Abstract
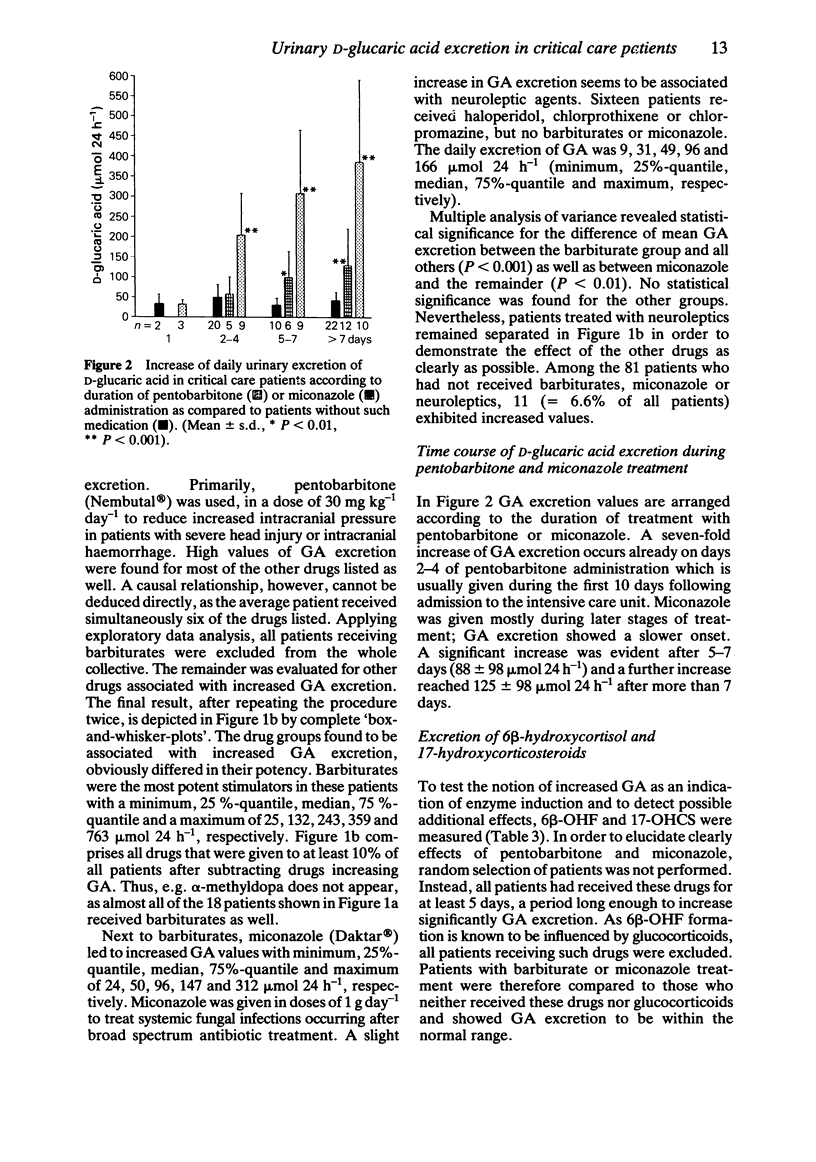
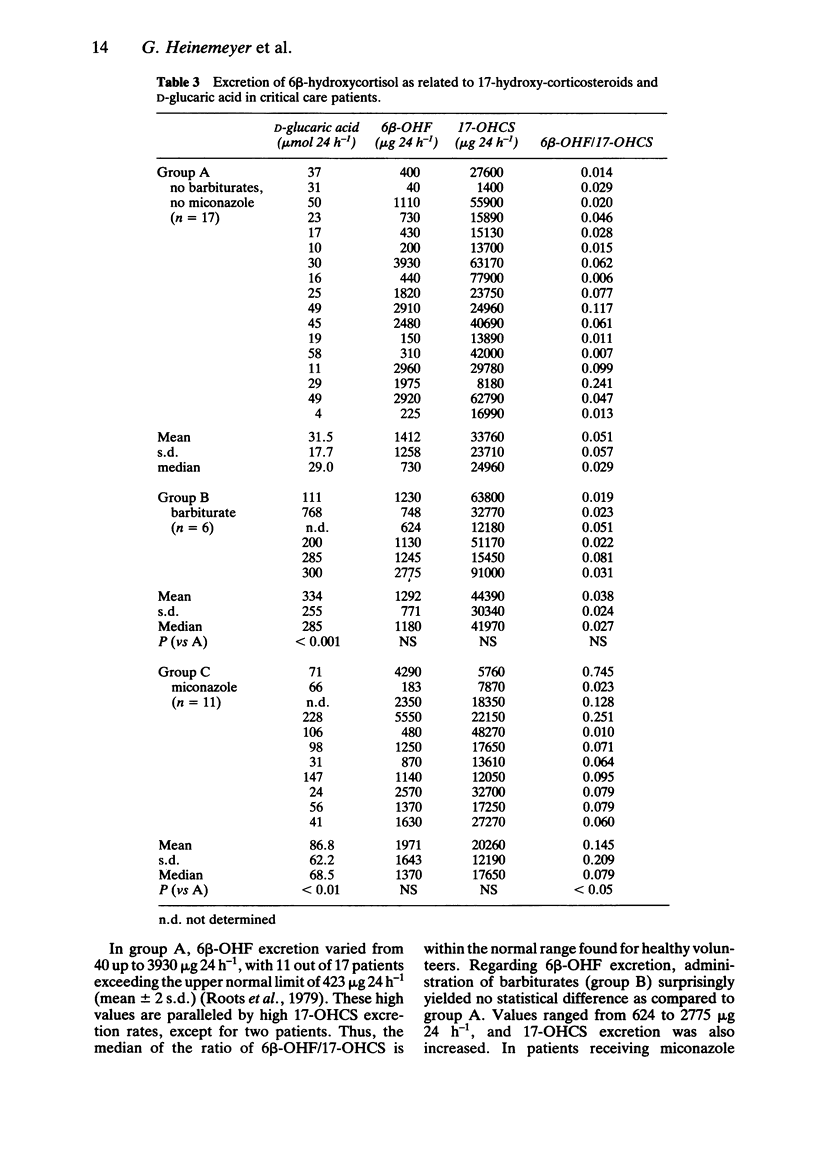
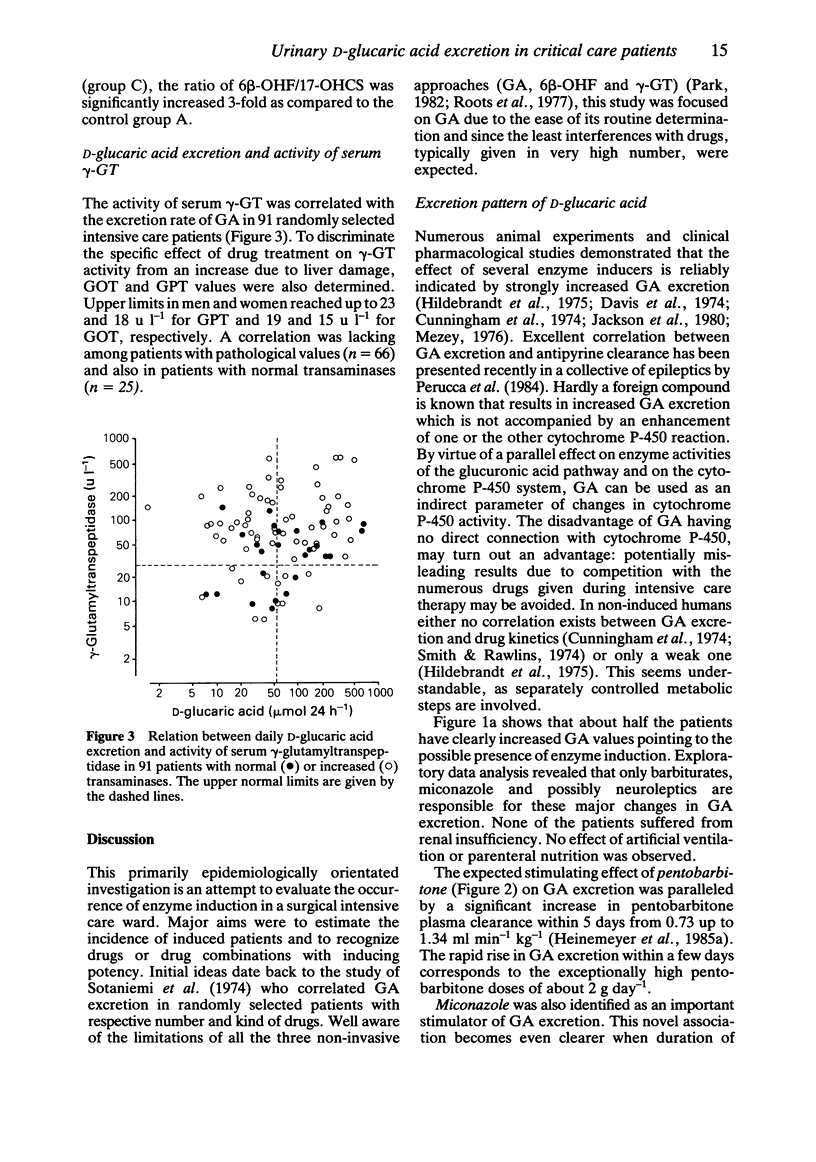
The incidence of increased drug metabolism activity as a consequence of multiple drug therapy at a surgical intensive care ward has been studied non-invasively by determinations of daily urinary D-glucaric acid (GA) excretion rates. Among 165 randomly selected patients, GA excretion was stimulated in 76 cases (= 46%). Exploratory data analysis showed that increases in GA excretion are primarily due to administration of barbiturates (pentobarbitone, Nembutal), miconazole (Daktar) and, to a lesser extent, neuroleptics. Surprisingly, the large number of simultaneously administered additional drugs failed to increase GA excretion. Urinary 6 beta-hydroxycortisol (6 beta-OHF) and 17-hydroxycorticosteroid (17-OHCS) excretion rates were correlated in 34 patients with GA excretion; patients not receiving known enzyme inducers showed low GA values but high 6 beta-OHF and 17-OHCS values, however, with a ratio of 6 beta-OHF/17-OHCS in the normal range. Patients receiving high dose pentobarbitone treatment failed to exhibit significantly increased 6 beta-OHF and 17-OHCS or 6 beta-OHF/17-OHCS values. Miconazole treatment resulted in a significantly increased ratio of 6 beta-OHF/17-OHCS. gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase activity in serum showed no correlation with GA excretion (n = 91).
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman M. L., Green O. C. Acute stimulation of cortisol metabolism by pentobarbital in man. Anesthesiology. 1971 Apr;34(4):365–369. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197104000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer D. D., Zilly W., Richter E. Influence of corticosteroid on hexobarbital and tolbutamide disposition. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Aug;24(2):208–212. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978242208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham J. L., Evans D. A. Urinary D-glucaric acid excretion and acetanilide pharmacokinetics before and during diphenylhydantoin administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1974 Aug 23;7(5):387–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00558212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANTZ A. G., KATZ F. H., JAILER J. W. 6-beta-hydroxy-cortisol: high levels in human urine in pregnancy and toxemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:41–43. