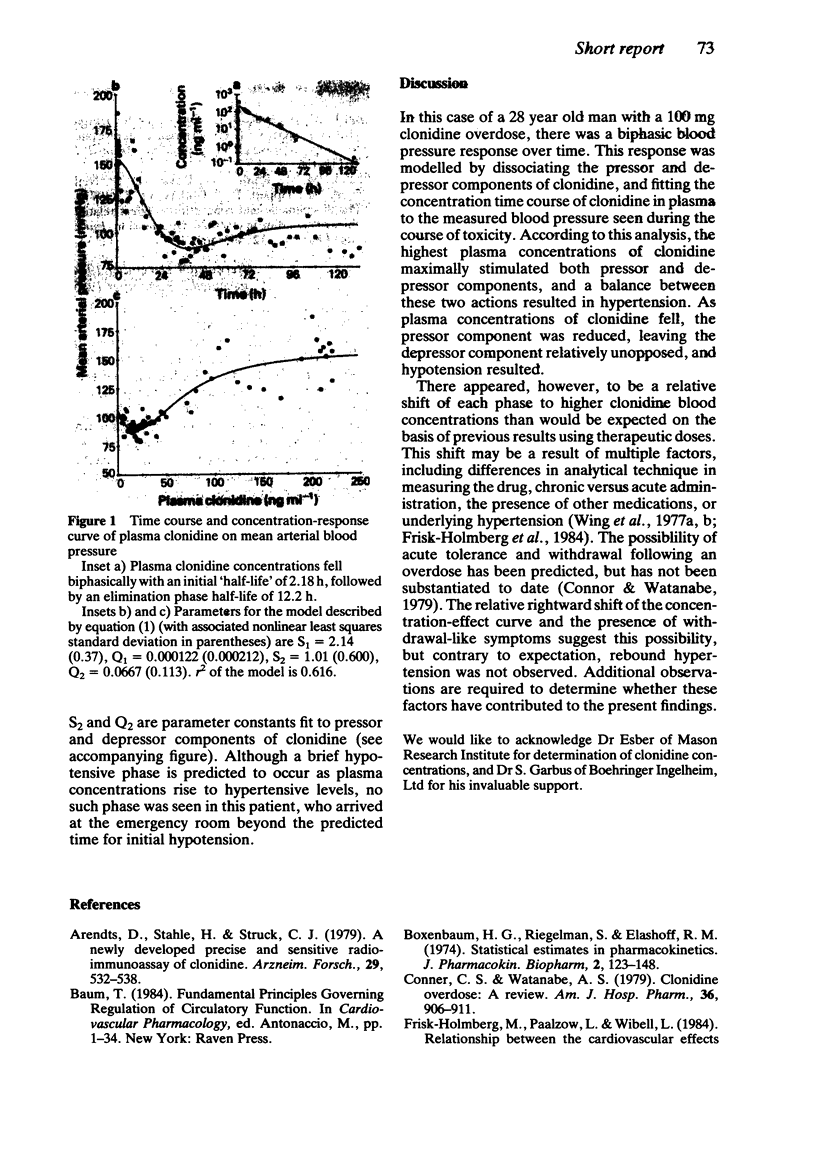
Abstract
The time course of toxicity in a 28 year old man following a 100 mg accidental overdose of clonidine hydrochloride is compared with the decline of plasma clonidine over 5 days. The concentration data were analyzed by nonlinear least squares regression, and fitted to a model which dissociated the blood pressure effects into pressor and depressor components. According to this analysis, there appeared to be two phases of toxicity over time--a hypertensive, and a hypotensive phase. The hypotensive and the hypertensive phases may result primarily through differential stimulation of central alpha 2-, alpha 1-, and vascular post-synaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors as plasma concentrations fall.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndts D., Stähle H., Struck C. J. A newly developed precise and sensitive radioimmunoassay for clonidine. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(3):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. G., Riegelman S., Elashoff R. M. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Apr;2(2):123–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner C. S., Watanabe A. S. Clonidine overdose: a review. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1979 Jul;36(7):906–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk-Holmberg M., Paalzow L., Wibell L. Relationship between the cardiovascular effects and steady-state kinetics of clonidine in hypertension. Demonstration of a therapeutic window in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;26(3):309–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00548760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger Central alpha-adrenergic systems as targets for hypotensive drugs. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;81:39–100. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paalzow L. K., Edlund P. O. Multiple receptor responses: a new concept to describe the relationship between pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics of a drug: studies on clonidine in the rat and cat. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1979 Oct;7(5):495–510. doi: 10.1007/BF01062391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L., Wing L. M., Dargie H. J., Hamilton C. A., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Clonidine withdrawal in hypertension. Changes in blood-pressure and plasma and urinary noradrenaline. Lancet. 1977 Jun 4;1(8023):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92715-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. M., Reid J. L., Davies D. S., Dargie H. J., Dollery C. T. Apparent resistance to hypotensive effect of clonidine. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 15;1(6054):136–138. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6054.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. M., Reid J. L., Davies D. S., Neill E. A., Tippett P., Dollery C. T. Pharmacokinetic and concentration-effect relationships of clonidine in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Dec 28;12(6):463–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00561067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


