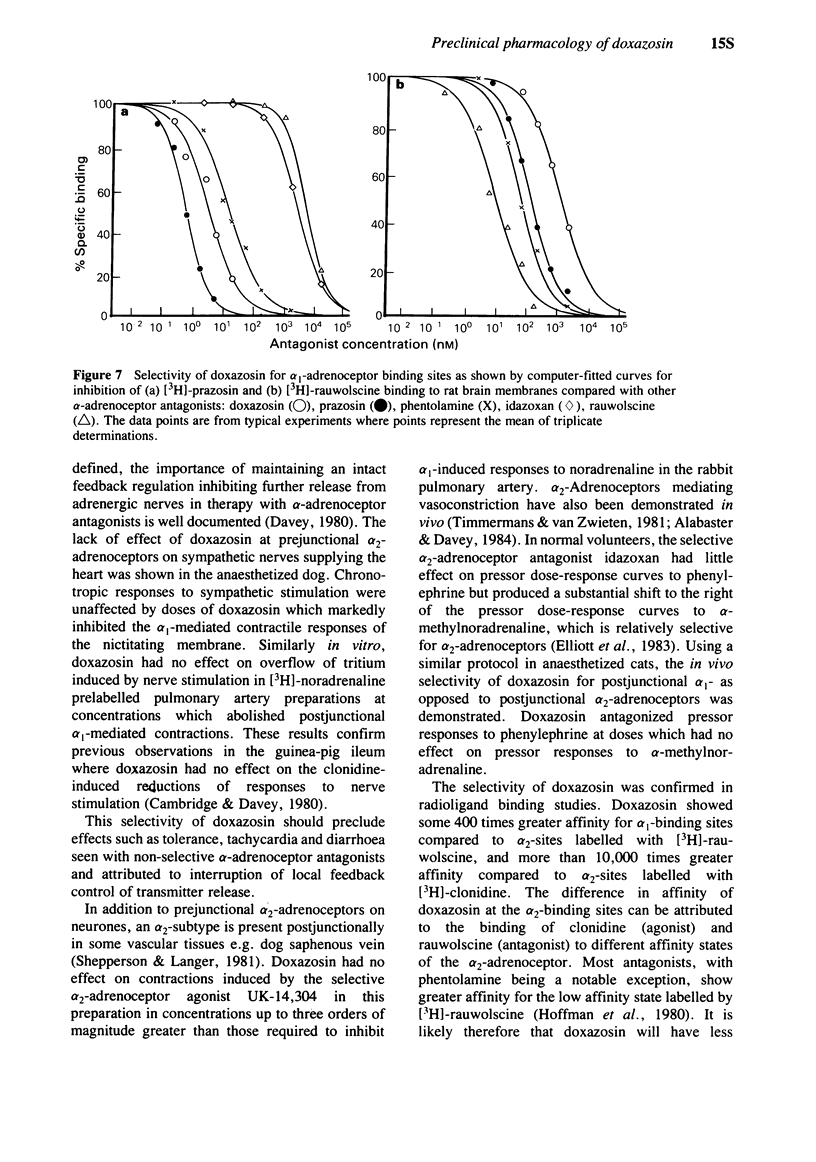
6 The high degree of selectivity of doxazosin for α1-adrenoceptor sites was confirmed by ligand binding studies in rat brain membranes where the mean ± s.e. mean Ki values (n = 6) for displacement of [3H]-prazosin, [3H]-rauwolscine and [3H]-clonidine were 1.1 ± 0.1 nM, 449 ± 61 nM and > 10 μM, respectively.
7 Pharmacological studies indicate therefore that the antihypertensive activity of doxazosin is a consequence of selective inhibition of postjunctional α1-adrenoceptors.
Keywords: α1-adrenoceptor antagonists, antihypertensives, doxazosin, pre- and post-junctional α-adrenoceptors
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alabaster V., Davey M. Precapillary vessels: effects of the sympathetic nervous system and of catecholamines. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984;6 (Suppl 2):S365–S376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., Meredith P. A., Sumner D. J., McLean K., Reid J. L. A pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic assessment of a new alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist, doxazosin (UK33274) in normotensive subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 May;13(5):699–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick M. H., Halttunen P., Himanen P., Huttunen M., Pörsti P., Pitkäjärvi T., Pöyhönen L., Pyykönen M. L., Reinikainen P., Salmela P. A long-term double-blind comparison of doxazosin and atenolol in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;21 (Suppl 1):55S–62S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengrass P., Bremner R. Binding characteristics of 3H-prazosin to rat brain alpha-adrenergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 May 1;55(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Michel T., Kilpatrick D. M., Lefkowitz R. J., Tolbert M. E., Gilman H., Fain J. N. Agonist versus antagonist binding to alpha-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4569–4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry B. D., U'Prichard D. C. [3H]rauwolscine (alpha-yohimbine): a specific antagonist radioligand for brain alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 17;76(4):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepperson N. B., Langer S. Z. The effects of the 2-amino-tetrahydronaphthalene derivative M7, a selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;318(1):10–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00503305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton W., Saxton C. A., Hernandez J., Prichard B. N. Postjunctional selectivity of alpha-blockade with prazosin, trimazosin, and UK-33,274 in man. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982;4 (Suppl 1):S145–S151. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198200041-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C., Bevan J. A. The release of H3-norepinephrine in arterial strips studied by the technique of superfusion and transmural stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Mar;172(1):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Kwa H. Y., Ali F. K., van Zwieten P. A. Prazosin and its analogues UK-18,596 and UK-33,274: a comparative study on cardiovascular effects and alpha-adrenoceptor blocking activities. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1980 Jun;245(2):218–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Mini-review. The postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptor. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;1(2):171–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Greenberg D. A., Snyder S. H. Binding characteristics of a radiolabeled agonist and antagonist at central nervous system alpha noradrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):454–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


