Abstract
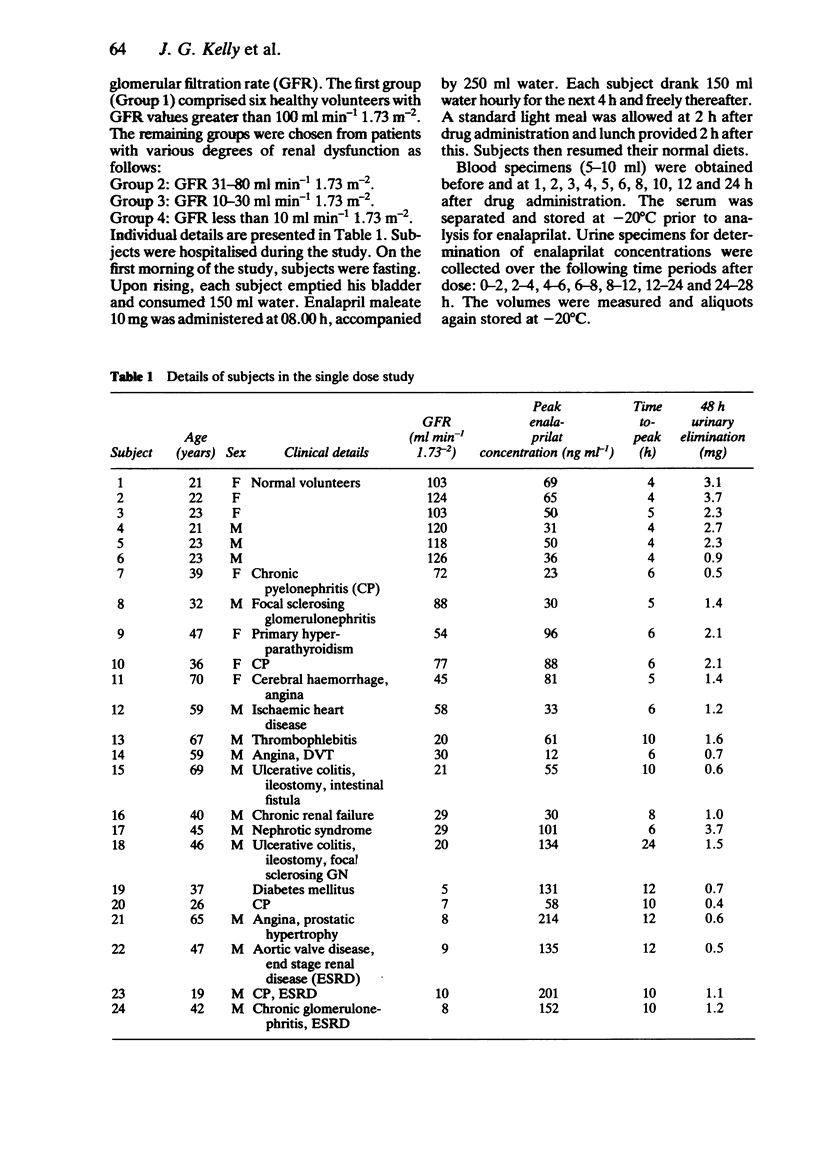
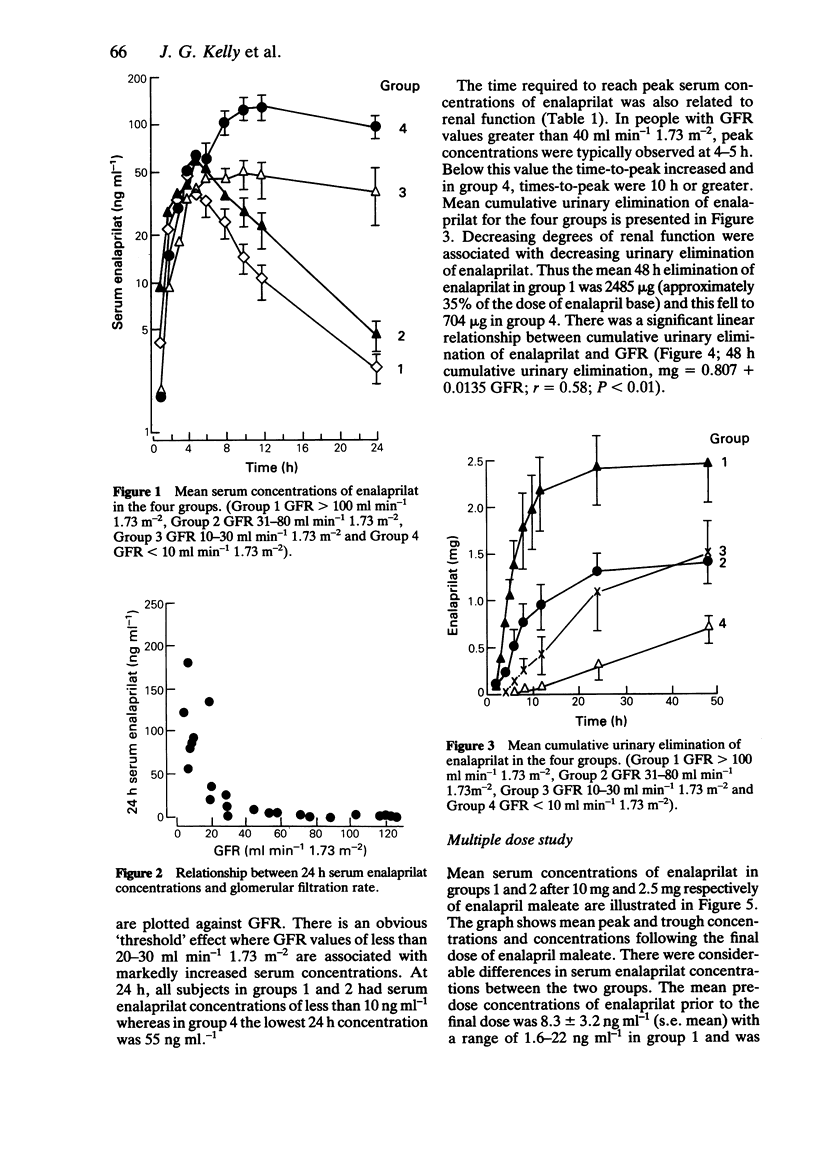
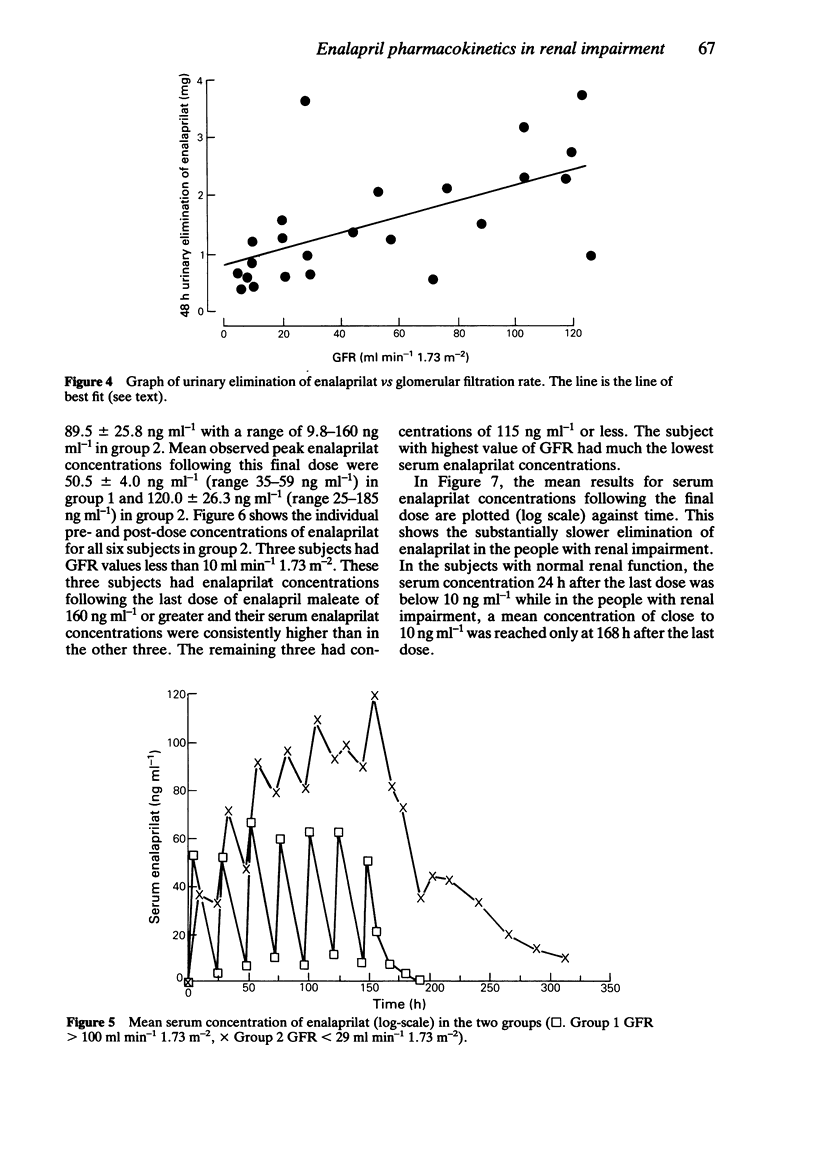
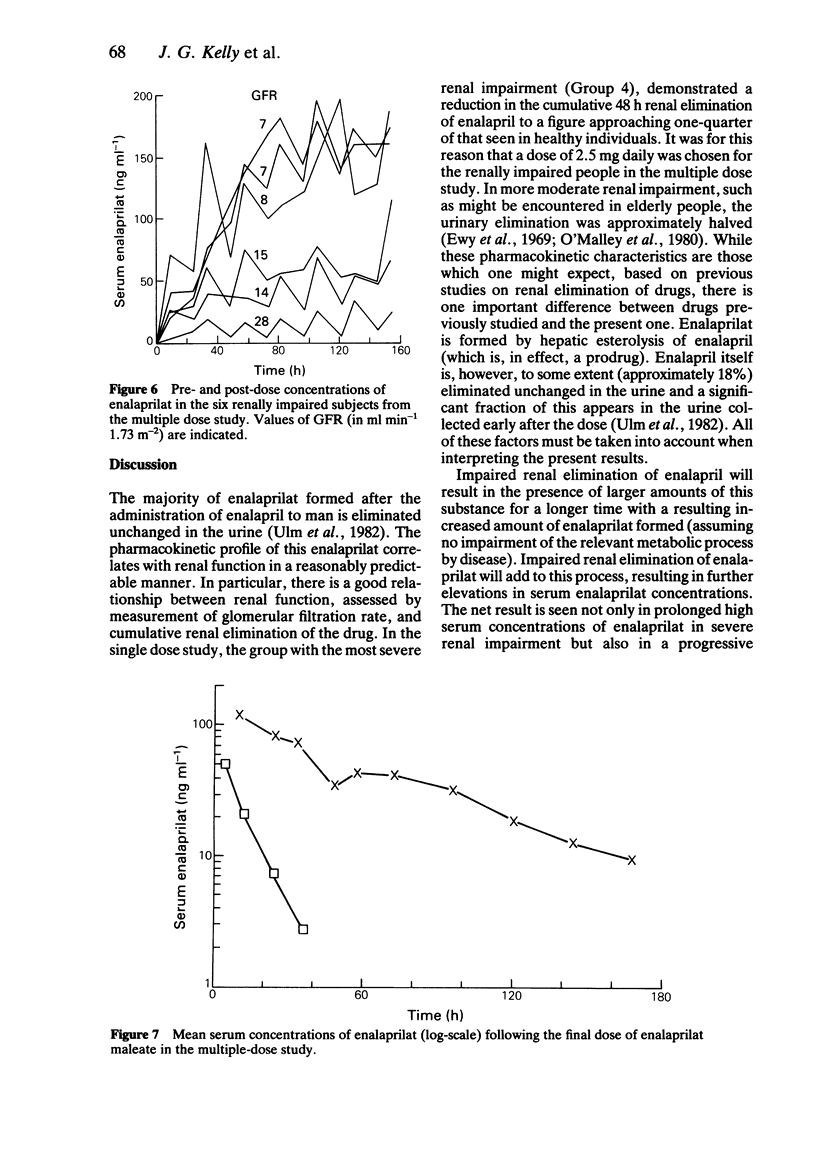
The pharmacokinetics of enalaprilat were studied after administration of single and multiple doses of enalapril maleate to people with normal and impaired renal function. Renal impairment was associated with higher serum concentrations of enalaprilat, longer times to peak concentrations, slower decline of serum concentrations and with reduced urinary elimination. Urinary elimination of enalaprilat was closely related to renal function. In patients with severe renal impairment (GFR values below 30 ml min-1 1.73 m-2) significantly smaller doses of enalapril maleate will be required than in patients with normal or less severely impaired renal function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ewy G. A., Kapadia G. G., Yao L., Lullin M., Marcus F. I. Digoxin metabolism in the elderly. Circulation. 