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay W. E., McKee J. I. Serum cortisol levels in severely stressed patients. Lancet. 1982 Jun 19;1(8286):1414–1415. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnham J. C., Saunders L., Stainton-Ellis D. M., Franklin C., Volans G., Turner P., Natunen T. The effect of repeated administration of diftalone on enzyme induction. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;30(7):407–409. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt A. G., Roots I., Speck M., Saalfrank K., Kewitz H. Evaluation of in vivo parameters of drug metabolizing enzyme activity in man after administration of clemastine, phenobarbital or placebo. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Jun 13;8(5):327–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00562658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson L., Homeida M., Roberts C. J. The features of hepatic enzyme induction with glutethimide in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;6(6):525–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb00877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampf D., Roots I., Hildebrandt A. G. Urinary excretion of D-glucaric acid, an indicator of drug metabolizing enzyme activity, in patients with impaired renal function. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;18(3):255–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00563008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindor K. D., Fleming C. R., Abrams A., Hirschkorn M. A. Liver function values in adults receiving total parenteral nutrition. JAMA. 1979 Jun 1;241(22):2398–2400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh C. A. Metabolism of d-glucuronolactone in mammalian systems. Identification of d-glucaric acid as a normal constituent of urine. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1042/bj0860077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezey E. Increased urinary excretion of D-glucaric acid in alcoholism. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;15(4):735–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemegeers C. J., Levron J. C., Awouters F., Janssen P. A. Inhibition and induction of microsomal enzymes in rat. A comparative study of four antimycotics: miconazole, econazole, clotrimazole and ketoconazole. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1981 May;251(1):26–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnhaus E. E., Park B. K. Measurement of urinary 6-beta-hydroxycortisol excretion as an in vivo parameter in the clinical assessment of the microsomal enzyme-inducing capacity of antipyrine, phenobarbitone and rifampicin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 26;15(2):139–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00609878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. K. Assessment of the drug metabolism capacity of the liver. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;14(5):631–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry W., Stamp T. C. Urinary D-glucaric acid excretion during rifampicin/isoniazid and anticonvulsant enzyme induction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 May;35(5):710–715. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucca E., Hedges A., Makki K. A., Ruprah M., Wilson J. F., Richens A. A comparative study of the relative enzyme inducing properties of anticonvulsant drugs in epileptic patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;18(3):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietbrock I., Lazarus G., Richter E., Breimer D. D. Hexobarbitone disposition at different stages of intensive care treatment. Br J Anaesth. 1981 Mar;53(3):283–293. doi: 10.1093/bja/53.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roots I., Holbe R., Hövermann W., Nigam S., Heinemeyer G., Hildebrandt A. G. Quantitative determination by HPLC of urinary 6beta-hydroxycortisol, an indicator of enzyme induction by rifampicin and antiepileptic drugs. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;16(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00644969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosalki S. B., Tarlow D., Rau D. Plasma gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase elevation in patients receiving enzyme-inducing drugs. Lancet. 1971 Aug 14;2(7720):376–377. