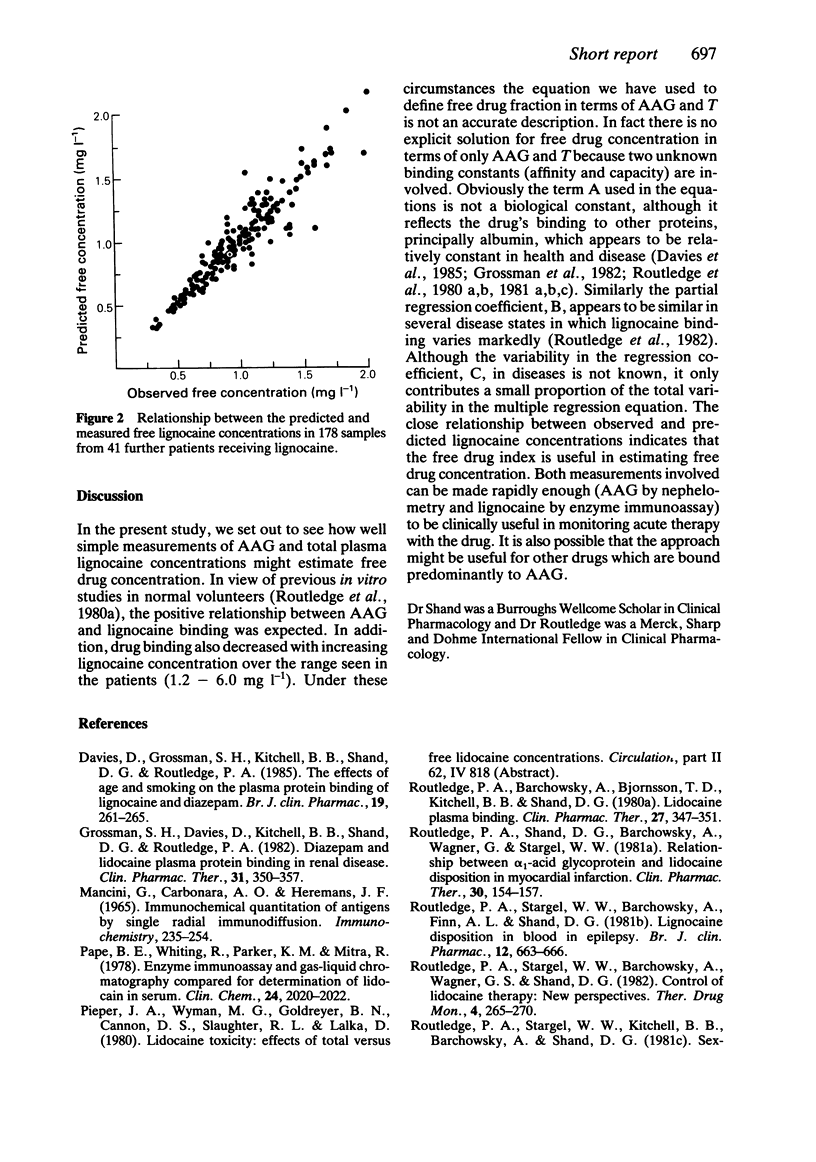
Abstract
A free lignocaine index was developed on the basis of measurements of plasma lignocaine and its principle binding protein, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) in 80 samples from 16 patients admitted to the coronary care unit and given prophylactic lignocaine therapy. The free drug fraction, fu, of lignocaine was determined by equilibrium dialysis and its relationship to AAG and total lignocaine concentration (T) defined by multiple linear regression analysis as l/fu = 1.45 + 0.023 (AAG) -0.129 (T) (multiple r = 0.872, P less than 0.001). This relationship was used to calculate the 'free lignocaine index' as fu X T and compared with the observed value obtained by equilibrium dialysis of 178 samples from 41 separate subjects who received lignocaine after suspected myocardial infarction. There was a highly significant relationship (r = 0.933, n = 178, P less than 0.001) between the observed and predicted values. We conclude that the free drug index may be useful in rapidly assessing the unbound (free) concentration of lignocaine in plasma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis D., Grossman S. H., Kitchell B. B., Shand D. G., Routledge P. A. The effects of age and smoking on the plasma protein binding of lignocaine and diazepam. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;19(2):261–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb02641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. H., Davis D., Kitchell B. B., Shand D. G., Routledge P. A. Diazepam and lidocaine plasma protein binding in renal disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Mar;31(3):350–357. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape B. E., Whiting R., Parker K. M., Mitra R. Enzyme immunoassay and gas--liquid chromatography compared for determination of lidocaine in serum. Clin Chem. 1978 Nov;24(11):2020–2022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Barchowsky A., Bjornsson T. D., Kitchell B. B., Shand D. G. Lidocaine plasma protein binding. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Mar;27(3):347–351. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Shand D. G., Barchowsky A., Wagner G., Stargel W. W. Relationship between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and lidocaine disposition in myocardial infarction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Aug;30(2):154–157. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Stargel W. W., Barchowsky A., Wagner G. S., Shand D. G. Control of lidocaine therapy: new perspectives. Ther Drug Monit. 1982;4(3):265–270. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198208000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Stargel W. W., Finn A. L., Barchowsky A., Shand D. G. Lignocaine disposition in blood in epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;12(5):663–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Stargel W. W., Kitchell B. B., Barchowsky A., Shand D. G. Sex-related differences in the plasma protein binding of lignocaine and diazepam. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;11(3):245–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A., Stargel W. W., Wagner G. S., Shand D. G. Increased alpha-1-acid glycoprotein and lidocaine disposition in myocardial infarction. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Nov;93(5):701–704. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-5-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


