Abstract
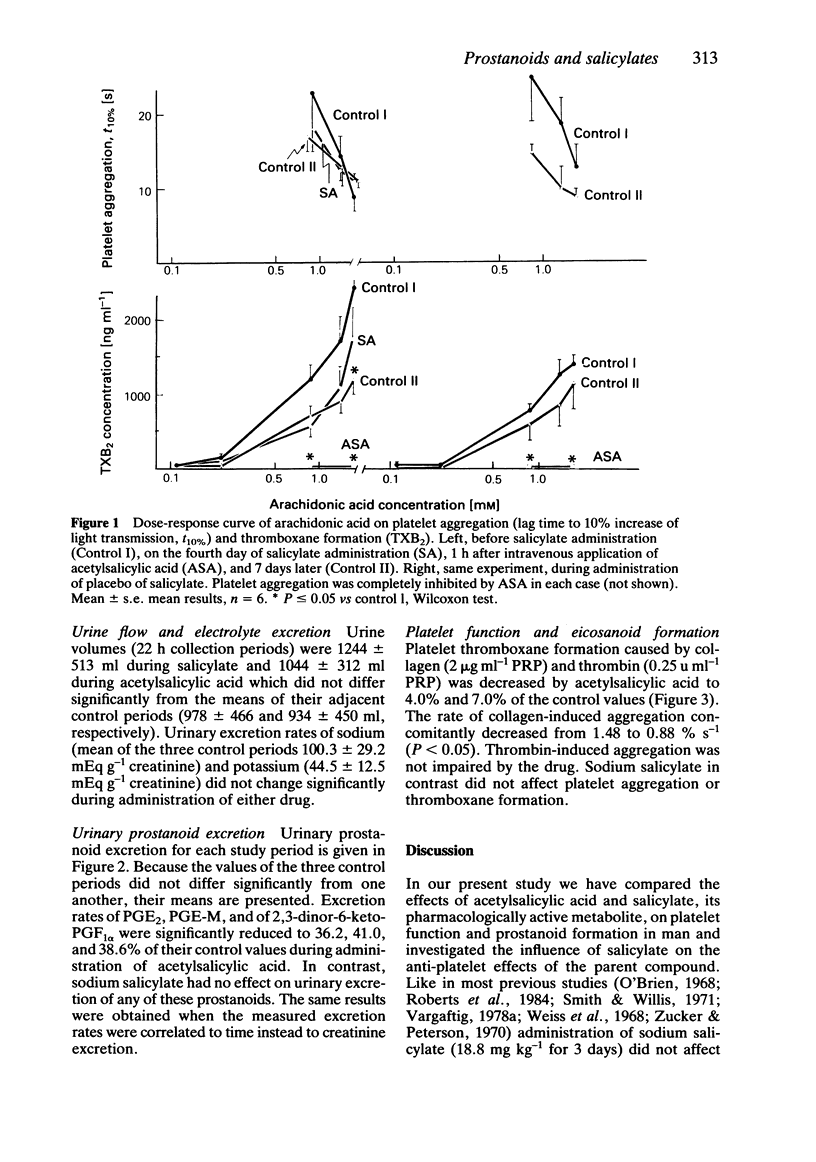
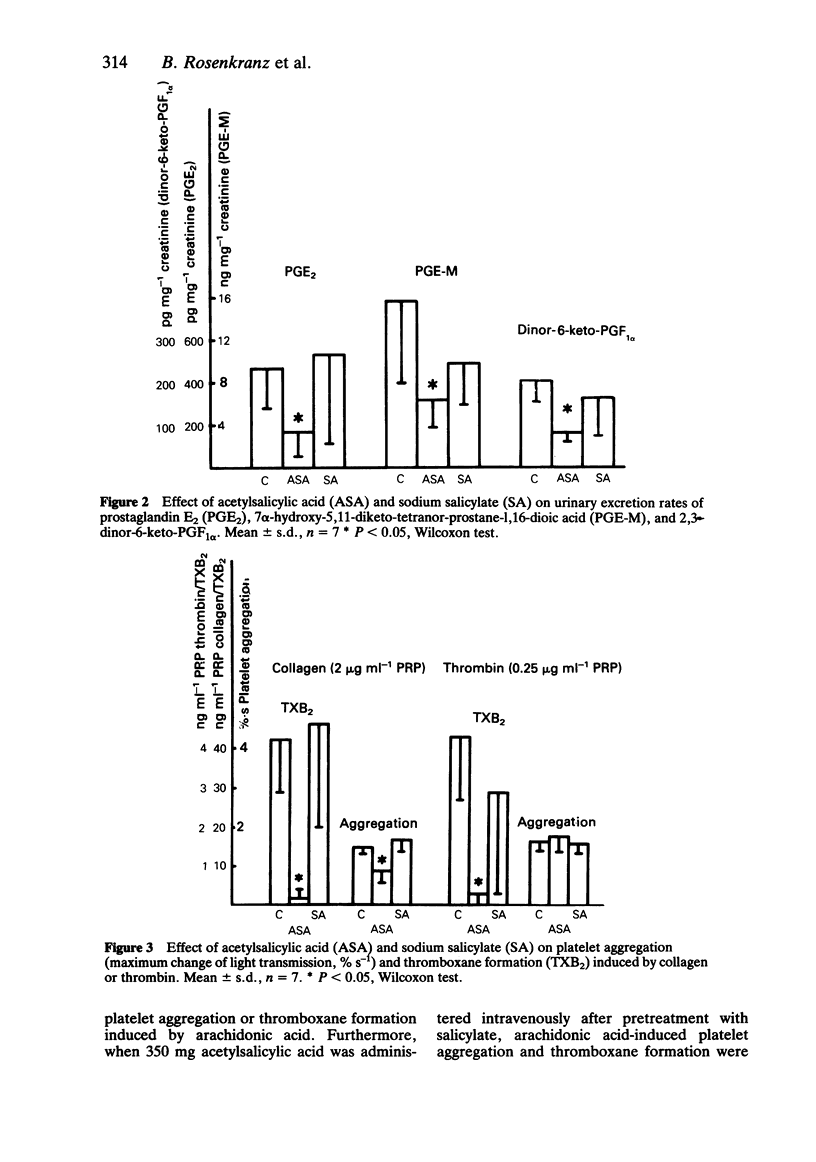
The present study was designed to investigate the effects of salicylate on the antiplatelet action of acetylsalicylic acid as well as on in vivo prostanoid formation and platelet function in healthy volunteers. In the first study six female volunteers received 350 mg acetylsalicylic acid intravenously, with and without previous oral administration of sodium salicylate (1200 mg daily for 3 days). Urinary prostanoid excretion as well as platelet aggregation and thromboxane formation were measured before and during salicylate and after acetylsalicylic acid. In the second study seven female volunteers received sodium salicylate (52.6 mg kg-1) or acetylsalicylic acid (60.7 mg kg-1) for 8 days in a randomized cross-over protocol. Urinary prostanoid excretion, platelet aggregation and thromboxane formation as well as salicylate plasma concentrations were determined before, during and after administration of each drug. Sodium salicylate did not impair the complete suppression of arachidonic acid-induced platelet thromboxane formation and aggregation obtained by the single intravenous dose of acetylsalicylic acid in the first study. Sodium salicylate in the second study did not affect urinary excretion of prostaglandin E2, its major urinary metabolite (7 alpha-hydroxy-5,11-diketo-tetranor-prostane-1,16-dioic acid), and 2,3-dinor-6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha, the main urinary metabolite of epoprostenol (prostacyclin, PGI2). In contrast, acetylsalicylic acid significantly decreased excretion rates of these prostanoids by 64, 59 and 61%, respectively. In both studies platelet aggregation and thromboxane formation induced by collagen, thrombin or arachidonic acid were not significantly affected by salicylate administration, whereas acetylsalicylic acid inhibited platelet aggregation induced by all three agents as well as thrombin- and arachidonic acid induced thromboxane formation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M., McDonald J. W. Interference by sulfinpyrazone and salicylate of aspirin inhibition of platelet cyclooxygenase activity. Prostaglandins Med. 1979 Dec;3(6):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(79)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson D. C., Collier H. O. Salicylates: molecular mechanism of therapeutic action. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1980;17:233–288. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brantmark B., Hedner U., Melander A., Wåhlin-Boll E. Salicylate inhibition of antiplatelet effect of aspirin. Lancet. 1981 Dec 12;2(8259):1349–1349. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan M. R., Hirsh J. Effect of aspirin and salicylate on platelet-vessel wall interactions in rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):403–406. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Upton R. A., Williams R. L. Improved liquid-chromatography of aspirin, salicylate, and salicyluric acid in plasma, with a modification for determining aspirin metabolites in urine. Clin Chem. 1982 May;28(5):1200–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl M. L., Puustinen T., Uotila P. Sodium salicylate interferes with the inhibitory effects of aspirin and indomethacin on human platelets. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1983 Sep;12(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(83)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl M. L., Uotila P. Salicylate does not interfere with aspirin in human blood in vivo. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1984 Feb;13(2):169–170. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(84)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Cerletti C., de Castellarnau C., Livio M., Galletti F., Latini R., de Gaetano G. Salicylate-aspirin interaction in the rat. Evidence that salicylate accumulating during aspirin administration may protect vascular prostacyclin from aspirin-induced inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1108–1112. doi: 10.1172/JCI110336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Cerletti C., de Gaetano G. Interaction of salicylate and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with aspirin on platelet and vascular cyclo-oxygenase activity. Thromb Res Suppl. 