1969 Apr;39(4):449–453. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.39.4.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. M., Sweet C. S., Ulm E. H., Backlund E. P., Morris A. A., Weitz D., Bohn D. L., Wenger H. C., Vassil T. C., Stone C. A. Effect of N-[(S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-L-Ala-L-Pro and its ethyl ester (MK-421) on angiotensin converting enzyme in vitro and angiotensin I pressor responses in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):552–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchett A. A., Harris E., Tristram E. W., Wyvratt M. J., Wu M. T., Taub D., Peterson E. R., Ikeler T. J., ten Broeke J., Payne L. G. A new class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):280–283. doi: 10.1038/288280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till A. E., Gomez H. J., Hichens M., Bolognese J. A., McNabb W. R., Brooks B. A., Noormohamed F., Lant A. F. Pharmacokinetics of repeated single oral doses of enalapril maleate (MK-421) in normal volunteers. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1984 Jul-Sep;5(3):273–280. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2510050309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocco D. J., deLuna F. A., Duncan A. E., Vassil T. C., Ulm E. H. The physiological disposition and metabolism of enalapril maleate in laboratory animals. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982 Jan-Feb;10(1):15–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulm E. H., Hichens M., Gomez H. J., Till A. E., Hand E., Vassil T. C., Biollaz J., Brunner H. R., Schelling J. L. Enalapril maleate and a lysine analogue (MK-521): disposition in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;14(3):357–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