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghvi A., Taddeini L., Wight C. Determination of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids with p-hydrazinobenzenesulfonic acid-phosphoric acid. Anal Chem. 1973 Jan;45(1):207–210. doi: 10.1021/ac60323a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. E., Rawlins M. D. Prediction of drug oxidation rates in man: lack of correlation with serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and urinary excretion of D-glucaric acid and 6 beta-hydroxycortisol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1974;7(1):71–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00614394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotaniemi E. A., Medzihradsky F., Eliasson G. Glucaric acid as an indicator of use of enzyme-inducing drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Apr;15(4):417–423. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974154417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Passananti G. T., Glenwright P. A., Dvorchik B. H. Studies on the disposition of antipyrine, aminopyrine, and phenacetin using plasma, saliva, and urine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Sep;18(3):259–272. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975183259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S. The antipyrine test in clinical pharmacology: conceptions and misconceptions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Sep;26(3):275–286. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979263275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERK E. E., Jr, MACGEE J., SHOLITON L. J. ALTERED CORTISOL METABOLISM IN ADVANCED CANCER AND OTHER TERMINAL ILLNESSES: EXCRETION OF 6-HYDROXYCORTISOL. Metabolism. 1964 Dec;13:1425–1438. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(64)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield J. B., Moss D. W., Neale G., Orme M., Breckenridge A. Changes in plasma -glutamyl transpeptidase activity associated with alterations in drug metabolism in man. Br Med J. 1973 Feb 10;1(5849):316–318. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5849.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. H., Whitaker S. B., Welch C. B., Teller D. N. Hepatic enzyme induction patterns and phenothiazine side effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Oct;34(4):533–538. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Iwai K. Letter: Induction of hepatic cortisol-6-hydroxylase by rifampicin. Lancet. 1976 Aug 14;2(7981):366–367. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