1983;4:153–159. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90371-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F., Charbonnel B., Maclouf J. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins Falpha, E1 and E2 in human plasma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezer E., Palosi E., Hajós G., Szporny L. Antagonism of the gastrointestinal ulcerogenic effect of some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents by sodium salicylate. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;28(8):655–656. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb02824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falardeau P., Oates J. A., Brash A. R. Quantitative analysis of two dinor urinary metabolites of prostaglandin I2. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer C., Meese C. O., Klotz U. A stable isotope method for the quantification of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid in plasma and urine. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1984 Oct;11(10):539–544. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200111009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Wilson T. W., Sweetman B. J., Smigel M., Nies A. S., Carr K., Watson J. T., Oates J. A. Urinary prostaglandins. Identification and origin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):763–770. doi: 10.1172/JCI107987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in man. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):720–726. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. On the metabolism of prostaglandins E 1 and E 2 in man. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6713–6721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Harvey E. A., Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. The effects of antiinflammatory drugs on the production of prostaglandins in vivo. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1976;1:105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Winter C. A., Sadowski S. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr Multiple sites on prostaglandin cyclooxygenase are determinants in the action of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2053–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Siess W. The role of phospholipase C in platelet responses. Life Sci. 1983 Sep 12;33(11):1011–1018. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Tsuchiya T. Salicylate accumulation kinetics in man. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 31;287(9):430–432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208312870903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H., Mrongovius R., Seyberth H. W. Improved sample preparation for the quantitative mass spectrometric determination of prostaglandins in biological samples. J Chromatogr. 1981 Dec 11;226(2):450–454. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)86079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitelius E., Brantmark B., Fredholm B., Hedner U., Forshell G. P., Wåhlin-Boll E., Melander A. Actions and interactions of acetylsalicylic acid, salicylic acid and diflunisal on platelet aggregation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;27(2):165–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00544040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. R. Effects of salicylates on human platelets. Lancet. 1968 Apr 13;1(7546):779–783. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani P., Filabozzi P., Patrono C. Selective cumulative inhibition of platelet thromboxane production by low-dose aspirin in healthy subjects. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1366–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI110576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrono C., Wennmalm A., Ciabattoni G., Nowak J., Pugliese F., Cinotti G. A. Evidence for an extra-renal origin of urinary prostaglandin E2 in healthy men. Prostaglandins. 1979 Oct;18(4):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philp R. B., Paul M. L. Non-interference by salicylate with aspirin inhibition of arterial thrombosis in rats. Prostaglandins Med. 1981 Aug;7(2):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(81)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. S., McLeod L. J., Cossum P. A., Vial J. H. Inhibition of platelet function by a controlled release acetylsalicylic acid formulation--single and chronic dosing studies. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;27(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Chen M. A role for prostaglandin E in defective insulin secretion and carbohydrate intolerance in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):747–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI108827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz B., Fischer C., Boeynaems J. M., Frölich J. C. Metabolic disposition of prostaglandin E1 in man. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 7;750(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz B., Fischer C., Weimer K. E., Frölich J. C. Metabolism of prostacyclin and 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha in man. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10194–10198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B. The prostanoids in hemostasis and thrombosis: a review. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jun;99(3):743–804. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Walker J. R., Slack J. A. Aspirin, salicylate and prostaglandins. Agents Actions. 1979 Dec;9(5-6):483–487. doi: 10.1007/BF01968116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The mode of action of aspirin-like drugs. Agents Actions. 1978 Jun;8(4):430–431. doi: 10.1007/BF01968671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B. Salicylic acid fails to inhibit generation of thromboxane A2 activity in platelets after in vivo administration to the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;30(2):101–104. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B. The inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase of rabbit platelets by aspirin is prevented by salicylic acid and by phenanthrolines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Aug 1;50(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viinikka L., Salokannel J., Ylikorkala O. Effect of prolonged treatment with acetylsalicylic acid and dipyridamole on platelet thromboxane A2 production in atherosclerotic subjects. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1983 May;11(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(83)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Aledort L. M., Kochwa S. The effect of salicylates on the hemostatic properties of platelets in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2169–2180. doi: 10.1172/JCI105903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Higgs G. A., Eakins K. E., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Selective inhibition of prostaglandin production in inflammatory exudates and gastric mucosa. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):271–273. doi: 10.1038/284271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Peterson J. Effect of acetylsalicylic acid, other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, and dipyridamole on human blood platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):66–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Castellarnau C., Cerletti C., Dejana E., Galletti F., Latini R., Livio M., de Gaetano G. Salicylate-aspirin interaction and thrombosis prevention trials. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Jun 30;45(3):294–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


